Abstract
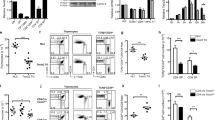
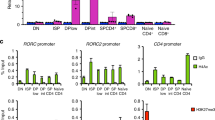
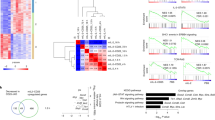
Cell differentiation involves activation and silencing of lineage-specific genes. Here we show that the transcription factor Runx3 is induced in T helper type 1 (TH1) cells in a T-bet-dependent manner, and that both transcription factors T-bet and Runx3 are required for maximal production of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and silencing of the gene encoding interleukin 4 (Il4) in TH1 cells. T-bet does not repress Il4 in Runx3-deficient TH2 cells, but coexpression of Runx3 and T-bet induces potent repression in those cells. Both T-bet and Runx3 bind to the Ifng promoter and the Il4 silencer, and deletion of the silencer decreases the sensitivity of Il4 to repression by either factor. Our data indicate that cytokine gene expression in TH1 cells may be controlled by a feed-forward regulatory circuit in which T-bet induces Runx3 and then 'partners' with Runx3 to direct lineage-specific gene activation and silencing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 January 2007
In the version of this article initially published online, two labels in Figure 1e are reversed and two sequences in Figure 7a are reversed. The labels ‘IB: Runx3’ and ‘IB: T-bet’ should be switched, and the sequences for ‘HS IV probe’ and ‘T-box mutant’ should be switched. The errors have been corrected for all versions of the article.
References
Szabo, S.J., Sullivan, B.M., Peng, S.L. & Glimcher, L.H. Molecular mechanisms regulating Th1 immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 713–758 (2003).
Berenson, L.S., Ota, N. & Murphy, K.M. Issues in T-helper 1 development—resolved and unresolved. Immunol. Rev. 202, 157–174 (2004).
Ansel, K.M., Djuretic, I., Tanasa, B. & Rao, A. Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24, 607–656 (2006).
Stetson, D.B. et al. Th2 cells: orchestrating barrier immunity. Adv. Immunol. 83, 163–189 (2004).
Grogan, J.L. et al. Basal chromatin modification at the IL-4 gene in helper T cells. J. Immunol. 171, 6672–6679 (2003).
Baguet, A. & Bix, M. Chromatin landscape dynamics of the Il4-Il13 locus during T helper 1 and 2 development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 11410–11415 (2004).
Ansel, K.M., Lee, D.U. & Rao, A. An epigenetic view of helper T cell differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 4, 616–623 (2003).
Spilianakis, C.G. & Flavell, R.A. Long-range intrachromosomal interactions in the T helper type 2 cytokine locus. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1017–1027 (2004).
Reiner, S.L. Epigenetic control in the immune response. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14 (Suppl. 1), R41–R46 (2005).
Szabo, S.J. et al. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 100, 655–669 (2000).
Lee, D.U., Avni, O., Chen, L. & Rao, A. A distal enhancer in the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) locus revealed by genome sequence comparison. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 4802–4810 (2004).
Shnyreva, M. et al. Evolutionarily conserved sequence elements that positively regulate IFN-γ expression in T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 12622–12627 (2004).
Afkarian, M. et al. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 3, 549–557 (2002).
Mullen, A.C. et al. Hlx is induced by and genetically interacts with T-bet to promote heritable TH1 gene induction. Nat. Immunol. 3, 652–658 (2002).
Zheng, W.P. et al. Up-regulation of Hlx in immature Th cells induces IFN-γ expression. J. Immunol. 172, 114–122 (2004).
Usui, T. et al. T-bet regulates Th1 responses through essential effects on GATA-3 function rather than on IFNG gene acetylation and transcription. J. Exp. Med. 203, 755–766 (2006).
Hwang, E.S., Szabo, S.J., Schwartzberg, P.L. & Glimcher, L.H. T helper cell fate specified by kinase-mediated interaction of T-bet with GATA-3. Science 307, 430–433 (2005).
Lee, G.R., Kim, S.T., Spilianakis, C.G., Fields, P.E. & Flavell, R.A. T helper cell differentiation: regulation by cis elements and epigenetics. Immunity 24, 369–379 (2006).
Nardone, J., Lee, D.U., Ansel, K.M. & Rao, A. Bioinformatics for the 'bench biologist': how to find regulatory regions in genomic DNA. Nat. Immunol. 5, 768–774 (2004).
Agarwal, S., Avni, O. & Rao, A. Cell-type-restricted binding of the transcription factor NFAT to a distal IL-4 enhancer in vivo. Immunity 12, 643–652 (2000).
Solymar, D.C., Agarwal, S., Bassing, C.H., Alt, F.W. & Rao, A. A 3′ enhancer in the IL-4 gene regulates cytokine production by Th2 cells and mast cells. Immunity 17, 41–50 (2002).
Mohrs, M. et al. Deletion of a coordinate regulator of type 2 cytokine expression in mice. Nat. Immunol. 2, 842–847 (2001).
Fields, P.E., Lee, G.R., Kim, S.T., Bartsevich, V.V. & Flavell, R.A. Th2-specific chromatin remodeling and enhancer activity in the Th2 cytokine locus control region. Immunity 21, 865–876 (2004).
Lee, G.R., Fields, P.E., Griffin, T.J. & Flavell, R.A. Regulation of the Th2 cytokine locus by a locus control region. Immunity 19, 145–153 (2003).
Lee, D.U. & Rao, A. Molecular analysis of a locus control region in the T helper 2 cytokine gene cluster: a target for STAT6 but not GATA3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16010–16015 (2004).
Tanaka, S. et al. The Interleukin-4 enhancer CNS-2 is regulated by Notch signals and controls initial expression in NKT cells and memory-type CD4 T cells. Immunity 24, 689–701 (2006).
Ansel, K.M. et al. Deletion of a conserved Il4 silencer impairs T helper type 1–mediated immunity. Nat. Immunol. 5, 1251–1259 (2004).
Levanon, D. & Groner, Y. Structure and regulated expression of mammalian RUNX genes. Oncogene 23, 4211–4219 (2004).
Lee, J., Ahnn, J. & Bae, S.C. Homologs of RUNX and CBFβ/PEBP2β in C. elegans. Oncogene 23, 4346–4352 (2004).
Taniuchi, I. & Littman, D.R. Epigenetic gene silencing by Runx proteins. Oncogene 23, 4341–4345 (2004).
Durst, K.L. & Hiebert, S.W. Role of RUNX family members in transcriptional repression and gene silencing. Oncogene 23, 4220–4224 (2004).
Westendorf, J.J. & Hiebert, S.W. Mammalian runt-domain proteins and their roles in hematopoiesis, osteogenesis, and leukemia. J. Cell. Biochem. 75 (Suppl. S32), 51–58 (1999).
Blyth, K., Cameron, E.R. & Neil, J.C. The RUNX genes: gain or loss of function in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 376–387 (2005).
Lian, J.B. et al. Regulatory controls for osteoblast growth and differentiation: role of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 14, 1–41 (2004).
de Bruijn, M.F. & Speck, N.A. Core-binding factors in hematopoiesis and immune function. Oncogene 23, 4238–4248 (2004).
Zhong, J., Pevny, L. & Snider, W.D. 'Runx'ing towards sensory differentiation. Neuron 49, 325–327 (2006).
Taniuchi, I. et al. Differential requirements for Runx proteins in CD4 repression and epigenetic silencing during T lymphocyte development. Cell 111, 621–633 (2002).
Woolf, E. et al. Runx3 and Runx1 are required for CD8 T cell development during thymopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7731–7736 (2003).
Sato, T. et al. Dual functions of Runx proteins for reactivating CD8 and silencing CD4 at the commitment process into CD8 thymocytes. Immunity 22, 317–328 (2005).
Grueter, B. et al. Runx3 regulates integrin αE/CD103 and CD4 expression during development of CD4−/CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 175, 1694–1705 (2005).
Yarmus, M. et al. Groucho/transducin-like Enhancer-of-split (TLE)-dependent and -independent transcriptional regulation by Runx3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 7384–7389 (2006).
Komine, O. et al. The Runx1 transcription factor inhibits the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into the Th2 lineage by repressing GATA3 expression. J. Exp. Med. 198, 51–61 (2003).
Cho, J.Y., Grigura, V., Murphy, T.L. & Murphy, K. Identification of cooperative monomeric Brachyury sites conferring T-bet responsiveness to the proximal IFN-γ promoter. Int. Immunol. 15, 1149–1160 (2003).
Agarwal, S. & Rao, A. Modulation of chromatin structure regulates cytokine gene expression during T cell differentiation. Immunity 9, 765–775 (1998).
Takemoto, N. et al. Th2-specific DNAse I–hypersensitive sites in the murine IL-13 and IL-4 intergenic region. Int. Immunol. 10, 1981–1985 (1998).
Cirillo, L.A. et al. Opening of compacted chromatin by early developmental transcription factors HNF3 (FoxA) and GATA-4. Mol. Cell 9, 279–289 (2002).
Medina, K.L. et al. Assembling a gene regulatory network for specification of the B cell fate. Dev. Cell 7, 607–617 (2004).
Davidson, E.H. Genomic Regulatory Systems: Development and Evolution (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 2001).
Hutchins, A.S. et al. Cutting edge: a critical role for gene silencing in preventing excessive type 1 immunity. J. Immunol. 175, 5606–5610 (2005).
Brenner, O. et al. Loss of Runx3 function in leukocytes is associated with spontaneously developed colitis and gastric mucosal hyperplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 16016–16021 (2004).
Fainaru, O. et al. Runx3 regulates mouse TGF-β-mediated dendritic cell function and its absence results in airway inflammation. EMBO J. 23, 969–979 (2004).
Finotto, S. et al. Development of spontaneous airway changes consistent with human asthma in mice lacking T-bet. Science 295, 336–338 (2002).
Fainaru, O., Shseyov, D., Hantisteanu, S. & Groner, Y. Accelerated chemokine receptor 7–mediated dendritic cell migration in Runx3 knockout mice and the spontaneous development of asthma-like disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10598–10603 (2005).
Levanon, D. et al. The Runx3 transcription factor regulates development and survival of TrkC dorsal root ganglia neurons. EMBO J. 21, 3454–3463 (2002).
Ranganath, S. et al. GATA-3-dependent enhancer activity in IL-4 gene regulation. J. Immunol. 161, 3822–3826 (1998).
Aziz-Aloya, R.B. et al. Expression of AML1-d, a short human AML1 isoform, in embryonic stem cells suppresses in vivo tumor growth and differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 5, 765–773 (1998).
Le, X.F. et al. Regulation of AML2/CBFA3 in hematopoietic cells through the retinoic acid receptor α-dependent signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21651–21658 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Glimcher for Tbx21−/− mice, polyclonal antibody to T-bet, and Runx1 and Runx3 pCDNA3 expression plasmids; R. Locksley for DO11.10 Tcra,Tcrb transgenic Tcra−/− mice; K. Murphy for the parent retroviral vector GFP-RV; V. Heissmeyer for the pMSCV-IRES-Thy1.1 vector; G.P. Nolan for Phoenix cells; D. Bolton and L. Smith for technical support; J. Chermesh and R. Saka for help with animal husbandry; and F. Cruz-Guilloty and M. Keir for advice. Supported by the National Institutes of Health (AI44432 and HL67664 to A.R.), Sandler Program for Asthma Research (A.R.), The Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (K.M.A.) and the Israel Science Foundation (Y.G. and D.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I.M.D. did all the experiments with the direction and supervision of K.M.A. and A.R.; and D.L. and V.N. assisted in the analysis of Runx3-deficient T cells under the supervision of Y.G.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Runx1 and Tbx21 mRNA expression. (PDF 971 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Runx3 regulates IL-2 production. (PDF 371 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Runx1 can bind the Ifng promoter and Il4 silencer. (PDF 302 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Quantification of HS IV-dependent Runx3- and T-bet-mediated IL-4 repression. (PDF 372 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Conserved T-box and Runx consensus binding sequences in HS IV. (PDF 469 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djuretic, I., Levanon, D., Negreanu, V. et al. Transcription factors T-bet and Runx3 cooperate to activate Ifng and silence Il4 in T helper type 1 cells. Nat Immunol 8, 145–153 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1424
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1424
This article is cited by
-
IL-6 prevents Th2 cell polarization by promoting SOCS3-dependent suppression of IL-2 signaling
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
The role of transcription factors in shaping regulatory T cell identity
Nature Reviews Immunology (2023)
-
An αvβ3 integrin checkpoint is critical for efficient TH2 cell cytokine polarization and potentiation of antigen-specific immunity
Nature Immunology (2023)
-
Multi-omic analysis reveals dynamic changes of three-dimensional chromatin architecture during T cell differentiation
Communications Biology (2023)
-
MicroRNA-19a Inhibition Directly and Indirectly Ameliorates Th2 Airway Inflammation in Asthma by Targeting RUNX3
Inflammation (2023)