Abstract
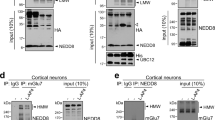
NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors (NMDARs) are targeted to dendrites and anchored at the post-synaptic density (PSD) through interactions with PDZ proteins. However, little is known about how these receptors are sorted from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus to the synapse. Here, we find that synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP102) interacts with the PDZ-binding domain of Sec8, a member of the exocyst complex. Our results show that interactions between SAP102 and Sec8 are involved in the delivery of NMDARs to the cell surface in heterologous cells and neurons. Furthermore, they suggest that an exocyst–SAP102–NMDAR complex is an important component of NMDAR trafficking.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Petralia, R.S., Rubio, M.E., Wang, Y.-X. & Wenthold, R.J. in Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Vol. 18. Glutamate (eds. Ottersen, O.P. & Storm-Mathisen, J.) 145–182 (Elsevier, New York, 2000).
Garner, C.C., Nash, J. & Huganir, R.L. PDZ Domains in synapse assembly and signalling. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 274–280 (2000).
Scannevin, R.H. & Huganir, R.L. Postsynaptic organization and regulation of excitatory synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 1, 133–141 (2000).
Sheng, M. & Sala, C. PDZ domains and the organization of supramolecular complexes. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1–29 (2001).
Tomita, S., Nicoll, R.A. & Bredt, D.S. PDZ protein interactions regulating glutamate receptor function and plasticity. J. Cell Biol. 153, F19–F24 (2001).
Kittler, J.T. & Moss, S.J. Neurotransmitter receptor trafficking and the regulation of synaptic strength. Traffic 2, 437–448 (2001).
Standley, S., Roche, K.W., McCallum, J., Sans, N. & Wenthold, R.J. PDZ domain suppression of an ER retention signal in NMDA receptor NR1 splice variants. Neuron 28, 887–898 (2000).
Scott, D.B., Blanpied, T.A., Swanson, G.T., Zhang, C. & Ehlers, M.D. An NMDA receptor ER retention signal regulated by phosphorylation and alternative splicing. J. Neurosci. 21, 3063–3072 (2001).
Xia, H., Hornby, Z.D. & Malenka, R.C. An ER retention signal explains differences in surface expression of NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits. Neuropharmacology 41, 714–723 (2001).
Sans, N. et al. Synapse-associated protein 97 selectively associates with a subset of AMPA receptors early in their biosynthetic pathway. J. Neurosci. 21, 7506–7516 (2001).
Hayashi, Y. et al. Driving AMPA receptors into synapses by LTP and CaMKII: requirement for GluR1 and PDZ domain interaction. Science 287, 2262–2267 (2000).
Shi, S., Hayashi, Y., Esteban, J.A. & Malinow, R. Subunit-specific rules governing AMPA receptor trafficking to synapses in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell 105, 331–343 (2001).
Bowser, R., Muller, H., Govindan, B. & Novick, P. Sec8p and Sec15p are components of a plasma membrane-associated 19. 5S particle that may function downstream of Sec4p to control exocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 118, 1041–1056 (1992).
Hsu, S.C. et al. The mammalian brain rsec6/8 complex. Neuron 17, 1209–1219 (1996).
Hsu, S.C., Hazuka, C.D., Foletti, D.L. & Scheller, R.H. Targeting vesicles to specific sites on the plasma membrane: the role of the sec6/8 complex. Trends Cell Biol. 9, 150–153 (1999).
Hazuka, C.D. et al. The sec6/8 complex is located at neurite outgrowth and axonal synapse assembly domains. J. Neurosci. 19, 1324–1334 (1999).
Yeaman, C., Grindstaff, K.K., Wright, J.R. & Nelson, W.J. Sec6/8 complexes on trans-Golgi network and plasma membrane regulate late stages of exocytosis in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 155, 593–604 (2001).
Vega, I.E. & Hsu, S.C. The exocyst associates with microtubules to mediate vesicle targeting and neurite outgrowth. J. Neurosci. 21, 3839–3848 (2001).
Shin, D.M., Zhao, X.S., Zeng, W., Mozhayeva, M. & Muallem, S. The mammalian Sec6/8 complex interacts with Ca2+ signaling complexes and regulates their activity. J. Cell Biol. 150, 1101–1112 (2000).
Novick, P. & Guo, W. Ras family therapy: Rab, Rho and Ral talk to the exocyst. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 247–249 (2002).
Muller, B.M. et al. SAP102, a novel postsynaptic protein that interacts with NMDA receptor complexes in vivo. Neuron 17, 255–265 (1996).
Lau, L.F. et al. Interaction of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex with a novel synapse-associated protein, SAP102. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21622–21628 (1996).
Makino, K. et al. Cloning and characterization of NE-dlg: a novel human homolog of the Drosophila discs large (dlg) tumor suppressor protein interacts with the APC protein. Oncogene 22, 2425–2433 (1997).
Sans, N. et al. A developmental change in NMDA receptor-associated proteins at hippocampal synapses. J. Neurosci. 20, 1260–1271 (2000).
Kee, Y. et al. Subunit structure of the mammalian exocyst complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 14438–14443 (1997).
Hawkins, L.M., Chazot, P.L. & Stephenson, F.A. Biochemical evidence for the co-association of three N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) R2 subunits in recombinant NMDA receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 27211–27218 (1999).
McIlhinney, R.A.J. et al. Assembly, intracellular targeting and cell surface expression of the human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits NR1a and NR2A in transfected cells. Neuropharmacology 37, 1355–1367 (1998).
Okabe, S., Miwa, A. & Okado, H. Alternative splicing of the C-terminal domain regulates cell surface expression of the NMDA receptor NR1 subunit. J. Neurosci. 15, 7781–7792 (1999).
Cik, M., Chazot, P.L. & Stephenson, F.A. Optimal expression of cloned NMDAR1/NMDAR2A heteromeric glutamate receptors: a biochemical characterization. Biochem. J. 296, 877–883 (1993).
Losi, G., Prybylowski, K., Fu, Z., Luo, J.H. & Vicini S. Silent synapses in developing cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 1263–1270 (2002).
Prybylowski, K. et al. Relationship between availability of NMDA receptor subunits and their expression at the synapse. J. Neurosci. 22, 8902–8910 (2002).
Harris, B.Z. & Lim, W.A. Mechanism and role of PDZ domains in signaling complex assembly. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3219–3231 (2001).
Ma, D. & Jan, L.Y. ER transport signals and trafficking of potassium channels and receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 287–292 (2002).
Grindstaff, K.K. et al. Sec6/8 complex is recruited to cell-cell contacts and specifies transport vesicle delivery to the basal-lateral membrane in epithelial cells. Cell 93, 731–740 (1998).
Hsu, S.C. et al. Subunit composition, protein interactions, and structures of the mammalian brain sec6/8 complex and septin filaments. Neuron 20, 1111–1122 (1998).
Sprengel, R. et al. Importance of the intracellular domain of NR2 subunits for NMDA receptor function in vivo. Cell 92, 279–289 (1998).
Mori, H. et al. Role of the carboxy-terminal region of the GluR epsilon2 subunit in synaptic localization of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuron 21, 571–580 (1998).
Barria, A. & Malinow, R. Subunit-specific NMDA receptor trafficking to synapses. Neuron 35, 345–353 (2002).
Tovar, K.R. & Westbrook, G.L. Mobile NMDA receptors at hippocampal synapses. Neuron 34, 255–264 (2002).
Rumbaugh, G. & Vicini, S. Distinct synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in developing cerebellar granule neurons. J. Neurosci. 19, 10603–10610 (1999).
Tovar, K.R. & Westbrook, G.L. The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J. Neurosci. 19, 4180–4188 (1999).
Ehlers, M.D. Reinsertion or degradation of AMPA receptors determined by activity-dependent endocytic sorting. Neuron 28, 511–525 (2000).
Roche, K.W. et al. Molecular determinants of NMDA receptor internalization. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 794–802 (2001).
Vissel, B., Krupp, J.J., Heinemann, S.F. & Westbrook, G.L. A use-dependent tyrosine dephosphorylation of NMDA receptors is independent of ion flux. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 587–596 (2001).
Snyder, E.M., Philpot, B.D., Huber, K.M., Dong, X., Fallon, J.R. & Bear, M.F. Internalization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in response to mGluR activation. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1079–1085 (2001).
Chazot, P.L. & Stephenson, F.A. Biochemical evidence for the existence of a pool of unassembled C2 exon-containing NR1 subunits of the mammalian forebrain NMDA receptor. J. Neurochem. 68, 507–516 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank C.C. Garner for providing the SAP102 cDNA, S.C. Hsu for providing the Sec6 and Sec8 cDNAs and the GST–Exo70 and Sec10 constructs, J.H. Luo for the YFP–NR1-1 construct, A. de Blas for the GABAAR anti-α1 antibody and β3 cDNA, F.A. Stephenson for the Myc- and Flag-tagged NR2B constructs and R.L. Huganir for the GRIP antibody. We would also like to thank C.Y. Wang, L. Hawkins, S. Standley and M. Montcouquiol for helpful comments and discussion, P. Wang for excellent technical assistance, and Z. Fu and G. Losi for cerebellar granule cell cultures. Animals were handled in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH publication 85–23; NIDCD protocol #1022-01). This work was supported by the National institute of deafness and other communication disorders (NIDCD), Pharmacology research associate (PRAT) Fellowship Program (National institute of general medical sciences (NIGMS), K.P.), and National institute of mental health (NIMH, S.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sans, N., Prybylowski, K., Petralia, R. et al. NMDA receptor trafficking through an interaction between PDZ proteins and the exocyst complex. Nat Cell Biol 5, 520–530 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb990
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb990
This article is cited by
-
Altered methylation pattern in EXOC4 is associated with stroke outcome: an epigenome-wide association study
Clinical Epigenetics (2022)
-
Exo70 intracellular redistribution after repeated mild traumatic brain injury
Biological Research (2021)
-
Synaptic tau: A pathological or physiological phenomenon?
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2021)
-
Enriched Environment and Social Isolation Affect Cognition Ability via Altering Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Density in Mice Hippocampus
Neurochemical Research (2020)
-
The Exocyst Component Exo70 Modulates Dendrite Arbor Formation, Synapse Density, and Spine Maturation in Primary Hippocampal Neurons
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)