Abstract
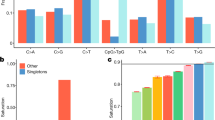
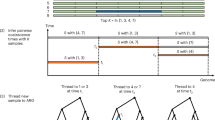
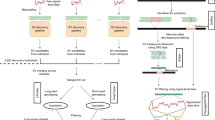
Genetic studies aimed at understanding the molecular basis of complex human phenotypes require the genotyping of many thousands of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across large numbers of individuals1. Public efforts have so far identified over two million common human SNPs2; however, the scoring of these SNPs is labor-intensive and requires a substantial amount of automation. Here we describe a simple but effective approach, termed whole-genome sampling analysis (WGSA), for genotyping thousands of SNPs simultaneously in a complex DNA sample without locus-specific primers or automation. Our method amplifies highly reproducible fractions of the genome across multiple DNA samples and calls genotypes at >99% accuracy. We rapidly genotyped 14,548 SNPs in three different human populations and identified a subset of them with significant allele frequency differences between groups. We also determined the ancestral allele for 8,386 SNPs by genotyping chimpanzee and gorilla DNA. WGSA is highly scaleable and enables the creation of ultrahigh density SNP maps for use in genetic studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardlie, K.G., Kruglyak, L. & Seielstad, M. Patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3, 299–309 (2002).
Sachidanandam, R. et al. The International SNP Map Working Group. A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature 409, 928–933 (2001).
Kwok, P.-Y. Methods for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2, 235–258 (2001).
Syvanen, A.-C. Accessing genetic variation: genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 930–942 (2001).
Lipshutz, R.J., Fodor, S.P., Gingeras, T.R. & Lockhart, D.J. High density synthetic oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 21(1 Suppl), 20–24 (1999).
Lisitsyn, N., Lisitsyn, N. & Wigler, M. Cloning the differences between two complex genomes. Science 259, 946–51 (1993).
Lucito, R. et al. Genetic analysis using genomic representations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4487–4492 (1998).
Vos, P. et al. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 4407–4414 (1995).
Altshuler, D. et al. An SNP map of the human genome generated by reduced representation shotgun sequencing. Nature 407, 513–516 (2000).
Dong, S. et al. Flexible use of high-density oligonucleotide arrays for single-nucleotide polymorphism discovery and validation. Genome Res. 11, 1418–1424 (2001).
Liu, W.-m. et al. Algorithms for large scale genotyping microarrays. Bioinformatics, (2003), in the press.
Weir, B.S. Genetic Data Analysis II (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 1996).
Bowcock, A.M. et al. Drift, admixture, and selection in human evolution: a study with DNA polymorphisms. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 839–843 (1991).
Collins-Schramm, H. et al. Ethnic-difference markers for use in mapping by admixture linkage disequilibrium. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70, 737–750 (2002).
Briscoe, D., Stephens, J.C. & O'Brien, S.J. Linkage disequilibrium in admixed populations: applications in gene mapping. J. Hered. 85, 59–63 (1994).
Parra, E.J. et al. Estimating African-American admixture proportions by use of population-specific alleles. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63, 1839–1851 (1998).
McKeigue, P.M., Carpenter, J.R., Parra, E.J. & Shriver, M.D. Estimation of admixture and detection of linkage in admixed populations by a Bayesian approach: application to African-American populations. Ann. Hum. Genet. 64, 171–186 (2000).
Hacia, J.G. Genome of the apes. Trends Genet. 17, 637–645 (2001).
Hacia, J.G. et al. Determination of ancestral alleles for human single-nucleotide polymorphisms using high-density oligonucleotide arrays. Nat. Genet. 22, 164–167 (1999).
Cargill, M. et al. Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat. Genet. 22, 231–238 (1999).
Watterson, G.A. & Guess, H.A. Is the most frequent allele the oldest? Theor. Pop. Biol. 11, 141–160 (1977).
Cavalli-Sforza, L.L., Menozzi, P. & Piazza, A. The History and Geography of Human Genes (Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 1994).
Gabriel, S.B. et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296, 2225–2229 (2002).
Lindblad-Toh, K. et al. Loss-of-heterozygosity analysis of small-cell lung carcinomas using single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 1001–1005 (2000).
Liu, W.-m. et al. Rank-based algorithms for analysis of microarrays. in Microarrays: Optical Technologies and Informatics (eds. Bittner, M.L., Chen, Y., Dorsel, A.N. & Dougherty, E.R.) Proc. SPIE 4266, 56–67 (2001).
Collins, F.S., Brooks, L.D. & Chakravarti, A. A DNA polymorphism discovery resource for research on human genetic variation. Genome Res. 8, 1229–1231 (1998).
Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987).
Picoult-Newberg, L. et al. Mining SNPs from EST databases. Genome Res. 9, 167–174 (1999).
Patil, N. et al. Blocks of limited haplotype diversity revealed by high-resolution scanning of human chromosome 21. Science 294, 1719–1723 (2001).
Fan, J.-B. et al. Paternal origins of complete hydatidiform moles proven by whole genome single-nucleotide phaplotyping. Genomics 79, 58–62 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank David Altshuler, Eric Lander, Thomas Gingeras, Richard Rava, Michael Shapero and Jon McAuliffe for helpful suggestions and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
G.C.K., H.M., S.D., W.-M.L., J.H., G.L., X.S., M.C., W.C., J.Z., W.L., G.Y., X.D., T.R., Z.H., S.P.A.F. & K.W.J. are or were employed by Affymetrix, a commercial entity that manufactures and sells synthetic DNA microarrays based on the technology described in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennedy, G., Matsuzaki, H., Dong, S. et al. Large-scale genotyping of complex DNA. Nat Biotechnol 21, 1233–1237 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt869
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt869
This article is cited by
-
Genomic medicine on the frontier of precision medicine
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2021)
-
High-density genetic map construction and QTLs identification for plant height in white jute (Corchorus capsularis L.) using specific locus amplified fragment (SLAF) sequencing
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
High-Density Genetic Linkage Map Construction and Quantitative Trait Locus Mapping for Hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge)
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Efficiency of SNP and SSR-based analysis of genetic diversity, population structure, and relationships among cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) germplasm from East Africa and IITA inbred lines
Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology (2017)
-
Transcriptomic SNP discovery for custom genotyping arrays: impacts of sequence data, SNP calling method and genotyping technology on the probability of validation success
BMC Research Notes (2016)