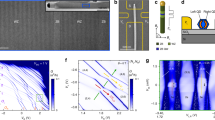
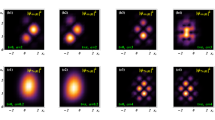
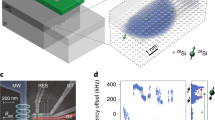
Abstract
Motion of electrons can influence their spins through a fundamental effect called spin–orbit interaction. This interaction provides a way to control spins electrically and thus lies at the foundation of spintronics1. Even at the level of single electrons, the spin–orbit interaction has proven promising for coherent spin rotations2. Here we implement a spin–orbit quantum bit (qubit) in an indium arsenide nanowire, where the spin–orbit interaction is so strong that spin and motion can no longer be separated3,4. In this regime, we realize fast qubit rotations and universal single-qubit control using only electric fields; the qubits are hosted in single-electron quantum dots that are individually addressable. We enhance coherence by dynamically decoupling the qubits from the environment. Nanowires offer various advantages for quantum computing: they can serve as one-dimensional templates for scalable qubit registers, and it is possible to vary the material even during wire growth5. Such flexibility can be used to design wires with suppressed decoherence and to push semiconductor qubit fidelities towards error correction levels. Furthermore, electrical dots can be integrated with optical dots in p–n junction nanowires6. The coherence times achieved here are sufficient for the conversion of an electronic qubit into a photon, which can serve as a flying qubit for long-distance quantum communication.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Datta, S. & Das, B. Electronic analog of the electrooptic modulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 665–667 (1990)
Nowack, K. C., Koppens, F. H. L., Nazarov, Y. V. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Coherent control of a single electron spin with electric fields. Science 318, 1430–1433 (2007)
Fasth, C., Fuhrer, A., Samuelson, L., Golovach, V. N. & Loss, D. Direct measurement of the spin-orbit interaction in a two-electron InAs nanowire quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 266801 (2007)
Pfund, A., Shorubalko, I., Ensslin, K. & Leturcq, R. Spin-state mixing in InAs double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 76, 161308 (2007)
Minot, E. D. et al. Single quantum dot nanowire LEDs. Nano Lett. 7, 367–371 (2007)
van Weert, M. H. M. et al. Selective excitation and detection of spin states in a single nanowire quantum dot. Nano Lett. 9, 1989–1993 (2009)
Nadj-Perge, S. et al. Disentangling the effects of spin-orbit and hyperfine interactions on spin blockade. Phys. Rev. B 81, 201305 (2010)
Pioro-Ladriere, M. et al. Electrically driven single-electron spin resonance in a slanting Zeeman field. Nature Phys. 4, 776–779 (2008)
Hanson, R., Kouwenhoven, L. P., Petta, J. R., Tarucha, S. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 1217–1265 (2007)
Pfund, A., Shorubalko, I., Ensslin, K. & Leturcq, R. Suppression of spin relaxation in an InAs nanowire double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 036801 (2007)
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Control and detection of singlet-triplet mixing in a random nuclear field. Science 309, 1346–1350 (2005)
Johnson, A. C. et al. Triplet-singlet spin relaxation via nuclei in a double quantum dot. Nature 435, 925–928 (2005)
Rashba, E. I. & Efros, A. L. Orbital mechanisms of electron-spin manipulation by an electric field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 126405 (2003)
Kato, Y. et al. Gigahertz electron spin manipulation using voltage-controlled g-tensor modulation. Science 299, 1201–1204 (2003)
Laird, E. A. et al. Hyperfine-mediated gate-driven electron spin resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 246601 (2007)
Golovach, V. N., Borhani, M. & Loss, D. Electric-dipole-induced spin resonance in quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 74, 165319 (2006)
Danon, J. & Nazarov, Y. V. Pauli spin blockade in the presence of strong spin-orbit coupling. Phys. Rev. B 80, 041301 (2009)
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006)
Pryor, C. E. & Flatte, M. E. Lande g factors and orbital momentum quenching in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 026804 (2006)
Berezovsky, J., Mikkelsen, M. H., Stoltz, N. G., Coldren, L. A. & Awschalom, D. D. Picosecond coherent optical manipulation of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Science 320, 349–352 (2008)
Koppens, F. H. L. et al. Universal phase shift and nonexponential decay of driven single-spin oscillations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 106803 (2007)
Obata, T. et al. Coherent manipulation of individual electron spin in a double quantum dot integrated with a micromagnet. Phys. Rev. B 81, 085317 (2010)
Koppens, F. H. L., Nowack, K. C. & Vandersypen, L. M. K. Spin echo of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 236802 (2008)
Press, D., Ladd, T. D., Zhang, B. Y. & Yamamoto, Y. Complete quantum control of a single quantum dot spin using ultrafast optical pulses. Nature 456, 218–221 (2008)
Foletti, S., Bluhm, H., Mahalu, D., Umansky, V. & Yacoby, A. Universal quantum control of two-electron spin quantum bits using dynamic nuclear polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 903–908 (2009)
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005)
Bluhm, H. et al. Long coherence of electron spins coupled to a nuclear spin bath. Preprint at 〈http://arxiv.org/abs/1005.2995〉 (2010)
Barthel, C., Medford, J., Marcus, C. M., Hanson, M. P. & Gossard, A. C. Interlaced dynamical decoupling and coherent operation of a singlet-triplet qubit. Preprint at 〈http://arxiv.org/abs/1007.4255〉 (2010)
Reilly, D. J. et al. Suppressing spin qubit dephasing by nuclear state preparation. Science 321, 817–821 (2008)
Fuchs, G. D., Dobrovitski, V. V., Toyli, D. M., Heremans, F. J. & Awschalom, D. D. Gigahertz dynamics of a strongly driven single quantum spin. Science 326, 1520–1522 (2009)
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Nowack, R. Schouten, M. Laforest, K. Zuo, M. Hocevar, R. Algra, J. van Tilburg, M. Scheffler, G. de Lange, V. Dobrovitski, J. Danon, R. Hanson, R. Liu, Yu. V. Nazarov and L. Vandersypen for their help. This work has been supported by NWO/FOM (the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research), an ERC Advanced Grant and through the DARPA program QUEST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.N.-P., S.M.F. and L.P.K. designed the experiments. S.N.-P. and S.M.F. performed the measurements and analysed the data. E.P.A.M.B. provided nanowires. All authors wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
The file contains Supplementary text, Supplementary Figures 1-5 with legends and additional references. (PDF 423 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadj-Perge, S., Frolov, S., Bakkers, E. et al. Spin–orbit qubit in a semiconductor nanowire. Nature 468, 1084–1087 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09682
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09682
This article is cited by
-
Galilean invariant dynamics in an emergent spin-orbit coupled Zeeman lattice
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Direct manipulation of a superconducting spin qubit strongly coupled to a transmon qubit
Nature Physics (2023)
-
On-demand electrical control of spin qubits
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)
-
Singlet and triplet Cooper pair splitting in hybrid superconducting nanowires
Nature (2022)
-
Ultrafast coherent control of a hole spin qubit in a germanium quantum dot
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.