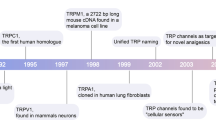
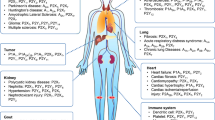
Abstract
P2X receptors are membrane ion channels activated by the binding of extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP). For years their functional significance was consigned to distant regions of the autonomic nervous system, but recent work indicates several further key roles, such as afferent signalling, chronic pain, and in autocrine loops of endothelial and epithelial cells. P2X receptors have a molecular architecture distinct from other ion channel protein families, and have several unique functional properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holton, P. The liberation of adenosine triphosphate on antidromic stimulation of sensory nerves. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 145, 494–504 (1959)
Burnstock, G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol. Rev. 24, 509–581 (1972)
Ralevic, V. & Burnstock, G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 413–492 (1998)
Zimmermann, H. Extracellular metabolism of ATP and other nucleotides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 362, 299–309 (2000)
North, R. A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 82, 1013–1067 (2002)
Valera, S. et al. A new class of ligand-gated ion channel defined by P2X receptor for extracellular ATP. Nature 371, 516–519 (1994)
Brake, A. J., Wagenbach, M. J. & Julius, D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature 371, 519–523 (1994)
Nicke, A. et al. P2X1 and P2X3 receptors form stable trimers: a novel structural motif of ligand-gated ion channels. EMBO J. 17, 3016–3028 (1998)
Barrera, N. P., Ormond, S. J., Henderson, R. M., Murrell-Lagnado, R. D. & Edwardson, J. M. Atomic force microscopy imaging demonstrates that P2X2 receptors are trimers but that P2X6 receptor subunits do not oligomerize. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10759–10765 (2005)
Jiang, L. H. et al. Subunit arrangement in P2X receptors. J. Neurosci. 23, 8903–8910 (2003)
Roberts, J. A. & Evans, R. J. ATP binding at human P2X1 receptors. Contribution of aromatic and basic amino acids revealed using mutagenesis and partial agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 9043–9055 (2004)
Nagaya, N., Tittle, R. K., Saar, N., Dellal, S. S. & Hume, R. I. An intersubunit zinc binding site in rat P2X2 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 25982–25993 (2005)
Unwin, N. Refined structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 4 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 346, 967–989 (2005)
Madden, D. R. The structure and function of glutamate receptor ion channels. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 3, 91–101 (2002)
Bo, X. et al. Pharmacological and biophysical properties of the human P2X5 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 63, 1407–1416 (2003)
Ding, S. & Sachs, F. Ion permeation and block of P2X2 purinoceptors: single channel recordings. J. Membr. Biol. 172, 215–223 (1999)
Egan, T. M. & Khakh, B. S. Contribution of calcium ions to P2X channel responses. J. Neurosci. 24, 3413–3420 (2004)
Doyle, D. A. Structural changes during ion channel gating. Trends Neurosci. 27, 298–302 (2004)
Miyazawa, A., Fujiyoshi, Y. & Unwin, N. Structure and gating mechanism of the acetylcholine receptor pore. Nature 424, 949–955 (2003)
Khakh, B. S., Bao, X., Labarca, C. & Lester, H. A. Neuronal P2X receptor-transmitter-gated cation channels change their ion selectivity in seconds. Nature Neurosci. 2, 322–330 (1999)
Doyle, D. A. Molecular insights into ion channel function. Mol. Membr. Biol. 21, 221–225 (2004)
Fisher, J. A., Girdler, G. & Khakh, B. S. Time resolved measurement of state specific P2X ion channel cytosolic gating motions. J. Neurosci. 24, 10475–10487 (2004)
Miyazawa, A., Fujiyoshi, Y., Stowell, M. & Unwin, N. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at 4.6Å resolution: transverse tunnels in the channel wall. J. Mol. Biol. 288, 765–786 (1999)
Chaumont, S., Jiang, L. H., Penna, A., North, R. A. & Rassendren, F. Identification of a trafficking motif involved in the stabilization and polarization of P2X receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 29628–29638 (2004)
Royle, S. J., Bobanovic, L. K. & Murrell-Lagnado, R. D. Identification of a non-canonical tyrosine-based endocytic motif in an ionotropic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 35378–35385 (2002)
Eickhorst, A., Berson, A., Cockayne, D., Lester, H. A. & Khakh, B. S. Control of P2X2 channel permeability by the cytosolic domain. J. Gen. Physiol. 120, 119–131 (2002)
Denlinger, L. C. et al. Cutting edge: the nucleotide receptor P2X7 contains multiple protein- and lipid-interaction motifs including a potential binding site for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 167, 1871–1876 (2001)
Kim, M., Jiang, L. H., Wilson, H. L., North, R. A. & Surprenant, A. Proteomic and functional evidence for a P2X7 receptor signalling complex. EMBO J. 20, 6347–6358 (2001)
Masin, M., Kerschensteiner, D., Dumke, K., Rubio, M. E. & Soto, F. Fe65 interacts with P2X2 subunits at excitatory synapses and modulates receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 4100–4108 (2006)
Rubio, M. E. & Soto, F. Distinct localisation of P2X receptors at excitatory postsynaptic specializations. J. Neurosci. 21, 641–653 (2001)
Edwards, F. A., Gibb, A. J. & Colquhoun, D. ATP receptor-mediated synaptic currents in the central nervous system. Nature 359, 144–147 (1992)
Jo, Y. H. & Role, L. W. Coordinate release of ATP and GABA at in vitro synapses of lateral hypothalamic neurons. J. Neurosci. 22, 4794–4804 (2002)
Jo, Y.-H. & Schlichter, R. Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nature Neurosci. 2, 241–245 (1999)
Pankratov, Y. V., Lalo, U. V. & Krishtal, O. A. Role for P2X receptors in long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 22, 8363–8369 (2002)
Mulryan, K. et al. Reduced vas deferens contraction and male infertility in mice lacking P2X1 receptors. Nature 403, 86–89 (2000)
Ren, J. et al. P2X2 subunits contribute to fast synaptic excitation in myenteric neurons of the mouse small intestine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 552, 809–821 (2003)
Gu, J. G. & MacDermott, A. B. Activation of ATP P2X receptors elicits glutamate release from sensory neuron synapses. Nature 389, 749–753 (1997)
Khakh, B. S. & Henderson, G. ATP receptor-mediated enhancement of fast excitatory neurotransmitter release in the brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 372–378 (1998)
Nakatsuka, T. & Gu, J. G. ATP P2X receptor-mediated enhancement of glutamate release and evoked EPSCs in dorsal horn neurons of the rat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 21, 6522–6531 (2001)
Khakh, B. S., Gittermann, D., Cockayne, D. A. & Jones, A. ATP modulation of excitatory synapses onto interneurons. J. Neurosci. 23, 7426–7437 (2003)
Shigetomi, E. & Kato, F. Action potential-independent release of glutamate by Ca2+ entry through presynaptic P2X receptors elicits postsynaptic firing in the brainstem autonomic network. J. Neurosci. 24, 3125–3135 (2004)
Bowser, D. N. & Khakh, B. S. ATP excites interneurons and astrocytes to increase synaptic inhibition in neuronal networks. J. Neurosci. 24, 8606–8620 (2004)
Kawamura, M., Gachet, C., Inoue, K. & Kato, F. Direct excitation of inhibitory interneurons by extracellular ATP mediated by P2Y1 receptors in the hippocampal slice. J. Neurosci. 24, 10835–10845 (2004)
Wieraszko, A., Goldsmith, G. & Seyfried, T. N. Stimulation-dependent release of adenosine triphosphate from hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 485, 244–250 (1989)
Gordon, G. R. et al. Norepinephrine triggers release of glial ATP to increase postsynaptic efficacy. Nature Neurosci. 8, 1078–1086 (2005)
Davalos, D. et al. ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nature Neurosci. 8, 752–758 (2005)
Wang, X. et al. P2X7 receptor inhibition improves recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature Med. 10, 821–827 (2004)
Dulla, C. G. et al. Adenosine and ATP link PCO2 to cortical excitability via pH. Neuron 48, 1011–1023 (2005)
Tsuda, M. et al. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 424, 778–783 (2003)
Coull, J. A. et al. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438, 1017–1021 (2005)
Bleehen, T. & Keele, C. A. Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain 3, 367–377 (1977)
Hamilton, S. G., Warburton, J., Bhattacharjee, A., Ward, J. & McMahon, S. B. ATP in human skin elicits a dose-related pain response which is potentiated under conditions of hyperalgesia. Brain 123, 1238–1246 (2000)
Chen, C. C. et al. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 377, 428–431 (1995)
Lewis, C. et al. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 377, 432–435 (1995)
Khakh, B. S., Humphrey, P. P. & Surprenant, A. Electrophysiological properties of P2X-purinoceptors in rat superior cervical, nodose and guinea-pig coeliac neurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 484, 385–395 (1995)
Cockayne, D. A. et al. Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice. Nature 407, 1011–1015 (2000)
Souslova, V. et al. Warm-coding deficits and aberrant inflammatory pain in mice lacking P2X3 receptors. Nature 407, 1015–1017 (2000)
North, R. A. The P2X3 subunit: a molecular target in pain therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 4, 833–840 (2003)
Jarvis, M. F. et al. A-317491, a novel potent and selective non-nucleotide antagonist of P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors, reduces chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain in the rat. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 17179–17184 (2002)
Kirkup, A. J., Booth, C. E., Chessell, I. P., Humphrey, P. P. & Grundy, D. Excitatory effect of P2X receptor activation on mesenteric afferent nerves in the anaesthetised rat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 520, 551–563 (1999)
Galligan, J. J. Enteric P2X receptors as potential targets for drug treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 141, 1294–1302 (2004)
Finger, T. E. et al. ATP signaling is crucial for communication from taste buds to gustatory nerves. Science 310, 1495–1499 (2005)
Gourine, A. V. On the peripheral and central chemoreception and control of breathing: an emerging role of ATP. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 568, 715–724 (2005)
Gourine, A. V., Llaudet, E., Dale, N. & Spyer, K. M. ATP is a mediator of chemosensory transduction in the central nervous system. Nature 436, 108–111 (2005)
Cockcroft, S. & Gomperts, B. D. ATP induces nucleotide permeability in rat mast cells. Nature 279, 541–542 (1979)
Gordon, J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem. J. 233, 309–319 (1986)
Surprenant, A., Rassendren, F., Kawashima, E., North, R. A. & Buell, G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 272, 735–738 (1996)
Solle, M. et al. Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X7 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 125–132 (2001)
Labasi, J. M. et al. Absence of the P2X7 receptor alters leukocyte function and attenuates an inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 168, 6436–6445 (2002)
Ke, H. Z. et al. Deletion of the P2X7 nucleotide receptor reveals its regulatory roles in bone formation and resorption. Mol. Endocrinol. 17, 1356–1367 (2003)
Virginio, C., MacKenzie, A., Rassendren, F. A., North, R. A. & Surprenant, A. Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nature Neurosci. 2, 315–321 (1999)
Jiang, L. H. et al. N-methyl-d-glucamine and propidium dyes utilize different permeation pathways at rat P2X7 receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 289, C1295–C1302 (2005)
Elliott, J. I. et al. Membrane phosphatidylserine distribution as a non-apoptotic signalling mechanism in lymphocytes. Nature Cell Biol. 7, 808–816 (2005)
Chessell, I. et al. Disruption of the P2X7 purinoceptor gene abolishes chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 114, 386–396 (2005)
Ma, W. et al. Pore properties and pharmacological features of the P2X receptor channel in airway ciliated cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 571, 503–517 (2006)
Yamamoto, K. et al. Impaired flow-dependent control of vascular tone and remodeling in P2X4-deficient mice. Nature Med. 12, 133–137 (2006)
Agboh, K. C., Webb, T. E., Evans, R. J. & Ennion, S. J. Functional characterization of a P2X receptor from Schistosoma mansoni. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41650–41657 (2004)
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff of the LMB Visual Aids Unit and J. A. Fisher for help with the illustrations. Work in our laboratories is supported by the MRC, EMBO, HFSP, NIH and Wellcome Trust. We regret that space limitations prevented us from citing many important original papers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khakh, B., Alan North, R. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature 442, 527–532 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04886
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04886
This article is cited by
-
Targeting Pannexin-1 Channels: Addressing the ‘Gap’ in Chronic Pain
CNS Drugs (2024)
-
Disruption of MAM integrity in mutant FUS oligodendroglial progenitors from hiPSCs
Acta Neuropathologica (2024)
-
Dorsal root ganglia P2X4 and P2X7 receptors contribute to diabetes-induced hyperalgesia and the downregulation of electroacupuncture on P2X4 and P2X7
Purinergic Signalling (2023)
-
ALPK1 Expressed in IB4-Positive Neurons of Mice Trigeminal Ganglions Promotes MIA-Induced TMJ pain
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Ivermectin Protects Against Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Mice by Modulating the Th17/Treg Balance Involved in the IL-2/STAT5 Pathway
Inflammation (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.