Abstract
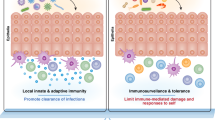
Organs such as the liver, uterus and lung possess hallmark immunotolerant features, making these organs important for sustaining self-homeostasis. These organs contain a relatively large amount of negative regulatory immune cells, which are believed to take part in the regulation of immune responses. Because natural killer cells constitute a large proportion of all lymphocytes in these organs, increasing attention has been given to the roles that these cells play in maintaining immunotolerance. Here, we review the distribution, differentiation, phenotypic features and functional features of natural killer cells in these immunotolerant organs, in addition to the influence of local microenvironments on these cells and how these factors contribute to organ-specific diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martini A, Burgio GR . Tolerance and auto-immunity: 50 years after Burnet. Eur J Pediatr 1999; 158: 769–775.
Bach JF . Induction of immunological tolerance using monoclonal antibodies: applications to organ transplantation and autoimmune disease. C R Biol 2006; 329: 260–262.
Sakaguchi S, Powrie F, Ransohoff RM . Re-establishing immunological self-tolerance in autoimmune disease. Nat Med 2012; 18: 54–58.
Kang TH, Mao CP, La V, Chen A, Hung CF, Wu TC . Innovative DNA vaccine to break immune tolerance against tumor self-antigen. Hum Gene Ther 2012; 24: 181–188.
Veenbergen S, Samsom JN . Maintenance of small intestinal and colonic tolerance by IL-10-producing regulatory T cell subsets. Curr Opin Immunol 2012; 24: 269–276.
Beland K, Lapierre P, Djilali-Saiah I, Alvarez F . Liver restores immune homeostasis after local inflammation despite the presence of autoreactive T cells. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e48192.
Tiegs G, Lohse AW . Immune tolerance: what is unique about the liver. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: 1–6.
Gregoire C, Chasson L, Luci C, Tomasello E, Geissmann F, Vivier E et al. The trafficking of natural killer cells. Immunol Rev 2007; 220: 169–182.
Wang J, Li F, Zheng M, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z . Lung natural killer cells in mice: phenotype and response to respiratory infection. Immunology 2012; 137: 37–47.
Trowsdale J, Betz AG . Mother's little helpers: mechanisms of maternal–fetal tolerance. Nat Immunol 2006; 7: 241–246.
Medzhitov R, Janeway C Jr . Innate immunity. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 338–344.
Murphy K, Travers P, Walport M, Janeway C . Janeway's Immunobiology. 8th ed. New York: Garland Science, 2012.
Cerwenka A, Lanier LL . Ligands for natural killer cell receptors: redundancy or specificity. Immunol Rev 2001; 181: 158–169.
Vivier E, Nunes JA, Vely F . Natural killer cell signaling pathways. Science 2004; 306: 1517–1519.
Nguyen-Pham TN, Yang DH, Nguyen TA, Lim MS, Hong CY, Kim MH et al. Optimal culture conditions for the generation of natural killer cell-induced dendritic cells for cancer immunotherapy. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 45–53.
Luevano M, Madrigal A, Saudemont A . Generation of natural killer cells from hematopoietic stem cells in vitro for immunotherapy. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 310–320.
Cheng M, Zhang J, Jiang W, Chen Y, Tian Z . Natural killer cell lines in tumor immunotherapy. Front Med 2012; 6: 56–66.
Caligiuri MA . Human natural killer cells. Blood 2008; 112: 461–469.
Inngjerdingen M, Kveberg L, Naper C, Vaage JT . Natural killer cell subsets in man and rodents. Tissue Antigens 2011; 78: 81–88.
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA . The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 2001; 22: 633–640.
Fauriat C, Long EO, Ljunggren HG, Bryceson YT . Regulation of human NK-cell cytokine and chemokine production by target cell recognition. Blood 2010; 115: 2167–2176.
Lanier LL . Up on the tightrope: natural killer cell activation and inhibition. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 495–502.
Sun JC, Lanier LL . NK cell development, homeostasis and function: parallels with CD8+ T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 645–657.
Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ . CD27 dissects mature NK cells into two subsets with distinct responsiveness and migratory capacity. J Immunol 2006; 176: 1517–1524.
Ndhlovu LC, Lopez-Verges S, Barbour JD, Jones RB, Jha AR, Long BR et al. Tim-3 marks human natural killer cell maturation and suppresses cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood 2012; 119: 3734–3743.
Bjorkstrom NK, Riese P, Heuts F, Andersson S, Fauriat C, Ivarsson MA et al. Expression patterns of NKG2A, KIR, and CD57 define a process of CD56dim NK-cell differentiation uncoupled from NK-cell education. Blood 2010; 116: 3853–3864.
Chan A, Hong DL, Atzberger A, Kollnberger S, Filer AD, Buckley CD et al. CD56bright human NK cells differentiate into CD56dim cells: role of contact with peripheral fibroblasts. J Immunol 2007; 179: 89–94.
Shi FD, Ljunggren HG, La Cava A, van Kaer L . Organ-specific features of natural killer cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 658–671.
Kim S, Iizuka K, Kang HS, Dokun A, French AR, Greco S et al. In vivo developmental stages in murine natural killer cell maturation. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 523–528.
Chiossone L, Chaix J, Fuseri N, Roth C, Vivier E, Walzer T . Maturation of mouse NK cells is a 4-stage developmental program. Blood 2009; 113: 5488–5496.
Ehlers M, Papewalis C, Stenzel W, Jacobs B, Meyer KL, Deenen R et al. Immunoregulatory natural killer cells suppress autoimmunity by down-regulating antigen-specific CD8+ T cells in mice. Endocrinology 2012; 153: 4367–4379.
Carrega P, Ferlazzo G . Natural killer cell distribution and trafficking in human tissues. Front Immunol 2012; 3: 347.
Tomasello E, Yessaad N, Gregoire E, Hudspeth K, Luci C, Mavilio D et al. Mapping of NKp46+ cells in healthy human lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. Front Immunol 2012; 3: 344.
Zhao E, Xu H, Wang L, Kryczek I, Wu K, Hu Y et al. Bone marrow and the control of immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 11–19.
Yokoyama WM, Kim S, French AR . The dynamic life of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2004; 22: 405–429.
Thapa M, Kuziel WA, Carr DJ . Susceptibility of CCR5-deficient mice to genital herpes simplex virus type 2 is linked to NK cell mobilization. J Virol 2007; 81: 3704–3713.
Hokeness KL, Kuziel WA, Biron CA, Salazar-Mather TP . Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and CCR2 interactions are required for IFN-alpha/beta-induced inflammatory responses and antiviral defense in liver. J Immunol 2005; 174: 1549–1556.
Salazar-Mather TP, Orange JS, Biron CA . Early murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection induces liver natural killer (NK) cell inflammation and protection through macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP-1alpha)-dependent pathways. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 1–14.
Gregoire C, Cognet C, Chasson L, Coupet CA, Dalod M, Reboldi A et al. Intrasplenic trafficking of natural killer cells is redirected by chemokines upon inflammation. Eur J Immunol 2008; 38: 2076–2084.
Beider K, Nagler A, Wald O, Franitza S, Dagan-Berger M, Wald H et al. Involvement of CXCR4 and IL-2 in the homing and retention of human NK and NK T cells to the bone marrow and spleen of NOD/SCID mice. Blood 2003; 102: 1951–1958.
Walzer T, Chiossone L, Chaix J, Calver A, Carozzo C, Garrigue-Antar L et al. Natural killer cell trafficking in vivo requires a dedicated sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 1337–1344.
Eksteen B, Afford SC, Wigmore SJ, Holt AP, Adams DH . Immune-mediated liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2007; 27: 351–366.
Kita H, Mackay IR, van de Water J, Gershwin ME . The lymphoid liver: considerations on pathways to autoimmune injury. Gastroenterology 2001; 120: 1485–1501.
Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z . Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 2008; 47: 729–736.
Yamagiwa S, Kamimura H, Ichida T . Natural killer cell receptors and their ligands in liver diseases. Med Mol Morphol 2009; 42: 1–8.
Cooper MA, Elliott JM, Keyel PA, Yang L, Carrero JA, Yokoyama WM . Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 1915–1919.
McIntyre KW, Welsh RM . Accumulation of natural killer and cytotoxic T large granular lymphocytes in the liver during virus infection. J Exp Med 1986; 164: 1667–1681.
Liaskou E, Wilson DV, Oo YH . Innate immune cells in liver inflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2012; 2012: 949157.
Hata K, Zhang XR, Iwatsuki S, van Thiel DH, Herberman RB, Whiteside TL . Isolation, phenotyping, and functional analysis of lymphocytes from human liver. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1990; 56: 401–419.
Norris S, Collins C, Doherty DG, Smith F, McEntee G, Traynor O et al. Resident human hepatic lymphocytes are phenotypically different from circulating lymphocytes. J Hepatol 1998; 28: 84–90.
Gordon SM, Chaix J, Rupp LJ, Wu J, Madera S, Sun JC et al. The transcription factors T-bet and Eomes control key checkpoints of natural killer cell maturation. Immunity 2012; 36: 55–67.
Jiang X, Chen Y, Peng H, Tian Z . Single line or parallel lines: NK cell differentiation driven by T-bet and Eomes. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 193–194.
Takeda K, Cretney E, Hayakawa Y, Ota T, Akiba H, Ogasawara K et al. TRAIL identifies immature natural killer cells in newborn mice and adult mouse liver. Blood 2005; 105: 2082–2089.
Lanier LL . NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 225–274.
Lanier LL . Natural killer cell receptor signaling. Curr Opin Immunol 2003; 15: 308–314.
Ishiyama K, Ohdan H, Ohira M, Mitsuta H, Arihiro K, Asahara T . Difference in cytotoxicity against hepatocellular carcinoma between liver and periphery natural killer cells in humans. Hepatology 2006; 43: 362–372.
Subleski JJ, Hall VL, Back TC, Ortaldo JR, Wiltrout RH . Enhanced antitumor response by divergent modulation of natural killer and natural killer T cells in the liver. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 11005–11012.
Krueger PD, Lassen MG, Qiao H, Hahn YS . Regulation of NK cell repertoire and function in the liver. Crit Rev Immunol 2011; 31: 43–52.
Jinushi M, Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Yamaguchi S, Sakamori R, Hiramatsu N et al. Natural killer cell and hepatic cell interaction via NKG2A leads to dendritic cell-mediated induction of CD4 CD25 T cells with PD-1-dependent regulatory activities. Immunology 2007; 120: 73–82.
Jinushi M, Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Kanto T, Miyagi T, Suzuki T et al. Negative regulation of NK cell activities by inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A leads to altered NK cell-induced modulation of dendritic cell functions in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6072–6081.
Tu Z, Bozorgzadeh A, Pierce RH, Kurtis J, Crispe IN, Orloff MS . TLR-dependent cross talk between human Kupffer cells and NK cells. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 233–244.
Lassen MG, Lukens JR, Dolina JS, Brown MG, Hahn YS . Intrahepatic IL-10 maintains NKG2A+Ly49− liver NK cells in a functionally hyporesponsive state. J Immunol 2010; 184: 2693–2701.
Spaan M, Janssen HL, Boonstra A . Immunology of hepatitis C virus infections. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2012; 26: 391–400.
Seeger C, Mason WS . Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2000; 64: 51–68.
Shi CC, Tjwa ET, Biesta PJ, Boonstra A, Xie Q, Janssen HL et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses the functional interaction between natural killer cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Viral Hepat 2012; 19: e26–e33.
Sun C, Fu B, Gao Y, Liao X, Sun R, Tian Z et al. TGF-beta1 down-regulation of NKG2D/DAP10 and 2B4/SAP expression on human NK cells contributes to HBV persistence. PLoS Pathog 2012; 8: e1002594.
Wu L, Zhang C, Zhang J . HMBOX1 negatively regulates NK cell functions by suppressing the NKG2D/DAP10 signaling pathway. Cell Mol Immunol 2011; 8: 433–440.
Dong Z, Wei H, Sun R, Hu Z, Gao B, Tian Z . Involvement of natural killer cells in PolyI:C-induced liver injury. J Hepatol 2004; 41: 966–973.
Chen Y, Sun R, Jiang W, Wei H, Tian Z . Liver-specific HBsAg transgenic mice are over-sensitive to Poly(I:C)-induced liver injury in NK cell- and IFN-gamma-dependent manner. J Hepatol 2007; 47: 183–190.
Yin W, Xu L, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z . Interleukin-15 suppresses hepatitis B virus replication via IFN-beta production in a C57BL/6 mouse model. Liver Int 2012; 32: 1306–1314.
Han Q, Zhang C, Zhang J, Tian Z . Involvement of activation of PKR in HBx-siRNA-mediated innate immune effects on HBV inhibition. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e27931.
Han Q, Zhang C, Zhang J, Tian Z . Reversal of hepatitis B virus-induced immune tolerance by an immunostimulatory 3p-HBx-siRNAs in a retinoic acid inducible gene I-dependent manner. Hepatology 2011; 54: 1179–1189.
Huang M, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z . Simultaneous knockdown of multiple ligands of innate receptor NKG2D high efficiently prevents NK cell-mediated fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology 2013; 57: 277–288.
Kramer B, Korner C, Kebschull M, Glassner A, Eisenhardt M, Nischalke HD et al. Natural killer p46High expression defines a natural killer cell subset that is potentially involved in control of hepatitis C virus replication and modulation of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2012; 56: 1201–1213.
Golden-Mason L, Cox AL, Randall JA, Cheng L, Rosen HR . Increased natural killer cell cytotoxicity and NKp30 expression protects against hepatitis C virus infection in high-risk individuals and inhibits replication in vitro. Hepatology 2010; 52: 1581–1589.
Nattermann J, Feldmann G, Ahlenstiel G, Langhans B, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U . Surface expression and cytolytic function of natural killer cell receptors is altered in chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2006; 55: 869–877.
Wei H, Wang H, Tian Z, Sun R . Activation of natural killer cells inhibits liver regeneration in toxin-induced liver injury model in mice via a tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2010; 299: G275–282.
Wegmann TG, Lin H, Guilbert L, Mosmann TR . Bidirectional cytokine interactions in the maternal–fetal relationship: is successful pregnancy a TH2 phenomenon? Immunol Today 1993; 14: 353–356.
Lash GE, Robson SC, Bulmer JN . Review: functional role of uterine natural killer (uNK) cells in human early pregnancy decidua. Placenta 2010; 31 Suppl: S87–S92.
Robson A, Harris LK, Innes BA, Lash GE, Aljunaidy MM, Aplin JD et al. Uterine natural killer cells initiate spiral artery remodeling in human pregnancy. FASEB J 2012; 26: 4876–4885.
Hanna J, Goldman-Wohl D, Hamani Y, Avraham I, Greenfield C, Natanson-Yaron S et al. Decidual NK cells regulate key developmental processes at the human fetal–maternal interface. Nat Med 2006; 12: 1065–1074.
Sargent IL, Borzychowski AM, Redman CW . NK cells and human pregnancy–an inflammatory view. Trends Immunol 2006; 27: 399–404.
Deniz G, Christmas SE, Brew R, Johnson PM . Phenotypic and functional cellular differences between human CD3-decidual and peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol 1994; 152: 4255–4261.
Manaster I, Mandelboim O . The unique properties of uterine NK cells. Am J Reprod Immunol 2010; 63: 434–444.
Hanna J, Mandelboim O . When killers become helpers. Trends Immunol 2007; 28: 201–206.
Higuma-Myojo S, Sasaki Y, Miyazaki S, Sakai M, Siozaki A, Miwa N et al. Cytokine profile of natural killer cells in early human pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol 2005; 54: 21–29.
Koopman LA, Kopcow HD, Rybalov B, Boyson JE, Orange JS, Schatz F et al. Human decidual natural killer cells are a unique NK cell subset with immunomodulatory potential. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 1201–1212.
Zhang J, Chen Z, Smith GN, Croy BA . Natural killer cell-triggered vascular transformation: maternal care before birth? Cell Mol Immunol 2011; 8: 1–11.
Karimi K, Arck PC . Natural killer cells: keepers of pregnancy in the turnstile of the environment. Brain Behav Immun 2010; 24: 339–347.
Mjosberg J, Berg G, Jenmalm MC, Ernerudh J . FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and T helper 1, T helper 2, and T helper 17 cells in human early pregnancy decidua. Biol Reprod 2010; 82: 698–705.
Xu C, Mao D, Holers VM, Palanca B, Cheng AM, Molina H . A critical role for murine complement regulator crry in fetomaternal tolerance. Science 2000; 287: 498–501.
Makrigiannakis A, Zoumakis E, Kalantaridou S, Coutifaris C, Margioris AN, Coukos G et al. Corticotropin-releasing hormone promotes blastocyst implantation and early maternal tolerance. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 1018–1024.
Chaouat G, Ledee-Bataille N, Dubanchet S, Zourbas S, Sandra O, Martal J . TH1/TH2 paradigm in pregnancy: paradigm lost? Cytokines in pregnancy/early abortion reexamining the TH1/TH2 paradigm. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2004; 134: 93–119.
Hiby SE, Walker JJ, O'Shaughnessy KM, Redman CW, Carrington M, Trowsdale J et al. Combinations of maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C genes influence the risk of preeclampsia and reproductive success. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 957–965.
Moffett A, Loke C . Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 584–594.
Sharkey AM, Gardner L, Hiby S, Farrell L, Apps R, Masters L et al. Killer Ig-like receptor expression in uterine NK cells is biased toward recognition of HLA-C and alters with gestational age. J Immunol 2008; 181: 39–46.
Blois SM, Ilarregui JM, Tometten M, Garcia M, Orsal AS, Cordo-Russo R et al. A pivotal role for galectin-1 in fetomaternal tolerance. Nat Med 2007; 13: 1450–1457.
Fu B, Li X, Sun R, Tong X, Ling B, Tian Z et al. Natural killer cells promote immune tolerance by regulating inflammatory TH17 cells at the human maternal–fetal interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; in press.
Zhu XY, Zhou YH, Wang MY, Jin LP, Yuan MM, Li DJ . Blockade of CD86 signaling facilitates a Th2 bias at the maternal–fetal interface and expands peripheral CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells to rescue abortion-prone fetuses. Biol Reprod 2005; 72: 338–345.
Guleria I, Khosroshahi A, Ansari MJ, Habicht A, Azuma M, Yagita H et al. A critical role for the programmed death ligand 1 in fetomaternal tolerance. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 231–237.
Poehlmann TG, Busch S, Mussil B, Winzer H, Weinert J, Mebes I et al. The possible role of the Jak/STAT pathway in lymphocytes at the fetomaternal interface. Chem Immunol Allergy 2005; 89: 26–35.
D'Addio F, Riella LV, Mfarrej BG, Chabtini L, Adams LT, Yeung M et al. The link between the PDL1 costimulatory pathway and Th17 in fetomaternal tolerance. J Immunol 2011; 187: 4530–4541.
Ayatollahi M, Geramizadeh B, Samsami A . Transforming growth factor beta-1 influence on fetal allografts during pregnancy. Transplant Proc 2005; 37: 4603–4604.
Blois SM, Barrientos G, Garcia MG, Orsal AS, Tometten M, Cordo-Russo RI et al. Interaction between dendritic cells and natural killer cells during pregnancy in mice. J Mol Med (Berl) 86: 2008; 837–852.
Karimi K, Blois SM, Arck PC . The upside of natural killers. Nat Med 2008; 14: 1184–1185.
Aluvihare VR, Kallikourdis M, Betz AG . Regulatory T cells mediate maternal tolerance to the fetus. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 266–271.
Croy BA, van den Heuvel MJ, Borzychowski AM, Tayade C . Uterine natural killer cells: a specialized differentiation regulated by ovarian hormones. Immunol Rev 2006; 214: 161–185.
Ozturk OG, Sahin G, Karacor ED, Kucukgoz U . Evaluation of KIR genes in recurrent miscarriage. J Assist Reprod Genet 2012; 29: 933–938.
Bao SH, Shuai W, Tong J, Wang L, Chen P, Sun J . Increased expression of Toll-like receptor 3 in decidual natural killer cells of patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous miscarriage. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2012; 165: 326–330.
Karami N, Boroujerdnia MG, Nikbakht R, Khodadadi A . Enhancement of peripheral blood CD56dim cell and NK cell cytotoxicity in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion or in vitro fertilization failure. J Reprod Immunol 2012; 95: 87–92.
Fukui A, Yokota M, Funamizu A, Nakamua R, Fukuhara R, Yamada K et al. Changes of NK cells in preeclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol 2012; 67: 278–286.
Dunk C, Ahmed A . Expression of VEGF-C and activation of its receptors VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 in trophoblast. Histol Histopathol 2001; 16: 359–375.
Molvarec A, Blois SM, Stenczer B, Toldi G, Tirado-Gonzalez I, Ito M et al. Peripheral blood galectin-1-expressing T and natural killer cells in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia. Clin Immunol 2011; 139: 48–56.
Zhang J, Dong Z, Zhou R, Luo D, Wei H, Tian Z . Isolation of lymphocytes and their innate immune characterizations from liver, intestine, lung and uterus. Cell Mol Immunol 2005; 2: 271–280.
Small CL, McCormick S, Gill N, Kugathasan K, Santosuosso M, Donaldson N et al. NK cells play a critical protective role in host defense against acute extracellular Staphylococcus aureus bacterial infection in the lung. J Immunol 2008; 180: 5558–5568.
Morrison BE, Park SJ, Mooney JM, Mehrad B . Chemokine-mediated recruitment of NK cells is a critical host defense mechanism in invasive aspergillosis. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1862–1870.
Schuster M, Tschernig T, Krug N, Pabst R . Lymphocytes migrate from the blood into the bronchoalveolar lavage and lung parenchyma in the asthma model of the brown Norway rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 161: 558–566.
Wissinger E, Goulding J, Hussell T . Immune homeostasis in the respiratory tract and its impact on heterologous infection. Semin Immunol 2009; 21: 147–155.
Robinson BW, Pinkston P, Crystal RG . Natural killer cells are present in the normal human lung but are functionally impotent. J Clin Invest 1984; 74: 942–950.
Weissman DN, deShazo RD, Banks DE . Modulation of natural killer cell function by human alveolar macrophages. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1986; 78: 571–577.
Bordignon C, Villa F, Allavena P, Introna M, Biondi A, Avallone R et al. Inhibition of natural killer activity by human bronchoalveolar macrophages. J Immunol 1982; 129: 587–591.
Roth MD, Golub SH . Inhibition of lymphokine-activated killer cell function by human alveolar macrophages. Cancer Res 1989; 49: 4690–4695.
Lauzon W, Lemaire I . Alveolar macrophage inhibition of lung-associated NK activity: involvement of prostaglandins and transforming growth factor-beta 1. Exp Lung Res 1994; 20: 331–349.
Wilsher ML, Hughes DA, Haslam PL . Immunomodulatory effects of pulmonary surfactant on natural killer cell and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. Clin Exp Immunol 1988; 74: 465–470.
Laouar Y, Sutterwala FS, Gorelik L, Flavell RA . Transforming growth factor-beta controls T helper type 1 cell development through regulation of natural killer cell interferon-gamma. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 600–607.
Ennis FA, Meager A, Beare AS, Qi YH, Riley D, Schwarz G et al. Interferon induction and increased natural killer-cell activity in influenza infections in man. Lancet 1981; 2: 891–893.
Nogusa S, Ritz BW, Kassim SH, Jennings SR, Gardner EM . Characterization of age-related changes in natural killer cells during primary influenza infection in mice. Mech Ageing Dev 2008; 129: 223–230.
Stein-Streilein J, Guffee J . In vivo treatment of mice and hamsters with antibodies to asialo GM1 increases morbidity and mortality to pulmonary influenza infection. J Immunol 1986; 136: 1435–1441.
Li F, Zhu H, Sun R, Wei H, Tian Z . Natural killer cells are involved in acute lung immune injury caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Virol 2012; 86: 2251–2258.
Al-Muhsen S, Casanova JL . The genetic heterogeneity of mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122: 1043–1051; quiz 1052–1043.
Cooper AM, Dalton DK, Stewart TA, Griffin JP, Russell DG, Orme IM . Disseminated tuberculosis in interferon gamma gene-disrupted mice. J Exp Med 1993; 178: 2243–2247.
Schierloh P, Yokobori N, Aleman M, Musella RM, Beigier-Bompadre M, Saab MA et al. Increased susceptibility to apoptosis of CD56dimCD16+ NK cells induces the enrichment of IFN-gamma-producing CD56bright cells in tuberculous pleurisy. J Immunol 2005; 175: 6852–6860.
Millman AC, Salman M, Dayaram YK, Connell ND, Venketaraman V . Natural killer cells, glutathione, cytokines, and innate immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2008; 28: 153–165.
Vankayalapati R, Wizel B, Weis SE, Safi H, Lakey DL, Mandelboim O et al. The NKp46 receptor contributes to NK cell lysis of mononuclear phagocytes infected with an intracellular bacterium. J Immunol 2002; 168: 3451–3457.
Venketaraman V, Millman A, Salman M, Swaminathan S, Goetz M, Lardizabal A et al. Glutathione levels and immune responses in tuberculosis patients. Microb Pathog 2008; 44: 255–261.
Guerra C, Johal K, Morris D, Moreno S, Alvarado O, Gray D et al. Control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by activated natural killer cells. Clin Exp Immunol 2012; 168: 142–152.
Dhiman R, Periasamy S, Barnes PF, Jaiswal AG, Paidipally P, Barnes AB et al. NK1.1+ cells and IL-22 regulate vaccine-induced protective immunity against challenge with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol 2012; 189: 897–905.
Lloyd CM, Robinson DS . Allergen-induced airway remodelling. Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 1020–1032.
Jira M, Antosova E, Vondra V, Strejcek J, Mazakova H, Prazakova J . Natural killer and interleukin-2 induced cytotoxicity in asthmatics. I. Effect of acute antigen-specific challenge. Allergy 1988; 43: 294–298.
Timonen T, Stenius-Aarniala B . Natural killer cell activity in asthma. Clin Exp Immunol 1985; 59: 85–90.
Wei H, Zhang J, Xiao W, Feng J, Sun R, Tian Z . Involvement of human natural killer cells in asthma pathogenesis: natural killer 2 cells in type 2 cytokine predominance. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 841–847.
Ishikawa H, Sasaki H, Fukui T, Fujita K, Kutsukake E, Matsumoto T . Mice with asthma are more resistant to influenza virus infection and NK cells activated by the induction of asthma have potentially protective effects. J Clin Immunol 2012; 32: 256–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Sun, C., Tian, Z. et al. NK cells in immunotolerant organs. Cell Mol Immunol 10, 202–212 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Functional integration of natural killer cells in a microfluidically perfused liver on-a-chip model
BMC Research Notes (2023)
-
Natural killer cells: a promising immunotherapy for cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Prevention of liver metastases through perioperative acute CpG-C immune stimulation
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2020)
-
Natural killer cells in liver diseases
Frontiers of Medicine (2018)
-
NK cells are negatively regulated by sCD83 in experimental autoimmune uveitis
Scientific Reports (2017)