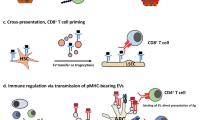
Abstract
Because of its unique blood supply, the liver maintains a special local immune tolerogenic microenvironment. Moreover, the liver can impart this immune tolerogenic effect on other organs, thus inducing systemic immune tolerance. The network of hepatic regulatory cells is an important mechanism underlying liver tolerance. Many types of liver-resident antigen-presenting cells (APCs) have immune regulatory function, and more importantly, they can also induce the differentiation of circulating immune cells into regulatory cells to further extend systemic tolerance. Thus, the liver can be seen as a type of ‘school’, where liver APCs function as ‘teachers’ and circulating immune cells function as ‘students.’
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallegos AM, Bevan MJ . Central tolerance: good but imperfect. Immunol Rev 2006; 209: 290–296.
Palmer E . Negative selection–learing out the bad apples from the T-cell repertoire. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 383–391.
Bouneaud C, Kourilsky P, Bousso P . Impact of negative selection on the T cell repertoire reactive to a self-peptide: a large fraction of T cell clones escapes clonal deletion. Immunity 2000; 13: 829–840.
Bertolino P, McCaughan GW, Bowen DG . Role of primary intrahepatic T-cell activation in the ‘liver tolerance effect’. Immunol Cell Biol 2002; 80: 84–92.
Calne RY, Sells RA, Pena JR, Davis DR, Millard PR, Herbertson BM et al. Induction of immunological tolerance by porcine liver allografts. Nature 1969; 223: 472–476.
Cantor HM, Dumont AE . Hepatic suppression of sensitization to antigen absorbed into the portal system. Nature 1967; 215: 744–745.
Triger DR, Cynamon MH, Wright R . Studies on hepatic uptake of antigen. I. Comparison of inferior vena cava and portal vein routes of immunization. Immunology 1973; 25: 941–950.
Protzer U, Maini MK, Knolle PA . Living in the liver: hepatic infections. Nat Rev Immunol 2012; 12: 201–213.
Huang L, Soldevila G, Leeker M, Flavell R, Crispe IN . The liver eliminates T cells undergoing antigen-triggered apoptosis in vivo. Immunity 1994; 1: 741–749.
Mehal WZ, Juedes AE, Crispe IN . Selective retention of activated CD8+ T cells by the normal liver. J Immunol 1999; 163: 3202–3210.
Zhao E, Xu H, Wang L, Kryczek I, Wu K, Hu Y et al. Bone marrow and the control of immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 11–19.
Polakos NK, Cornejo JC, Murray DA, Wright KO, Treanor JJ, Crispe IN et al. Kupffer cell-dependent hepatitis occurs during influenza infection. Am J Pathol 2006; 168: 1169–1178; quiz 1404–1165.
Rastellini C, Lu L, Ricordi C, Starzl TE, Rao AS, Thomson AW . Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-stimulated hepatic dendritic cell progenitors prolong pancreatic islet allograft survival. Transplantation 1995; 60: 1366–1370.
Passini MA, Bu J, Fidler JA, Ziegler RJ, Foley JW, Dodge JC et al. Combination brain and systemic injections of AAV provide maximal functional and survival benefits in the Niemann–Pick mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007; 104: 9505–9510.
Luth S, Huber S, Schramm C, Buch T, Zander S, Stadelmann C et al. Ectopic expression of neural autoantigen in mouse liver suppresses experimental autoimmune neuroinflammation by inducing antigen-specific Tregs. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3403–3410.
Mingozzi F, Liu YL, Dobrzynski E, Kaufhold A, Liu JH, Wang Y et al. Induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX antigen by in vivo hepatic gene transfer. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 1347–1356.
Hoffman BE, Dobrzynski E, Wang L, Hirao L, Mingozzi F, Cao O et al. Muscle as a target for supplementary factor IX gene transfer. Human Gene Ther 2007; 18: 603–613.
Sakaguchi S . Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 345–352.
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM, Hafler DA . FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 490–500.
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M . Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 2008; 133: 775–787.
Walker LS, Chodos A, Eggena M, Dooms H, Abbas AK . Antigen-dependent proliferation of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 249–258.
Liang S, Alard P, Zhao Y, Parnell S, Clark SL, Kosiewicz M . M. Conversion of CD4+ CD25− cells into CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo requires B7 costimulation, but not the thymus. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 127–137.
Longhi MS, Ma Y, Bogdanos DP, Cheeseman P, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D . Impairment of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cells in autoimmune liver disease. J Hepatol 2004; 41: 31–37.
Lan RY, Cheng C, Lian ZX, Tsuneyama K, Yang GX, Moritoki Y et al. Liver-targeted and peripheral blood alterations of regulatory T cells in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2006; 43: 729–737.
Longhi MS, Hussain MJ, Mitry RR, Arora SK, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D et al. Functional study of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in health and autoimmune hepatitis. J Immunol 2006; 176: 4484–4491.
O'Garra A, Vieira P . Regulatory T cells and mechanisms of immune system control. Nat Med 2004; 10: 801–805.
Bopp T, Becker C, Klein M, Klein-Hessling S, Palmetshofer A, Serfling E et al. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate is a key component of regulatory T cell-mediated suppression. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1303–1310.
Wei HX, Chuang YH, Li B, Wei H, Sun R, Moritoki Y et al. CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells protect against T cell-mediated fulminant hepatitis in a TGF-beta-dependent manner in mice. J Immunol 2008; 181: 7221–7229.
Erhardt A, Biburger M, Papadopoulos T, Tiegs G . IL-10, regulatory T cells, and Kupffer cells mediate tolerance in concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Hepatology 2007; 45: 475–485.
Ward SM, Fox BC, Brown PJ, Worthington J, Fox SB, Chapman RW et al. Quantification and localisation of FOXP3+ T lymphocytes and relation to hepatic inflammation during chronic HCV infection. J Hepatol 2007; 47: 316–324.
Rushbrook SM, Ward SM, Unitt E, Vowler SL, Lucas M, Klenerman P et al. Regulatory T cells suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2005; 79: 7852–7859.
Boettler T, Spangenberg HC, Neumann-Haefelin C, Panther E, Urbani S, Ferrari C et al. T cells with a CD4+CD25+ regulatory phenotype suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2005; 79: 7860–7867.
Li W, Kuhr CS, Zheng XX, Carper K, Thomson AW, Reyes JD et al. New insights into mechanisms of spontaneous liver transplant tolerance: the role of Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Am J Transplant 2008; 8: 1639–1651.
Jiang X, Morita M, Sugioka A, Harada M, Kojo S, Wakao H et al. The importance of CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells in mouse hepatic allograft tolerance. Liver Transplant 2006; 12: 1112–1118.
Emoto M, Kaufmann SH . Liver NKT cells: an account of heterogeneity. Trends Immunol 2003; 24: 364–369.
Eberl G, Lees R, Smiley ST, Taniguchi M, Grusby MJ, MacDonald H . R. Tissue-specific segregation of CD1d-dependent and CD1d-independent NK T cells. J Immunol 1999; 162: 6410–6419.
Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L . The biology of NKT cells. Ann Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 297–336.
Kawano T, Cui J, Koezuka Y, Toura I, Kaneko Y, Motoki K et al. CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides. Science 1997; 278: 1626–1629.
Taniguchi M, Harada M, Kojo S, Nakayama T, Wakao H . The regulatory role of Valpha14 NKT cells in innate and acquired immune response. Ann Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 483–513.
van Kaer L . NKT cells: T lymphocytes with innate effector functions. Curr Opin Immunol 2007; 19: 354–364.
Kronenberg M . Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Ann Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 877–900.
Linsen L, Somers V, Stinissen P . Immunoregulation of autoimmunity by natural killer T cells. Hum Immunol 2005; 66: 1193–1202.
Novak J, Lehuen A . Mechanism of regulation of autoimmunity by iNKT cells. Cytokine 2011; 53: 263–270.
Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A . Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 501–513.
Hammond KJ, Kronenberg M . Natural killer T cells: natural or unnatural regulators of autoimmunity? Curr Opin Immunol 2003; 15: 683–689.
van Kaer L . Natural killer T cells as targets for immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases. Immunol Cell Biol 2004; 82: 315–322.
Yamamura T, Sakuishi K, Illes Z, Miyake S . Understanding the behavior of invariant NKT cells in autoimmune diseases. J Neuroimmunol 2007; 191: 8–15.
Wondimu Z, Santodomingo-Garzon T, Le T, Swain MG . Protective role of interleukin-17 in murine NKT cell-driven acute experimental hepatitis. Am J Pathol 2010; 177: 2334–2346.
La Cava A, van Kaer L, Fu Dong S . CD4+CD25+ Tregs and NKT cells: regulators regulating regulators. Trends Immunol 2006; 27: 322–327.
Santodomingo-Garzon T, Han J, Le T, Yang Y, Swain MG . Natural killer T cells regulate the homing of chemokine CXC receptor 3-positive regulatory T cells to the liver in mice. Hepatology 2009; 49: 1267–1276.
Hegde S, Fox L, Wang X, Gumperz JE . Autoreactive natural killer T cells: promoting immune protection and immune tolerance through varied interactions with myeloid antigen-presenting cells. Immunology 2010; 130: 471–483.
Karlmark KR, Weiskirchen R, Zimmermann HW, Gassler N, Ginhoux F, Weber C et al. Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology 2009; 50: 261–274.
Kitamura H, Iwakabe K, Yahata T, Nishimura S, Ohta A, Ohmi Y et al. The natural killer T (NKT) cell ligand alpha-galactosylceramide demonstrates its immunopotentiating effect by inducing interleukin (IL)-12 production by dendritic cells and IL-12 receptor expression on NKT cells. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1121–1128.
Nowak M, Stein-Streilein J . Invariant NKT cells and tolerance. Int Rev Immunol 2007; 26: 95–119.
Racanelli V, Rehermann B . The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 2006; 43: S54–62.
Crispe IN . The liver as a lymphoid organ. Ann Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 147–163.
Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z . Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 2008; 47: 729–736.
Trinchieri G . Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol 1989; 47: 187–376.
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S . Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 503–510.
McQueen KL, Parham P . Variable receptors controlling activation and inhibition of NK cells. Curr Opin Immunol 2002; 14: 615–621.
Lanier LL . NK cell recognition. Ann Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 225–274.
Wu L, Zhang C, Zhang J . HMBOX1 negatively regulates NK cell functions by suppressing the NKG2D/DAP10 signaling pathway. Cell Mol Immunol 2011; 8: 433–440.
Jiang X, Chen Y, Peng H, Tian Z . Single line or parallel lines: NK cell differentiation driven by T-bet and Eomes. Cell Mol Immunol 2012; 9: 193–194.
Lassen MG, Lukens JR, Dolina JS, Brown MG, Hahn YS . Intrahepatic IL-10 maintains NKG2A+Ly49- liver NK cells in a functionally hyporesponsive state. J Immunol 2010; 184: 2693–2701.
Raulet DH . Interplay of natural killer cells and their receptors with the adaptive immune response. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 996–1002.
Moretta A, Marcenaro E, Parolini S, Ferlazzo G, Moretta L . NK cells at the interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Cell death and differentiation 2008; 15: 226–233.
Zhang C, Zhang J, Tian Z . The regulatory effect of natural killer cells: do ‘NK-reg cells’ exist? Cell Mol Immunol 2006; 3: 241–254.
Saito S, Nakashima A, Myojo-Higuma S, Shiozaki A . The balance between cytotoxic NK cells and regulatory NK cells in human pregnancy. J Reprod Immunol 2008; 77: 14–22.
Deniz G, Erten G, Kucuksezer UC, Kocacik D, Karagiannidis C, Aktas E et al. Regulatory NK cells suppress antigen-specific T cell responses. J Immunol 2008; 180: 850–857.
Beilke JN, Kuhl NR, van Kaer L, Gill RG . NK cells promote islet allograft tolerance via a perforin-dependent mechanism. Nat Med 2005; 11: 1059–1065.
Crispe IN . Hepatic T cells and liver tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 51–62.
Yu G, Xu X, Vu MD, Kilpatrick ED, Li XC . NK cells promote transplant tolerance by killing donor antigen-presenting cells. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1851–1858.
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Fuchs A, Colonna M, Caligiuri MA . NK cell and DC interactions. Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 47–52.
Jinushi M, Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Yamaguchi S, Sakamori R, Hiramatsu N et al. Natural killer cell and hepatic cell interaction via NKG2A leads to dendritic cell-mediated induction of CD4 CD25 T cells with PD-1-dependent regulatory activities. Immunology 2007; 120: 73–82.
Liu C, Yu S, Kappes J, Wang J, Grizzle WE, Zinn KR et al. Expansion of spleen myeloid suppressor cells represses NK cell cytotoxicity in tumor-bearing host. Blood 2007; 109: 4336–4342.
Sinha P, Clements VK, Bunt SK, Albelda SM, Ostrand-Rosenberg S . Cross-talk between myeloid-derived suppressor cells and macrophages subverts tumor immunity toward a type 2 response. J Immunol 2007; 179: 977–983.
Huang B, Pan PY, Li Q, Sato AI, Levy DE, Bromberg J et al. Gr-1+CD115+ immature myeloid suppressor cells mediate the development of tumor-induced T regulatory cells and T-cell anergy in tumor-bearing host. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1123–1131.
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S . Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 162–174.
Nagaraj S, Schrum AG, Cho HI, Celis E, Gabrilovich DI . Mechanism of T cell tolerance induced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol 2010; 184: 3106–3116.
Greten TF, Manns MP, Korangy F . Myeloid derived suppressor cells in human diseases. Int Immunopharm 2011; 11: 802–807.
Hoechst B, Voigtlaender T, Ormandy L, Gamrekelashvili J, Zhao F, Wedemeyer H et al. Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor. Hepatology 2009; 50: 799–807.
Santodomingo-Garzon T, Swain MG . Role of NKT cells in autoimmune liver disease. Autoimmun Rev 2011; 10: 793–800.
Chou HS, Hsieh CC, Yang HR, Wang L, Arakawa Y, Brown K et al. Hepatic stellate cells regulate immune response by way of induction of myeloid suppressor cells in mice. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1007–1019.
Chen S, Akbar SM, Abe M, Hiasa Y, Onji M . Immunosuppressive functions of hepatic myeloid-derived suppressor cells of normal mice and in a murine model of chronic hepatitis B virus. Clin Exp Immunol 2011; 166: 134–142.
Cripps JG, Wang J, Maria A, Blumenthal I, Gorham JD . Type 1 T helper cells induce the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the inflamed Tgfb1 knockout mouse liver. Hepatology 2010; 52: 1350–1359.
Ilkovitch D, Lopez DM . The liver is a site for tumor-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation and immunosuppression. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 5514–5521.
Wick MJ, Leithauser F, Reimann J . The hepatic immune system. Crit Rev Immunol 2002; 22: 47–103.
Wong J, Johnston B, Lee SS, Bullard DC, Smith CW, Beaudet AL et al. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2782–2790.
Bertolino P, Bowen DG, McCaughan GW, Fazekas de St Groth B . Antigen-specific primary activation of CD8+ T cells within the liver. J Immunol 2001; 166: 5430–5438.
von Oppen N, Schurich A, Hegenbarth S, Stabenow D, Tolba R, Weiskirchen R et al. Systemic antigen cross-presented by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells induces liver-specific CD8 T-cell retention and tolerization. Hepatology 2009; 49: 1664–1672.
Oo YH, Adams DH . The role of chemokines in the recruitment of lymphocytes to the liver. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: 45–54.
Oo YH, Weston CJ, Lalor PF, Curbishley SM, Withers DR, Reynolds GM et al. Distinct roles for CCR4 and CXCR3 in the recruitment and positioning of regulatory T cells in the inflamed human liver. J Immunol 2010; 184: 2886–2898.
Ju C, McCoy JP, Chung CJ, Graf ML, Pohl LR . Tolerogenic role of Kupffer cells in allergic reactions. Chem Res Toxicol 2003; 16: 1514–1519.
Callery MP, Kamei T, Flye MW . Kupffer cell blockade inhibits induction of tolerance by the portal venous route. Transplantation 1989; 47: 1092–1094.
Sato K, Yabuki K, Haba T, Maekawa T . Role of Kupffer cells in the induction of tolerance after liver transplantation. J Surg Res 1996; 63: 433–438.
Kuniyasu Y, Marfani SM, Inayat IB, Sheikh SZ, Mehal WZ . Kupffer cells required for high affinity peptide-induced deletion, not retention, of activated CD8+ T cells by mouse liver. Hepatology 2004; 39: 1017–1027.
Knolle P, Schlaak J, Uhrig A, Kempf P, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Gerken G . Human Kupffer cells secrete IL-10 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. J Hepatol 1995; 22: 226–229.
You Q, Cheng L, Kedl RM, Ju C . Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2008; 48: 978–990.
Roland CR, Walp L, Stack RM, Flye MW . Outcome of Kupffer cell antigen presentation to a cloned murine Th1 lymphocyte depends on the inducibility of nitric oxide synthase by IFN-gamma. J Immunol 1994; 153: 5453–5464.
Carambia A, Herkel J . CD4 T cells in hepatic immune tolerance. J Autoimmun 2010; 34: 23–28.
Breous E, Somanathan S, Vandenberghe LH, Wilson JM . Hepatic regulatory T cells and Kupffer cells are crucial mediators of systemic T cell tolerance to antigens targeting murine liver. Hepatology 2009; 50: 612–621.
Schmieg J, Yang G, Franck RW, van Rooijen N, Tsuji M . Glycolipid presentation to natural killer T cells differs in an organ-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102: 1127–1132.
Warren A, Le Couteur DG, Fraser R, Bowen DG, McCaughan GW, Bertolino P . T lymphocytes interact with hepatocytes through fenestrations in murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatology 2006; 44: 1182–1190.
Bertolino P, Trescol-Biemont MC, Rabourdin-Combe C . Hepatocytes induce functional activation of naive CD8+ T lymphocytes but fail to promote survival. Eur J Immunol 1998; 28: 221–236.
Holz LE, Benseler V, Bowen DG, Bouillet P, Strasser A, O'Reilly L et al. Intrahepatic murine CD8 T-cell activation associates with a distinct phenotype leading to Bim-dependent death. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 989–997.
Wiegard C, Wolint P, Frenzel C, Cheruti U, Schmitt E, Oxenius A et al. Defective T helper response of hepatocyte-stimulated CD4 T cells impairs antiviral CD8 response and viral clearance. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 2010–2018.
Amsen D, Blander JM, Lee GR, Tanigaki K, Honjo T, Flavell RA . Instruction of distinct CD4 T helper cell fates by different notch ligands on antigen-presenting cells. Cell 2004; 117: 515–526.
Wahl C, Bochtler P, Schirmbeck R, Reimann J . Type I IFN-producing CD4 Valpha14i NKT cells facilitate priming of IL-10-producing CD8 T cells by hepatocytes. J Immunol 2007; 178: 2083–2093.
Knolle PA, Gerken G . Local control of the immune response in the liver. Immunol Rev 2000; 174: 21–34.
Knolle PA, Schmitt E, Jin S, Germann T, Duchmann R, Hegenbarth S et al. Induction of cytokine production in naive CD4+ T cells by antigen-presenting murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but failure to induce differentiation toward Th1 cells. Gastroenterology 1999; 116: 1428–1440.
Diehl L, Schurich A, Grochtmann R, Hegenbarth S, Chen L, Knolle PA . Tolerogenic maturation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes B7-homolog 1-dependent CD8+ T cell tolerance. Hepatology 2008; 47: 296–305.
Limmer A, Ohl J, Wingender G, Berg M, Jungerkes F, Schumak B et al. Cross-presentation of oral antigens by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells leads to CD8 T cell tolerance. Eur J Immunol 2005; 35: 2970–2981.
Liu W, Tang L, Zhang G, Wei H, Cui Y, Guo L et al. Characterization of a novel C-type lectin-like gene, LSECtin: demonstration of carbohydrate binding and expression in sinusoidal endothelial cells of liver and lymph node. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 18748–18758.
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Flies DB, van Deursen JM, Chen L . B7-H1 determines accumulation and deletion of intrahepatic CD8+ T lymphocytes. Immunity 2004; 20: 327–336.
Kruse N, Neumann K, Schrage A, Derkow K, Schott E, Erben U et al. Priming of CD4+ T cells by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells induces CD25low forkhead box protein 3- regulatory T cells suppressing autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2009; 50: 1904–1913.
Schildberg FA, Hegenbarth SI, Schumak B, Scholz K, Limmer A, Knolle PA . Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells veto CD8 T cell activation by antigen-presenting dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol 2008; 38: 957–967.
Sato M, Suzuki S, Senoo H . Hepatic stellate cells: unique characteristics in cell biology and phenotype. Cell Struct Funct 2003; 28: 105–112.
Winau F, Hegasy G, Weiskirchen R, Weber S, Cassan C, Sieling PA et al. Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating T cell responses. Immunity 2007; 26: 117–129.
Yu MC, Chen CH, Liang X, Wang L, Gandhi CR, Fung JJ et al. Inhibition of T-cell responses by hepatic stellate cells via B7-H1-mediated T-cell apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 2004; 40: 1312–1321.
Yang HR, Hsieh CC, Wang L, Fung JJ, Lu L, Qian S . A critical role of TRAIL expressed on cotransplanted hepatic stellate cells in prevention of islet allograft rejection. Microsurgery 2010; 30: 332–337.
Jiang G, Yang HR, Wang L, Wildey GM, Fung J, Qian S et al. Hepatic stellate cells preferentially expand allogeneic CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in an IL-2-dependent manner. Transplantation 2008; 86: 1492–1502.
Yang HR, Chou HS, Gu X, Wang L, Brown KE, Fung JJ et al. Mechanistic insights into immunomodulation by hepatic stellate cells in mice: a critical role of interferon-gamma signaling. Hepatology 2009; 50: 1981–1991.
Steptoe RJ, Patel RK, Subbotin VM, Thomson AW . Comparative analysis of dendritic cell density and total number in commonly transplanted organs: morphometric estimation in normal mice. Transplant Immunol 2000; 8: 49–56.
Woo J, Lu L, Rao AS, Li Y, Subbotin V, Starzl TE et al. Isolation, phenotype, and allostimulatory activity of mouse liver dendritic cells. Transplantation 1994; 58: 484–491.
Thomson AW, Lu L . Are dendritic cells the key to liver transplant tolerance? Immunol Today 1999; 20: 27–32.
Bamboat ZM, Stableford JA, Plitas G, Burt BM, Nguyen HM, Welles AP et al. Human liver dendritic cells promote T cell hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol 2009; 182: 1901–1911.
Li G, Kim YJ, Broxmeyer HE . Macrophage colony-stimulating factor drives cord blood monocyte differentiation into IL-10highIL-12absent dendritic cells with tolerogenic potential. J Immunol 2005; 174: 4706–4717.
Rutella S, Bonanno G, Procoli A, Mariotti A, de Ritis DG, Curti A et al. Hepatocyte growth factor favors monocyte differentiation into regulatory interleukin (IL)-10++IL-12low/neg accessory cells with dendritic-cell features. Blood 2006; 108: 218–227.
Cabillic F, Rougier N, Basset C, Lecouillard I, Quelvennec E, Toujas L et al. Hepatic environment elicits monocyte differentiation into a dendritic cell subset directing Th2 response. J Hepatol 2006; 44: 552–559.
Kingham TP, Chaudhry UI, Plitas G, Katz SC, Raab J, DeMatteo RP . Murine liver plasmacytoid dendritic cells become potent immunostimulatory cells after Flt-3 ligand expansion. Hepatology 2007; 45: 445–454.
Probst HC, McCoy K, Okazaki T, Honjo T, van den Broek M . Resting dendritic cells induce peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance through PD-1 and CTLA-4. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 280–286.
Biswas SK, Lopez-Collazo E . Endotoxin tolerance: new mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance. Trends Immunol 2009; 30: 475–487.
Khanna A, Morelli AE, Zhong C, Takayama T, Lu L, Thomson AW . Effects of liver-derived dendritic cell progenitors on Th1- and Th2-like cytokine responses in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol 2000; 164: 1346–1354.
Goubier A, Dubois B, Gheit H, Joubert G, Villard-Truc F, Asselin-Paturel C et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells mediate oral tolerance. Immunity 2008; 29: 464–475.
Moseman EA, Liang X, Dawson AJ, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Krieg AM, Liu YJ et al. Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells activated by CpG oligodeoxynucleotides induce the generation of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2004; 173: 4433–4442.
Tokita D, Sumpter TL, Raimondi G, Zahorchak AF, Wang Z, Nakao A et al. Poor allostimulatory function of liver plasmacytoid DC is associated with pro-apoptotic activity, dependent on regulatory T cells. J Hepatol 2008; 49: 1008–1018.
Horstmann B, Zinser E, Turza N, Kerek F, Steinkasserer A . MCS-18, a novel natural product isolated from Helleborus purpurascens, inhibits dendritic cell activation and prevents autoimmunity as shown in vivo using the EAE model. Immunobiology 2007; 212: 839–853.
Feng S . Long-term management of immunosuppression after pediatric liver transplantation: is minimization or withdrawal desirable or possible or both? Curr Opin Organ Transplant 2008; 13: 506–512.
Orlando G, Soker S, Wood K . Operational tolerance after liver transplantation. J Hepatol 2009; 50: 1247–1257.
LoDuca PA, Hoffman BE, Herzog RW . Hepatic gene transfer as a means of tolerance induction to transgene products. Curr Gene Ther 2009; 9: 104–114.
Kren BT, Unger GM, Sjeklocha L, Trossen AA, Korman V, Diethelm-Okita BM et al. Nanocapsule-delivered Sleeping Beauty mediates therapeutic Factor VIII expression in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells of hemophilia A mice. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 2086–2099.
Han Q, Zhang C, Zhang J, Tian Z . Reversal of hepatitis B virus-induced immune tolerance by an immunostimulatory 3p-HBx-siRNAs in a retinoic acid inducible gene I-dependent manner. Hepatology 2011; 54: 1179–1189.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Project (973 project) (No. 2013CB944902) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31021061 and 91029303). We thank from Dr Fudong Shi from Tian Jing Medical University, China, for critically reading the manuscript and providing suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Tian, Z. The liver works as a school to educate regulatory immune cells. Cell Mol Immunol 10, 292–302 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Synthetically glycosylated antigens for the antigen-specific suppression of established immune responses
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023)
-
Clinical and molecular correlates of response to immune checkpoint blockade in urothelial carcinoma with liver metastasis
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2022)
-
A Multi-institutional, Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to Bone Treated with Combination Ipilimumab and Nivolumab
Targeted Oncology (2021)
-
Liver metastasis restrains immunotherapy efficacy via macrophage-mediated T cell elimination
Nature Medicine (2021)
-
Imaging features and prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT detection of soft-tissue metastasis from lung cancer: a retrospective study
BMC Cancer (2020)