Abstract
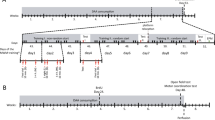
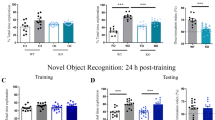
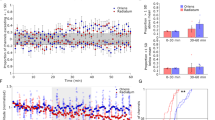
SYNAPTIC plasticity dependent on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors is thought to underlie certain types of learning and memory1–3. In support of this, both hippocampal long-term potentiation and spatial learning in a watermaze are impaired by blocking NMDA receptors with a selective antagonist D(-)-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (AP5)4 or by a mutation in one of the receptor subunits5. Here we report, however, that the AP5-induced learning deficit can be almost completely prevented if rats are pretrained in a different watermaze before administration of the drug. This is not because of stimulus generalization, and occurs despite learning of the second task remaining hippocampus dependent. An A PS5-induced learning deficit is, however, still seen if the animals are pretrained using a non-spatial task. Thus, despite its procedural simplicity, the watermaze may involve multiple cognitive processes with distinct pharmacological properties; although required for some component of spatial learning, NMDA receptors may not be required for encoding the spatial representation of a specific environment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collingridge, G. L., Kehl, S. J. & McLennan, H. J. Physiol., Lond. 334, 33–46 (1983).
Morris, R. G. M. In Excitatory Amino Acids in Health and Disease (ed. Lodge, D.) 297–320 (Wiley, Chichester, 1988).
Bliss, T. V. P. & Collingridge, G. L. Nature 361, 31–39 (1993).
Morris, R. G. M., Anderson, E., Lynch, G. & Baudry, M. Nature 319, 774–776 (1986).
Sakimura, K. et al. Nature 373, 151–155 (1995).
Davis, S., Butcher, S. P. & Morris, R. G. M. J. Neurosci. 12, 21–34 (1992).
Morris, R. G. M. J. Neurosci. 9, 3040–3057 (1989).
Salt, T. E. Nature 322, 263–265 (1986).
Sillito, A. M., Murphy, P. C. & Salt, T. E. Neuroscience 34, 273–280 (1990).
Fox, K., Sato, H. & Daw, N. J. Neurophysiol. 64, 1413–1428 (1990).
Alford, S. & Brodin, L. In The NMDA Receptor 2nd edn (eds Collingridge, G. L. & Watkins, J. C.) 277–293 (Oxford Univ. Press. 1994).
Heale, V. & Harley, C. Pharmac. Biochem. Behav. 36, 145–149 (1990).
Caramanos, Z. & Shapiro, M. L. Behav. Neurosci. 108, 30–43 (1994).
Jarrard, L. E. J. Neurosci. Meth. 29, 251–259 (1989).
Squire, L. R. Psychol. Rev. 99, 195–231 (1992).
Kolb, B., Sutherland, R. J. & Whishaw, I. Q. Behav. Neurosci. 97, 13–27 (1983).
DiMattia, B. D. & Kesner, R. P. Behav. Neurosci. 102, 471–480 (1988).
Sutherland, R. J., Whishaw, I. Q. & Kolb, B. J. Neurosci. 8, 1863–1872 (1988).
Brandeis, R., Brandys, Y. & Yehuda, S. Int. J. Neurosci. 48, 29–69 (1989).
O'Keefe, J. & Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map (Oxford Univ. Press, 1978).
Johnston, D., Williams, S. H., Jaffe, D. & Gray, R. A. Rev. Physiol. 54, 489–505 (1992).
Wilson, M. A. & McNaughton, B. L. Science 261, 1055–1058 (1993).
Barnes, C. A. et al. J. Neurosci. 14, 5793–5806 (1994).
Sutherland, N. S. & Mackintosh, N. J. Mechanisms of Animal Discrimination Learning (Academic, London, 1970).
Morris, R. G. M., Garrud, P., Rawlins, J. N. P. & O'Keefe, J. Nature 297, 681–683 (1982).
Johnson-Laird, P. N. Mental Models (Cambridge Univ. Press. 1983).
Butcher, S. P., Hamberger, A. & Morris, R. G. M. Expl Brain Res. 83, 521–526 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bannerman, D., Good, M., Butcher, S. et al. Distinct components of spatial learning revealed by prior training and NMDA receptor blockade. Nature 378, 182–186 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/378182a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/378182a0
This article is cited by
-
Vγ1 and Vγ4 gamma-delta T cells play opposing roles in the immunopathology of traumatic brain injury in males
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Evaluating endophenotypes for bipolar disorder
International Journal of Bipolar Disorders (2021)
-
Neural substrates involved in the cognitive information processing in teleost fish
Animal Cognition (2021)
-
Memory: Axioms and Facts
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2021)
-
Metaplasticity contributes to memory formation in the hippocampus
Neuropsychopharmacology (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.