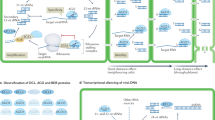
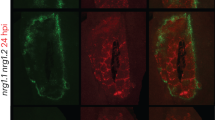
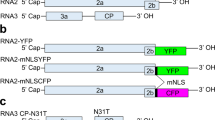
Abstract
Gene silencing was perceived initially as an unpredictable and inconvenient side effect of introducing transgenes into plants. It now seems that it is the consequence of accidentally triggering the plant's adaptive defence mechanism against viruses and transposable elements. This recently discovered mechanism, although mechanistically different, has a number of parallels with the immune system of mammals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mayo, M. A. Developments in plant virus taxonomy since the publication of the 6th ICTV report. Arch. Virol. 144, 1659–1666 (1999).
Bennetzen, J. L. Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 42, 251–269 (2000).
Kumar, A. & Bennetzen, J. L. Plant retrotransposons. Annu. Rev. Genet. 33, 479–452 (1999).
Martienssen, R. Transposons, DNA methylation and gene control. Trends Genet. 14, 263–264 (1998).
Rothstein, S. J., Dimaio, J., Strand, M. & Rice, D. Stable and inheritable inhibition of the expression of nopaline synthase in tobacco expressing antisense RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8439–8443 (1987).
Simons, R. W. & Kleckner, N. Translational control of IS10 transposition. Cell 34, 683–691 (1983).
Hamilton, A. J., Lycett, G. W. & Grierson, D. Antisense gene that inhibits synthesis of the hormone ethylene in transgenic plants. Nature 346, 284–287 (1990).
Napoli, C., Lemieux, C. & Jorgensen, R. Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans. Plant Cell 7, 599–609 (1990).
Van der Krol, A. R., Mur, L. A., Beld, K., Mol, J. N. M. & Stuitje, A. R. Flavonoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to suppression of gene expression. Plant Cell 2, 291–299 (1990).
De Carvalho, F. et al. Suppression of the β-1,3 glucanase transgene expression in homozygous plants. EMBO J. 11, 2595–2602 (1992).
Powell-Abel, P. et al. Delay of disease development in transgenic plants that express the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene. Science 232, 738–743 (1986).
Lindbo, J. A. & Dougherty, W. G. Untranslatable transcripts of the tobacco etch virus coat protein gene sequence can interfere with tobacco etch virus replication in transgenic plants and protoplasts. Virology 189, 725–733 (1992).
Dougherty, W. G. & Parks, T. D. Transgenes and gene suppression: telling us something new? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7, 399–405 (1995).
English, J. J., Mueller, E. & Baulcombe, D. C. Suppression of virus accumulation in transgenic plants exhibiting silencing of nuclear genes. Plant Cell 8, 787–797 (1996).
Tanzer, M. M., Thompson, W. F., Law, M. D., Wernsman, E. A. & Ukenes, S. Characterization of post-transcriptionally suppressed transgene expression that confers resistance to tobacco etch virus infection in tobacco. Plant Cell 9, 1411–1423 (1997).
Voinnet, O., Vain, P., Angell, S. & Baulcombe, D. C. Systemic spread of sequence-specific transgene RNA degradation in plants is initiated by localized introduction of ectopic promoterless DNA. Cell 95, 177–187 (1998).
Wassenegger, M. & Pelissier, T. A model for RNA-mediated gene silencing in higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 37, 349–362 (1998).
Waterhouse, P. M., Graham, M. W. & Wang, M.-B. Virus resistance and gene silencing in plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci USA 95, 13959–13964 (1998).
Wang, M.-B. & Waterhouse, P. M. High efficiency silencing of a β-glucuronidase gene in rice is correlated with repetitive transgene structure but is independent of DNA methylation. Plant Mol. Biol. 43, 67–82 (2000).
Smith, N. A. et al. Total silencing by intron-spliced hairpin RNAs. Nature 407, 319–320 (2000).
Stam, M. et al. Distinct features of post-transcriptional gene silencing by antisense transgenes in single copy and inverted T-DNA repeat loci. Plant J. 21, 27–42 (2000).
Morris T. J. & Dodds, J. A. Isolation and analysis of double stranded RNA from virus-infected plant and fungal tissue. Phytopathology 69, 854–858 (1979).
Blumenthal, T. & Carmichael, G. G. RNA replication: function and structure of Qβ replicase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 48, 525–548 (1979).
Buck, K. W. Replication of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 354, 613–627 (1999).
Ogawa, T., Hori, T. & Ishida, I. Virus-induced death in plants expressing the mammalian 2′,5′ oligoadenylate system. Nature Biotechnol. 14, 1566–1569 (1996).
Baulcombe, D. C. Fast forward genetics based in virus-induced gene silencing. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2, 109–113 (1999).
Lee, K. Y., Baden, C., Howie, W. J., Bedbrook, J. & Dunsmuir, P. Post-transcriptional gene silencing of ACC synthase in tomato results from cytoplasmic RNA degradation. Plant J. 12, 1127–1137 (1997).
Metzlaff, M., O'Dell, M., Cluster, P. D. & Flavell, R. B. RNA-mediated RNA degradation and chalcone synthase A silencing in Petunia . Cell 88, 845–854 (1997).
Hamilton, A. J. & Baulcombe, D. C. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286, 950–952 (1999).
Mette, M. F., Aufatz, W., van der Winden, J., Matzke, M. A & Matzke, A. J. M. Transcriptional silencing and promoter methylation triggered by double stranded RNA. EMBO J. 19, 5194–5201 (2000).
Llave, C., Kasschau, K. D. & Carrington, J. C. Virus-encoded suppressor of posttranscriptional gene silencing targets a maintenance step in the silencing pathway. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 13401–13406 (2000).
Dalmay, T., Hamilton, A., Rudd, S., Angell, S. & Baulcombe, D. C. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene in Arabidopsis is required for post-transcriptional gene silencing mediated by a transgene but not by a virus. Cell 101, 543–553 (2000).
Hutvagner, G., Mlynarova, L. & Nap, J. P. Detailed characterization of the posttranscriptional gene-silencing-related small RNA in a GUS gene-silenced tobacco. RNA 6, 1445–1454 (2000).
Fire, A. et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature 391, 806–811 (1998).
Kennerdel, J. R. & Carthew, R. W. Use of dsRNA-mediated genetic interference to demonstrate that frizzled and frizzled 2 act in the wingless pathway. Cell 95, 1017–1026 (1998).
Zamore, P. D., Tuschl, T., Sharp, P. A. & Bartel, D. P. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101, 25–33 (2000).
Yang, D., Lu, H. & Erickson, J. W. Evidence that processed small dsRNAs may mediate sequence-specific mRNA degradation during RNAi in Drosophila embryos. Curr. Biol. 10, 1191–1200 (2000).
Hammond, S. C., Bernstein, E., Beach, D. & Hannon, G. J. An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404, 293–296 (2000).
Bernstein, E., Caudy, A. A., Hammond, S. M. & Hannon, G. J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366 (2001).
Elbashir, S. M., Lendeckel, W. & Tuschl, T. RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev. 15, 188–200 (2001).
Holtorf, H., Schob, H., Kunz, C., Waldvogel, R. & Meins, F. Stochastic and nonstochastic post-transcriptional silencing of chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase genes involves increased RNA turnover—possible role for ribosome-independent RNA degradation. Plant Cell 11, 471–483 (1999).
Zou, C., Zhang, Z., Wu, S. & Osterman, J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rabbit eIF2C protein. Gene 211, 187–194 (1998).
Cogoni, C. & Macino, G. Gene silencing in Neurospora crassa requires a protein homologous to RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Nature 399, 166–169 (1999).
Mourrain, P. et al. Arabidopsis SGS2 and SGS3 genes are required for posttranscriptional gene silencing and natural virus resistance. Cell 101, 533–542 (2000).
Smardon, A. et al. EGO-1 is related to RNA-directed RNA polymerase and functions in germ-line development and RNA interference in C. elegans . Curr. Biol. 10, 169–178 (2000).
Catalanotto, C., Azzalin, G., Macino, G. & Cogoni, C. Gene silencing in worms and fungi. Nature 404, 245 (2000).
Tabara, H. et al. The rde-I gene, RNA interference, and transposon silencing in C. elegans . Cell 99, 123–132 (1999).
Fagard, M., Boutet, S., Morel, J.-B., Bellini, C. & Vaucheret, H. AGO1, QDE-2, and RDE-1 are related proteins required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants, quelling in fungi and RNA interference in animals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11650–11654 (2000).
Ketting, R. F., Haverkamp, T. H. A., van Luenen, H. G. A. & Plasterk, R. H. A. mut-7 of C. elegans, required for transposon silencing and RNA interference, is a homolog of Werner Syndrome helicase and RNase D. Cell 99, 133–141 (1999).
Domeier, M. E. et al. A link between RNA interference and nonsense-mediated decay in Caenorhabditis elegans . Science 289, 1928–1930 (2000).
Cogoni, C. & Macino, G. Post-transcriptional gene silencing in Neurospora by a ReqQ DNA helicase. Science 286, 342–344 (1999).
Wu-Scarf, D., Jeong, B.-R., Zhang, C. & Cerutti, H. Transgene and transposon silencing in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by a DEAH-box RNA helicase. Science 290, 1159–1162 (2000).
Dalmay, T., Horsefield, R., Braunstein, T. H. & Baulcombe, D. C. SDE3 encodes an RNA helicase required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in Arabidopsis . EMBO J. 20, 2069–2077 (2001).
Cerruti, L., Mian, N. & Bateman, A. Domains in gene silencing and cell differentiation proteins: the novel PAZ domain and redefinition of the Piwi domain. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 481–482 (2000).
Kooter, J. M., Matzke, M. A. & Meyer, P. Listening to the silent genes: transgene silencing, gene regulation and pathogen control. Trends. Plant Sci. 4, 340–347 (1999).
Morel, J.-B., Mourrain, P., Berlin, C. & Vaucheret, H. DNA methylation and chromatin structure mutants affect both post-transcriptional and transcriptional transgene silencing in Arabidopsis . Curr. Biol. 10, 1591–1594 (2001).
Jones, A. L. et al. De novo methylation and co-suppression induced by a cytoplasmically replicating plant RNA virus. EMBO J. 17, 6385–6393 (1998).
Wang, M.-B., Wesley, S. V., Finnegan, E. J., Smith, N. A. & Waterhouse, P. M. Replicating satellite RNA induces sequence specific DNA methylation and truncated transcripts in plants. RNA 7, 16–28 (2001).
Van Houdt, H., Ingelbrecht, I., van Montagu, M. & Depicker, A. Post-transcriptional silencing of a neomycin phosphotransferase II transgene correlates with the accumulation of unproductive RNAs and with increased cytosine methylation of 3′ flanking regions. Plant J. 12, 379–392 (1997).
Yoder, J. A., Walsh, C. P. & Bestor, T. H. Cytosine methylation and ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet. 13, 335–340 (1997).
Brutnell, T. P. & Dellaporta, S. L. Somatic inactivation and reactivation of Ac associated changes in cytosine methylation and transposase expression. Genetics 138, 213–225 (1994).
San Miguel, P. et al. Nested transposons in the intergenic regions of the maize genome. Science 257, 765–768 (1996).
Bennetzen, J. L. The contributions of retroelements to plant genome organisation, function and evolution. Trends Microbiol. 4, 347–353 (1993).
Kunze, R., Saedler, H. & Lonnig, W. E. Plant transposable elements. Adv. Bot. Res. 27, 331–470 (1997).
Bennetzen, J. L. The Mutator transposable element system of maize. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 204, 195–229 (1996).
Schlappi, M., Raina, R. & Fedoroff, N. Epigenetic regulation of the maize Spm transposable element: novel activation of a methylated promoter by TnpA. Cell 77, 427–437 (1994).
Liu, W. M., Maraia, R. J., Rubin, C. M. & Schmid, C. W. Alu transcripts: cytoplasmic localisation and regulation by DNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 1087–1095 (1994).
Singer, T., Yordan, C. & Martienssen, R. A. Robertson's Mutator transposons in A. thaliana are regulated by the chromatin-remodeling gene Decrease in DNA Methylation (DDM1). Genes Dev. 15, 591–602 (2001).
Miura, A. et al. Mobilization of transposons by a mutation abolishing full DNA methylation in Arabidopsis . Nature 411, 212–214 (2001).
Hirochika, H., Okamoto, H. & Kakutani, T. Silencing of retrotransposons in arabidopsis and reactivation by the ddm1 mutation. Plant Cell 12, 357–368 (2000).
Hershberger, R. J. Characterization of the major transcripts encoded by the regulatory MuDR transposable element of maize. Genetics 140, 1087–1098 (1995).
Covey, S. N., Al-Kaff, N. S., Langara, A. & Turner, D. S. Plants combat infection by gene silencing. Nature 385, 781–782 (1997).
Palauqui, J. C., Elmayan, T., Pollien, J. M. & Vaucheret, H. Systemic acquired silencing: transgene specific post transcriptional silencing is transmitted by grafting from silenced stocks to non-silenced scions. EMBO J. 16, 4738–4745 (1997).
Lucas, W. J. & Gilbertson, R. L. Plasmodesmata in relation to viral movement within leaf tissues. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 32, 387–411 (1994).
Ding, B., Kwon, M. O., Hammond, R. & Owens, R. Cell to cell movement of potato spindle tuber viroid. Plant J. 12, 931–936 (1997).
Lucas, W. J. et al. Selective trafficking of KNOTTED1 homoeodomain protein and its mRNA through plasmodesmata. Science 270, 1980–1983 (1995).
Kuhn, C., Franceschi, V. R., Schulz, A., Lemoine, R. & Frommer, W. B. Macromolecular trafficking indicated by localisation and turnover of sucrose in enucleate sieve elements. Science 275, 1298–1300 (1997).
Ruiz-Medrano, R., Xocosnostle-Cazares, B. & Lucas, W. J. Phloem long-distance transport of CmNACP mRNA: implications for supracellular regulation in plants. Development 126, 4405–4419 (1999).
Sasaki, T., Chino, M., Hayashi, H. & Fujiwara, T. Detection of mRNA species in phloem sap. Plant Cell Physiol. 39, 895–897 (1998)
Kasschau, K. D. & Carrington J. C. A counter-defensive strategy of plant viruses: suppression of post-transcriptional gene silencing. Cell 95, 461–470 (1998).
Marathe, M. et al. Plant viral suppressors of post-transcriptional silencing do not suppress transcriptional silencing. Plant J. 22, 51–59 (2000).
Ratcliff, F., Harrison, B. D. & Baulcombe, D. C. A similarity between viral defense and gene silencing in plants. Science 276, 1558–1560 (1997).
Ratcliff, F. G., MacFarlane, S. S. & Baulcombe, D. C. Gene silencing without DNA: RNA mediated cross protection between viruses. Plant Cell 11, 1207–1215 (1999).
Brigneti, G. et al. Viral pathogenicity determinants are suppressors of transgene silencing in Nicotiana bentamiana . EMBO J. 17, 6739–6746 (1998).
Li, H. W. et al. Strong host resistance targeted against a viral suppressor of the plant gene silencing defence mechanism. EMBO J. 18, 2683–2691 (1999).
Voinnet, O., Lederer, C. & Baulcombe, D. C. A viral movement protein prevents spread of the gene silencing signal in Nicotiana benthamiana . Cell 103, 157–167 (2000).
Mallory, A. C. et al. HC-Pro suppression of gene silencing eliminates the small RNAs but not the transgene methylation or the mobile signal. Plant Cell 13, 571–583 (2001).
Jacobsen, S. E., Running, M. P. & Meyerowitz, E. M. Disruption of an RNA helicase/RNaseIII gene in Arabidopsis causes unregulated cell division in floral meristems. Development 126, 5231–5243 (1999).
Anandakshmi, R. et al. A calmodulin-related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 290, 142–144 (2000).
Wang, M.-B., Abbott, D. & Waterhouse, P. M. A single copy of a virus-derived transgene encoding hairpin RNA gives immunity to barley yellow dwarf virus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1, 347–356 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank M.-A. Grandbastion, R. Hull and our colleagues at P.I. for being so generous with their time and knowledge. Thanks also to V. Vance for access to her manuscript before publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waterhouse, P., Wang, MB. & Lough, T. Gene silencing as an adaptive defence against viruses. Nature 411, 834–842 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35081168
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35081168
This article is cited by
-
Silencing of a Nicotiana benthamiana ascorbate oxidase gene reveals its involvement in resistance against cucumber mosaic virus
Planta (2024)
-
Geminiviral betasatellites: critical viral ammunition to conquer plant immunity
Archives of Virology (2023)
-
Field application of nanoliposomes delivered quercetin by inhibiting specific hsp70 gene expression against plant virus disease
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.