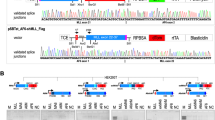
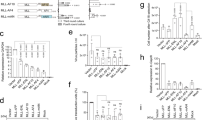
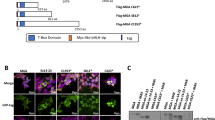
Abstract
Chromosomal translocations that fuse the mixed lineage leukemia gene (MLL) to a variety of unrelated partner genes are frequent in pediatric leukemias. The novel combination of genetic material leads to the production of active oncoproteins that depend on the contributions of both constituents. In a search for a common function amongst the diverse group of MLL fusion partners we constructed artificial fusions joining MLL with generic transactivator and repressor domains (acidic blob, GAL4 transactivator domain, Herpes simplex VP16 activation domain, KRAB repressor domain). Of all constructs tested, only MLL-VP16 was able to transform primary bone marrow cells and to induce a block of early myeloid differentiation like an authentic MLL fusion. Interestingly, the transformation capability of the artificial MLL fusions was correlated with the transcriptional potential of the resulting chimeric protein but it was not related to the strength of the isolated transactivation domain that was joined to MLL. These results prove for the first time that a general biological function – transactivation – might be the common denominator of many MLL fusion partners.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dimartino JF, Cleary ML . MLL rearrangements in haematological malignancies: lessons from clinical and biological studies. Br J Haematol 1999; 106: 614–626.
Ayton PM, Cleary ML . Molecular mechanisms of leukemogenesis mediated by MLL fusion proteins. Oncogene 2001; 20: 5695–5707.
Huret JL, Dessen P, Bernheim A . An atlas of chromosomes in hematological malignancies. Example: 11q23 and MLL partners. Leukemia 2001; 15: 987–989.
Djabali M, Selleri L, Parry P, Bower M, Young BD, Evans GA . A trithorax-like gene is interrupted by chromosome 11q23 translocations in acute leukaemias. Nat Genet 1992; 2: 113–118.
Gu Y, Nakamura T, Alder H, Prasad R, Canaani O, Cimino G, Croce CM, Canaani E . The t(4;11) chromosome translocation of human acute leukemias fuses the ALL-1 gene, related to Drosophila trithorax, to the AF-4 gene. Cell 1992; 71: 701–708.
Tkachuk DC, Kohler S, Cleary ML . Involvement of a homolog of Drosophila trithorax by 11q23 chromosomal translocations in acute leukemias. Cell 1992; 71: 691–700.
Ziemin-van der Poel S, McCabe NR, Gill HJ, Espinosa R III, Patel Y, Harden A, Rubinelli P, Smith SD, LeBeau MM, Rowley JD . Identification of a gene, MLL, that spans the breakpoint in 11q23 translocations associated with human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 10735–10739.
van Lohuizen M . The trithorax-group and polycomb-group chromatin modifiers: implications for disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1999; 9: 355–361.
Yu BD, Hess JL, Horning SE, Brown GA, Korsmeyer SJ . Altered Hox expression and segmental identity in Mll-mutant mice. Nature 1995; 378: 505–508.
Yagi H, Deguchi K, Aono A, Tani Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T . Growth disturbance in fetal liver hematopoiesis of Mll-mutant mice. Blood 1998; 92: 108–117.
Hess JL, Yu BD, Li B, Hanson R, Korsmeyer SJ . Defects in yolk sac hematopoiesis in Mll-null embryos. Blood 1997; 90: 1799–1806.
Corral J, Lavenir I, Impey H, Warren AJ, Forster A, Larson TA, Bell S, McKenzie AN, King G, Rabbitts TH . An Mll-AF9 fusion gene made by homologous recombination causes acute leukemia in chimeric mice: a method to create fusion oncogenes. Cell 1996; 85: 853–861.
Dobson CL, Warren AJ, Pannell R, Forster A, Lavenir I, Corral J, Smith AJ, Rabbitts TH . The Mll-AF9 gene fusion in mice controls myeloproliferation and specifies acute myeloid leukaemogenesis. EMBO J 1999; 18: 3564–3574.
Dobson CL, Warren AJ, Pannell R, Forster A, Rabbitts TH . Tumorigenesis in mice with a fusion of the leukaemia oncogene Mll and the bacterial lacZ gene. EMBO J 2000; 19: 843–851.
Lavau C, Du C, Thirman M, Zeleznik-Le N . Chromatin-related properties of CBP fused to MLL generate a myelodysplastic-like syndrome that evolves into myeloid leukemia. EMBO J 2000; 19: 4655–4664.
Luo RT, Lavau C, Du C, Simone F, Polak PE, Kawamata S, Thirman MJ . The elongation domain of ELL is dispensable but its ELL-associated factor 1 interaction domain is essential for MLL-ELL-induced leukemogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 5678–5687.
Slany RK, Lavau C, Cleary ML . The oncogenic capacity of HRX-ENL requires the transcriptional transactivation activity of ENL and the DNA binding motifs of HRX. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 122–129.
Prasad R, Yano T, Sorio C, Nakamura T, Rallapalli R, Gu Y, Leshkowitz D, Croce CM, Canaani E . Domains with transcriptional regulatory activity within the ALL1 and AF4 proteins involved in acute leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 12160–12164.
DiMartino JF, Miller T, Ayton PM, Landewe T, Hess JL, Cleary ML, Shilatifard A . A carboxy-terminal domain of ELL is required and sufficient for immortalization of myeloid progenitors by MLL-ELL. Blood 2000; 96: 3887–3893.
Simone F, Polak PE, Kaberlein JJ, Luo RT, Levitan DA, Thirman MJ . EAF1, a novel ELL-associated factor that is delocalized by expression of the MLL-ELL fusion protein. Blood 2001; 98: 201–209.
Ida K, Kitabayashi I, Taki T, Taniwaki M, Noro K, Yamamoto M, Ohki M, Hayashi Y . Adenoviral E1A-associated protein p300 is involved in acute myeloid leukemia with t(11;22)(q23;q13). Blood 1997; 90: 4699–4704.
Sobulo OM, Borrow J, Tomek R, Reshmi S, Harden A, Schlegelberger B, Housman D, Doggett NA, Rowley JD, Zeleznik-Le NJ . MLL is fused to CBP, a histone acetyltransferase, in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with a t(11;16)(q23;p13.3). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8732–8737.
Hawley RG, Lieu FH, Fong AZ, Hawley TS . Versatile retroviral vectors for potential use in gene therapy. Gene Ther 1994; 1: 136–138.
Sadowski I, Ptashne M . A vector for expressing GAL4(1–147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 7539.
Butler LH, Slany R, Cui X, Cleary ML, Mason DY . The HRX proto-oncogene product is widely expressed in human tissues and localizes to nuclear structures. Blood 1997; 89: 3361–3370.
Lavau C, Szilvassy SJ, Slany R, Cleary ML . Immortalization and leukemic transformation of a myelomonocytic precursor by retrovirally transduced HRX-ENL. EMBO J 1997; 16: 4226–4237.
So CW, Cleary ML . MLL-AFX requires the transcriptional effector domains of AFX to transform myeloid progenitors and transdominantly interfere with forkhead protein function. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 6542–6552.
Schreiner S, Birke M, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Zilles O, Greil J, Slany RK . MLL-ENL causes a reversible and myc-dependent block of myelomonocytic cell differentiation. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 6480–6486.
Lavau C, Luo RT, Du C, Thirman MJ . Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer of MLL-ELL transforms primary myeloid progenitors and causes acute myeloid leukemias in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10984–10989.
Birke M, Schreiner S, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Mahr K, Titgemeyer F, Slany RK . The MT domain of the proto-oncoprotein MLL binds to CpG-containing DNA and discriminates against methylation. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: 958–965.
Schreiner SA, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Fey GH, Slany RK . The leukemogenic fusion of MLL with ENL creates a novel transcriptional transactivator. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1525–1533.
Garcia-Cuellar MP, Zilles O, Schreiner SA, Birke M, Winkler TH, Slany RK . The ENL moiety of the childhood leukemia-associated MLL-ENL oncoprotein recruits human Polycomb 3. Oncogene 2001; 20: 411–419.
Hemenway CS, de Erkenez AC, Gould GC . The polycomb protein MPc3 interacts with AF9, an MLL fusion partner in t(9;11)(p22;q23) acute leukemias. Oncogene 2001; 20: 3798–3805.
Garcia-Cuellar MP, Schreiner SA, Birke M, Hamacher M, Fey GH, Slany RK . ENL, the MLL fusion partner in t(11;19), binds to the c-Abl interactor protein 1 (ABI1) that is fused to MLL in t(10;11). Oncogene 2000; 19: 1744–1751.
Debernardi S, Bassini A, Jones LK, Chaplin T, Linder B, de Bruijn DR, Meese E, Young BD . The MLL fusion partner AF10 binds GAS41, a protein that interacts with the human SWI/SNF complex. Blood 2002; 99: 275–281.
Brock HW, van Lohuizen M . The Polycomb group-no longer an exclusive club?. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2001; 11: 175–181.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Frank Rauscher III for the gift of the KRAB repressor plasmid. The authors wish to thank Renate Zimmermann for technical assistance and Georg Fey for continuous support. This work was supported by grant SFB466/C7 and partially by grants SFB473/B10 and SL27/4–1 from the DFG. RKS is a recipient of a Ria Freifrau-von-Fritsch Stiftung career development award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeisig, B., Schreiner, S., García-Cuéllar, MP. et al. Transcriptional activation is a key function encoded by MLL fusion partners. Leukemia 17, 359–365 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402804
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402804
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting intrinsically disordered proteins involved in cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2020)
-
Chromosomal rearrangement involving 11q23 locus in chronic myelogenous leukemia: a rare phenomenon frequently associated with disease progression and poor prognosis
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015)
-
Both SEPT2 and MLL are down-regulated in MLL-SEPT2therapy-related myeloid neoplasia
BMC Cancer (2009)
-
The eleven-nineteen-leukemia protein ENL connects nuclear MLL fusion partners with chromatin
Oncogene (2005)
-
New insight into the molecular mechanisms of MLL-associated leukemia
Leukemia (2005)