Abstract
In a three-year follow-up study of 69 patients found that erectile dysfunction (ED) impairs many elderly men’s life: up to 25% of the men aged 65 y and 80% of those aged 75 y suffer from erectile dysfunction. The most effective non-surgical treatment of ED is intracavernosal pharmacotherapy, and the most common vasoactive agent currently used is prostaglandin E1 (PGE1). The purpose of this study was to assess the long-term outcome of PGE1 treatment and the patients’ overall satisfaction with their sexual life.
Sixty-nine patients who had started ICI therapy three years earlier were invited to a control examination. The mean age of the patients was 60.5 y. The patients filled in a questionnaire, which included questions about the use of PGE1 treatment at home. All the patients evaluated their own satisfaction with their erection, ejaculation, orgasm and libido on a visual analytical scale (VAS, 0–100%). A clinical examination was made, and the penile shaft was examined by ultrasonography. Erection with the home dose of PGE1 was estimated by Rigiscan, and the degree of erection was also estimated clinically (grades 0–5) by a doctor.
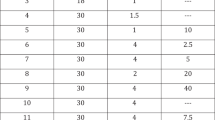
The most common doses of PGE1 used at home were between 10 and 20 m (58%), 46.4% of the patients had discontinued PGE1 therapy, the mean time of using PGE1 was 23.3 months. The mean coital frequency with PGE1 was 2.8 times per month. 34.8% of the patients (24 out of 69) reported that their own spontaneous erections had improved after the beginning of PGE1 therapy. The most common problem was hematomas in 10.1% of the patients (7 out of 69), which, however, were small and did not cause discontinuation of the therapy. There were three instances of priapism (4.3%), and four patients (5.8%) had fibrosis in ultrasonography. The patients’ satisfaction with their erection at home was 67.3% with PGE1.
The mean coital frequency with PGE1 therapy was quite low, 2.8 times per month, even though the patients’ mean age was only 60.5 y, one reason may be the high price of PGE1 injections. The rate of improvement of spontaneous erections while using PGE1 was quite high, accounting for 34.8% of the patients. Most of the patients who discontinued the PGE1 therapy had a psychogenic etiology. There were no systemic side-effects with PGE1. Only 7.2% of the patients had prolonged pain after the injection, leading to drug discontinuation.
It can be concluded that treatment with intracavernous injections of PGE1 is well tolerated and involves only minor problems. The patients’ satisfaction with their erections at home with PGE1 therapy was good. Precise determination of the home dose of PGE1 and the teaching of the technique of injection are important at the beginning of this treatment modality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunelius, P., Lukkarinen, O. Intracavernous self-injection of prostaglandin E1 in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 11, 21–24 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900377
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900377
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Men’s beliefs about treatment for erectile dysfunction—what influences treatment use? A systematic review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
Accuracy of MRI without intracavernosal prostaglandin E1 injection in staging, preoperative evaluation, and operative planning of penile cancer
Abdominal Radiology (2021)
-
Correlation between peak systolic velocity and diameter of cavernosal arteries in flaccid versus dynamic state for the evaluation of erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2017)
-
Gene transfer for the therapy of erectile dysfunction: progress in the 21st century
International Journal of Impotence Research (2006)
-
A prospective randomized study to optimize the dosage of trimix ingredients and compare its efficacy and safety with prostaglandin E1
International Journal of Impotence Research (2005)