Abstract
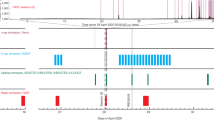
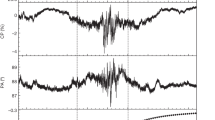
THE nature of the γ-ray source 'Geminga' (2CG195 + 04) is a problem of considerable importance in high-energy astrophysics. First discovered in 1972 by the SAS-2 satellite1, Geminga emits virtually all its power at energies above 50 MeV, and at energies above 100 MeV is the second brightest source in the γ-ray sky survey made by the Cos-B satellite2. It eluded identification at all other wavelengths until the Einstein Observatory found an unusual soft X-ray source, 1E0630 + 178, in its error box3. This source also has a claimed twenty-fifth magnitude optical counterpart4–6. This distinctive set of properties is reminiscent of the Vela pulsar, except for the absence of radio emission7 or a synchroton nebula3. We have made a more sensitive soft X-ray observation of the Geminga field using Rosat, and have detected coherent pulsations from 1E0630+178 at a period of 0.237s. This result confirms suggestions3–6,8,9 that Geminga is, like Vela, a γ-ray pulsar. We speculate that Geminga is somewhat the older of the two. With this discovery we consider the mystery of Geminga largely solved.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fichtel, C. E. et al. Astrophys. J. 198, 163–182 (1975).
Swanenburg, B. N. et al. Astrophys. J. 243, L69–L73 (1981).
Bignami, G. F., Caraveo, P. A. & Lamb, R. C. Astrophys. J. 272, L9–L13 (1983).
Bignami, G. F. et al. Astrophys. J. 319, 358 (1987).
Halpern, J. P. & Tytler, D. Astrophys. J. 330, 201–217 (1988).
Bignami, G. F., Caraveo, P. A. & Paul, J. A. Astr. Astrophys. 202, L1 (1988).
Spoelstra, T. A. & Hermsen, W. Astr. Astrophys. 135, 135–140 (1984).
Halpern, J. P. in Proc. GRO Science Workshop (ed Johnson, N.) 4-166–4-173 (1989).
Ruderman, M. & Cheng, K. S. Astrophys. J. 335, 306–318 (1988).
Trümper, J. et al. Adv. Space Res. 2, 241–249 (1983).
Bignami, G. F., Caraveo, P. A. & Paul, J. A. Nature 310, 464–469 (1984).
Bignami, G. F. in The Origin and Evolution of Neutron Stars (eds Helfand, D. J. & Huang, J. H.) 465–474 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1987).
Caraveo, P. A. & Bignami, G. F. in The Origin and Evolution of Neutron Stars 545 (eds Helfand, D. J. & Huang, J. H.) (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1987).
Romani, R. W. Astrophys. J. 313, 718–726 (1987).
Ögelman, H., Finley, J. P., Aschenbach, B., Trümper, J. & Zimmermann, U. Bull. Am. astr. Soc. 23, 1349 (1991).
Chen, K. & Ruderman, M. Astrophys. J. (in the press).
Bignami, G. F. & Hermsen, W. A. Rev. Astr. Astrophys. 21, 67–108 (1983).
Seward, F. D. & Harnden, F. R. H. Jr Astrophys. J. 256, L45–L47 (1982).
Wilson, R. B., Finger, M. H., Fishman, G. J., Meegan, C. A. & Paciesas, W. S. IAU Circ. No. 5429 (1992).
Kniffen, D. A. et al. IAU Circ. No. 5485 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halpern, J., Holt, S. Discovery of soft X-ray pulsations from the γ-ray source Geminga. Nature 357, 222–224 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/357222a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/357222a0
This article is cited by
-
Prospective study on observations of γ-ray sources in the Galaxy using the HADAR experiment
Frontiers of Physics (2022)
-
AstroSat-CZTI as a hard X-ray pulsar monitor
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (2021)
-
Some highlights of the first four years of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
Frontiers of Physics (2013)
-
The Geminga fraction
Astrophysics and Space Science (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.