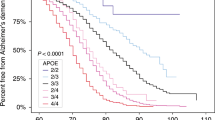
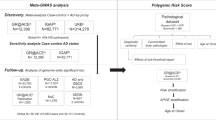
Abstract
The gene coding for the amyloid protein, a component of neuritic plaques found in brain tissue from patients with Alzheimer's disease, has been localized to chromosome 21, and neighbouring polymorphic DNA markers segregate with Alzheimer's disease in several large families. These data, and the association of Alzheimer's disease with Down's syndrome, suggest that overproduction of the amyloid protein, or production of an abnormal variant of the protein, may be the underlying pathological change causing Alzheimer's disease. We have identified a restriction fragment length polymorphism of the A4-amyloid gene, and find recombinants in two Alzheimer's disease families between Alzheimer's disease and the A4-amyloid locus. This demonstrates that the gene for plaque core A4-amyloid cannot be the locus of a defect causing Alzheimer's disease in these families. These data indicate that alterations in the plaque core amyloid gene cannot explain the molecular pathology for all cases of Alzheimer's disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terry, R. D. & Katzman, R. Ann. Neurol 114, 497–506 (1983).
Brun, A. in Alzheimer's Disease; the Standard Reference (ed. Reisberg, B.) 37–47 (1983).
Heston, L. L., Mastri, A. R., Anderson, V. E. & White, J. Arch. gen. Psychiat. 38, 1085–1090 (1981).
Heyman, A. et al. Ann. Neurol. 14, 507–515 (1983).
Wisniewski, K. E. et al. Neurology 35, 957–961 (1985).
Cook, R. H., Ward, B. E. & Austin, J. H. Neurology 29, 1402–1412 (1979).
Goudsmit, J. et al. J. neurol. Sci. 49, 79–89 (1981).
Nee, L. E. et al. Arch. Neurol. 40, 203–208 (1983).
St. George-Hyslop, P. H. et al. Science 235, 885–889 (1987).
Summit, R. L. in Trisomy 21 (Down's Syndrome) Research Perspective (eds De la Cruz, F. F. & Gerald, P. S.) 225–235 (University Park Press, Baltimore, 1981).
Glenner, G. G. & Wong, C. W. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 120, 885–890 (1984).
Masters, C. L. et al. Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 4245–4249 (1985).
Roher, A., Wolfe, D., Palutke, M. & Kukuruga, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 2662–2666 (1986).
Selkoe, D. J., Abraham, C. R., Polinshy, M. B. & Duffy, L. K. J. Neurochem. 46, 1820–1834 (1986).
Masters, C. L. et al. EMBO J. 4, 2757–2763 (1985).
Wong, C. W., Quaranta, V. & Glenner, G. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 8729–8732 (1985).
Kang, J. et al. Nature 325, 733–735 (1987).
Goldgaber, D., Lerman, M. I., McBridge, O. W., Saffiotti, U. & Gajdusek, D. C. Science 235, 877–880 (1987).
Tanzi, R. E. et al. Science 235, 880–884 (1987).
Robakis, K. K. et al. Lancet i, 384–385 (1987).
Delabar, J.-M. et al. Science 235, 1390–1392 (1987).
Levanon, D. et al. EMBO J. 4, 77–84 (1985).
Lovett, M. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 144, 1069–1075 (1987).
Clayten, P. J. & Martin, R. in Clinical Aspects of Alzheimer's Disease and Senile Dementia (eds Miller, N. E. & Cohen, G. D.) 47–59 (Raven, New York, 1981).
Lathrop, J. M., Lalouel, J. M., Julier, C. & Ott, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 3443–3446 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broeckhoven, C., Genthe, A., Vandenberghe, A. et al. Failure of familial Alzheimer's disease to segregate with the A4-amyloid gene in several European families. Nature 329, 153–155 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/329153a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/329153a0
This article is cited by
-
The molecular genetics of Alzheimer's disease
Molecular Neurobiology (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.