Abstract
Germinal centers (GC) of secondary lymphoid tissues are critical to mounting a high-affinity humoral immune response. B cells within the GC undergo rapid clonal expansion and selection while diversifying their antibody genes. Although it is generally believed that GC B cells employ a unique proliferative program to accommodate these processes, little is known about how the GC-associated cell cycle is orchestrated. The D-type cyclins constitute an important component of the cell cycle engine that enables the cells to respond to physiological changes. Cell type- and developmental stage-specific roles of D-type cyclins have been described but the cyclin D requirement during GC reaction has not been addressed. In this study, we report that cyclin D3 is largely dispensable for proliferation and Ig class switching of in vitro activated B cells. In contrast, GC development in Ccnd3−/− mice is markedly impaired, as is the T cell-dependent antibody response. Within the GC, although both switched and unswitched B cells are affected by cyclin D3 inactivation, the IgM− pool is more severely reduced. Interestingly, despite a compensatory increase in cyclin D2 expression, a significant number of Ccnd3−/− GC B cells accumulate in quiescent G0 state. Lastly, although cyclin D3 inactivation did not disrupt BCL6 expression in GC B cells, it completely blocked the GC promoting effect of BCL6 overexpression, suggesting that cyclin D3 acts downstream of BCL6 to regulate GC formation. This is the first demonstration that cyclin D3 plays an important and unique role at the GC stage of B cell development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Germinal centers (GCs) are dynamic functional niches within secondary lymphoid tissues that are critical to a high-affinity humoral immune response. After immunization with T cell-dependent antigens, naïve B cells that have been activated by cognate T cells migrate to the boundary between the B and T cell areas and initiate rapid focal expansion which quickly leads to the formation of GCs. Within the GC, B cells diversify their Ig genes by two distinct genetic mechanisms: class switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM). CSR enables production of antibodies other than the IgM and IgD isotypes while SHM introduces point mutations into the variable regions of Ig genes, which leads to Ig affinity maturation when higher-affinity clones are positively selected 1, 2. Within the GC, B cells are segregated into dark zone and light zone compartments, where they are referred to as centroblasts and centrocytes, respectively. The transit of B cells between these two compartments and the specific features of GC B cells in these areas have been subjects of significant interest 3, 4. In a standard model, SHM and most of the cell proliferation occur in the dark zone while CSR and positive/negative selection occur in the light zone as a result of B cell interactions with follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. Unswitched, IgM+ GC B cells are exclusively found in the FDC (light) zone while the majority of the switched, IgM– GC B cells occupy the non-FDC (dark) zone 3. After exiting the GC, selected B cells further differentiate to become memory or plasma cells. The GC stage of B cell development has a number of unique features. For instance, because CSR and SHM generate several types of DNA damage that are intrinsically linked to the DNA damage response, it has been suggested that GC B cells execute a modified DNA damage signaling pathway that dampens the threshold for cell cycle checkpoint activation 5.
Available evidence also suggests that the cell cycle engine itself may operate differently in GC B cells compared to other mitotic cells. A hallmark of the GC response is the extremely fast proliferation of GC B cells, with cell division time estimated to be as short as 6-12 h, placing them among the fastest-cycling cells in higher eukaryotes 4. Curiously, c-Myc and NF-κB, two transcription factors thought to be required for all proliferating cells, are specifically down-regulated when B cells enter the GC 5, 6. A close examination of the relationship between cell proliferation and BCL6, the master regulator of GC formation, also raises the possibility that GC B cells may use different cell cycle regulators. A recent genome-wide BCL6 promoter binding study revealed that in normal GC B cells, BCL6 inhibits a number of genes known to promote cell proliferation, including c-Myc, cyclin D1, cyclin D2, Pim1, and JunB 7. We have previously reported that by suppressing c-Myc, cyclin D2, and the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway, BCL6 exerts a strong negative effect on the G1-S transition in macrophages 8. Thus, it is likely that in GC B cells as well as in macrophages, BCL6-mediated silencing of proliferation related genes will have a significant impact on cell cycle control. As many of these BCL6 target genes function in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, an attractive hypothesis is that the G1 phase is differentially regulated in GC B cells compared to other types of cells. To our knowledge, the only direct study that compared the role of cell cycle regulators in GC and non-GC B cells found that the cyclin-dependent-kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p18INK4c is dispensable for GC but is required for post-GC plasma cell differentiation 9.
In mammalian cells, the G1-cyclins include cyclin D1, D2, and D3. These D-type cyclins form heterodimeric complexes with and activate the kinase activities of either Cdk4 or Cdk6. In turn, activated Cdk4/6 hyperphosphorylates Rb and related pocket proteins, i.e. p107 and p130, leading to their release from the E2F factors and transcriptional activities required for G1-S progression 10. Unlike other cyclins whose expression oscillates with the cell cycle phases, D-type cyclins are primarily regulated by mitogenic and oncogenic stimuli and are expressed in developmentally programmed tissue-specific patterns 11. They are particularly important to hematopoietic cells as deficiency in all three (D1, D2 and D3) leads to a profound defect in expansion of hematopoietic stem cells and lineage-committed progenitors, while apparently sparing other cell lineages in the developing mouse embryo 12. In certain cell types, a switch from one D-type cyclin to another coincides with a change in control of cell proliferation during differentiation. In T cells, a switch from cyclin D2 to cyclin D3 is important during their transition from cytokine-dependent proliferation in the double negative stage-3 (DN-3) to the pre-TCR-dependent proliferative burst in DN-4 13. Similarly, as pro-B cells differentiate into large pre-B cells in the bone marrow, the newly assembled pre-BCR not only triggers an increase in cyclin D3 protein but also shifts the expansion of the pre-B cell pool to a cyclin D3-dependent mode 14. The D-type cyclins also play prominent roles in tumorigenesis. Their expression is often upregulated by major oncogenic pathways. In addition, gene amplification and chromosomal translocation can also lead to their aberrant expression and activity in many types of tumors. With respect to GC-derived B cell malignancies, the cyclin D3 gene CCND3 is rearranged and over-expressed in some patients with diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL), and its overexpression predicts poor clinical outcome 15, 16.
Gene expression profiling and histological analyses have demonstrated that B cells undertake a D2 to D3 switch upon entering the GCs 17, 18, 19. It is unclear, however, whether this phenomenon simply reflects the GC-associated upregulation of BCL6, a strong inhibitor of cyclin D2 20, or serves a biological mandate due to a specific requirement for cyclin D3 function. Here we report that while cyclin D3 is largely dispensable for the development and proliferation of follicular B cells, GC formation and T cell-dependent antibody responses are notably impaired in cyclin D3 knock-out (KO) mice. Moreover, genetic analyses reveal that cyclin D3 functions at a step downstream of BCL6 in GC formation.
Results
Cyclin D3 is preferentially expressed in the GC dark zone
To extend to mice the observations made in human that initiation of GCs is associated with a shift in expression from cyclin D2 to D3 17, 18, cyclin D3 was examined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in spleen sections from wild type (WT) C57BL/6 mice after immunization with sheep red blood cells (SRBC). As expected, cyclin D3 protein was readily detected in murine GCs (Figure 1A, arrows indicate examples of stained GCs) and in human tonsillar GCs (Figure 1F depicts two GCs), while the surrounding B cell follicles and T cell zones were uniformly negative. Occasional cyclin D3+ cells were also detected in murine splenic subcapsular areas and red pulp (Figure 1A, arrowhead). Absence of such stains from spleen sections of cyclin D3 KO mice showed the specificity of this polyclonal cyclin D3 antibody (Supplementary information, Figure S1A). Double IHC stains with lineage markers revealed that virtually all cyclin D3+ cells within the GC were B cells (B220+, Figure 1C, arrow) that bound the GC-defining marker peanut agglutinin (PNA+, Figure 1D, arrow) and were not T cells (CD3−, Figure 1E). We noted that not all cells within the GC were stained and that the pattern of cyclin D3 positivity was suggestive of a polarized distribution within the GC. Indeed, double stains for cyclin D3 and CD21/CD35, markers of FDC, indicated that many of the brightly stained cyclin D+ cells are localized to the non-FDC zone (Figure 1B), which is analogous to the dark zone of human tonsilar GCs. We next examined patterns of cyclin D3 expression in human tonsils, where the GC dark and light zones can be readily resolved histologically. Although expressed throughout tonsilar GCs, cyclin D3 displayed a clear gradient across most of the GC cross sections (Figure 1F, arrow indicates more intense stain than arrowhead). Double-stains with the pan-B marker CD79a revealed the follicular mantle with a characteristic strong and uniform CD79a expression (Figure 1G, asterisk). As the GC light zone is adjacent to the mantle zone, this double-stain allowed unequivocal designation of the intense Cyclin D3 staining area as the dark zone (Figure 1G). The designation of light and dark zone was further corroborated by a double-stain for cyclin D3 and the pan-T cell marker CD3 in the next serial section, as the light zone contains more GC T cells than the dark zone 4 (Figure 1I). High power images of the double stained sections confirmed that, consistent with our observation in murine GCs, cyclin D3+ cells within tonsilar GCs are also predominantly B cells (Figure 1H) and not T cells (Figure 1J).
Cyclin D3 is expressed in B220+PNA+ GC B cells and predominantly in the dark zone. (A-E) Spleen sections collected 14 days after immunization of WT mice were stained with antibodies for either cyclin D3 (blue) alone (in A) or in combination with other stains in brown; (B) CD21/CD35; (C) B220; (D) PNA; (E) CD3. Arrows in (A) GCs that were positively stained for cyclin D3. Arrowhead in (A) Cyclin D3+ cells in red pulp. Arrows in (C-E) indicate that cyclin D3+ cells are B220+ (in C), PNA+ (in D), and that CD3+ cells lack detectable cyclin D3 stain (in E). Human tonsil sections were stained in panels (F-J). (F) Cyclin D3 stain is enriched in one part of a GC (arrow) compared to another (arrowhead). (G) Adjacent section stained for cyclin D3 (blue) and CD79a (brown) to identify B cells within the GC as well as the follicular mantle (asterisk). Note that the mantle zone B cells are uniformly negative for cyclin D3. (H) Magnified view of the boxed region in (G) illustrates CD79a+ cyclin D3+ GC B cells (arrowheads). Note a CD79a+ cyclin D3− plasma cell (arrow). (I) Adjacent section stained for cyclin D3 (blue) and CD3 (brown) to corroborate the designation of light and dark zone. (J) Magnified view of the boxed region in (I) shows CD3+cyclin D3− GC T cells (arrows, examples). Scale bars are 100 μm for (A); 200 μm for (B); 10 μm for (C-E, H, J); and 200 μm for (F, G, I).
Mild reduction of follicular B cells and increased marginal zone B cells in Ccnd3−/− mice
Although cyclin D3 inactivation causes a marked but incomplete block at the pro-B to pre-B transition stage 14, development and function of a subset of mature B cells known as B-1a cells are normal in Ccnd3−/− mice 21. In addition, the total number of B-2 B cells in the spleen of these mice is also close to normal 21, suggesting that the size of the B cell pool may have largely recovered by the time of the mature B cell stage. Thus, we focused our analysis on the subsets of splenic B-2 B cells in the Ccnd3−/− mice. As shown in Figure 2A, cyclin D3 deficiency caused a ∼50% reduction in immature B cells, a phenotype likely due to the early developmental defect. In line with this interpretation, there was no skewing between the T1 and T2 fractions within the transitional B cell gate (Figure 2B). This result suggests that survival and maturation at the transitional stage are cyclin D3-independent. Interestingly, the total number of mature B cells in the Ccnd3−/− spleen was comparable to that in the WT controls and even slightly increased (Figure 2A), which is likely due to the compensatory homeostatic population expansion observed by Cooper et al. 14. These mature B cells were capable of forming normal splenic architecture in Ccnd3−/− mice, including red and white pulp and grossly normal B cell follicles (Supplementary information, Figure S1B and S1C). When the mature B cells were further divided into follicular (Fo) and marginal zone (MZ) subsets, a 17% reduction in Fo B cells was revealed, and this was accompanied by a two-fold increase in MZ B cells (Figure 2C). Published work suggests that selection of transitional B cells into the B-1, MZ and Fo pool is guided in part by BCR signaling strength 22, 23. Thus, the reciprocal changes in Fo vs MZ B cells in the Ccnd3−/− mice invite the speculation that cyclin D3 deficiency may alter the effective BCR signaling strength perceived by the nuclear differentiation program.
Splenic B cell subsets in WT and cyclin D3 KO mice. (A) Mature and transitional B cell subsets were identified as B220+AA4.1− and B220+AA4.1+, respectively. (B) The transitional B cell gate was used to identify T1 (CD21−HSAhi) and T2 (CD21hiHSAhi) subsets. A significant decrease in immature B cells and an increase in mature B cells were observed in Ccnd3−/− mice compared to WT controls. The transitional T1 and T2 subsets remained unchanged in these mice. (C) The mature B cell gate was used to identify marginal zone (CD21hiCD23−) and follicular (CD21intCD23+) B cell subsets. The Ccnd3−/− mice also displayed a 2-fold increase in MZ B cells and a reduction in Fo B cells. Four WT and five Ccnd3−/− mice were analyzed. Representative dot plots are shown. Columns in the graphs represent mean and SEM of each genotype. P values of two-tailed Student t tests are also shown in the graphs.
Severe impairment of GC reaction in Ccnd3−/− mice
To study the GC response, Ccnd3−/− and WT control mice were immunized with SRBC, which triggered the formation of a large number of GCs in the WT spleen 14 days after the immunization (Figure 3A, arrow indicates a GC). In contrast, the frequency of PNA+ GCs was reduced ∼3-fold in the Ccnd3−/− animals (Figure 3B and 3D, 0.897 vs 3.34 GC per mm2, P < 0.0001), and the average size of the GCs was also reduced to about half of that in WT controls (Figure 3E, genotype mean 7 823 μm2 vs 15 970 μm2, P < 0.01). To corroborate these histological measurements, single-cell suspensions of lymph nodes and spleen were stained with PNA and antibodies to B220 and CD95 (Fas). In the absence of cyclin D3, the number of B220+PNAhiCD95hi GC B cells was reduced to 30-40% of the control levels (Figure 3C), consistent with our histological analysis. A kinetic difference in GC formation was unlikely to be the cause, as similar defects were observed on day 7 (data not shown). Taken together, the reductions in both the number and size of GCs suggest that cyclin D3 is required both at the onset and during the expansion phase of GC development.
GC size and frequency are reduced in Ccnd3−/− mice. Representative images of spleen sections from WT littermate (A) and Ccnd3−/− mice (B) stained for the GC marker PNA (brown) 14 days after immunization with SRBC. Scale bars are 0.5 mm; arrow, a PNA-stained GC. (C) Flow-cytometric enumeration of B220+PNAhiCD95hi splenocytes (top) and LN cells (bottom). Spleen and LN data are representative of 12 and 2 animals, respectively, for each genotype. (D) Loss of cyclin D3 caused a ∼3-fold decrease in GC frequency. Five WT and seven cyclin D3-deficient mice were analyzed, P < 0.0001, error bars are SEM. (E) Loss of cyclin D3 caused a ∼2-fold decrease in GC size. Each column in the graph corresponds to an individual mouse; each point is an individual GC, P < 0.01. P values are based on two-tailed Student t tests.
Defective antibody response in Ccnd3−/− mice
In order to determine whether the structural defect in GC formation also translates to a functional perturbation in the T-cell dependent antibody response, CSR and affinity maturation were evaluated in vivo. Basal serum levels of most Ig subtypes were comparable between WT and Ccnd3−/− animals, with the latter showing a modest but statistically significant elevation of IgG1 and a decrease in IgG2b concentrations (Figure 4A). Next, animals were immunized with the T-dependent antigen 4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl-acetyl (NP)-KLH and boosted 21 days and again 42 days later to elicit secondary and tertiary antibody responses 24 (experimental scheme summarized in Supplementary information, Figure S2). Ccnd3−/− animals produced significantly lower serum anti-NP titers of all subclasses tested except IgM and IgA (Figure 4B). We studied the IgG1 response in more detail, as this is the main anti-NP subclass elicited in vivo. An impairment in total NP-specific IgG1 primary titers was observed in Ccnd3−/− mice (Figure 4C) (P = 0.0264), which persisted after the first NP-KLH boost (P = 0.0010) but was ameliorated by the tertiary immunization (P = 0.32). The abnormalities in GC development are likely to be the main cause of these defects, although in vitro CSR assays in isolated B cells suggested that a minor contribution may also come from suboptimal switching to IgG1 (Supplementary information, Figure S3). Ccnd3−/− mice exhibited statistically significant impairments in affinity maturation as measured either by anti-NP3 titers (Figure 4D) or by anti-NP3 titers normalized to the total anti-NP response (Figure 4E) (P < 0.0001). Interestingly, the secondary immunization markedly raised the anti-NP affinity of Ccnd3−/− sera such that the genotype difference essentially disappeared (P = 0.16) and this trend persisted through the tertiary response (P = 0.53) (Figure 4E). Collectively, these results indicate that cyclin D3 plays an important role in affinity maturation in vivo. However, the initial impairments in both the affinity and magnitude of the T-dependent antibody response could be overcome by selective forces during repeated immunizations.
T-cell dependent antibody response is defective in the absence of cyclin D3. Column scatter plots display ELISA data for KO (white) and WT controls (black) mice. Each point is an individual animal. Statistical analysis is detailed in the Materials and Methods section. Significant P values (<0.05) are emboldened and underlined. (A) Resting Ig levels. (B) NP-specific antibodies 13 days after primary immunization. ELISA plate coat was NP20-BSA. NP-specific titers for each subclass are given in arbitrary units. (C, D) NP-specific IgG1 levels. Serum samples were collected 13 days after the primary immunization (“primary”) and 5 days after each boost (“secondary” and “tertiary”, see Supplementary information, Figure S2 for experimental scheme). In (C) the plate coat was NP30-BSA, which binds low- and high-affinity antibodies. In (D) the plate coat was NP3-BSA, which binds only high-affinity antibodies. In (E), the ratio of NP3 to NP30 binding is plotted as an index of affinity maturation. Error bars are SEM.
GC B cells in vivo, unlike in vitro activated naïve B cells, depend upon cyclin D3 for continued progression through cell cycle
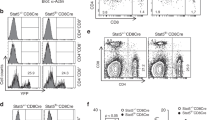
To provide a molecular basis for the in vivo GC-associated phenotypes, we examined the role of cyclin D3 in cell cycle regulation. We first used propidium-iodide DNA content staining to analyze cell cycle profiles of in vitro stimulated naïve B cells. Three days after stimulation, Ccnd3−/− B cells accumulated slightly more in G1 phase than their WT controls (Figure 5A and 5B). Although this trend was true for both LPS+IL4 and LPS treated cells, the genotype difference for the G0/1 fraction reached statistical significance only in LPS+IL4 cultures (61.7% for KO vs 57.6% for WT, P = 0.0401, asterisk in Figure 5A). Considering the small differences, however, we conclude that cyclin D3 inactivation has only a very minor effect on in vitro B cell proliferation, a notion that is further supported by results from CFSE-dilution and thymidine-incorporation assays (not shown). As these observations in stimulated naïve B cells did not explain the dramatic defects in the generation and expansion of GCs in Ccnd3−/− mice (Figure 3), we next analyzed the cell cycle status of GC B cells in vivo. The cell cycle profiles we observed in diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained WT B220+PNAhi GC B cells (Figure 5D) were consistent with those previously reported based on BrdU incorporation 25. Among the few Ccnd3−/− B cells that managed to acquire a PNAhi GC phenotype, there was a 2-fold decrease in the S phase fraction (Figure 5C and 5D, 15.4% vs 31.5%, P = 0.0007) and a corresponding increase in the G0/1 fraction (77.8% vs 61.6%, P = 0.0032). Compared to the in vitro observations of stimulated B cells, this defect was much more pronounced and is consistent with a specific requirement for cyclin D3 when B cells are recruited into the GC response in vivo. Two possibilities exist to account for the cell cycle profiling differences in Figure 5C: either the G1-to-S phase transition was delayed in the absence of cyclin D3 or a smaller fraction of Ccnd3−/− GC B cells were actively going through cell cycle. To distinguish these two scenarios, we stained spleen sections of immunized mice with PNA and Ki67 and scored PNA+ GC B cells based on their Ki67 status (Figure 5E and 5F). While WT PNA+ GC B cells contained only 25% Ki67− cells, this non-mitotic fraction was dramatically increased to 60% in Ccnd3−/− mice (Figure 5G). Interestingly, by extrapolating frequency of non-mitotic Ki67− cells to the cell cycle phase distribution analysis, we estimate that 51% of WT, mitotic GC B cells are in S and G2/M phases compared to 56% in Ccnd3−/− GCs. Therefore, although a sizable fraction of Ccnd3−/− GC B cells dropped out of cell cycle and became quiescent, those that remained cycling apparently transitioned from G1 to S phase normally.
GC B cells in vivo, but not in vitro-activated mature B cells, require cyclin D3 for proliferation. (A, B) PI staining was used to examine cell cycle profiles of primary splenic B cells stimulated for 3 days as indicated. n = 4, asterisk indicates P < 0.05. (C, D) DAPI-based cell cycle profiles of B220+PNAhi GC B cells 11 days after SRBC immunization. (C) Mean and SEM of 4 KO (white bars) and 3 WT control mice (grey bars). (D) Representative cell cycle profiles of KO and WT GC B cells. (E) Spleens prepared as in Figure 1 were stained with PNA (brown) and Ki67 (blue). Many Ccnd3−/− PNA+ GC cells do not express Ki67. Scale bars are 30 μm. (F) Individual PNA+ cells from 10 Ccnd3−/− and 6 WT GCs were manually scored as Ki67+ (white bar) or Ki67− (dark bar). (G) Normalization of data from panel (F) demonstrates that 75% of PNA+ GC B cells in WT mice were Ki67+, compared to only 40% in Ccnd3−/− mice (P < 0.0001). All error bars are SEM.
Cyclin D3 deficiency reduces the pool of both unswitched and switched GC B cells
Because many brightly stained cyclin D3+ cells are found in the non-FDC zone within the GC (Figure 1B and 1F), we next asked the question whether the requirement for cyclin D3 differs between different pools of GC B cells. Because in murine GCs unswitched IgM+ B cells are exclusively located within the FDC zone (light zone) while the majority of switched (IgM−) cells are found in the non-FDC zone (dark zone) 3, we gated GC B cells into IgM+ and IgM− subsets (Figure 6A and 6B) and analyzed their proliferative capacity based on 6 h BrdU labeling (Figure 6C-6F). As shown in Figure 6A and 6B, 14 days after SRBC immunization, WT GCs contained equal number of switched and unswitched B cells. In comparison, only 38% of Ccnd3−/− GC B cells were IgM−. Because the total number of GC B cells is reduced 2-3 fold in Ccnd3−/− animals (Figure 3C and data not shown), the number of Ccnd3−/− IgM+ and IgM− cells is roughly ∼36% and ∼22% of the corresponding WT levels. We also examined cell proliferation in switched and unswitched GC B cells by in vivo BrdU pulse-labeling. Consistent with a number of prior reports showing more mitotic activity in the non-FDC zone, in WT animals, we detected 42% BrdU+ cells in the IgM− pool compared to 35% in the IgM+ fraction (Figure 6E and 6F). In the Ccnd3−/− GCs, these numbers were reduced to 25% and 23% for IgM− and IgM+ compartment, respectively. Thus, cyclin D3 inactivation affected cell proliferation in these two pools to a similar degree.
Cyclin D3 is required for expansion of both IgM+ and IgM− compartments within the GC. Splenocytes, isolated from mice that were SRBC-immunized 14 days previously and exposed to BrdU for 6 h before sacrifice, were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Representative profile of splenic B220+PNA+CD95hi GC cells assayed for expression of IgM. (B) Averaged results from (A) showing WT GCs contained comparable numbers of IgM+ and IgM− cells, while Ccnd3−/− GCs had more IgM+ than IgM− cells (58% vs 42%, n = 2 WT and 3 KO, P = 0.068). (C) B220+CD95hi GC cells from Ccnd3−/− and WT mice were analyzed for the expression of IgM and incorporation of BrdU (n = 2 WT and 2 KO). (D) Among all GC B cells, 39% incorporated BrdU in the WT mice compared to 23% in Ccnd3−/− animals (P = 0.009). Comparable reductions in BrdU uptake were observed in the IgM+ (E, P = 0.013) and IgM− (F, P = 0.042) compartments. All error bars are SEM.
Change in expression of cell cycle regulators in Ccnd3−/− B cells
To obtain mechanistic insights into the phenotypes described above, expression of several regulators of the G1-S checkpoint was compared in Ccnd3−/− and WT B cells. First, lysates of in vitro activated splenic B cells were assayed by western blot (Figure 7A). In resting splenic B cells (day 0), both cyclin D2 and D3 were barely detectable. Upon stimulation with LPS or LPS+IL4, both cyclins were strongly upregulated within 24 h, as previously reported 26. While cyclin D2 protein persisted throughout the 3-day treatment, the levels of cyclin D3 started to taper on day 3. In addition, when treated with LPS+IL4, both WT and KO cells contained notably less total Rb protein compared to those stimulated with LPS only. Compared to WT control, cyclin D3 KO cells expressed more cyclin D2 and cyclin E upon LPS stimulation (Figure 7A, most obvious on day 1). A mild difference in cyclin D2 was also seen in LPS+IL4 treated cells on day 2. No reproducible differences in the expression of Cdk4/6 were observed. An important indicator of the G1-S transition is the hyper-phosphorylated form of Rb, which is a target of cyclin-Cdk kinase activity. In WT cells subjected to either treatment, abundance of phospho-Rb (Ser807/811) peaked on day 2, which corresponded temporally with cells entering the late G1 phase of the first cell division. In the absence of cyclin D3, LPS-treated cells on day 1 and LPS+IL4-treated cells on day 2 contained slightly reduced amounts of phospho-Rb, consistent with the minor attenuation in G1-S transition shown in Figure 5A and 5B. These results indicate that cyclin D3 inactivation caused only a minor reduction in the overall kinase activity responsible for Rb hyperphosphorylation and the subsequent G1-S transition.
Effect of cyclin D3 inactivation on expression of selected G1 regulators in LPS-stimulated B cells and GC B cells. (A) Splenic B cells were stimulated as indicated, and whole cell lysates were used in western blot analysis of selected G1 phase regulators. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA expression in flow-sorted naïve (B220+PNAlo) and GC (B220+PNAhi) B cells. The ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the fold-change in cyclin D3 KO cells relative to WT control levels. Means and SD based on 2-4 animals per genotype are plotted.
As the scarcity of the murine GC B cells precludes western blot-based protein expression analysis, we resorted to quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) to evaluate expression of four proliferation-related markers (Ccnd2, Trp53, Cdkn1b, and Myc) and the GC master regulator, Bcl6. Flow-sorted naïve and GC B cells were analyzed side-by-side for comparison (Figure 7B). In unstimulated naïve B cells, cyclin D3 inactivation did not affect expression of any of the five genes analyzed (Figure 7B, light gray bars), which is in general agreement with the protein data on cyclin D2 and four other cell cycle regulators (Figure 7A, day 0). In GC B cells (Figure 7B, dark gray bars), while Bcl6, Trp53 (encoding murine p53) and Myc remained largely unchanged following the loss of cyclin D3, two interesting changes were detected. First, Ccnd3−/− GC B cells showed a 3-fold increase over WT controls in Cdkn1b mRNA, which encodes p27Kip1, an integral brake in the G1 phase that inactivates cyclin E/A-Cdk2 10. The cause for this change is currently unknown but may be a consequence of increased quiescent G0 cells within the Ccnd3−/− GC B cells, cyclin D2 mRNA was elevated by more than 5-fold as an apparent compensatory response to cyclin D3 ablation. Our attempt to stain cyclin D2 protein in murine tissue sections was not successful despite the use of two cyclin D2-specific antibodies and a number of variations in the IHC protocol. In summary, these results suggest that within the GC microenvironment, cyclin D3 plays a critical and non-redundant role in the cell cycle entry that cannot be fulfilled even by a 5-fold increase in cyclin D2 expression.
Cyclin D3 inactivation blocks the effect of a BCL6 transgene on GC development
Bcl6 is a transcription repressor highly expressed within the GC, and it has a well-documented role in GC development and function 5. Bcl6 KO mice completely lack PNA+ GCs and have pronounced defects in the T-cell dependent antibody response 27, 28. Because cyclin D3 and Bcl6 share similar expression patterns within the GC, i.e. expressed at higher levels in the dark zone than in the light zone (Figure 1) 29, and because the cyclin D3 KO phenotype resembles that of a “hypomorphic” Bcl6 allele, we investigated the relationship between cyclin D3 and Bcl6 in the context of GC development. First, we examined the influence of cyclin D3 inactivation on Bcl6 expression. IHC revealed that those splenic GCs that formed in the Ccnd3−/− mice were Bcl6 positive (Figure 8A), indicating that Bcl6 upregulation at the onset of GC formation is cyclin D3 independent. Next, to test the role of cyclin D3 in maintenance of BCL6 expression, we used RNA interference to inactivate cyclin D3 in three human DLBCL cell lines that have been previously characterized to be germinal center B cell (GCB)-like, SuDHL6, Ly7, and Val 30. Most of the GCB-like DLBCL cell lines co-express high levels of BCL6 and cyclin D3 (not shown). Although each of two different cyclin D3-specific siRNA oligos drastically reduced the endogenous cyclin D3 levels 2 days after transfection, BCL6 protein levels in the three GCB cell lines remained largely unchanged (Figure 8B and data not shown). Taken together, these observations suggest that in GC B cells, neither the induction nor the maintenance of Bcl6 requires cyclin D3. Next, we asked whether cyclin D3 is required for Bcl6 function. To address this issue, we introduced the BCL6-overexpressing allele, Iμ-HA-BCL6, into the cyclin D3 KO background. The Iμ-HA-BCL6 allele was generated by inserting the BCL6 cDNA downstream of the Iμ promoter in the Ig heavy chain locus 31. In this mouse model, an extra dose of BCL6 is produced in cells poised to undergo CSR. The Iμ-HA-BCL6 allele markedly increases GC formation especially in unimmunized animals by lowering the threshold of antigen stimulation 31. In our cohort, 6-fold more spontaneous GCs developed in mice carrying the Iμ-HA-BCL6 allele than in WT controls (Figure 8C and 8D). However, on the Ccnd3−/− background, spontaneous GC formation remained at a WT-like, negligible level despite the presence of the Iμ-HA-BCL6 allele. A similar, albeit milder, trend was also observed with respect to the size of the GCs in that Iμ-HA-BCL6 doubled the average GC size (2.03 vs 1.04 × 104 μm2, P = 0.07), an effect that was completely abrogated by cyclin D3-deficiency (Figure 8E). These results indicate that cyclin D3 functions downstream of BCL6 during GC development in vivo.
Cyclin D3 works downstream of Bcl6 in GC development. (A) Cross-sections of mouse spleens 14 days after SRBC immunization were stained with antibodies against Bcl6. Scale bars are 100 μm. (B) The GCB-like DLBCL cell line SuDHL6 was treated with either a control (ctrl) or two different cyclin D3 siRNA oligos (#1 and #2). At the indicated times after transfection, expression of the endogenous BCL6 and cyclin D3 proteins were analyzed by western blotting. GDI was used as a loading control. Similar results were obtained from two other GCB-like DLBCL lines Ly7 and Val (not shown). (C-E) The Ccnd3−/− mice were bred to mice carrying the Iμ-HA-BCL6 knock-in allele. Spontaneous GC formation in spleens of unimmunized mice was examined by PNA staining and quantified as in Figure 3. (C) Representative PNA-stained spleen sections from each indicated genotype are shown. Scale bars are 1 mm. (D) The frequency of GC initiation is plotted as the number of GCs per mm2. Error bars are SEM. (E) The column scattered plot shows the size of GCs in each animal. Each column corresponds to an individual mouse; each point is an individual GC. All significant P values based on two-tailed Student t tests are shown above the graphs. There was no significant difference between the WT and the Iμ-HA-BCL6 Ccnd3−/− groups either in GC number or size.
Discussion
As part of our effort to understand how the cell cycle is regulated in GC B cells, we have characterized mature B cell development and the GC response in cyclin D3 KO mice. We found that cyclin D3 deficiency caused a notable expansion of MZ B cells, but only a slight reduction in the pool of Fo B cells. In terms of cell proliferation and immunological functions, the requirement for cyclin D3 is also very different between Fo and GC B cells. While cyclin D3 is largely dispensable for proliferation and CSR of in vitro stimulated Fo B cells, GC formation and function were notably impaired in the cyclin D3 KO mice because a significant fraction of the GC B cells exist in quiescent state. Lastly, genetic analysis revealed that cyclin D3 controls a step downstream of BCL6 in GC formation.
Our observations point to stage- and context-dependent requirements for different D-type cyclin molecules. When naïve B cells were stimulated in vitro by LPS or LPS/IL-4, cyclin D2 and cyclin D3 were both upregulated with the same kinetics as cells entered G1 phase of the cell cycle. However, D3 ablation caused only minor changes in Cdk4/6 activity based on phospho-Rb (Ser807/811) and G1-S transition (Figures 5A, 5B, and 7A). Because the level of cyclin D2 was elevated in Ccnd3−/− cells, it is possible that both cyclin D2 and D3 normally participate in Cdk4/6 activation but the lost cyclin D3 function was compensated for by the increased supply of cyclin D2 (Figure 7A). The notion that cyclin D2 and D3 are functionally interchangeable in LPS-stimulated B cell is also supported by a prior study 32. Lam et al. reported that in LPS-stimulated Ccnd2−/− B cells, cyclin D3 alone was sufficient to promote cell cycle progression. Functional compensation between cyclin D2 and D3 can also be observed when only one cyclin molecule is normally expressed. For example, WT native B cells stimulated by anti-IgM or CD40L use only cyclin D2 to drive the cell cycle. However, in Ccnd2−/− B cells, cyclin D3 can be induced belatedly and can support cell proliferation once it is expressed 32. Similarly, although WT B-1a cells only use cyclin D3, Ccnd3−/− B-1a cells proliferate normally due to ectopic activation of cyclin D2 21.
In contrast to these examples of redundancy, there are specific stages in lymphocyte development where cyclin D3 clearly plays a unique role. In T cell leukemias driven by the pre-TCR-p56Lck pathway, the oncogenic activity of cyclin D3 was not fulfilled by cyclin D2 13. Similarly, the requirement for cyclin D3 at the transition step from pro-B to pre-B can only be partially compensated by cyclin D2 14. The results from the current study demonstrate that when GC B cells were deprived of cyclin D3, cell cycle and GC functions were significantly impaired even with 5-fold overexpression of cyclin D2 mRNA, which is not normally expressed in either human or mouse GCs 17, 33. If cyclin D2 protein was indeed elevated following its mRNA increase, this ectopically expressed cyclin D2 may have been responsible for the continued cell cycle progression of proliferating Ccnd3−/− GC B cells (Figure 5). On the other hand, the dramatically increased frequency of Ki67− quiescent B cells in the Ccnd3−/− GCs indicates that although cyclin D3 is dispensable for cell cycle progression, it plays a unique and non-redundant role either by keeping proliferating GC B cells within cell cycle or by enabling periodic cell cycle re-entry in response to mitogenic signals. In this regard, it is worth noting that embryonic fibroblasts lacking all three D-type cyclins proliferated normally but displayed enhanced requirement for mitogenic signals during cell cycle re-entry 12. Another interesting observation made in this study is that cyclin D3 inactivation had a greater impact on switched IgM− B cells compared to unswitched IgM+ B cells (Figure 6B). Because BrdU incorporation was similarly affected in these two compartments (Figure 6E and 6F), our data suggest that CSR was reduced in Ccnd3−/− GCs. As CSR is coupled to cell division numbers and SHM preferentially targets post-switched cells 2, 34, it is possible that most if not all of the in vivo CSR and SHM defects were secondary to the cell cycle abnormality caused by cyclin D3 deficiency. Although our IHC study indicates that most brightly stained cyclin D3+ B cells were in the non-FDC zone occupied by post-switched cells, the FDC zone did contain cyclin D3+ B cells. With this in mind, the reduction in BrdU incorporation within both IgM+ and IgM− compartments indicates that cyclin D3 controls proliferation of both switched and as-yet-unswitched GC B cells. This study did not directly evaluate the recall response of memory B cells. However, as the amplitude and affinity of the anti-NP response in Ccnd3−/− animals improved markedly with boosting immunizations (Figure 4C-4E), and because reactivated memory B cells in vivo do not transit through GC to become plasma cells 35, 36, our data are most consistent with the interpretation that some memory B cells were generated in the absence of cyclin D3 and that their subsequent activation and differentiation during the recall response were less dependent on cyclin D3 compared to the primary response.
In knock-out mouse models engineered to inactivate individual members of the same gene family, phenotypic differences are often observed and always invite two competing explanations: unique biochemical properties versus differences in spatial-temporal expression patterns of the family members. In general, mice deficient for only one D-type cyclin are viable with only subtle defects affecting selected cell lineages in the adult animals 37. Surprisingly, mice lacking two or even all three D-type cyclins do not exhibit an overt defect in the core cell cycle program, although they succumb to various developmental abnormalities in specific organ systems 12, 38. This suggests that when it comes to the G1 cyclin/Cdk functions, there is sufficient redundancy in the core cell cycle engine to compensate for the loss of individual D-type cyclins or all three of them. Therefore, the observed lineage-specific defects in cyclin D knock-out animals must be attributed either to lineage/stage-specific expression of the cyclin D molecules or to cell-cycle independent properties where the three cyclin D molecules are known to differ 37, 39. Among the three D-type cyclins, cyclin D1 attracted the earliest attention to its function as a transcription cofactor 40. Increasing evidence also points to a similar role for cyclin D3. For example, cyclin D3 can suppress trans-activation function of AML1 by competing with CBFβ for AML1 binding 41. Cyclin D3 can also attenuate androgen receptor activity by modulating its ligand-dependent conformation and chromatin binding activities 42. We have shown in this work that during the GC response, cyclin D3 is dispensable for Bcl6 upregulation and maintenance yet is strictly required for the ability of overexpressed Bcl6 to promote spontaneous GC formation (Figure 8). As Bcl6 is a sequence-specific transcription repressor, it will be interesting to determine in future studies whether cyclin D3 has cell cycle-independent roles within the GC context and how it functions downstream of Bcl6 to regulate GC formation and function.
Both B and T cells that participate in the GC response require the transcription factor Bcl6. The T cell dependence on Bcl6 was revealed by three recent studies with the demonstration that Bcl6 is both necessary and sufficient to drive the lineage specification of Tfh cells 43, 44, 45. This raises a question as to whether the cyclin D3 requirement in GC response resides with GC B cells or with Tfh cells. Our IHC study suggests that in both human and mouse, the cyclin D3 expressing cells within the GC bear B cell surface markers (Figure 1C and 1H). We did not detect cyclin D3 in CD3+ T cells within the GC (Figure 1E and 1J). Furthermore, the Iμ-HA-BCL6 allele is specifically expressed in B cells. Thus, in the experiments shown in Figure 7C-7E, the genetic interaction between cyclin D3 and Bcl6 took place primarily within the B cell context.
Our work also supports the notion that upregulation of cyclin D3 in B cell development coincides with a shift in the mode of cell proliferation control and is subject to complex regulation. Unlike the cyclins that operate in later G1 and other phases of the cell cycle whose levels oscillate with the cell cycle phases, D-type cyclins are activated by extracellular mitogenic signals, and their levels and activity do not rise and fall in a cyclic fashion. At the moment, the nature of the stimuli that initiate and maintain proliferation of GC B cells is poorly defined, as is the precise signaling requirement for the cyclin D2 to D3 shift. More specifically, in WT GC B cells, silencing of cyclin D2 is likely the direct consequence of Bcl6 upregulation because cyclin D2 is a Bcl6 target gene 20 yet the signals required for cyclin D3 upregulation remain obscure. Signals transduced through the B cell receptor and CD40 are well known to participate in the GC reaction, but they only upregulate cyclin D2 and not D3 in naïve B cells 32. IL-21 is another Tfh-derived factor required for GC development, but as a single agent, it is incapable of activating cyclin D3 in cultured naïve B cells (result not shown). Meanwhile, although LPS can induce both cyclin D2 and D3, B cell-intrinsic Toll-like receptors can amplify but are not required for the GC response 46. It is possible that upregulation of cyclin D3 has a complex cell signaling requirement which incorporates both T cell help and appropriate BCR signals, and that the regulation may happen at both the transcription and post-transcription levels 14. Studying cyclin D3 regulation in pre-B cells, Mandal et al. reported that pre-BCR-mediated Ras-MEK-Erk activation can silence cyclin D3 expression leading to cell cycle exit and initiation of IgΚ recombination 47. Within the GC microenvironment, the Ras-MEK-Erk cascade can be activated when B cells encounter antigen signals presented by FDCs in the light zone. Our observation that cyclin D3 expression is highest in the dark (non-FDC) zone is consistent with the idea that this signaling pathway may also function to shut off cyclin D3 in activated centrocytes, which may be subject to positive/negative section based on their BCR affinity. A better understanding of the mechanisms controlling cyclin D3 expression should facilitate the elucidation of GC initiation and termination processes, long-standing quests in the field of B cell immunology.
In summary, characterization of the cyclin D3 KO mice reveals that this cyclin D molecule is largely dispensable for B cell proliferation and CSR in vitro but is critically required for cell cycle regulation and in vivo functions of GC B cells. Our observations not only establish an essential role for cyclin D3 during GC response, but they also highlight the differences between GC-associated and in vitro B cell proliferation and expand our appreciation for the cell type- and tissue-specific functions of the D-type cyclin molecules.
Materials and Methods
Mice and tonsils
Human tonsils were obtained as discarded material from routine tonsillectomies with approval of the Institutional Review Boards of AECOM and Montefiore Medical Center in accordance with Helsinki protocols. Ccnd3−/− mice 13 and the Iμ-HA-BCL6 mice 31 were described previously and were housed in the AECOM barrier facility. For histology, mice were injected i.p. with 2 × 108 SRBC (Colorado Serum Co.) in PBS on days 0 and 8; spleens were harvested on day 14. For cell cycle and gene expression, spleens were harvested 10-11 days after the first immunization. IHC was performed following previously described procedure 48 with the antibodies and conditions summarized in Supplementary information, Table S1.
NP immunization and ELISA
10-12-week-old mice were immunized with NP-KLH as previously described 27, as were ELISA for resting serum Ab and NP-specific Ab response. The immunization and bleeding scheme is illustrated in Supplementary information, Figure S2. Serial dilutions and standard curves were performed to calculate Ab concentrations based on 1/2 Vmax using GraphPad Prism. For statistical analysis, NP-specific Ab titers were log-transformed to obtain normal distributions.
GC size and number
Overlapping images of entire spleen cross sections were reconstructed using “photomerge” (Photoshop CS3). Each GC was measured in ImageJ. The area of the entire cross section was used to determine frequency of GC per mm2.
Flow cytometry and sorting
For B cell subset analysis, splenocytes isolated from WT and cyclin D3 KO mice were stained with fluorochrome-labeled antibodies specific for B220 (RA3-6B2), CD21/CD35 (7G6), CD23 (B3B4), heat-stable Ag (HSA; M1/69) (BD Biosciences) and AA4.1 (eBioscience) at 4 °C for 30 min and then washed with PBS/1% BSA. Five-color flow cytometry was performed using an LSR II instrument (BD Biosciences) and the data were analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star, Inc.). At least 10 000 B cell-gated events were analyzed per mouse. To enumerate GC B cells, a combination of antibodies were used after Fc blocking (BD Biosciences): PNA-FITC (Vector Laboratory), PerCP anti-B220 (RA3-6B2), PE anti-CD95 (Jo2) (BD Biosciences), Cy5-anti-IgM (Jackson ImmunoResearch). For in vivo cell cycle experiments, after surface staining, cells were fixed in 70% EtOH, incubated for ≥ 2 h at −20 °C, washed, and resuspended in 1 μg/ml DAPI, 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS. For in vitro cell cycle experiments, isolated B cells were stimulated as in Supplementary information, Figure S3 and stained with propidium iodide. The Watson algorithm was used to quantify cell cycle fractions in FlowJo software. For BrdU incorporation assays, mice that were SRBC-immunized 14 days before were injected i.p. with 1 mg BrdU. Six hours later, spleens were harvested and 5 million splenocytes were surface-stained with Alexa 700-anti-B220 (RA3-6B2) (BioLegend), PE-anti-CD95, Cy5-anti-IgM, and further processed for permeabilization and staining with Phoenix Green-anti-BrdU (Phoenix Flow systems) according to a previously published method 3. For qRT-PCR experiments, RNA was isolated from GC B cells sorted by a MoFlo instrument directly into Buffer RLT (Qiagen RNeasy Micro) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
siRNA-mediated cyclin D3 knock-down
GCB-like DLBCL cell lines SuDHL6, Ly7 and Val were maintained in IMDM medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Transient transfections were performed with the Nucleofector Kit T and program G16 (Amaxa Biosystems, Gaithersburg, MD). Ten micrograms of siRNA oligos were used in each transfection of 5-10 million cells. Whole cell lysates harvested at indicated time points after transfection were subject to western blot analyses. The two cyclin D3 siRNA oligos are part of the Stealth™ Select 3 RNAi Set from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA): 5′-UGG CCA UGA ACU ACC UGG AUC GCU A-3′ (#1), and 5′-GCU ACA GAU UAU ACC UUU GCC AUG U-3′ (#2). The scrambled control oligos were also synthesized by Invitrogen.
Western blot and qRT-PCR
Splenic B cells were isolated and stimulated as described 49. Western blots and qRT-PCR were performed as described 50 except that cDNA from GC B cells was synthesized using iScript (BioRad). Primer sequences are provided in Supplementary information, Table S2.
Statistical analysis
Unpaired two-tailed Student t-tests and Wilcoxon ranked sum tests were used where appropriate. For GC size, in vitro CSR, and serum NP response, experimental replicates performed at different times yielded variation among control animals, likely due to different batches of stimulants. In these cases, P-values were obtained using SAS by fitting a linear mixed effects model with fixed effects for genotype and experiment date and a random mouse effect to account for correlation in replicate measurements from the same mouse. The SAS analyses were performed by the Einstein Biostatistics Shared Resource core.
Online Supplementary Material
Supplementary information, Table S1 contains information on the antibodies used in the IHC and western blot analyses. Supplementary information, Table S2 lists sequences of the qRT-PCR primers. Supplementary information, Figure S1 demonstrates that the specificity of the cyclin D3 antibody used in the IHC study and that the spleen architecture is largely unaffected by cyclin D3 deficiency. Supplementary information, Figure S2 illustrates the NP-KLH immunization and animal bleeding schedule. Supplementary information, Figure S3 shows that cyclin D3 deficiency caused a moderate reduction in CSR to IgG1 but no effect on CSR to IgG3 in vitro.
Abbreviations
- CSR:
-
(class switch recombination)
- Cdk:
-
(cyclin dependent kinase)
- DAPI:
-
(diamidino-2-phenylindole)
- DLBCL:
-
(diffuse large B cell lymphoma)
- DN:
-
(double negative)
- FDC:
-
(follicular dendritic cell)
- Fo:
-
(follicular B cells)
- GC:
-
(germinal center)
- IHC:
-
(immunohistochemistry)
- KO:
-
(knock-out)
- LN:
-
(lymph node)
- MZ:
-
(marginal zone)
- NP:
-
(nitrophenyl)
- PNA:
-
(peanut agglutinin)
- PI:
-
(propidium iodide)
- SHM:
-
(somatic hypermutation)
- Tfh:
-
(T follicular helper cells)
References
Stavnezer J, Guikema JE, Schrader CE . Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination. Annu Rev Immunol 2008; 26:261–292.
Peled JU, Kuang FL, Iglesias-Ussel MD, et al. The biochemistry of somatic hypermutation. Annu Rev Immunol 2008; 26:481–511.
Wang Y, Carter RH . CD19 regulates B cell maturation, proliferation, and positive selection in the FDC zone of murine splenic germinal centers. Immunity 2005; 22:749–761.
Allen CD, Okada T, Cyster JG . Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity 2007; 27:190–202.
Klein U, Dalla-Favera R . Germinal centres: role in B-cell physiology and malignancy. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8:22–33.
Shaffer AL, Rosenwald A, Hurt EM, et al. Signatures of the immune response. Immunity 2001; 15:375–385.
Ci W, Polo JM, Cerchietti L, et al. The BCL6 transcriptional program features repression of multiple oncogenes in primary B-cells and is deregulated in DLBCL. Blood 2009; 113:5536–5548.
Yu RY, Wang X, Pixley FJ, et al. BCL-6 negatively regulates macrophage proliferation by suppressing autocrine IL-6 production. Blood 2005; 105:1777–1784.
Tourigny MR, Ursini-Siegel J, Lee H, et al. CDK inhibitor p18 (INK4c) is required for the generation of functional plasma cells. Immunity 2002; 17:179–189.
Massague J . G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature 2004; 432:298–306.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 1999; 13:1501–1512.
Kozar K, Ciemerych MA, Rebel VI, et al. Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-Cyclins. Cell 2004; 118:477–491.
Sicinska E, Aifantis I, Le Cam L, et al. Requirement for cyclin D3 in lymphocyte development and T cell leukemias. Cancer Cell 2003; 4:451–461.
Cooper AB, Sawai CM, Sicinska E, et al. A unique function for cyclin D3 in early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2006; 7:489–497.
Sonoki T, Harder L, Horsman DE, et al. Cyclin D3 is a target gene of t(6;14)(p21.1;q32.3) of mature B-cell malignancies. Blood 2001; 98:2837–2844.
Filipits M, Jaeger U, Pohl G, et al. Cyclin D3 is a predictive and prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8:729–733.
Hogerkorp CM, Borrebaeck CA . The human CD77- B cell population represents a heterogeneous subset of cells comprising centroblasts, centrocytes, and plasmablasts, prompting phenotypical revision. J Immunol 2006; 177:4341–4349.
Doglioni C, Chiarelli C, Macri E, et al. Cyclin D3 expression in normal, reactive and neoplastic tissues. J Pathol 1998; 185:159–166.
Teramoto N, Pokrovskaja K, Szekely L, et al. Expression of cyclin D2 and D3 in lymphoid lesions. Int J Cancer 1999; 81:543–550.
Shaffer AL, Yu X, He Y, et al. BCL-6 represses genes that function in lymphocyte differentiation, inflammation, and cell cycle control. Immunity 2000; 13:199–212.
Mataraza JM, Tumang JR, Gumina MR, et al. Disruption of cyclin D3 blocks proliferation of normal B-1a cells, but loss of cyclin D3 is compensated by cyclin D2 in cyclin D3-deficient mice. J Immunol 2006; 177:787–795.
Wen L, Brill-Dashoff J, Shinton SA, et al. Evidence of marginal-zone B cell-positive selection in spleen. Immunity 2005; 23:297–308.
Casola S, Otipoby KL, Alimzhanov M, et al. B cell receptor signal strength determines B cell fate. Nat Immunol 2004; 5:317–327.
Takahashi Y, Dutta PR, Cerasoli DM, Kelsoe G . In situ studies of the primary immune response to (4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrophenyl)Acetyl. V. affinity maturation develops in two stages of clonal selection. J Exp Med 1998; 187:885–895.
Wang Y, Brooks SR, Li X, et al. The physiologic role of CD19 cytoplasmic tyrosines. Immunity 2002; 17:501–514.
Lam EWF, Glassford J, Banerji L, et al. Cyclin D3 compensates for loss of cyclin D2 in mouse B-lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor and CD40. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:3479–3484.
Ye BH, Cattoretti G, Shen Q, et al. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2- type inflammation. Nat Genet 1997; 16:161–170.
Dent AL, Shaffer AL, Yu X, Allman D, Staudt LM . Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science 1997; 276:589–592.
Cattoretti G, Chang CC, Cechova K, et al. BCL-6 protein is expressed in germinal-center B cells. Blood 1995; 86:45–53.
Kuppers R, Klein U, Schwering I, et al. Identification of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cell-specific genes by gene expression profiling. J Clin Invest 2003; 111:529–537.
Cattoretti G, Pasqualucci L, Ballon G, et al. Deregulated BCL6 expression recapitulates the pathogenesis of human diffuse large B cell lymphomas in mice. Cancer Cell 2005; 7:445–455.
Lam EW, Glassford J, Banerji L, et al. Cyclin D3 compensates for loss of cyclin D2 in mouse B-lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor and CD40. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:3479–3484.
Luckey CJ, Bhattacharya D, Goldrath AW, et al. Memory T and memory B cells share a transcriptional program of self-renewal with long-term hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103:3304–3309.
Tangye SG, Hodgkin PD . Divide and conquer: the importance of cell division in regulating B-cell responses. Immunology 2004; 112:509–520.
Toellner KM, Gulbranson-Judge A, Taylor DR, Sze DM, MacLennan IC . Immunoglobulin switch transcript production in vivo related to the site and time of antigen-specific B cell activation. J Exp Med 1996; 183:2303–2312.
Benson MJ, Elgueta R, Schpero W, et al. Distinction of the memory B cell response to cognate antigen versus bystander inflammatory signals. J Exp Med 2009; 206:2013–2025.
Satyanarayana A, Kaldis P . Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene 2009; 28:2925–2939.
Kozar K, Sicinski P . Cell cycle progression without cyclin D-CDK4 and cyclin D-CDK6 complexes. Cell Cycle 2005; 4:388–391.
Mullany LK, White P, Hanse EA,et al. Distinct proliferative and transcriptional effects of the D-type cyclins in vivo. Cell Cycle 2008; 7:2215–2224.
Lamb J, Ramaswamy S, Ford HL, et al. A mechanism of cyclin D1 action encoded in the patterns of gene expression in human cancer. Cell 2003; 114:323–334.
Peterson LF, Boyapati A, Ranganathan V,et al. The hematopoietic transcription factor AML1 (RUNX1) is negatively regulated by the cell cycle protein cyclin D3. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25:10205–10219.
Olshavsky NA, Groh EM, Comstock CE, et al. Cyclin D3 action in androgen receptor regulation and prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008; 27:3111–3121.
Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, Ditoro D,et al. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science 2009; 325:1006–1010.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Martinez GJ, et al. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science 2009; 325:1001–1005.
Yu D, Rao S, Tsai LM, et al. The Transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity 2009; 31:457–468.
Meyer-Bahlburg A, Khim S, Rawlings DJ . B cell intrinsic TLR signals amplify but are not required for humoral immunity. J Exp Med 2007; 204:3095–3101.
Mandal M, Powers SE, Ochiai K, et al. Ras orchestrates exit from the cell cycle and light-chain recombination during early B cell development. Nat Immunol 2009; 10:1110–1117.
Cattoretti G, Shaknovich R, Smith PM, et al. Stages of germinal center transit are defined by B cell transcription factor coexpression and relative abundance. J Immunol 2006; 177:6930–6939.
Bardwell PD, Woo CJ, Wei K, et al. Altered somatic hypermutation and reduced class-switch recombination in exonuclease 1-mutant mice. Nat Immunol 2004; 5:224–229.
Mendez LM, Polo JM, Yu JJ, et al. CtBP is an essential corepressor for BCL6 autoregulation. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28:2175–2186.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Riccardo Dalla-Favera (Columbia University, USA) for sharing the Iμ-HA-BCL6 mouse strain, Drs Ulf Klein (Columbia University, USA) and Liang Zhu (Albert Einstein College of Medicine (AECOM), USA) for insightful suggestions, Dr Mimi Kim (AECOM) for expert statistical analysis, Drs Sergio Roa, Lydia Zhao and Susan Buhl (AECOM), and Lucas Tsikitas (Weill Cornell College of Medicine, USA) for their invaluable technical support. We are also indebted to Drs Arthur Skoultchi, Liang Zhu and Ganjam Kalpana (AECOM) for reagents. The AECOM Flow Cytometry Facility and Histopathology Facility are gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported by the Medical Scientist Training Program T32GM007288 (J.U.P.) and grants from the National Institutes of Health R01 CA85573 (B.H.Y), R01 CA72649 and CA102705 (M.D.S.), K08 CA127353 (R.S.), R01 AR049126 and AI051392 (B.D.), and P01 CA109901 (P.S). Support also came from the Harry Eagle Chair provided by the National Women's Division to M.D.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
(Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary information
Figure S1
Histological validation of Cyclin D3 antibody and characterization of B cell splenic architecture in KO animals. (PDF 138 kb)
Figure S2
Schematic illustration of the immunization and bleeding schedule used to elicit T-cell dependent anti-NP response in Figure 4. (PDF 86 kb)
Figure S3
Class Switch Recombination to IgG1 is moderately impaired in the absence of cyclin D3. (PDF 26 kb)
Table S1
Antibodies used for IHC and Western Blot analyses. (PDF 52 kb)
Table S2
Sequences of qRT-PCR primers. (PDF 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peled, J., Yu, J., Venkatesh, J. et al. Requirement for cyclin D3 in germinal center formation and function. Cell Res 20, 631–646 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.55
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.55
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Immunomodulation by anticancer cell cycle inhibitors
Nature Reviews Immunology (2020)
-
TLR7, a third signal for the robust generation of spontaneous germinal center B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Flip the switch: BTG2–PRMT1 protein complexes antagonize pre-B-cell proliferation to promote B-cell development
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Paradoxical role of Id proteins in regulating tumorigenic potential of lymphoid cells
Frontiers of Medicine (2018)
-
Activation of TLR7 increases CCND3 expression via the downregulation of miR-15b in B cells of systemic lupus erythematosus
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2016)