The September 2015 issue of Nature Neuroscience celebrates the 10th anniversary of channelrhodopsin-2 in neurons and features articles from the first and senior authors of the original paper along with a Q&A where a number of scientists reflect on the impact of optogenetics.
The September 2015 issue of Nature Neuroscience celebrates the 10th anniversary of channelrhodopsin-2 in neurons and features articles from the first and senior authors of the original paper along with a Q&A where a number of scientists reflect on the impact of optogenetics.
ORIGINAL PAPER
Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity
Edward S Boyden, Feng Zhang, Ernst Bamberg, Georg Nagel & Karl Deisseroth
Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/nn1525
The original Technical Report from the September 2005 issue of Nature Neuroscience.
Full Text | PDF
EDITORIAL

ChR2 coming of age
Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/nn.4103
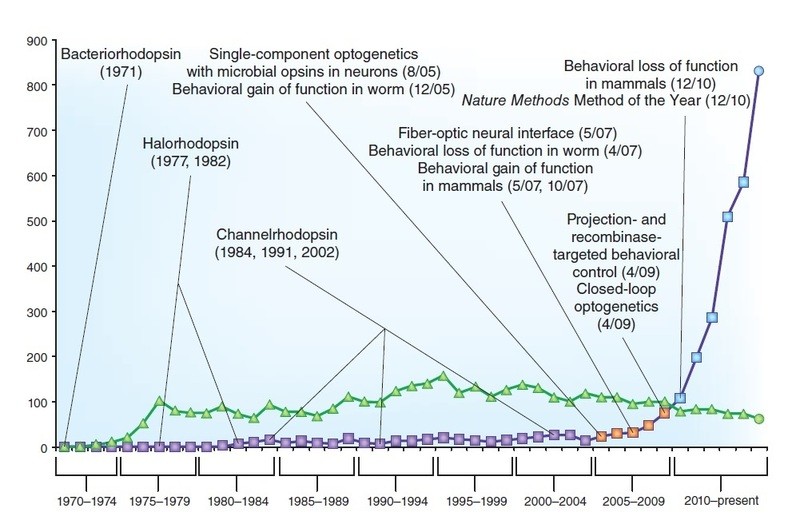
10 years ago, channelrhodopsin-2 was expressed in neurons and shown to control their activity. Nature Neuroscience considers how the field has developed since these early optogenetic experiments.
Full Text | PDF
OVERVIEW

Optogenetics and the future of neuroscience
Edward S Boyden
Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/nn.4094
Over ten years, optogenetics has become widespread. In this Overview, Ed Boyden argues that the full impact of optogenetics will emerge only when other toolsets mature and discusses how optogenetics has galvanized interest in neurotechnology development.
Full Text | PDF
Q & A

Optogenetics: 10 years after ChR2 in neurons—views from the community
Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/nn.4106
The tight spatio-temporal control of neuronal activity in genetically defined populations of neurons has been a long-standing goal in neuroscience. Nature Neuroscience invited the community to reflect on the state of the field and how optogenetics has affected their work. In this Q&A, 34 scientists share their thoughts.
Full Text | PDF
HISTORICAL COMMENTARY

Optogenetics: 10 years of microbial opsins in neuroscience
Karl Deisseroth
Nature Neuroscience, doi:10.1038/nn.4091
Modern optogenetics emerged from converging developments in microbial opsin engineering, genetic methods for targeting, and optical strategies for light delivery. In this Historical Commentary, Karl Deisseroth reflects on the optogenetic landscape.
Full Text | PDF