Abstract
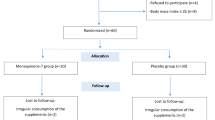
Anemia and immunological dysfunction (i.e. immunosenescence) are commonly found in older subjects and nutritional approaches are sought to counteract these phenomena. Spirulina is a filamentous and multicellular bule-green alga capable of reducing inflammation and also manifesting antioxidant effects. We hypothesized that Spirulina may ameliorate anemia and immunosenescence in senior citizens with a history of anemia. We enrolled 40 volunteers of both sexes with an age of 50 years or older who had no history of major chronic diseases. Participants took a Spirulina supplementation for 12 weeks and were administered comprehensive dietary questionnaires to determine their nutritional regimen during the study. Complete cell count (CCC) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) enzyme activity, as a sign of immune function, were determined at baseline and weeks 6 and 12 of supplementation. Thirty study participants completed the entire study and the data obtained were analyzed. Over the 12-week study period, there was a steady increase in average values of mean corpuscular hemoglobin in subjects of both sexes. In addition, mean corpuscular volume and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration also increased in male participants. Older women appeared to benefit more rapidly from Spirulina supplements. Similarly, the majority of subjects manifested increased IDO activity and white blood cell count at 6 and 12 weeks of Spirulina supplementation. Spirulina may ameliorate anemia and immunosenescence in older subjects. We encourage large human studies to determine whether this safe supplement could prove beneficial in randomized clinical trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weng NP . Aging of the immune system: how much can the adaptive immune system adapt? Immunity 2006; 24: 495–499.
Larbi A, Franceschi C, Mazzatti D, Solana R, Wikby A, Pawelec G . Aging of the immune system as a prognostic factor for human longevity. Physiology 2008; 23: 64–74.
Weinberger B, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Schwanninger A, Weiskopf D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B . Vaccines: biology of immune responses to vaccines in elderly persons. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1078–1084.
Targonski PV, Jacobson RM, Poland GA . Immunosenescence: role and measurement in influenza vaccine response among the elderly. Vaccine 2007; 25: 3066–3069.
McElhaney JE, Xie D, Hager WD, Barry MB, Wang Y, Kleppinger A et al. T cell responses are better correlates of vaccine protection in the elderly. J Immunol 2006; 176: 6333–6339.
Gnann JW Jr, Vaccination to prevent herpes zoster in older adults. J Pain 2008; 9: S31–S36.
Long BR, Michaelsson J, Loo CP, Ballan WM, Vu BA, Hecht FM et al. Elevated frequency of gamma interferon-producing NK cells in healthy adults vaccinated against influenza virus. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2008; 15: 120–130.
Carmel R . Nutritional anemias and the elderly. Semin Hematol 2008; 45: 225–234.
Thomas DR . Anemia: it's all about quality of life. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2007; 8: 80–82.
Clavel T, Haller D . Molecular interactions between bacteria, the epithelium, and the mucosal immune system in the intestinal tract: implications for chronic inflammation. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol 2007; 8: 25–43.
Mehandru S, Dandekar S . Role of the gastrointestinal tract in establishing infection in primates and humans. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 2008; 3: 22–27.
Wershil BK, Furuta GT . Gastrointestinal mucosal immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 121: S380–S383.
Abrahamson DR, Powers A, Rodewald R . Intestinal absorption of immune complexes by neonatal rats: a route of antigen transfer from mother to young. Science 1979; 206: 567–569.
Beutler B . Innate immunity: an overview. Mol Immunol 2004; 40: 845–859.
Khan Z, Bhadouria P, Bisen PS . Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2005; 6: 373–379.
Mao TK, van de Water J, Gershwin ME . Effects of a Spirulina-based dietary supplement on cytokine production from allergic rhinitis patients. J Med Food 2005; 8: 27–30.
Cingi C, Conk-Dalay M, Cakli H, Bal C . The effects of Spirulina on allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2008; 65: 1219–1223.
Pertovaara AR, Lehtimaki T, Karhunen PJ, Oja SS, Jylha M, Hervonen A et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in nonagenarians is markedly increased and predicts mortality. Mech Ageing Dev 2006; 127: 497–499.
Boeckner LS, Pullen CH, Walker SN, Abbott GW, Block T . Use and reliability of the world wide web version of the block health habits and history questionnaire with older rural women. J Nutr Educ Behav 2002; 34: S20–S24.
Boucher B, Cotterchio M, Kreiger N, Nadalin V, Block T, Block G . Validity and reliability of the Block98 food-frequency questionnaire in a sample of Canadian women. Public Health Nutr 2006; 9: 84–93.
Laich A, Neurauter G, Widner B, Fuchs D . More rapid method for simultaneous measurement of tryptophan and kynurenine by HPLC. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 579–581.
Pertovaara M, Hasan T, Raitala A, Oja SS, Yli-Kerttula U, Korpela M et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity is increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and predicts disease activation in the sunny season. Clin Exp Immunol 2007; 150: 274–278.
Widner B, Werner ER, Schennach H, Fuchs D . An HPLC method to determine tryptophan and kynurenine in serum simultaneously. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999; 467: 827–832.
Spence RK . Medical and economic impact of anemia in hospitalized patients. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2007; 64: S3–S10.
Gaskell H, Derry S, Andrew Moore R, McQuay HJ . Prevalence of anaemia in older persons: systematic review. BMC Geriatr 2008; 8: 1.
Bross MH, Soch K, Smith-Knuppel T . Anemia in older persons. Am Fam Physician 2010; 82: 480–487.
Ciferri O . Spirulina, the edible microorganism. Microbiol Rev 1983; 47: 551–578.
Farrar WV . Tecuitlatl: a glimpse of Aztec food technology. Nature 1966; 211: 341–342.
Cheong SH, Kim MY, Sok DE, Hwang SY, Kim JH, Kim HR et al. Spirulina prevents atherosclerosis by reducing hypercholesterolemia in rabbits fed a high-cholesterol diet. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 2010; 56: 34–40.
Torres-Duran PV, Miranda-Zamora R, Paredes-Carbajal MC, Mascher D, Diaz-Zagoya JC, Juarez-Oropeza MA . Spirulina maxima prevents induction of fatty liver by carbon tetrachloride in the rat. Biochem Mol Biol Int 1998; 44: 787–793.
Vadiraja BB, Gaikwad NW, Madyastha KM . Hepatoprotective effect of C-phycocyanin: protection for carbon tetrachloride and R-(+)-pulegone-mediated hepatotoxicty in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998; 249: 428–431.
Bhat VB, Madyastha KM . C-phycocyanin: a potent peroxyl radical scavenger in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 275: 20–25.
Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Ble-Castillo JL, Juarez-Oropeza MA, Diaz-Zagoya JC . Spirulina maxima prevents fatty liver formation in CD-1 male and female mice with experimental diabetes. Life Sci 2001; 69: 1029–1037.
Parikh P, Mani U, Iyer U . Role of Spirulina in the control of glycemia and lipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Food 2001; 4: 193–199.
Ble-Castillo JL, Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Miranda-Zamora R, Juarez-Oropeza MA, Diaz-Zagoya JC . Arthrospira maxima prevents the acute fatty liver induced by the administration of simvastatin, ethanol and a hypercholesterolemic diet to mice. Life Sci 2002; 70: 2665–2673.
Torres-Duran PV, Ferreira-Hermosillo A, Juarez-Oropeza MA . Antihyperlipemic and antihypertensive effects of Spirulina maxima in an open sample of Mexican population: a preliminary report. Lipids Health Dis 2007; 6: 33.
Forouzandeh F, Jalili RB, Germain M, Duronio V, Ghahary A . Differential immunosuppressive effect of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) on primary human CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2008; 309: 1–7.
Widner B, Ledochowski M, Fuchs D . Interferon-gamma-induced tryptophan degradation: neuropsychiatric and immunological consequences. Curr Drug Metab 2000; 1: 193–204.
Oertelt-Prigione S, Mao TK, Selmi C, Tsuneyama K, Ansari AA, Coppel RL et al. Impaired indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase production contributes to the development of autoimmunity in primary biliary cirrhosis. Autoimmunity 2008; 41: 92–99.
Howells DW, Hyland K, Smith I, Strobel S . Tryptophan and serotonin metabolism in familial erythrophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Inherit Metab Dis 1992; 15: 891–897.
Gregg R, Smith CM, Clark FJ, Dunnion D, Khan N, Chakraverty R et al. The number of human peripheral blood CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells increases with age. Clin Exp Immunol 2005; 140: 540–546.
Qi L . Mendelian randomization in nutritional epidemiology. Nutr Rev 2009; 67: 439–450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selmi, C., Leung, P., Fischer, L. et al. The effects of Spirulina on anemia and immune function in senior citizens. Cell Mol Immunol 8, 248–254 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.76
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.76
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Spirulina in fish immunity development: find the black box
Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries (2024)
-
Dietary exposure to trace elements (B, Ba, Li, Ni, Sr, and V) and toxic metals (Al, Cd, and Pb) from the consumption of commercial preparations of Spirulina platensis
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
Spirulina supplementation improves oxygen uptake in arm cycling exercise
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2020)
-
The potential of future foods for sustainable and healthy diets
Nature Sustainability (2018)
-
Effects of Spirulina platensis on DNA damage and chromosomal aberration against cadmium chloride-induced genotoxicity in rats
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2018)