Abstract
Hepatitis C imposes a significant burden on global healthcare. Chronic infection is associated with progressive inflammation of the liver which typically manifests in cirrhosis, organ failure and cancer. By virtue of elaborate evasion strategies, hepatitis C virus (HCV) succeeds as a persistent human virus. It has an extraordinary capacity to subvert the immune response enabling it to establish chronic infections and associated liver disease. Chemokines are low molecular weight chemotactic peptides that mediate the recruitment of inflammatory cells into tissues and back into the lymphatics and peripheral blood. Thus, they are central to the temporal and spatial distribution of effector and regulatory immune cells. The interactions between chemokines and their cognate receptors help shape the immune response and therefore, have a major influence on the outcome of infection. However, chemokines represent a target for modulation by viruses including the HCV. HCV is known to modulate chemokine expression in vitro and may therefore enable its survival by subverting the immune response in vivo through altered leukocyte chemotaxis resulting in impaired viral clearance and the establishment of chronic low-grade inflammation. In this review, the roles of chemokines in acute and chronic HCV infection are described with a particular emphasis placed on chemokine modulation as a means of immune subversion. We provide an in depth discussion of the part played by chemokines in mediating hepatic fibrosis while addressing the potential applications for these chemoattractants in prognostic medicine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lavanchy D . Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17: 107–115.
Shepard CW, Finelli L, Alter MJ . Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis 2005; 5: 558–567.
Brown RS . Hepatitis C and liver transplantation. Nature 2005; 436: 973–978.
Pickett BE, Striker R, Lefkowitz EJ . Evidence for separation of HCV subtype 1a into two distinct clades. J Viral Hepat 2011; 18: 608–618.
Poynard T, Yuen MF, Ratziu V, Lai CL . Viral hepatitis C. Lancet 2003; 362: 2095–2100.
Barth H, Liang TJ, Baumert TF . Hepatitis C virus entry: molecular biology and clinical implications. Hepatology 2006; 44: 527–535.
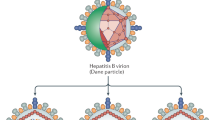
Nielsen SU, Bassendine MF, Martin C, Lowther D, Purcell PJ, King BJ et al. Characterization of hepatitis C RNA-containing particles from human liver by density and size. J Gen Virol 2008; 89( Pt 10): 2507–2517.
Chisari FV . Unscrambling hepatitis C virus–host interactions. Nature 2005; 436: 930–932.
Penin F, Dubuisson J, Rey FA, Moradpour D, Pawlotsky JM . Structural biology of hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 2004; 39: 5–19.
Nakano T, Lau GM, Sugiyama M, Mizokami M . An updated analysis of hepatitis C virus genotypes and subtypes based on the complete coding region. Liver Int 2012; 32: 339–345.
Moradpour D, Penin F, Rice CM . Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007; 5: 453–463.
Callendret B, Walker C . A siege of hepatitis: immune boost for viral hepatitis. Nat Med 2011; 17: 252–253.
Bowen DG, Walker CM . Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 2005; 436: 946–952.
Vollmar B, Menger MD . The hepatic microcirculation: mechanistic contributions and therapeutic targets in liver injury and repair. Physiol Rev 2009; 89: 1269–1339.
Aird WC . Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res 2007; 100: 174–190.
McCuskey RS . Morphological mechanisms for regulating blood flow through hepatic sinusoids. Liver 2000; 20: 3–7.
Nemeth E, Baird AW, O'Farrelly C . Microanatomy of the liver immune system. Seminars in immunopathology. 2009; 31: 333–343.
Racanelli V, Rehermann B . The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 2006; 43( 2 Suppl 1): S54–S62.
Tiegs G, Lohse AW . Immune tolerance: what is unique about the liver. J Autoimmunity 2010; 34: 1–6.
Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z . Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 2008; 47: 729–736.
Thomson AW, Knolle PA . Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 753–766.
Crispe IN . Liver antigen-presenting cells. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 357–365.
Szabo G, Billiar TR, Machida K, Crispe IN, Seki E . Toll-like receptor signaling in liver diseases. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010; 2010: 971270.
Crispe IN . Hepatic T cells and liver tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 51–62.
Crispe IN . The liver as a lymphoid organ. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 147–163.
Winau F, Hegasy G, Weiskirchen R, Weber S, Cassan C, Sieling PA et al. Ito cells are liver-resident antigen-presenting cells for activating T cell responses. Immunity 2007; 26: 117–129.
Li Z, Diehl AM . Innate immunity in the liver. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2003; 19: 565–571.
Bottcher JP, Knolle PA, Stabenow D . Mechanisms balancing tolerance and immunity in the liver. Dig Dis 2011; 29: 384–390.
Petrovic D, Stamataki Z, Dempsey E, Golden-Mason L, Freeley M, Doherty D et al. Hepatitis C virus targets the T cell secretory machinery as a mechanism of immune evasion. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1846–1853.
Kanto T, Hayashi N . Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection: multifaceted strategies subverting innate and adaptive immunity. Intern Med 2006; 45: 183–191.
Petrovic D, Dempsey E, Doherty DG, Kelleher D, Long A . Hepatitis C virus–T-cell responses and viral escape mutations. Eur J Immunol 2012; 42: 17–26.
Klenerman P, Thimme R . T cell responses in hepatitis C: the good, the bad and the unconventional. Gut 2012; 61: 1226–1234.
Nakamoto N, Cho H, Shaked A, Olthoff K, Valiga ME, Kaminski M et al. Synergistic reversal of intrahepatic HCV-specific CD8 T cell exhaustion by combined PD-1/CTLA-4 blockade. PLoS Pathog 2009; 5: e1000313.
Rehermann B . Hepatitis C virus versus innate and adaptive immune responses: a tale of coevolution and coexistence. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 1745–1754.
Dolganiuc A, Chang S, Kodys K, Mandrekar P, Bakis G, Cormier M et al. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein-induced, monocyte-mediated mechanisms of reduced IFN-alpha and plasmacytoid dendritic cell loss in chronic HCV infection. J Immunol 2006; 177: 6758–6768.
Urbani S, Amadei B, Fisicaro P, Tola D, Orlandini A, Sacchelli L et al. Outcome of acute hepatitis C is related to virus-specific CD4 function and maturation of antiviral memory CD8 responses. Hepatology 2006; 44: 126–139.
Agrati C, Nisii C, Oliva A, D'Offizi G, Montesano C, Pucillo LP et al. Lymphocyte distribution and intrahepatic compartmentalization during HCV infection: a main role for MHC-unrestricted T cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 2002; 50: 307–316.
Spengler U, Nattermann J . Immunopathogenesis in hepatitis C virus cirrhosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 2007; 112: 141–155.
Tripathy AS, Shankarkumar U, Chadha MS, Ghosh K, Arankalle VA . Association of HLA alleles with hepatitis C infection in Maharashtra, western India. Indian J Med Res 2009; 130: 550–555.
Viola A, Luster AD . Chemokines and their receptors: drug targets in immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2008; 48: 171–197.
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O . Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 2000; 12: 121–127.
Kehrl JH . Chemoattractant receptor signaling and the control of lymphocyte migration. Immunol Res 2006; 34: 211–227.
Choi WT, An J . Biology and clinical relevance of chemokines and chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR5 in human diseases. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2011; 236: 637–647.
Mellado M, Rodriguez-Frade JM, Manes S, Martinez AC . Chemokine signaling and functional responses: the role of receptor dimerization and TK pathway activation. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 397–421.
Eberlein J, Nguyen TT, Victorino F, Golden-Mason L, Rosen HR, Homann D . Comprehensive assessment of chemokine expression profiles by flow cytometry. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 907–923.
Allen SJ, Crown SE, Handel TM . Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 787–820.
Fernandez EJ, Lolis E . Structure, function, and inhibition of chemokines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2002; 42: 469–499.
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S . Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 678–689.
Petri B, Bixel MG . Molecular events during leukocyte diapedesis. FEBS J 2006; 273: 4399–4407.
Thelen M, Stein JV . How chemokines invite leukocytes to dance. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 953–959.
Thimme R, Binder M, Bartenschlager R . Failure of innate and adaptive immune responses in controlling hepatitis C virus infection. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2012; 36: 663–683.
Kang W, Shin EC . Clinical implications of chemokines in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Yonsei Med J 2011; 52: 871–878.
Wald O, Weiss ID, Galun E, Peled A . Chemokines in hepatitis C virus infection: pathogenesis, prognosis and therapeutics. Cytokine 2007; 39: 50–62.
Heydtmann M, Adams DH . Chemokines in the immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C infection. Hepatology 2009; 49: 676–688.
Bromley SK, Mempel TR, Luster AD . Orchestrating the orchestrators: chemokines in control of T cell traffic. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 970–980.
Fallahi P, Ferri C, Ferrari SM, Corrado A, Sansonno D, Antonelli A . Cytokines and HCV-related disorders. Clin Dev Immunol 2012; 2012: 468107.
Baker MS, Chen X, Rotramel A, Nelson J, Kaufman DB . Proinflammatory cytokines induce NF-kappaB-dependent/NO-independent chemokine gene expression in MIN6 beta cells. J Surg Res 2003; 110: 295–303.
Capone F, Costantini S, Guerriero E, Calemma R, Napolitano M, Scala S et al. Serum cytokine levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Cytokine Netw 2010; 21: 99–104.
Airoldi I, Ribatti D . Regulation of angiostatic chemokines driven by IL-12 and IL-27 in human tumors. J Leukoc Biol 2011; 90: 875–882.
Costantini S, Capone F, Guerriero E, Marfella R, Sorice A, Maio P et al. Cytokinome profile of patients with type 2 diabetes and/or chronic hepatitis C infection. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e39486.
Coma G, Pena R, Blanco J, Rosell A, Borras FE, Este JA et al. Treatment of monocytes with interleukin (IL)-12 plus IL-18 stimulates survival, differentiation and the production of CXC chemokine ligands (CXCL)8, CXCL9 and CXCL10. Clin Exp Immunol 2006; 145: 535–544.
Amin MA, Mansfield PJ, Pakozdi A, Campbell PL, Ahmed S, Martinez RJ et al. Interleukin-18 induces angiogenic factors in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue fibroblasts via distinct signaling pathways. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 1787–1797.
Murakami M, Hirano T . The pathological and physiological roles of IL-6 amplifier activation. Int J Biol Sci 2012; 8: 1267–1280.
Jacobsen ML, Ronn SG, Bruun C, Larsen CM, Eizirik DL, Mandrup-Poulsen T et al. IL-1beta-induced chemokine and Fas expression are inhibited by suppressor of cytokine signalling-3 in insulin-producing cells. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 281–288.
Farci P, Wollenberg K, Diaz G, Engle RE, Lai ME, Klenerman P et al. Profibrogenic chemokines and viral evolution predict rapid progression of hepatitis C to cirrhosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 14562–14567.
Szabo G, Dolganiuc A . Subversion of plasmacytoid and myeloid dendritic cell functions in chronic HCV infection. Immunobiology 2005; 210: 237–247.
Lau AH, de Creus A, Lu L, Thomson AW . Liver tolerance mediated by antigen presenting cells: fact or fiction? Gut 2003; 52: 1075–1078.
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Vecchi A, Locati M . The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 677–686.
Simpson KJ, Henderson NC, Bone-Larson CL, Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM, Kunkel SL . Chemokines in the pathogenesis of liver disease: so many players with poorly defined roles. Clin Sci (Lond) 2003; 104: 47–63.
Nattermann J, Zimmermann H, Iwan A, von Lilienfeld-Toal M, Leifeld L, Nischalke HD et al. Hepatitis C virus E2 and CD81 interaction may be associated with altered trafficking of dendritic cells in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2006; 44: 945–954.
Bonacchi A, Petrai I, Defranco RM, Lazzeri E, Annunziato F, Efsen E et al. The chemokine CCL21 modulates lymphocyte recruitment and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2003; 125: 1060–1076.
Oo YH, Shetty S, Adams DH . The role of chemokines in the recruitment of lymphocytes to the liver. Dig Dis 2010; 28: 31–44.
Asselah T, Bieche I, Laurendeau I, Paradis V, Vidaud D, Degott C et al. Liver gene expression signature of mild fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2005; 129: 2064–2075.
Zhdanov KV, Gusev DA, Chirskii VS, Sysoev KA, Iakubovskaia LA, Shakhmanov DM et al. Chronic HCV-infection and expression of mRNA of CC-chemokines and their receptors. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 2008; ( 4): 73–78. Russian.
Neuman MG, Benhamou JP, Marcellin P, Valla D, Malkiewicz IM, Katz GG et al. Cytokine–chemokine and apoptotic signatures in patients with hepatitis C. Transl Res 2007; 149: 126–136.
Decalf J, Fernandes S, Longman R, Ahloulay M, Audat F, Lefrerre F et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiate a complex chemokine and cytokine network and are a viable drug target in chronic HCV patients. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 2423–2437.
Matsuno K, Nomiyama H, Yoneyama H, Uwatoku R . Kupffer cell-mediated recruitment of dendritic cells to the liver crucial for a host defense. Dev Immunol 2002; 9: 143–149.
Heydtmann M . Macrophages in hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections. J Virol 2009; 83: 2796–2802.
Salazar-Mather TP, Hokeness KL . Cytokine and chemokine networks: pathways to antiviral defense. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2006; 303: 29–46.
Simpson KJ, Henderson NC, Bone-Larson CL, Lukacs NW, Hogaboam CM, Kunkel SL . Chemokines in the pathogenesis of liver disease: so many players with poorly defined roles. Clin Sci 2003; 104: 47–63.
Boisvert J, Kunkel EJ, Campbell JJ, Keeffe EB, Butcher EC, Greenberg HB . Liver-infiltrating lymphocytes in end-stage hepatitis C virus: subsets, activation status, and chemokine receptor phenotypes. J Hepatol 2003; 38: 67–75.
Wisniewska-Ligier M, Wozniakowska-Gesicka T, Glowacka E, Lewkowicz P, Banasik M, Tchorzewski H . Involvement of innate immunity in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C in children. Scand J Immunol 2006; 64: 425–432.
Helbig KJ, Ruszkiewicz A, Lanford RE, Berzsenyi MD, Harley HA, McColl SR et al. Differential expression of the CXCR3 ligands in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and their modulation by HCV in vitro. J Virol. 2009; 83: 836–846.
Polyak SJ, Khabar KS, Rezeiq M, Gretch DR . Elevated levels of interleukin-8 in serum are associated with hepatitis C virus infection and resistance to interferon therapy. J Virol 2001; 75: 6209–6211.
Wagoner J, Austin M, Green J, Imaizumi T, Casola A, Brasier A et al. Regulation of CXCL-8 (interleukin-8) induction by double-stranded RNA signaling pathways during hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol 2007; 81: 309–318.
Hoshida Y, Kato N, Yoshida H, Wang Y, Tanaka M, Goto T et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein and hepatitis activity are associated through transactivation of interleukin-8. J Infect Dis 2005; 192: 266–275.
Bataller R, Paik YH, Lindquist JN, Lemasters JJ, Brenner DA . Hepatitis C virus core and nonstructural proteins induce fibrogenic effects in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2004; 126: 529–540.
Kadoya H, Nagano-Fujii M, Deng L, Nakazono N, Hotta H . Nonstructural proteins 4A and 4B of hepatitis C virus transactivate the interleukin 8 promoter. Microbiol Immunol 2005; 49: 265–273.
Szabo G, Chang S, Dolganiuc A . Altered innate immunity in chronic hepatitis C infection: cause or effect? Hepatology 2007; 46: 1279–1290.
Sillanpaa M, Kaukinen P, Melen K, Julkunen I . Hepatitis C virus proteins interfere with the activation of chemokine gene promoters and downregulate chemokine gene expression. J Gen Virol 2008; 89( Pt 2): 432–443.
Gale M Jr ., Foy EM . Evasion of intracellular host defence by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005; 436( 7053): 939–945.
Apolinario A, Majano PL, Lorente R, Nunez O, Clemente G, Garcia-Monzon C . Gene expression profile of T-cell-specific chemokines in human hepatocyte-derived cells: evidence for a synergistic inducer effect of cytokines and hepatitis C virus proteins. J Viral Hepat 2005; 12: 27–37.
Helbig KJ, Ruszkiewicz A, Semendric L, Harley HA, McColl SR, Beard MR . Expression of the CXCR3 ligand I-TAC by hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis C and its correlation with hepatic inflammation. Hepatology 2004; 39: 1220–1229.
Zeremski M, Petrovic LM, Chiriboga L, Brown QB, Yee HT, Kinkhabwala M et al. Intrahepatic levels of CXCR3-associated chemokines correlate with liver inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2008; 48: 1440–1450.
Cruise MW, Lukens JR, Nguyen AP, Lassen MG, Waggoner SN, Hahn YS . Fas ligand is responsible for CXCR3 chemokine induction in CD4+ T cell-dependent liver damage. J Immunol 2006; 176: 6235–6244.
Curbishley SM, Eksteen B, Gladue RP, Lalor P, Adams DH . CXCR 3 activation promotes lymphocyte transendothelial migration across human hepatic endothelium under fluid flow. Am J Pathol 2005; 167: 887–899.
Larrubia JR, Benito-Martinez S, Calvino M, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Parra-Cid T . Role of chemokines and their receptors in viral persistence and liver damage during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14: 7149–7159.
Butera D, Marukian S, Iwamaye AE, Hembrador E, Chambers TJ, Di Bisceglie AM et al. Plasma chemokine levels correlate with the outcome of antiviral therapy in patients with hepatitis C. Blood 2005; 106: 1175–1182.
Eksteen B, Miles A, Curbishley SM, Tselepis C, Grant AJ, Walker LS et al. Epithelial inflammation is associated with CCL28 production and the recruitment of regulatory T cells expressing CCR10. J Immunol 2006; 177: 593–603.
Lichterfeld M, Leifeld L, Nischalke HD, Rockstroh JK, Hess L, Sauerbruch T et al. Reduced CC chemokine receptor (CCR) 1 and CCR5 surface expression on peripheral blood T lymphocytes from patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. J Infect Dis 2002; 185: 1803–1807.
Larrubia JR, Calvino M, Benito S, Sanz-de-Villalobos E, Perna C, Perez-Hornedo J et al. The role of CCR5/CXCR3 expressing CD8+ cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol 2007; 47: 632–641.
Ahlenstiel G, Woitas RP, Rockstroh J, Spengler U . CC-chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) in hepatitis C—at the crossroads of the antiviral immune response? J Antimicrob Chemother 2004; 53: 895–898.
Coenen M, Nattermann J . The role of CCR5 in HCV infection. Eur J Med Res 2010; 15: 97–101.
Shi FD, Ljunggren HG, La Cava A, van Kaer L . Organ-specific features of natural killer cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2011; 11: 658–671.
Neuman MG, Schmilovitz-Weiss H, Hilzenrat N, Bourliere M, Marcellin P, Trepo C et al. Markers of inflammation and fibrosis in alcoholic hepatitis and viral hepatitis C. Int J Hepatol 2012; 2012: 231210.
Freeman AJ, Marinos G, Ffrench RA, Lloyd AR . Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C virus infection. Immunol Cell Biol 2001; 79: 515–536.
Choi SW, Hildebrandt GC, Olkiewicz KM, Hanauer DA, Chaudhary MN, Silva IA et al. CCR1/CCL5 (RANTES) receptor–ligand interactions modulate allogeneic T-cell responses and graft-versus-host disease following stem-cell transplantation. Blood 2007; 110: 3447–3455.
Seki E, de Minicis S, Gwak GY, Kluwe J, Inokuchi S, Bursill CA et al. CCR1 and CCR5 promote hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 1858–1870.
Neumann-Haefelin C, Timm J, Spangenberg HC, Wischniowski N, Nazarova N, Kersting N et al. Virological and immunological determinants of intrahepatic virus-specific CD8+ T-cell failure in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2008; 47: 1824–1836.
Barnaba V . Hepatitis C virus infection: a “liaison a trois” amongst the virus, the host, and chronic low-level inflammation for human survival. J Hepatol 2010; 53: 752–761.
Soo HM, Garzino-Demo A, Hong W, Tan YH, Tan YJ, Goh PY et al. Expression of a full-length hepatitis C virus cDNA up-regulates the expression of CC chemokines MCP-1 and RANTES. Virology 2002; 303: 253–277.
Katsounas A, Trippler M, Wang B, Polis M, Lempicki RA, Kottilil S et al. CCL5 mRNA is a marker for early fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C and is regulated by interferon-alpha therapy and toll-like receptor 3 signalling. J Viral Hepat 2012; 19: 128–137.
Ruggieri A, Franco M, Gatto I, Kumar A, Rapicetta M . Modulation of RANTES expression by HCV core protein in liver derived cell lines. BMC Gastroenterol 2007; 7: 21.
Golden-Mason L, Palmer B, Klarquist J, Mengshol JA, Castelblanco N, Rosen HR . Upregulation of PD-1 expression on circulating and intrahepatic hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells associated with reversible immune dysfunction. J Virol 2007; 81: 9249–9258.
Gao B, Radaeva S, Park O . Liver natural killer and natural killer T cells: immunobiology and emerging roles in liver diseases. J Leuk Biol 2009; 86: 513–528.
Geissmann F, Cameron TO, Sidobre S, Manlongat N, Kronenberg M, Briskin MJ et al. Intravascular immune surveillance by CXCR6+ NKT cells patrolling liver sinusoids. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e113.
Heydtmann M, Lalor PF, Eksteen JA, Hubscher SG, Briskin M, Adams DH . CXC chemokine ligand 16 promotes integrin-mediated adhesion of liver-infiltrating lymphocytes to cholangiocytes and hepatocytes within the inflamed human liver. J Immunol 2005; 174: 1055–1062.
Paust S, von Andrian UH . Natural killer cell memory. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 500–508.
Guidotti LG, Iannacone M . Effector CD8 T cell trafficking within the liver. Mol Immunol 2013; 55: 94–99.
Kim CH, Kunkel EJ, Boisvert J, Johnston B, Campbell JJ, Genovese MC et al. Bonzo/CXCR6 expression defines type 1-polarized T-cell subsets with extralymphoid tissue homing potential. J Clin Invest 2001; 107: 595–601.
Gaida MM, Gunther F, Wagner C, Friess H, Giese NA, Schmidt J et al. Expression of the CXCR6 on polymorphonuclear neutrophils in pancreatic carcinoma and in acute, localized bacterial infections. Clin Exp Immunol 2008; 154: 216–223.
Northfield JW, Kasprowicz V, Lucas M, Kersting N, Bengsch B, Kim A et al. CD161 expression on hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells suggests a distinct pathway of T cell differentiation. Hepatology 2008; 47: 396–406.
Mormone E, George J, Nieto N . Molecular pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and current therapeutic approaches. Chem Biol Interact 2011; 193: 225–231.
Li JT, Liao ZX, Ping J, Xu D, Wang H . Molecular mechanism of hepatic stellate cell activation and antifibrotic therapeutic strategies. J Gastroenterol 2008; 43: 419–428.
Friedman SL . Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 2008; 88: 125–172.
Coulon S, Heindryckx F, Geerts A, van Steenkiste C, Colle I, van Vlierberghe H . Angiogenesis in chronic liver disease and its complications. Liver Int 2011; 31: 146–162.
Giatromanolaki A, Kotsiou S, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis E . Angiogenic factor expression in hepatic cirrhosis. Mediators Inflamm 2007; 2007: 67187.
Thabut D, Shah V . Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in chronic liver disease: new targets for the treatment of portal hypertension? J Hepatol 2010; 53: 976–980.
Strieter RM, Belperio JA, Burdick MD, Keane MP . CXC chemokines in angiogenesis relevant to chronic fibroproliferation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2005; 4: 23–26.
Chaparro M, Sanz-Cameno P, Trapero-Marugan M, Garcia-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R . Mechanisms of angiogenesis in chronic inflammatory liver disease. Ann Hepatol 2007; 6: 208–213.
Lemos QT, Andrade ZA . Angiogenesis and experimental hepatic fibrosis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2010; 105: 611–614.
Zhu AX, Duda DG, Sahani DV, Jain RK . HCC and angiogenesis: possible targets and future directions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011; 8: 292–301.
Capece D, Fischietti M, Verzella D, Gaggiano A, Cicciarelli G, Tessitore A et al. The inflammatory microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: a pivotal role for tumor-associated macrophages. Biomed Res Int 2013; 2013: 187204.
Kim MY, Baik SK, Lee SS . Hemodynamic alterations in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Korean J Hepatol 2010; 16: 347–352.
Kanematsu M, Osada S, Amaoka N, Goshima S, Kondo H, Kato H et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma and the surrounding liver and correlation with MRI findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005; 184: 832–841.
Yu DC, Chen J, Ding YT . Hypoxic and highly angiogenic non-tumor tissues surrounding hepatocellular carcinoma: the ‘niche’ of endothelial progenitor cells. Int J Mol Sci 2010; 11: 2901–2909.
Bozova S, Elpek GO . Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in experimental cirrhosis: correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis. Apmis 2007; 115: 795–801.
Brodsky SV, Mendelev N, Melamed M, Ramaswamy G . Vascular density and VEGF expression in hepatic lesions. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2007; 16: 373–377.
Park YN, Kim YB, Yang KM, Park C . Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis in the early stage of multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000; 124: 1061–1065.
Mathonnet M, Descottes B, Valleix D, Labrousse F, Denizot Y . VEGF in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding cirrhotic liver tissues. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: 830–831.
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM . Chemokines as mediators of neovascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 1928–1936.
van Sweringen HL, Sakai N, Quillin RC, Bailey J, Schuster R, Blanchard J et al. Roles of hepatocyte and myeloid CXC chemokine receptor-2 in liver recovery and regeneration after ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Hepatology 2013; 57: 331–338.
Huang F, Geng XP . Chemokines and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16: 1832–1836.
Teicher BA, Fricker SP . CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 2927–2931.
Kruglov EA, Nathanson RA, Nguyen T, Dranoff JA . Secretion of MCP-1/CCL2 by bile duct epithelia induces myofibroblastic transdifferentiation of portal fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 290: G765–G771.
Farci P, Wollenberg K, Diaz G, Engle RE, Lai ME, Klenerman P et al. Profibrogenic chemokines and viral evolution predict rapid progression of hepatitis C to cirrhosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 14562–14567.
Wasmuth HE, Tacke F, Trautwein C . Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis 2010; 30: 215–225.
Wasmuth HE, Weiskirchen R . Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: modulation of stellate cells by chemokines. Z Gastroenterol 2010; 48: 38–45.
Bataller R, Lemon SM . Fueling fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 14293–14294.
Hong KH, Ryu J, Han KH . Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced angiogenesis is mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Blood 2005; 105: 1405–1407.
Arefieva TI, Kukhtina NB, Antonova OA, Krasnikova TL . MCP-1-stimulated chemotaxis of monocytic and endothelial cells is dependent on activation of different signaling cascades. Cytokine 2005; 31: 439–446.
Yu DC, Chen J, Sun XT, Zhuang LY, Jiang CP, Ding YT . Mechanism of endothelial progenitor cell recruitment into neo-vessels in adjacent non-tumor tissues in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 435.
Dagouassat M, Suffee N, Hlawaty H, Haddad O, Charni F, Laguillier C et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)/CCL2 secreted by hepatic myofibroblasts promotes migration and invasion of human hepatoma cells. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 1095–1108.
Heinrichs D, Berres ML, Nellen A, Fischer P, Scholten D, Trautwein C et al. The chemokine CCL3 promotes experimental liver fibrosis in mice. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e66106.
Lu P, Nakamoto Y, Nemoto-Sasaki Y, Fujii C, Wang H, Hashii M et al. Potential interaction between CCR1 and its ligand, CCL3, induced by endogenously produced interleukin-1 in human hepatomas. Am J Pathol 2003; 162: 1249–1258.
Zimmermann HW, Seidler S, Nattermann J, Gassler N, Hellerbrand C, Zernecke A et al. Functional contribution of elevated circulating and hepatic non-classical CD14CD16 monocytes to inflammation and human liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e11049.
Yang X, Lu P, Fujii C, Nakamoto Y, Gao JL, Kaneko S et al. Essential contribution of a chemokine, CCL3, and its receptor, CCR1, to hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 1869–1876.
Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Brenner DA . Human hepatic stellate cells express CCR5 and RANTES to induce proliferation and migration. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2003; 285: G949–G958.
Zhang JP, Yan J, Xu J, Pang XH, Chen MS, Li L et al. Increased intratumoral IL-17-producing cells correlate with poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Hepatol 2009; 50: 980–989.
Soliman HH, Nagy H, Kotb N, Alm El-Din MA . The role of chemokine CC ligand 20 in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Markers 2012; 27: e125–e131.
Chen KJ, Lin SZ, Zhou L, Xie HY, Zhou WH, Taki-Eldin A et al. Selective recruitment of regulatory T cell through CCR6–CCL20 in hepatocellular carcinoma fosters tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e24671.
Lee Y, Friedman SL . Fibrosis in the liver: acute protection and chronic disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2010; 97: 151–200.
Kanzler I, Tuchscheerer N, Steffens G, Simsekyilmaz S, Konschalla S, Kroh A et al. Differential roles of angiogenic chemokines in endothelial progenitor cell-induced angiogenesis. Basic Res Cardiol 2013; 108: 310.
Salcedo R, Oppenheim JJ . Role of chemokines in angiogenesis: CXCL12/SDF-1 and CXCR4 interaction, a key regulator of endothelial cell responses. Microcirculation 2003; 10: 359–370.
Mehrad B, Keane MP, Strieter RM . Chemokines as mediators of angiogenesis. Thromb Haemost 2007; 97: 755–762.
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Mestas J, Gomperts B, Keane MP, Belperio JA . Cancer CXC chemokine networks and tumour angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer 2006; 42: 768–778.
Liu Z, Yang L, Xu J, Zhang X, Wang B . Enhanced expression and clinical significance of chemokine receptor CXCR2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Res 2011; 166: 241–246.
Kryczek I, Wei S, Keller E, Liu R, Zou W . Stroma-derived factor (SDF-1/CXCL12) and human tumor pathogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292: C987–C995.
Hong F, Tuyama A, Lee TF, Loke J, Agarwal R, Cheng X et al. Hepatic stellate cells express functional CXCR4: role in stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha-mediated stellate cell activation. Hepatology 2009; 49: 2055–2067.
Li W, Gomez E, Zhang Z . Immunohistochemical expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and CXCR4 ligand receptor system in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2007; 26: 527–533.
Schimanski CC, Bahre R, Gockel I, Muller A, Frerichs K, Horner V et al. Dissemination of hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated via chemokine receptor CXCR4. Br J Cancer 2006; 95: 210–217.
Petit I, Jin D, Rafii S . The SDF-1–CXCR4 signaling pathway: a molecular hub modulating neo-angiogenesis. Trends Immunol 2007; 28: 299–307.
Duda DG, Kozin SV, Kirkpatrick ND, Xu L, Fukumura D, Jain RK . CXCL12 (SDF1alpha)–CXCR4/CXCR7 pathway inhibition: an emerging sensitizer for anticancer therapies? Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2074–2080.
Chu H, Zhou H, Liu Y, Liu X, Hu Y, Zhang J . Functional expression of CXC chemokine recepter-4 mediates the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases from mouse hepatocarcinoma cell lines with different lymphatic metastasis ability. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 39: 197–205.
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Sebastiani M, Ferrari D et al. High values of CXCL10 serum levels in mixed cryoglobulinemia associated with hepatitis C infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103: 2488–2494.
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Ferrari SM, Colaci M, Fallahi P . Immunopathogenesis of HCV-related endocrine manifestations in chronic hepatitis and mixed cryoglobulinemia. Autoimmun Rev 2008; 8: 18–23.
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Ferrari SM, Colaci M, Sansonno D, Fallahi P . Endocrine manifestations of hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2009; 5: 26–34.
Sansonno D, Tucci FA, Troiani L, Lauletta G, Montrone M, Conteduca V et al. Increased serum levels of the chemokine CXCL13 and up-regulation of its gene expression are distinctive features of HCV-related cryoglobulinemia and correlate with active cutaneous vasculitis. Blood 2008; 112: 1620–1627.
Berenguer J, Fernandez-Rodriguez A, Jimenez-Sousa MA, Cosin J, Zarate P, Micheloud D et al. High plasma CXCL10 levels are associated with HCV-genotype 1, and higher insulin resistance, fibrosis, and HIV viral load in HIV/HCV coinfected patients. Cytokine 2012; 57: 25–29.
Berres ML, Trautwein C, Schmeding M, Eurich D, Tacke F, Bahra M et al. Serum chemokine CXC ligand 10 (CXCL10) predicts fibrosis progression after liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection. Hepatology 2011; 53: 596–603.
Diago M, Castellano G, Garcia-Samaniego J, Perez C, Fernandez I, Romero M et al. Association of pretreatment serum interferon gamma inducible protein 10 levels with sustained virological response to peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy in genotype 1 infected patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2006; 55: 374–379.
Florholmen J, Kristiansen MG, Steigen SE, Sorbye SW, Paulssen EJ, Kvamme JM et al. A rapid chemokine response of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha, MIP-1beta and the regulated on activation, normal T expressed and secreted chemokine is associated with a sustained virological response in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Clin Microbiol Infect 2011; 17: 204–209.
Pawlotsky JM . Mechanisms of antiviral treatment efficacy and failure in chronic hepatitis C. Antiviral Res 2003; 59: 1–11.
Romero AI, Lagging M, Westin J, Dhillon AP, Dustin LB, Pawlotsky JM et al. Interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible protein-10: association with histological results, viral kinetics, and outcome during treatment with pegylated IFN-alpha 2a and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 2006; 194: 895–903.
Yamauchi K, Akbar SM, Horiike N, Michitaka K, Onji M . Increased serum levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha in chronic viral hepatitis: prognostic importance of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat 2002; 9: 213–220.
Kusano F, Tanaka Y, Marumo F, Sato C . Expression of C–C chemokines is associated with portal and periportal inflammation in the liver of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Lab Invest 2000; 80: 415–422.
Costantini S, Castello G, Colonna G . Human cytokinome: a new challenge for systems biology. Bioinformation 2010; 5: 166–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology website.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fahey, S., Dempsey, E. & Long, A. The role of chemokines in acute and chronic hepatitis C infection. Cell Mol Immunol 11, 25–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.37
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.37
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in anti- PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for solid cancers
Molecular Cancer (2023)
-
Nanoparticle accumulation in liver may induce resistance to immune checkpoint blockade therapy
Nano Research (2023)
-
Strategies Targeting the Innate Immune Response for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Liver Fibrosis
Drugs (2021)
-
The Significance of HCV Viral Load in the Incidence of HCC: a Correlation Between Mir-122 and CCL2
Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer (2020)
-
NKG2A is a NK cell exhaustion checkpoint for HCV persistence
Nature Communications (2019)