Abstract
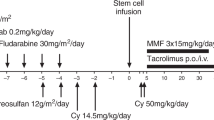
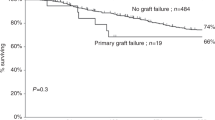
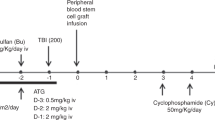
Haploidentical haematopoietic SCT (HSCT) using T-cell-replete grafts and post-transplant high-dose CY has found increasing acceptance. Our purpose was to evaluate the feasibility and outcome of this strategy as second HSCT incorporating donor change for acute leukaemia relapse after a first allogeneic transplantation. The courses of 20 consecutive adults (median age 37 years, 12 male) with AML (n=14), ALL (n=5) and acute bi-phenotypic leukaemia (n=1) were analysed retrospectively. Conditioning consisted of fludarabine, CY and either melphalan or TBI or tresosulfan+/–etoposide. Engraftment was achieved in 17 (85%), and a second remission was induced in 15 patients (75%) on day +30. The rate of grade II–IV acute GvHD was 35%, while chronic GvHD occurred in five patients. Most commonly observed grade III–IV toxicities were mucositis (30%), hyperbilirubinemia (20%), elevation of transaminases (20%) and creatinine (20%), while invasive fungal infection affected 30%. One-year non-relapse mortality (NRM) was 36%. At a median follow-up of 17 months, estimated 1-year OS was 45%, and 1-year relapse-free survival was 33%. This strategy was feasible and allowed for successful engraftment with a moderate rate of toxicity. Early outcome and NRM are at least comparable with results after a second HSCT from HLA-matched donors without donor change at HSCT2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, Kapelushnik Y, Aker M, Cividalli G et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood 1998; 91: 756–763.
Schmid C, Labopin M, Nagler A, Niederwieser D, Castagna L, Tabrizi R et al. Treatment, risk factors, and outcome of adults with relapsed AML after reduced intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012; 119: 1599–1606.
Pawson R, Potter MN, Theocharous P, Lawler M, Garg M, Yin JA et al. Treatment of relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation with reduced intensity conditioning (FLAG +/-Ida) and second allogeneic stem cell transplant. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: 622–629.
Schmid C, Schleuning M, Aschan J, Ringden O, Hahn J, Holler E et al. Low-dose ARAC, donor cells, and GM-CSF for treatment of recurrent acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1430–1433.
Schroeder T, Czibere A, Platzbecker U, Bug G, Uharek L, Luft T et al. Azacitidine and donor lymphocyte infusions as first salvage therapy for relapse of AML or MDS after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 2013; 27: 1229–1235.
Sharma M, Ravandi F, Bayraktar UD, Chiattone A, Bashir Q, Giralt S et al. Treatment of FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with sorafenib. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2011; 17: 1874–1877.
Pollyea DA, Artz AS, Stock W, Daugherty C, Godley L, Odenike OM et al. Outcomes of patients with AML and MDS who relapse or progress after reduced intensity allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 1027–1032.
Eapen M, Giralt SA, Horowitz MM, Klein JP, Wagner JE, Zhang MJ et al. Second transplant for acute and chronic leukemia relapsing after first HLA-identical sibling transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 34: 721–727.
Shaw BE, Mufti GJ, Mackinnon S, Cavenagh JD, Pearce RM, Towlson KE et al. Outcome of second allogeneic transplants using reduced-intensity conditioning following relapse of haematological malignancy after an initial allogeneic transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 42: 783–789.
Duus JE, Stiff PJ, Choi J, Parthasarathy M, Rodriguez T, Toor AA . Second allografts for relapsed hematologic malignancies: feasibility of using a different donor. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 35: 261–264.
Christopeit M, Kuss O, Finke J, Bacher U, Beelen DW, Bornhauser M et al. Second allograft for hematologic relapse of acute leukemia after first allogeneic stem-cell transplantation from related and unrelated donors: the role of donor change. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 3259–3271.
Luznik L, O'Donnell PV, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Leffell MS, Zahurak M et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2008; 14: 641–650.
Ciurea SO, Mulanovich V, Saliba RM, Bayraktar UD, Jiang Y, Bassett R et al. Improved early outcomes using a T cell replete graft compared with T cell depleted haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012; 18: 1835–1844.
Kasamon YL, Luznik L, Leffell MS, Kowalski J, Tsai HL, Bolanos-Meade J et al. Nonmyeloablative HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation with high-dose posttransplantation cyclophosphamide: effect of HLA disparity on outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010; 16: 482–489.
Dong L, Gao Z-Y, Yu X-J, Tan X-Y, Liu J-H, Lu F et al. HLA disparity is associated with improved outcomes in hematological malignancies after family HLA-mismatched /haploidentical HCT but not URD. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2012; 120: 2014.
Kanda Y, Chiba S, Hirai H, Sakamaki H, Iseki T, Kodera Y et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from family members other than HLA-identical siblings over the last decade (1991-2000). Blood 2003; 102: 1541–1547.
Schmid C, Schleuning M, Ledderose G, Tischer J, Kolb HJ . Sequential regimen of chemotherapy, reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem-cell transplantation, and prophylactic donor lymphocyte transfusion in high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 5675–5687.
Schmid C, Schleuning M, Schwerdtfeger R, Hertenstein B, Mischak-Weissinger E, Bunjes D et al. Long-term survival in refractory acute myeloid leukemia after sequential treatment with chemotherapy and reduced-intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2006; 108: 1092–1099.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1813–1821.
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V, Jaques D, Budach V et al. CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 2003; 13: 176–181.
Kaplan E, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005; 106: 2912–2919.
Bosi A, Laszlo D, Labopin M, Reffeirs J, Michallet M, Gluckman E et al. Second allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in acute leukemia: results of a survey by the European Cooperative Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 3675–3684.
Michallet M, Tanguy ML, Socie G, Thiebaut A, Belhabri A, Milpied N et al. Second allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation in relapsed acute and chronic leukaemias for patients who underwent a first allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: a survey of the Societe Francaise de Greffe de moelle (SFGM). Br J Haematol 2000; 108: 400–407.
Platzbecker U, Binder M, Schmid C, Rutt C, Ehninger G, Bornhauser M . Second donation of hematopoietic stem cells from unrelated donors for patients with relapse or graft failure after allogeneic transplantation. Haematologica 2008; 93: 1276–1278.
Hosing C, Saliba RM, Shahjahan M, Estey EH, Couriel D, Giralt S et al. Disease burden may identify patients more likely to benefit from second allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 36: 157–162.
Kedmi M, Resnick IB, Dray L, Aker M, Samuel S, Gesundheit B et al. A retrospective review of the outcome after second or subsequent allogeneic transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 483–489.
Magenau J, Tobai H, Pawarode A, Braun T, Peres E, Reddy P et al. Clofarabine and busulfan conditioning facilitates engraftment and provides significant antitumor activity in nonremission hematologic malignancies. Blood 2011; 118: 4258–4264.
Radich JP, Sanders JE, Buckner CD, Martin PJ, Petersen FB, Bensinger W et al. Second allogeneic marrow transplantation for patients with recurrent leukemia after initial transplant with total-body irradiation-containing regimens. J Clin Oncol 1993; 11: 304–313.
Marr KA, Carter RA, Crippa F, Wald A, Corey L . Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 909–917.
Pirsch JD, Maki DG . Infectious complications in adults with bone marrow transplantation and T-cell depletion of donor marrow. Increased susceptibility to fungal infections. Ann Int Med 1986; 104: 619–631.
Rieger CT, Ostermann H, Kolb HJ, Fiegl M, Huppmann S, Morgenstern N et al. A clinical cohort trial of antifungal combination therapy: efficacy and toxicity in haematological cancer patients. Ann Hematol 2008; 87: 915–922.
Rieger CT, Rieger H, Kolb HJ, Peterson L, Huppmann S, Fiegl M et al. Infectious complications after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: incidence in matched-related and matched-unrelated transplant settings. Transpl Infect Dis 2009; 11: 220–226.
Martino R, Badell I, Brunet S, Sureda A, Nomdedeu J, Altes A et al. Second bone marrow transplantation for leukemia in untreated relapse. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 14: 589–593.
Al-Qurashi F, Ayas M, Al Sharif F, Ibrahim E, Sahovic E, Al Mahr M et al. Second allogeneic bone marrow transplantation after myeloablative conditioning analysis of 43 cases from single institution. Hematology 2004; 9: 123–129.
Khouri IF, Keating M, Korbling M, Przepiorka D, Anderlini P, O'Brien S et al. Transplant-lite: induction of graft-versus-malignancy using fludarabine-based nonablative chemotherapy and allogeneic blood progenitor-cell transplantation as treatment for lymphoid malignancies. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 2817–2824.
Barrett AJ, Locatelli F, Treleaven JG, Gratwohl A, Szydlo R, Zwaan FE . Second transplants for leukaemic relapse after bone marrow transplantation: high early mortality but favourable effect of chronic GVHD on continued remission. A report by the EBMT Leukaemia Working Party. Br J Haematol 1991; 79: 567–574.
Kishi K, Takahashi S, Gondo H, Shiobara S, Kanamaru A, Kato S et al. Second allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for post-transplant leukemia relapse: results of a survey of 66 cases in 24 Japanese institutes. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 19: 461–466.
Mrsic M, Horowitz MM, Atkinson K, Biggs JC, Champlin RE, Ehninger G et al. Second HLA-identical sibling transplants for leukemia recurrence. Bone Marrow Transplant 1992; 9: 269–275.
Grullich C, Bertz H, Spyridonidis A, Muller CI, Finke J . A fludarabine, thiotepa reduced toxicity conditioning regimen designed specifically for allogeneic second haematopoietic cell transplantation after failure of previous autologous or allogeneic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008; 41: 845–850.
Tomonari A, Iseki T, Ooi J, Nagayama H, Sato H, Takahashi T et al. Second allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for leukemia relapse after first allogeneic transplantation: outcome of 16 patients in a single institution. Int J Hematol 2002; 75: 318–323.
Bassan R, Hoelzer D . Modern therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2011; 29: 532–543.
Dohner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Buchner T, Burnett AK et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010; 115: 453–474.
Acknowledgements
We thank the medical staff of our transplant wards for excellent care of our patients and M Rothmayer for transplantation coordination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tischer, J., Engel, N., Fritsch, S. et al. Second haematopoietic SCT using HLA-haploidentical donors in patients with relapse of acute leukaemia after a first allogeneic transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 49, 895–901 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.83
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.83
This article is cited by
-
Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia: an overview of prevention and treatment
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Reduced dose of posttransplant cyclophosphamide in HLA-haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)
-
Allogene Blutstammzelltransplantation: Etabliertes und Neues
InFo Hämatologie + Onkologie (2021)
-
Geriatric nutritional risk index as a useful prognostic factor in second allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Annals of Hematology (2020)
-
Donor selection for a second allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML patients relapsing after a first transplant: a study of the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT
Blood Cancer Journal (2019)