Abstract
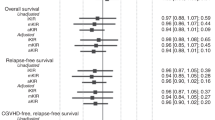
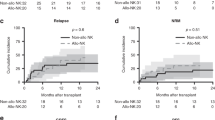
The impact of activating KIR (aKIR) and inhibitory KIR (iKIR) on OS, relapse-related mortality (RRM) and acute GVHD (aGVHD) was prospectively studied in 84 adults with high-risk hematologic malignancies receiving reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) T-cell depleted hematopoietic SCT (HSCT) from haploidentical related donors. In this clinical model, freedom from RRM is dependent on GVL effect. Patients were divided into myeloid (n=49) and lymphoid (n=35) malignancy groups. KIR-ligand and ligand-ligand models were studied in both GVH and rejection directions and statistically correlated with outcome measures. In the myeloid group, OS was higher (P=0.009) and RRM was lower (P=0.036) in patients missing HLA-C group2 ligand to donor iKIR. OS was higher if patients had >1 missing ligand (P=0.018). In lymphoid malignancy, missing ligand to donor KIR had no impact on OS or RRM. However, OS was better with donor aKIR 2DS2 (P=0.028). There was a trend towards shorter OS in recipient with KIR 2DS1, 2DS5 and 3DS1, although sample sizes were too small to provide inferential statistics. Findings in lymphoid malignancy patients should be further studied. These results suggest that the absence of appropriate HLA ligands in the recipient to donor iKIR may induce GVL without aGVHD in myeloid malignancy patients undergoing TCD-RIC transplants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science 2002; 295: 2097–2100.
Hale G, Zhang MJ, Bunjes D, Prentice HG, Spence D, Horowitz MM et al. Improving the outcome of bone marrow transplantation by using CD52 monoclonal antibodies to prevent graft-versus-host disease and graft rejection. Blood 1998; 92: 4581–4590.
Morris E, Thomson K, Craddock C, Mahendra P, Milligan D, Cook G et al. Outcomes after alemtuzumab-containing reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation regimen for relapsed and refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2004; 104: 3865–3871.
Rizzieri DA, Koh LP, Long GD, Gasparetto C, Sullivan KM, Horwitz M et al. Partially matched, nonmyeloablative allogeneic transplantation: clinical outcomes and immune reconstitution. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 690–697.
Barrett AJ . Understanding and harnessing the graft-versus-leukaemia effect. Br J Haematol 2008; 142: 877–888.
Trowsdale J . Genetic and functional relationships between MHC and NK receptor genes. Immunity 2001; 15: 363–374.
Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Biassoni R, Mingari MC et al. Receptors for HLA class-I molecules in human natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol 1996; 14: 619–648.
Lanier LL . NK cell receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 1998; 16: 359–393.
Long EO . Regulation of immune responses through inhibitory receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 1999; 17: 875–904.
Long EO . Immunology Signal sequences stop killer cells. Nature 1998; 391: 740–743.
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S . Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 503–510.
Pende D, Marcenaro S, Falco M, Martini S, Bernardo ME, Montagna D et al. Anti-leukemia activity of alloreactive NK cells in KIR ligand-mismatched haploidentical HSCT for pediatric patients: evaluation of the functional role of activating KIR and redefinition of inhibitory KIR specificity. Blood 2009; 113: 3119–3129.
Moretta A, Sivori S, Vitale M, Pende D, Morelli L, Augugliaro R et al. Existence of both inhibitory (p58) and activatory (p50) receptors for HLA-C molecules in human natural killer cells. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 875–884.
Stewart CA, Laugier-Anfossi F, Vely F, Saulquin X, Riedmuller J, Tisserant A et al. Recognition of peptide-MHC class I complexes by activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005; 102: 13224–13229.
Gratama JW, Sutherland DR, Keeney M . Flow cytometric enumeration and immunophenotyping of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Semin Hematol 2001; 38: 139–147.
Sutherland DR, Anderson L, Keeney M, Nayar R, Chin-Yee I . The ISHAGE guidelines for CD34+ cell determination by flow cytometry. International Society of Hematotherapy and Graft Engineering. J Hematother 1996; 5: 213–226.
Rizzieri DA, Dev P, Long GD, Gasparetto C, Sullivan KM, Horwitz M et al. Response and toxicity of donor lymphocyte infusions following T-cell depleted non-myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic SCT from 3-6/6 HLA matched donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 43: 327–333.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE . Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: new representations of old estimators. Stat Med 1999; 18: 695–706.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. JAm Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Mantel C, Luo Z, Hendrie P, Broxmeyer HE . Steel factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor act together to enhance choline-lipid turnover during synergistically stimulated proliferation of the human factor dependent cell line, M07E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993; 97: 978–984.
Giebel S, Locatelli F, Lamparelli T, Velardi A, Davies S, Frumento G et al. Survival advantage with KIR ligand incompatibility in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Blood 2003; 102: 814–819.
Davies SM, Ruggieri L, DeFor T, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Miller JS et al. Evaluation of KIR ligand incompatibility in mismatched unrelated donor hematopoietic transplants. Blood 2002; 100: 3825–3827.
Brunstein CG, Wagner JE, Weisdorf DJ, Cooley S, Noreen H, Barker JN et al. Negative effect of KIR alloreactivity in recipients of umbilical cord blood transplant depends on transplantation conditioning intensity. Blood 2009; 113: 5628–5634.
Cooley S, Trachtenberg E, Bergemann TL, Saeteurn K, Klein J, Le CT et al. Donors with group B KIR haplotypes improve relapse-free survival after unrelated hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 726–732.
Hsu KC, Keever-Taylor CA, Wilton A, Pinto C, Heller G, Arkun K et al. Improved outcome in HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia predicted by KIR and HLA genotypes. Blood 2005; 105: 4878–4884.
Gagne K, Busson M, Bignon JD, Balere-Appert ML, Loiseau P, Dormoy A et al. Donor KIR3DL1/3DS1 gene and recipient Bw4 KIR ligand as prognostic markers for outcome in unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2009; 15: 1366–1375.
Farag SS, Bacigalupo A, Eapen M, Hurley C, Dupont B, Caligiuri MA et al. The effect of KIR ligand incompatibility on the outcome of unrelated donor transplantation: a report from the center for international blood and marrow transplant research, the European blood and marrow transplant registry, and the Dutch registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2006; 12: 876–884.
Venstrom JM, Gooley TA, Spellman S, Pring J, Malkki M, Dupont B et al. Donor activating KIR3DS1 is associated with decreased acute GVHD in unrelated allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2010; 115: 3162–3165.
Giebel S, Nowak I, Dziaczkowska J, Czerw T, Wojnar J, Krawczyk-Kulis M et al. Activating killer immunoglobulin-like receptor incompatibilities enhance graft-versus-host disease and affect survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol 2009; 83: 343–356.
Locatelli F, Pende D, Maccario R, Mingari MC, Moretta A, Moretta L . Haploidentical hemopoietic stem cell transplantation for the treatment of high-risk leukemias: how NK cells make the difference. Clin Immunol 2009; 133: 171–178.
Willemze R, Rodrigues CA, Labopin M, Sanz G, Michel G, Socie G et al. KIR-ligand incompatibility in the graft-versus-host direction improves outcomes after umbilical cord blood transplantation for acute leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 492–500 [Erratum appears in Leukemia. 2009 Mar;23(3):630].
Caligiuri MA . Human natural killer cells. Blood 2008; 112: 461–469.
Cambiaggi A, Darche S, Guia S, Kourilsky P, Abastado JP, Vivier E . Modulation of T-cell functions in KIR2DL3 (CD158b) transgenic mice. Blood 1999; 94: 2396–2402.
Cooley S, McCullar V, Wangen R, Bergemann TL, Spellman S, Weisdorf DJ et al. KIR reconstitution is altered by T cells in the graft and correlates with clinical outcomes after unrelated donor transplantation. Blood 2005; 106: 4370–4376.
Fehniger TA, Carson WE, Caligiuri MA . Costimulation of human natural killer cells is required for interferon gamma production. Transplant Proc 1999; 31: 1476–1478.
Middleton D, Gonzelez F . The extensive polymorphism of KIR genes. Immunology 2010; 129: 8–19.
Miller JS . How killers kill. Blood 2008; 112: 213.
Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Capanni M, Urbani E, Carotti A, Aloisi T et al. Donor natural killer cell allorecognition of missing self in haploidentical hematopoietic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: challenging its predictive value. Blood 2007; 110: 433–440.
Shilling HG, McQueen KL, Cheng NW, Shizuru JA, Negrin RS, Parham P . Reconstitution of NK cell receptor repertoire following HLA-matched hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2003; 101: 3730–3740.
Velardi A, Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Aversa F, Christiansen FT . Natural killer cell allorecognition of missing self in allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation: a tool for immunotherapy of leukemia. Curr Opin Immunol 2009; 21: 525–530.
Yu J, Venstrom JM, Liu XR, O’Reilly R, Pring J, Hasan RS et al. Breaking tolerance to self, circulating natural killer cells expressing inhibitory KIR for non-self HLA exhibit effector function following T-cell depleted allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 2009; 113: 3875–3884.
Cook MA, Milligan DW, Fegan CD, Darbyshire PJ, Mahendra P, Craddock CF et al. The impact of donor KIR and patient HLA-C genotypes on outcome following HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 1521–1526.
Bishara A, De SD, Witt CC, Brautbar C, Christiansen FT, Or R et al. The beneficial role of inhibitory KIR genes of HLA class I NK epitopes in haploidentically mismatched stem cell allografts may be masked by residual donor-alloreactive T cells causing GVHD. Tissue Antigens 2004; 63: 204–211.
Acknowledgements
NJC is supported by PO1 (NJC) 2PO1-CA047741-16A1 from NIH; DAR is a Leukemia Lymphoma Society Scholar in Clinical Research.
Author contribution: VKP conceptualized and designed the study, collected clinical data, analyzed the data, wrote the manuscript and led all the coordination efforts; DAR and NJC were involved with conceptualizing, designing and overseeing the study, development of the transplant protocol, collection of clinical data and manuscript preparation; DFC was involved in conceptualizing the study, generation of HLA and KIR typing data in the laboratory, data analysis and editing the manuscript; GB was involved in statistical analysis, review of the data and manuscript preparation; NLR was involved with conceptualizing the study, laboratory support and manuscript preparation; ADO and AC contributed to laboratory studies; KMS, JPC, MEH, CG and GDL were involved with the collection of clinical data and manuscript preparation; YY contributed in manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, DF., Prasad, V., Broadwater, G. et al. Differential impact of inhibitory and activating Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIR) on high-risk patients with myeloid and lymphoid malignancies undergoing reduced intensity transplantation from haploidentical related donors. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 817–823 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.181
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2011.181