Abstract
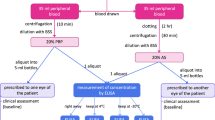
Current treatment of ocular GVHD (oGVHD), represented by systemic immunosuppressive regimens and local therapies (mainly artificial tears and corticosteroids), gives unsatisfactory results. We investigated the safety and efficacy of autologous plasma rich in PDGFs to treat oGVHD unresponsive to standard medications. A total of 23 patients with refractory oGVHD (grade II–IV) unresponsive to standard therapy were treated with autologous plasma rich in PDGFs eye drops (PRGD) four times/day for 6 months. Symptoms and signs (best visual acuity, Schirmer’s test and tear break up time (TBUT), evaluation of the anterior segment and fluorescein and lissamine staining) were always assessed by the same ophthalmologist. Patients were defined as ‘responders’ when showing improvement for total complaints and at least one sign. At 30 days of treatment, 17 patients (73.9%) were classified as responders. The symptom that improved most was photophobia (improved in 19 patients, 82.6%). TBUT improved in 20 patients (86.9%) and anterior segment score in 19 patients (82.6%). Response was maintained over time. No serious adverse events occurred. PRGD proved to be safe and effective in treating oGVHD and may be a valid treatment option from the early stages of the disease to avoid irreversible ocular damage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E . Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet 2009; 373: 1550–1561.
Balaram M, Rashid S, Dana R . Chronic ocular surface disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Ocul Surf 2005; 3: 203–211.
Westeneng AC, Hettinga Y, Lokhorst H, Verdonck L, van Dorp S, Rothova A . Ocular graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Cornea 2010; 29: 758–763.
Uchino M, Ogawa Y, Uchino Y, Mori T, Okamoto S, Tsubota K . Comparison of stem cell sources in the severity of dry eye after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Ophthalmol 2011; 96: 34–37.
Riemens A, te Boome L, Imhof S, Kuball J, Rothova A . Current insights into ocular graft-versus-host disease. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2010; 21: 485–494.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2005; 11: 945–956.
Khanal S, Tomlinson A . Tear physiology in dry eye associated with chronic GvHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 2012; 47: 115–119.
Tabbara KF, Al-Ghamdi A, Al-Mohareb F, Ayas M, Chaudhri N, Al-Sharif F et al. Ocular findings after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Ophthalmology 2009; 116: 1624–1629.
Wang Y, Ogawa Y, Dogru M, Tatematsu Y, Uchino M, Kamoi M et al. Baseline profiles of ocular surface and tear dynamics after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with or without chronic GVHD-related dry eye. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009; 45: 1077–1083.
Doughty MJ, Glavin S . Efficacy of different dry eye treatments with artificial tears or ocular lubricants: a systematic review. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2009; 29: 573–583.
Lelli GJ, Musch DC, Gupta A, Farjo QA, Nairus TM, Mian SI . Ophthalmic cyclosporine use in ocular GVHD. Cornea 2006; 25: 635–638.
Fox RI, Chan R, Michelson JB, Belmont JB, Michelson PE . Beneficial effect of artificial tears made with autologous serum in patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Arthritis Rheum 1984; 27: 459–461.
Tsubota K, Goto E, Fujita H, Ono M, Inoue H, Saito I et al. Treatment of dry eye by autologous serum application in Sjogren’s syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol 1999; 83: 390–395.
Rocha EM, Pelegrino FS, de Paiva CS, Vigorito AC, de Souza CA . GVHD dry eyes treated with autologous serum tears. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 1101–1103.
Ogawa Y, Okamoto S, Mori T, Yamada M, Mashima Y, Watanabe R et al. Autologous serum eye drops for the treatment of severe dry eye in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 31: 579–583.
Chiang CC, Lin JM, Chen WL, Tsai YY . Allogeneic serum eye drops for the treatment of severe dry eye in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Cornea 2007; 26: 861–863.
van Setten GB, Viinikka L, Tervo T, Pesonen K, Tarkkanen A, Perheentupa J . Epidermal growth factor is a constant component of normal human tear fluid. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1989; 227: 184–187.
Anitua E, Andia I, Ardanza B, Nurden P, Nurden AT . Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost 2004; 91: 4–15.
Martinez-Zapata MJ, Marti-Carvajal A, Sola I, Bolibar I, Angel Exposito J, Rodriguez L et al. Efficacy and safety of the use of autologous plasma rich in platelets for tissue regeneration: a systematic review. Transfusion 2009; 49: 44–56.
Sandri G, Bonferoni MC, Rossi S, Ferrari F, Mori M, Del Fante C et al. Platelet lysate formulations based on mucoadhesive polymers for the treatment of corneal lesions. J Pharm Pharmacol 2010; 63: 189–198.
Del Fante C, Perotti C, Bonferoni MC, Rossi S, Sandri G, Ferrari F et al. Platelet lysate mucoadhesive formulation to treat oral mucositis in graft versus host disease patients: a new therapeutic approach. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011; 12: 893–899.
Hartwig D, Harloff S, Liu L, Schlenke P, Wedel T, Geerling G . Epitheliotrophic capacity of a growth factor preparation produced from platelet concentrates on corneal epithelial cells: a potential agent for the treatment of ocular surface defects? Transfusion 2004; 44: 1724–1731.
Design and conduct of clinical trials: report of the Clinical Trials Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf 2007; 5: 153–162.
Behrens A, Doyle JJ, Stern L, Chuck RS, McDonnell PJ, Azar DT et al. Dysfunctional tear syndrome: a Delphi approach to treatment recommendations. Cornea 2006; 25: 900–907.
Schiffman RM, Christianson MD, Jacobsen G, Hirsch JD, Reis BL . Reliability and validity of the ocular surface disease index. Arch Ophthalmol 2000; 118: 615–621.
Rossi GCM, Pasinetti GM, Scudeller L, Milano G, Mazzone A, Raimondi M et al. The Italian version of the Glaucoma Symptom Scale questionnaire: translation, validation and reliability. J Glaucoma, 21: (in press; manuscript number JOG-D-10-00291R2).
Lee BL, Gutierrez P, Gordon M, Wilson MR, Cioffi GA, Ritch R et al. The Glaucoma Symptom Scale. A brief index of glaucoma-specific symptoms. Arch Ophthalmol 1998; 116: 861–866.
Bron AJ, Evans VE, Smith JA . Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea 2003; 22: 640–650.
Bachmann B, Taylor RS, Cursiefen C . The association between corneal neovascularization and visual acuity: a systematic review. Acta Ophthalmol (doi:10.1111/j.1755-3768.2011.02312.x).
Dell S, Peters S, Muther P, Kociok N, Joussen AM . The role of PDGF receptor inhibitors and PI3-kinase signaling in the pathogenesis of corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006; 47: 1928–1937.
Yu FS, Yin J, Xu K, Huang J . Growth factors and corneal epithelial wound healing. Brain Res Bull 2010; 81: 229–235.
Imanishi J, Kamiyama K, Iguchi I, Kita M, Sotozono C, Kinoshita S . Growth factors: importance in wound healing and maintenance of transparency of the cornea. Prog Retin Eye Res 2000; 19: 113–129.
Wilson SE, Mohan RR, Mohan RR, Ambròsio R, Hong J, Lee J . The corneal wound healing response: cytokine-mediated interaction of the epithelium, stroma, and inflammatory cells. Prog Retin Eye Res 2001; 20: 625–637.
Alio JL, Colecha JR, Pastor S, Rodriguez A, Artola A . Symptomatic dry eye treatment with autologous platelet-rich plasma. Ophthalmic Res 2007; 39: 124–129.
Alio JL, Pastor S, Ruiz-Colecha J, Rodriguez A, Artola A . Treatment of ocular surface syndrome after LASIK with autologous platelet-rich plasma. J Refract Surg 2007; 23: 617–619.
Lopez-Plandolit S, Morales MC, Freire V, Etxebarria J, Duran JA . Plasma rich in growth factors as a therapeutic agent for persistent corneal epithelial defects. Cornea 2010; 29: 843–848.
Geremicca W, Fonte C, Vecchio S . Blood components for topical use in tissue regeneration: evaluation of corneal lesions treated with platelet lysate and considerations on repair mechanisms. Blood Transfus 2010; 8: 107–112.
Lopez-Plandolit S, Morales MC, Freire V, Grau AE, Duran JA . Efficacy of plasma rich in growth factors for the treatment of dry eye. Cornea 2011; 30: 1312–1317.
Eppley BL, Woodell JE, Higgins J . Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: implications for wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004; 114: 1502–1508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pezzotta, S., Fante, C., Scudeller, L. et al. Autologous platelet lysate for treatment of refractory ocular GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 47, 1558–1563 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.64
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.64
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The disposable bandage soft contact lenses therapy and anterior segment optical coherence tomography for management of ocular graft-versus-host disease
BMC Ophthalmology (2021)
-
Autologous Blood Products: When, Where, and How?
Current Ophthalmology Reports (2021)
-
Long-term safety and efficacy of autologous platelet lysate drops for treatment of ocular GvHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)