Abstract
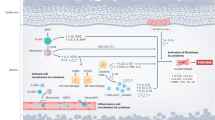
Treatment of sclerodermatous chronic GVHD (cGVHD) remains disappointing. Imatinib mesylate enables selective, dual inhibition of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) and PDGF pathways. Recently, the drug's effects on fibroblasts have been reported in both in vitro and in vivo studies. The inhibition of fibroblast growth and decreased collagen production in dermal fibroblasts is thus a logical therapeutic approach. Two patients who developed refractory sclerodermatous cGVHD following allo-SCT received imatinib mesylate at the dose of 400 mg/day. In both patients, the scleroderma symptoms disappeared within 3 months of initiation of the treatment. At the time of this report, the two patients were both alive and had a very good skin response. This report shows that imatinib is effective in patients with refractory sclerodermatous cGVHD. Considering its well-documented clinical profile in other diseases, imatinib is a promising candidate for the treatment of sclerodermatous cGVHD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suciu S, Mandelli F, de Witte T, Zittoun R, Gallo E, Labar B et al. Allogeneic compared with autologous stem cell transplantation in the treatment of patients younger than 46 years with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete remission (CR1): an intention-to-treat analysis of the EORTC/GIMEMAAML-10 trial. Blood 2003; 102: 1232–1240.
Hunault M, Harousseau JL, Delain M, Truchan-Graczyk M, Cahn JY, Witz F et al. Better outcome of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia after early genoidentical allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) than after late high-dose therapy and autologous BMT: a GOELAMS trial. Blood 2004; 104: 3028–3037.
Sanders JE, Im HJ, Hoffmeister PA, Gooley TA, Woolfrey AE, Carpenter PA et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for infants with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2005; 105: 3749–3756.
Micol JB, Berthon C, Tricot S, Terriou L, Darre S, Cracco P et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with fludarabine and 2-Gy TBI-based conditioning regimen for chronic hematological malignancy: a study of 25 consecutive patients and a literature review. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 321–329.
Yakoub-Agha I, de La Salmoniere P, Ribaud P, Sutton L, Wattel E, Kuentz M et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: a long-term study of 70 patients-report of the French society of bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 963–971.
Baudard M, Vincent A, Moreau P, Kergueris MF, Harousseau JL, Milpied N . Mycophenolate mofetil for the treatment of acute and chronic GVHD is effective and well tolerated but induces a high risk of infectious complications: a series of 21 BM or PBSC transplant patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 287–295.
Marcellus DC, Altomonte VL, Farmer ER, Horn TD, Freemer CS, Grant J et al. Etretinate therapy for refractory sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1999; 93: 66–70.
Skert C, Patriarca F, Sperotto A, Cerno M, Fili C, Zaja F et al. Sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, predictors and outcome. Haematologica 2006; 91: 258–261.
Giralt SA, Arora M, Goldman JM, Lee SJ, Maziarz RT, McCarthy PL et al. Impact of imatinib therapy on the use of allogeneic haematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2007; 137: 461–467.
O′Brien SG, Deininger MW . Imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Semin Hematol 2003; 40 (2 Suppl 2): 26–30.
Blanke C . Current management of GIST. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2004; 2: 280–283.
Vuorinen K, Gao F, Oury TD, Kinnula VL, Myllarniemi M . Imatinib mesylate inhibits fibrogenesis in asbestos-induced interstitial pneumonia. Exp Lung Res 2007; 33: 357–373.
Chaudhary NI, Roth GJ, Hilberg F, Muller-Quernheim J, Prasse A, Zissel G et al. Inhibition of PDGF, VEGF and FGF signalling attenuates fibrosis. Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 976–985.
Daniels CE, Wilkes MC, Edens M, Kottom TJ, Murphy SJ, Limper AH et al. Imatinib mesylate inhibits the profibrogenic activity of TGF-beta and prevents bleomycin-mediated lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1308–1316.
Sandler C, Joutsiniemi S, Lindstedt KA, Juutilainen T, Kovanen PT, Eklund KK . Imatinib mesylate inhibits platelet derived growth factor stimulated proliferation of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 347: 31–35.
Soria A, Cario-Andre M, Lepreux S, Rezvani HR, Pasquet JM, Pain C et al. The effect of imatinib (Glivec) on scleroderma and normal dermal fibroblasts: a preclinical study. Dermatology 2008; 216: 109–117.
Rodnan GP, Lipinski E, Luksick J . Skin thickness and collagen content in progressive systemic sclerosis and localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 1979; 22: 130–140.
Guardiola P, Runde V, Bacigalupo A, Ruutu T, Locatelli F, Boogaerts MA et al. Retrospective comparison of bone marrow and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells for allogeneic stem cell transplantation using HLA identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2002; 99: 4370–4378.
Storek J, Gooley T, Siadak M, Bensinger WI, Maloney DG, Chauncey TR et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation may be associated with a high risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1997; 90: 4705–4709.
Gay S, Jones Jr RE, Huang GQ, Gay RE . Immunohistologic demonstration of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and sis-oncogene expression in scleroderma. J Invest Dermatol 1989; 92: 301–303.
George J, Roulot D, Koteliansky VE, Bissell DM . In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: a potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 12719–12724.
Johnson RJ, Raines EW, Floege J, Yoshimura A, Pritzl P, Alpers C et al. Inhibition of mesangial cell proliferation and matrix expansion in glomerulonephritis in the rat by antibody to platelet-derived growth factor. J Exp Med 1992; 175: 1413–1416.
Santiago B, Gutierrez-Canas I, Dotor J, Palao G, Lasarte JJ, Ruiz J et al. Topical application of a peptide inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta1 ameliorates bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis. J Invest Dermatol 2005; 125: 450–455.
Denton CP, Merkel PA, Furst DE, Khanna D, Emery P, Hsu VM et al. Recombinant human anti-transforming growth factor beta1 antibody therapy in systemic sclerosis: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled phase I/II trial of CAT-192. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 323–333.
Distler JH, Jungel A, Huber LC, Schulze-Horsel U, Zwerina J, Gay RE et al. Imatinib mesylate reduces production of extracellular matrix and prevents development of experimental dermal fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 56: 311–322.
Kiani A, Habermann I, Schake K, Neubauer A, Rogge L, Ehninger G . Normal intrinsic Th1/Th2 balance in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia not treated with interferon-alpha or imatinib. Haematologica 2003; 88: 754–761.
Leder C, Ortler S, Seggewiss R, Einsele H, Wiendl H . Modulation of T-effector function by imatinib at the level of cytokine secretion. Exp Hematol 2007; 35: 1266–1271.
Mohty M, Blaise D, Olive D, Gaugler B . Imatinib: the narrow line between immune tolerance and activation. Trends Mol Med 2005; 11: 397–402.
Acknowledgements
We are especially grateful to those two patients who kindly agreed for publication of their photos in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magro, L., Catteau, B., Coiteux, V. et al. Efficacy of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of refractory sclerodermatous chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 42, 757–760 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.252
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.252
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor levels matter in treating chronic GVHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2019)
-
Prospective evaluation of sequential treatment of sclerotic chronic graft versus host disease with rituximab and nilotinib
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)
-
Risk model incorporating donor IL6 and IFNG genotype and gastrointestinal GVHD can discriminate patients at high risk of steroid refractory acute GVHD
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Pre-transplantation risk factors to develop sclerotic chronic GvHD after allogeneic HSCT: A multicenter retrospective study from the Société Française de Greffe de Moelle et de Thérapie Cellulaire (SFGM-TC)
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Risk stratification of organ-specific GVHD can be improved by single-nucleotide polymorphism-based risk models
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)