Summary:
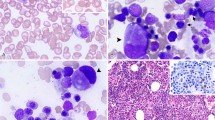
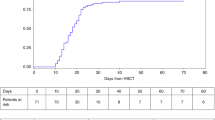
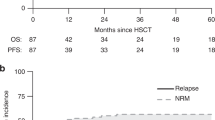
Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (aCML) occurs rarely and is associated with a poor prognosis when treated with conventional chemotherapy. We evaluated the outcome of aCML after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Nine patients were transplanted from HLA-identical siblings (n=4), HLA-compatible unrelated donors (n=4) or twin brother (n=1). Median follow-up was 55 months after transplant (range, 9.1–118.1 months). One patient who was transplanted in advanced disease with bone marrow from his twin brother relapsed 19 months post transplant. This patient was successfully retransplanted from the original donor. All patients remained in complete remission. Analysis of the leukocyte chimerism of peripheral white blood cells and bone marrow buffy coat cells by VNTR-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and single-nucleotide polymorphism real-time PCR revealed complete chimerism in all patients who had received an allogeneic transplant. One patient suffering from cerebral toxoplasmosis died 9 months post transplant. All other patients were alive at the time of analysis. Our findings suggest that the outcome of allogeneic or syngeneic transplantation in patients with aCML may not be worse than the outcome of transplantation for BCR-ABL-positive CML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vardiman JW, Brunning RD, Harris NL . Chronic myeloproliferative disease. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H and Vardiman JW (eds). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001, pp 15–44.
Shtalrid M, Talpaz M, Blick M et al. Philadelphia-negative chronic myelogenous leukemia with breakpoint cluster region rearrangement: molecular analysis, clinical characteristics, and response to therapy. J Clin Oncol 1988; 6: 1569–1575.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT et al. The chronic myeloid leukaemias: guidelines for distinguishing chronic granulocytic, atypical chronic myeloid, and chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. Proposals by the French–American–British Cooperative Leukaemia Group. Br J Haematol 1994; 87: 746–754.
Galton DA . Haematological differences between chronic granulocytic leukaemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 1992; 7: 343–350.
Aurich J, Duchayne E, Huguet-Rigal F et al. Clinical, morphological, cytogenetic and molecular aspects of series of Ph-negative chronic myeloid leukemias. Hematol Cell Ther 1998; 40: 149–158.
Vardiman JW, Imbert M, Pierre R et al. Atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia. In: Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H and Vardiman JW (eds). Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001, pp 53–54.
Montefusco E, Alimena G, Lo Coco F et al. Ph-negative and bcr-abl negative atypical chronic myelogenous leukemia: biological features and clinical outcome. Ann Hematol 1992; 65: 17–21.
Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, Shtalrid M et al. Philadelphia chromosome-negative chronic myelogenous leukemia without breakpoint cluster region rearrangement: a chronic myeloid leukemia with distinct clinical course. Blood 1990; 75: 445–452.
Oscier DG . Atypical chronic myeloid leukaemia, a distinct clinical entity related to the myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 1996; 92: 582–586.
Costello R, Sainty D, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Gabert J . Clinical and biological aspects of Philadelphia-negative/BCR-negative chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 1997; 25: 225–232.
Kurzrock R, Bueso-Ramos CE, Kantarjian H et al. BCR rearrangement-negative chronic myelogenous leukemia revisited. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2915–2926.
Hernandez JM, del Canizo MC, Cuneo A et al. Clinical, hematological and cytogenetic characteristics of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Ann Oncol 2000; 11: 441–444.
Kapaun P, Kabisch H, Held KR et al. Atypical chronic myelogenous leukemia in a patient with trisomy 8 mosaicism syndrome. Ann Hematol 1993; 66: 57–58.
Elmaagacli AH, Runkel K, Steckel N et al. A comparison of chimerism and minimal residual disease between four different allogeneic transplantation methods in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in first chronic phase. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 27: 809–815.
Thomas ED, Storb R, Clift RA et al. Bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1975; 292: 895–902.
Elmaagacli AH, Peceny R, Steckel N et al. Outcome of transplantation of highly purified peripheral blood CD34+ cells with T cell add-back compared to unmanipulated bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells from HLA-identical sibling donors in patients with first chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2003; 101: 446–453.
Alizadeh M, Bernard M, Danic B et al. Quantitative assessment of hematopoietic chimerism after bone marrow transplantation by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Blood 2002; 99: 4618–4625.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Non-parametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Cortes J, Giles F, O’Brien S et al. Results of imatinib mesylate therapy in patients with refractory or recurrent acute myeloid leukemia, high risk myelodysplastic syndrome, and myeloproliferative disorders. Cancer 2003; 97: 2760–2766.
Elmaagacli AH, Basoglu S, Peceny R et al. Improved disease-free-survival after transplantation of peripheral blood stem cells as compared to bone marrow from HLA-identical unrelated donors in patients with first chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 1130–1135.
Gratwohl A, Hermans J, Goldman JM et al. Risk assessment for patients with chronic leukemia before allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation. Lancet 1998; 352: 1087–1092.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Katja Ahrens, Melanie Kroll, and Ines Riepenhoff for their excellent technical performance of the BCR-ABL PCR, the VNTR-PCR and SNP real-time PCR analyses. This work was supported by grants of the Deutsche José Carreras Leukämie-Stiftung e.V. DJCLS-R02/11 and Deutsche Krebshilfe 70-3093-El4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koldehoff, M., Beelen, D., Trenschel, R. et al. Outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 34, 1047–1050 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704686
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704686
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Treatment of MDS/MPN and the MDS/MPN IWG International Trial: ABNL MARRO
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2019)
-
Recent Progress in Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia and Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2017)
-
An Exercise in Extrapolation: Clinical Management of Atypical CML, MDS/MPN-Unclassifiable, and MDS/MPN-RS-T
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2016)
-
The CSF3R T618I mutation as a disease-specific marker of atypical CML post allo-SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
I Walk the Other Line: Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Overlap Syndromes
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2014)