Abstract
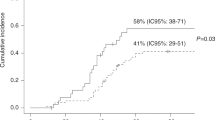
We conducted a retrospective review of the clinical features and outcome of adenovirus infection in 572 consecutive patients transplanted in a single centre over a 10 year period. One hundred patients (17%) had a total of 105 episodes of adenovirus infection diagnosed at a median of 18 days post transplant (range 2–150 days). The incidence was higher in children than adults (21% vs 9%, P < 0.001) and in unrelated donor vs matched sibling donor transplants (26% vs 9%, P < 0.001). Diarrhoea and fever were the most common presenting features. Reflecting these symptoms, the most common site of isolation was the stool. Serotypes 1, 2 and 7 were the most frequently seen (total of 41/68 or 60% of evaluable cases). In six patients (6%) adenovirus infection was the direct cause of death occurring at a median of 72 days post transplant (range 18–365 days). Five of these six patients had pulmonary involvement and four had associated graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Three further patients were considered to have severe adenoviral disease (total incidence 9%). Isolation of virus from multiple sites correlated with a poor outcome (P < 0.001). Comorbid viral infection was common in this group with 50% of all patients having other viruses isolated (predominantly polyoma virus and cytomegalovirus). We conclude that adenovirus is commonly isolated after bone marrow transplant and is a cause of significant morbidity but was a rare cause of mortality (6/572 = 1%) in our patient group as a whole. The relative infrequency of severe infection will make it difficult for the transplant physician to decide which patients should receive experimental antiviral drugs such as ribavirin and cidofovir or immunomodulatory therapy with donor white cell infusions. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 26, 1333–1338.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marks DI, Cullis JO, Ward KN et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia using sibling and volunteer unrelated donors. A comparison of complications in the first 2 years Ann Intern Med 1993 119: 207–214
Bowden RA . Other viruses after bone marrow transplantation. In: Forman SJ, Blume K, Thomas ED (eds) Bone Marrow Transplantation Blackwell: Boston 1994 pp 443–445
Meyers JD, Reed EC, Shepp DH et al. Acyclovir for prevention of cytomegalovirus infection and disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation New Engl J Med 1988 318: 70–75
McCarthy AJ, Kingman HM, Kelly C et al. The outcome of 26 patients with respiratory syncytial virus infection following allogeneic stem cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 24: 1315–1322
Shields AF, Hackman RC, Fife KH et al. Adenovirus infection in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation New Engl J Med 1985 312: 529–533
Wasserman R, August CS, Plotkin SA . Viral infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant patients Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988 7: 109–115
Flomenberg P, Babbitt J, Drobyski WR et al. Increasing incidence of adenovirus disease in bone marrow transplant recipients J Infect Dis 1994 169: 775–781
Cassano WF . Intravenous ribavirin therapy for adenovirus cystitis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1991 7: 247–248
Chen FE, Liang RH, Lo JY et al. Treatment of adenovirus-associated haemorrhagic cystitis with ganciclovir Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 20: 997–999
Izadifar-legrand F, Berrebi D, Faye A et al. Early diagnosis of adenovirus infection and treatment with cidofovir after bone marrow transplantation in children Blood 1999 94: 341a (Abstr.)
Oakhill A, Pamphilon DH, Potter MN et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children with relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second complete remission Br J Haematol 1996 94: 574–578
Green A, Clarke E, Hunt L et al. Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who receive T cell-depleted HLA mismatched marrow allografts from unrelated donors have an increased incidence of primary graft failure but a similar overall transplant outcome Blood 1999 94: 2236–2246
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA matched sibling donors Transplantation 1974 18: 295–304
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathological study of 20 Seattle patients Am J Med 1980 69: 204–217
Charles AK, Caul EO, Porter HJ, Oakhill A . Fatal adenovirus 32 infection in a bone marrow transplant recipient J Clin Pathol 1995 48: 779–781
Sencer SF, Haake RJ, Weisdorf DJ . Hemorrhagic cystitis after bone marrow transplantation. Risk factors and complications Transplantation 1993 56: 875–879
Davis D, Henslee PJ, Markesberry WR . Fatal adenovirus meningoencephalitis in a bone marrow transplant patient Ann Neurol 1988 23: 385–389
Ambinder RF, Burns W, Forman M et al. Hemorrhagic cystitis associated with adenovirus infection in bone marrow transplantation Arch Intern Med 1986 146: 1400–1401
Hale GE, Heslop HE, Krance RA et al. Adenovirus infection after pediatric bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 23: 277–282
Troussard X, Bauduer F, Gallet E et al. Virus recovery from stools of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1993 12: 573–576
Yolken RH, Bishop CA, Townsend TR et al. Infectious gastroenteritis in bone marrow transplant recipients New Engl J Med 1982 306: 1010–1012
Walter EA, Greenberg PD, Gilbert MJ et al. Reconstitution of cellular immunity against cytomegalovirus in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow by transfer of T-cell clones from the donor New Engl J Med 1995 333: 1038–1044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldwin, A., Kingman, H., Darville, M. et al. Outcome and clinical course of 100 patients with adenovirus infection following bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 26, 1333–1338 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702716
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702716