Abstract
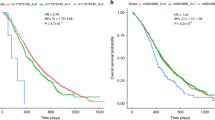
We investigated the possible influence of 86 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), known to associate with the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC), on overall survival and time to recurrence (TTR) in 733 Italian CRC patients followed up for up to 84 months after surgery. In the Cox multivariate analysis, adjusted for gender, age, pathological stage and adjuvant chemotherapy (yes/no), the risk of death significantly increased by rare allele count (P<0.05) for rs1801133 (MTHFR), rs4939827 (SMAD7), rs2306283 (SLCO1B1) and rs12898159 (BMP4), whereas for rs736775 (GPX3) the opposite was observed. Two additional SNPs associated with TTR, namely rs16892766 (downstream of EIF3H) and rs10749971 (COLCA2). Our findings show that some genetic variants previously found to associate with CRC risk are also associated with survival after treatment. The identification of alleles defining subgroups of patients with worse clinical outcome may have application in developing pharmacogenetic strategies aimed at personalizing CRC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM . Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2893–2917.
Huxley RR, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Clifton P, Czernichow S, Parr CL, Woodward M . The impact of dietary and lifestyle risk factors on risk of colorectal cancer: a quantitative overview of the epidemiological evidence. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 171–180.
Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK, Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M et al. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer—analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 78–85.
Houlston RS, Webb E, Broderick P, Pittman AM, Di Bernardo MC, Lubbe S et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies four new susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1426–1435.
Houlston RS, Cheadle J, Dobbins SE, Tenesa A, Jones AM, Howarth K et al. Meta-analysis of three genome-wide association studies identifies susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer at 1q41, 3q26.2, 12q13.13 and 20q13.33. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 973–977.
Lascorz J, Forsti A, Chen B, Buch S, Steinke V, Rahner N et al. Genome-wide association study for colorectal cancer identifies risk polymorphisms in German familial cases and implicates MAPK signalling pathways in disease susceptibility. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 1612–1619.
Tomlinson IP, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L, Broderick P, Howarth K, Pittman AM et al. A genome-wide association study identifies colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 10p14 and 8q23.3. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 623–630.
Tomlinson IP, Carvajal-Carmona LG, Dobbins SE, Tenesa A, Jones AM, Howarth K et al. Multiple common susceptibility variants near BMP pathway loci GREM1, BMP4, and BMP2 explain part of the missing heritability of colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002105.
Peters U, Hutter CM, Hsu L, Schumacher FR, Conti DV, Carlson CS et al. Meta-analysis of new genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer risk. Hum Genet 2012; 131: 217–234.
Tenesa A, Farrington SM, Prendergast JG, Porteous ME, Walker M, Haq N et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on 11q23 and replicates risk loci at 8q24 and 18q21. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 631–637.
Zanke BW, Greenwood CM, Rangrej J, Kustra R, Tenesa A, Farrington SM et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 8q24. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 989–994.
Lubbe SJ, Pittman AM, Olver B, Lloyd A, Vijayakrishnan J, Naranjo S et al. The 14q22.2 colorectal cancer variant rs4444235 shows cis-acting regulation of BMP4. Oncogene 2012; 31: 3777–3784.
Dai J, Gu J, Huang M, Eng C, Kopetz ES, Ellis LM et al. GWAS-identified colorectal cancer susceptibility loci associated with clinical outcomes. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 1327–1331.
Cicek MS, Slager SL, Achenbach SJ, French AJ, Blair HE, Fink SR et al. Functional and clinical significance of variants localized to 8q24 in colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 2009; 18: 2492–2500.
Tenesa A, Theodoratou E, Din FV, Farrington SM, Cetnarskyj R, Barnetson RA et al. Ten common genetic variants associated with colorectal cancer risk are not associated with survival after diagnosis. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 3754–3759.
Abuli A, Lozano JJ, Rodriguez-Soler M, Jover R, Bessa X, Munoz J et al. Genetic susceptibility variants associated with colorectal cancer prognosis. Carcinogenesis 2013; 34: 2286–2291.
Xing J, Myers RE, He X, Qu F, Zhou F, Ma X et al. GWAS-identified colorectal cancer susceptibility locus associates with disease prognosis. Eur J Cancer 2011; 47: 1699–1707.
Sargent D, Sobrero A, Grothey A, O'Connell MJ, Buyse M, Andre T et al. Evidence for cure by adjuvant therapy in colon cancer: observations based on individual patient data from 20 898 patients on 18 randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 872–877.
Andre T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3109–3116.
Marcuello E, Altes A, del Rio E, Cesar A, Menoyo A, Baiget M . Single nucleotide polymorphism in the 5' tandem repeat sequences of thymidylate synthase gene predicts for response to fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer 2004; 112: 733–737.
Thomas F, Motsinger-Reif AA, Hoskins JM, Dvorak A, Roy S, Alyasiri A et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genetic polymorphisms and toxicity to 5-FU-based chemoradiation in rectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2011; 105: 1654–1662.
Braun MS, Richman SD, Thompson L, Daly CL, Meade AM, Adlard JW et al. Association of molecular markers with toxicity outcomes in a randomized trial of chemotherapy for advanced colorectal cancer: the FOCUS trial. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5519–5528.
Pelucchi S, Mariani R, Calza S, Fracanzani AL, Modignani GL, Bertola F et al. CYBRD1 as a modifier gene that modulates iron phenotype in HFE p.C282Y homozygous patients. Haematologica 2012; 97: 1818–1825.
Clarke GM, Anderson CA, Pettersson FH, Cardon LR, Morris AP, Zondervan KT . Basic statistical analysis in genetic case-control studies. Nat Protoc 2011; 6: 121–133.
De Mattia E, Toffoli G . C677T and A1298C MTHFR polymorphisms, a challenge for antifolate and fluoropyrimidine-based therapy personalisation. Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 1333–1351.
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, Goyette P, Sheppard CA, Matthews RG et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat Genet 1995; 10: 111–113.
Niemi M, Pasanen MK, Neuvonen PJ . Organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1: a genetically polymorphic transporter of major importance for hepatic drug uptake. Pharmacol Rev 2011; 63: 157–181.
Innocenti F, Kroetz DL, Schuetz E, Dolan ME, Ramirez J, Relling M et al. Comprehensive pharmacogenetic analysis of irinotecan neutropenia and pharmacokinetics. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 2604–2614.
Phipps AI, Newcomb PA, Garcia-Albeniz X, Hutter CM, White E, Fuchs CS et al. Association between colorectal cancer susceptibility loci and survival time after diagnosis with colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2012; 143: 51–54.
Tenesa A, Dunlop MG . New insights into the aetiology of colorectal cancer from genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 353–358.
Xu Y, Pasche B . TGF-beta signaling alterations and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: R14–R20.
Pittman AM, Naranjo S, Jalava SE, Twiss P, Ma Y, Olver B et al. Allelic variation at the 8q23.3 colorectal cancer risk locus functions as a cis-acting regulator of EIF3H. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1001126.
Mahmood SF, Gruel N, Chapeaublanc E, Lescure A, Jones T, Reyal F et al. A siRNA screen identifies RAD21, EIF3H, CHRAC1 and TANC2 as driver genes within the 8q23, 8q24.3 and 17q23 amplicons in breast cancer with effects on cell growth, survival and transformation. Carcinogenesis 2014; 35: 670–682.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Valerie Matarese for scientific editing and writing support. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC, grant no. 12162). The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study, in the collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, or in the preparation, review or approval of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noci, S., Dugo, M., Bertola, F. et al. A subset of genetic susceptibility variants for colorectal cancer also has prognostic value. Pharmacogenomics J 16, 173–179 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2015.35
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2015.35
This article is cited by
-
Effects of the SLCO1B1 A388G single nucleotide polymorphism on the development, clinical parameters, treatment, and survival of multiple myeloma cases in a Polish population
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Gut microbiota composition in colorectal cancer patients is genetically regulated
Scientific Reports (2022)