Abstract
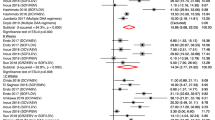
Polymorphism of interleukin 28B gene represents a powerful outcome predictor for interferon-based regimens in hepatitis C virus infection. However, some studies report conflicting results. The predictive value of interleukin 28B genotype over the outcome interferon-α/ribavirin treatment was thoroughly evaluated and compared with virological predictors of response. Literature revision was performed on PubMed. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) were calculated by fixed- or random-effects models. Heterogeneity and publication bias were also assessed. Sixty-two eligible papers including 20 290 patients were retrieved. Both polymorphisms (rs12979860 and rs8099917) were strongly associated with response (OR=4.09 and 4.00, respectively), however, the association was weaker for subjects infected with viral genotypes 2 and 3 (OR=1.52 and 1.49, respectively). Compared with interleukin 28B genotype, the association with response was lower for baseline viremia (OR=2.15) and higher for rapid virological response (OR=13.86). These results provide a critical evaluation of interleukin 28B genotype as a pharmacogenetic predictor in hepatitis C patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rauch A, Kutalik Z, Descombes P, Cai T, Di Iulio J, Mueller T et al. Genetic variation in IL28B is associated with chronic hepatitis C and treatment failure: a genome-wide association study. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 1338–1345.
Lavanchy D . The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int 2009; 29: 74–81.
Lauer GM, Walker BD . Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 41–52.
McHutchison JG, Bacon BR . Chronic hepatitis C: an age wave of disease burden. Am J Manag Care 2005; 11: S286–S295.
Blachier M, Leleu H, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Valla D-C, Roudot-Thoraval F . The burden of liver disease in Europe: a review of available epidemiological data. J Hepatol 2013; 58: 593–608.
Davis GL, Alter MJ, El-Serag H, Poynard T, Jennings LW . Aging of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected persons in the United States: a multiple cohort model of HCV prevalence and disease progression. Gastroenterology 2010; 138: 513–521.
Hoofnagle JH, Seeff LB . Peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2444–2451.
Alter HJ, Liang TJ . Hepatitis C: the end of the beginning and possibly the beginning of the end. Ann Intern Med 2012; 156: 317–318.
Ferenci P . Predictors of response to therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Semin Liver Dis 2004; 24: 25–31.
McHutchison JG, Lawitz EJ, Shiffman ML, Muir AJ, Galler GW, McCone J et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b or alfa-2a with ribavirin for treatment of hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med 2009; 36: 580–593.
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ et al. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009; 461: 399–401.
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N et al. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1105–1109.
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, Berg T, Weltman M, Abate ML et al. IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1100–1104.
Thompson AJ, Muir AJ, Sulkowski MS, Ge D, Fellay J, Shianna KV et al. Interleukin-28B polymorphism improves viral kinetics and is the strongest pretreatment predictor of sustained virologic response in genotype 1 hepatitis C virus. Gastroenterology 2010; 139: 120–129.
Bitetto D, Fattovich G, Fabris C, Ceriani E, Falleti E, Fornasiere E et al. Complementary role of vitamin D deficiency and the interleukin-28B rs12979860 C/T polymorphism in predicting antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2011; 53: 1118–1126.
Chen JY, Lin CY, Wang CM, Lin YT, Kuo SN, Shiu CF et al. IL28B genetic variations are associated with high sustained virological response (SVR) of interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy in Taiwanese chronic HCV infection. Genes Immun 2011; 12: 300–309.
Takita M, Hagiwara S, Arizumi T, Hayaishi S, Ueda T, Kitai S et al. Association of interleukin-28B and hepatitis C genotype 1 with a high viral load and response to pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy. Digestion 2011; 84: 56–61.
Umemura T, Joshita S, Yoneda S, Katsuyama Y, Ichijo T, Matsumoto A et al. Serum interleukin (IL)-10 and IL-12 levels and IL28B gene polymorphisms: pretreatment prediction of treatment failure in chronic hepatitis C. Antivir.Ther 2011; 16: 1073–1080.
Dill MT, Duong FH, Vogt JE, Bibert S, Bochud PY, Terracciano L et al. Interferon-induced gene expression is a stronger predictor of treatment response than IL28B genotype in patients with hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2011; 140: 1021–1031.
Kurosaki M, Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sakamoto N, Enomoto N, Honda M et al. Pre-treatment prediction of response to pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C using genetic polymorphism in IL28B and viral factors. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 439–448.
Liao XW, Ling Y, Li XH, Han Y, Zhang SY, Gu LL et al. Association of genetic variation in IL28B with hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance in the Chinese Han population. Antivir Ther 2011; 16: 141–147.
Lopez-Rodriguez R, Trapero-Marugan M, Borque MJ, Roman M, Hernandez-Bartolome A, Rodriguez-Munoz Y et al. Genetic variants of interferon-stimulated genes and IL-28B as host prognostic factors of response to combination treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2011; 90: 712–21.
Lyoo K, Song MJ, Hur W, Choi JE, Hong SW, Kim CW et al. Polymorphism near the IL28B gene in Korean hepatitis C virus-infected patients treated with peg-interferon plus ribavirin. J Clin Virol 2011; 52: 363–366.
Mangia A, Thompson AJ, Santoro R, Piazzolla V, Copetti M, Minerva N et al. Limited use of interleukin 28B in the setting of response-guided treatment with detailed on-treatment virological monitoring. Hepatology 2011; 54: 772–780.
Fattovich G, Covolo L, Bibert S, Askarieh G, Lagging M, Clement S et al. IL28B polymorphisms, IP-10 and viral load predict virological response to therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011; 33: 1162–1172.
de Rueda PM, Lopez-Nevot MA, Saenz-Lopez P, Casado J, Martin-Casares A, Palomares P et al. Importance of host genetic factors HLA and IL28B as predictors of response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Am.J.Gastroenterol. 2011; 106: 1246–54.
Halfon P, Bourliere M, Ouzan D, Maor Y, Renou C, Wartelle C et al. A single IL28B genotype SNP rs12979860 determination predicts treatment response in patients with chronic hepatitis C Genotype 1 virus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 23: 931–935.
Miyaaki H, Ichikawa T, Yatsuhashi H, Taura N, Miuma S, Usui T et al. Suppressor of cytokine signal 3 and IL28 genetic variation predict the viral response to peginterferon and ribavirin. Hepatol Res 2011; 41: 1216–1222.
Ridruejo E, Solano A, Marciano S, Galdame O, Adrover R, Cocozzella D et al. Genetic variation in interleukin-28B predicts SVR in hepatitis C genotype 1 Argentine patients treated with PEG IFN and ribavirin. Ann Hepatol 2011; 10: 452–457.
Scherzer TM, Hofer H, Staettermayer AF, Rutter K, Beinhardt S, Steindl-Munda P et al. Early virologic response and IL28B polymorphisms in patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 3 treated with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin. J Hepatol 2011; 54: 866–871.
Hashimoto Y, Ochi H, Abe H, Hayashida Y, Tsuge M, Mitsui F et al. Prediction of response to peginterferon-alfa-2b plus ribavirin therapy in Japanese patients infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 1b. J Med Virol 2011; 83: 981–988.
Hayashi K, Katano Y, Honda T, Ishigami M, Itoh A, Hirooka Y et al. Association of interleukin 28B and mutations in the core and NS5A region of hepatitis C virus with response to peg-interferon and ribavirin therapy. Liver Int 2011; 31: 1359–1365.
Hayes CN, Kobayashi M, Akuta N, Suzuki F, Kumada H, Abe H et al. HCV substitutions and IL28B polymorphisms on outcome of peg-interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy. Gut 2011; 60: 261–267.
Hsu CS, Hsu SJ, Chen HC, Tseng TC, Liu CH, Niu WF et al. Association of IL28B gene variations with mathematical modeling of viral kinetics in chronic hepatitis C patients with IFN plus ribavirin therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 3719–3724.
Sporea I, Popescu A, Curescu M, Sirli R, Dan I, Goldis A et al. The correlation of Il28B genotype with sustained virologic response in Romanian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepat Mon 2011; 11: 975–979.
Venegas M, Villanueva RA, Gonzalez K, Brahm J . IL28B polymorphisms associated with therapy response in Chilean chronic hepatitis C patients. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17: 3636–3639.
Yu ML, Huang CF, Huang JF, Chang NC, Yang JF, Lin ZY et al. Role of interleukin-28B polymorphisms in the treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection in Asian patients. Hepatology 2011; 53: 7–13.
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Hirakawa M, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, Suzuki Y et al. Amino acid substitution in HCV core/NS5A region and genetic variation near IL28B gene affect treatment efficacy to interferon plus ribavirin combination therapy. Intervirology 2012; 55: 231–241.
Asselah T, De Muynck S, Broet P, Masliah-Planchon J, Blanluet M, Bieche I et al. IL28B polymorphism is associated with treatment response in patients with genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 527–532.
De Nicola S, Aghemo A, Rumi MG, Galmozzi E, Valenti L, Soffredini R et al. Interleukin 28B polymorphism predicts pegylated interferon plus ribavirin treatment outcome in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4. Hepatology 2012; 55: 336–342.
Howell CD, Gorden A, Ryan KA, Thompson AJ, Ibrahim C, Fried M et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism upstream of interleukin 28B associated with phase 1 and phase 2 of early viral kinetics in patients infected with HCV genotype 1. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 557–563.
Cavalcante LN, Abe-Sandes K, Angelo AL, Machado TM, Lemaire DC, Mendes CM et al. IL28B polymorphisms are markers of therapy response and are influenced by genetic ancestry in chronic hepatitis C patients from an admixed population. Liver Int 2012; 32: 476–486.
Ciesla A, Bociaga-Jasik M, Sobczyk-Krupiarz I, Glowacki MK, Owczarek D, Cibor D et al. IL28B polymorphism as a predictor of antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18: 4892–4897.
Fischer J, Böhm S, Scholz M, Müller T, Witt H, George J et al. Combined effects of different interleukin-28B gene variants on the outcome of dual combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C virus type 1 infection. Hepatology 2012; 55: 1700–1710.
Guo X, Zhao Z, Xie J, Cai Q, Zhang X, Peng L et al. Prediction of response to pegylated-interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy in Chinese patients infected with different hepatitis C virus genotype. Virol.J 2012; 9: 123.
Huang CF, Yeh ML, Huang JF, Yang JF, Hsieh MY, Lin ZY et al. Host interleukin-28B genetic variants versus viral kinetics in determining responses to standard-of-care for Asians with hepatitis C genotype 1. Antiviral Res 2012; 93: 239–244.
Karchava M, Sharvadze L, Chkhartishvili N, Nelson K, Gochitashivli N, Gatserelia L et al. IL28B favorable genotype and ultrarapid viral response as the earliest treatment predictors of a sustained viral response in a Georgian cohort infected with the hepatitis C genotype 1. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 24: 817–823.
Ladero JM, Martin EG, Fernandez C, Carballo M, Devesa MJ, Martinez C et al. Predicting response to therapy in chronic hepatitis C: an approach combining interleukin-28B gene polymorphisms and clinical data. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 27: 279–285.
Martinez-Gomez LE, Chavez-Tapia NC, Burguete-Garcia AI, Aguilar-Olivos N, Madrid-Marina V, Roman-Bahena M et al. IL28B polymorphisms predict the response to chronic hepatitis C virus infection treatment in a Mexican population. Ann Hepatol 2012; 11: 876–881.
Petta S, Ferraro D, Camma C, Cabibi D, Di Cristina A, Di M V et al. Vitamin D levels and IL28B polymorphisms are related to rapid virological response to standard of care in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther 2012; 17: 823–831.
Ramos JA, Ramos AL, Hoffmann L, Perez RM, Coelho HS, Urmenyi TP et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism, rs129679860, in the IL28B locus is associated with the viral kinetics and a sustained virological response in a chronic, monoinfected hepatitis C virus genotype-1 Brazilian population treated with pegylated interferon-ribavirin. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2012; 107: 888–892.
Kim SR, El Shamy A, Imoto S, Kim KI, Ide YH, Deng L et al. Prediction of response to pegylated interferon/ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1b and high viral load. J Gastroenterol 2012; 47: 1143–1151.
Riva E, Scagnolari C, Monteleone K, Selvaggi C, Picardi A, Mazzarelli C et al. Interleukin-28B (IL-28B) single-nucleotide polymorphisms and interferon plus ribavirin treatment outcome in Italian chronically HCV-infected patients. J Viral Hepat 2012; 19: 650–653.
Shaker OG,. Sadik NA . Polymorphisms in interleukin-10 and interleukin-28B genes in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 4 and their effect on the response to pegylated interferon/ribavirin-therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 27: 1842–1849.
Tolmane I, Rozentale B, Keiss J, Ivancenko L, Subnikova N, Reinholde Z et al. Interleukin 28B gene polymorphism and association with chronic hepatitis C therapy results in Latvia. Hepat Res Treat 2012; 2012: 324090.
Valenti L, Aghemo A, Stattermayer AF, Maggioni P, De Nicola S, Motta BM et al. Implications of PNPLA3 polymorphism in chronic hepatitis C patients receiving peginterferon plus ribavirin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012; 35: 1434–1442.
Saito H, Ito K, Sugiyama M, Matsui T, Aoki Y, Imamura M et al. Factors responsible for the discrepancy between IL28B polymorphism prediction and the viral response to peginterferon plus ribavirin therapy in Japanese chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatol.Res 2012; 42: 958–965.
Ogawa E, Furusyo N, Murata M, Ikezaki H, Ihara T, Hayashi T et al. Insulin resistance undermines the advantages of IL28B polymorphism in the pegylated interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin treatment of chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 1. J Hepatol 2012; 57: 534–540.
Vidal-Castineira JR, Lopez-Vazquez A, Alonso-Arias R, Moro-Garcia MA, Martinez-Camblor P, Melon S et al. A predictive model of treatment outcome in patients with chronic HCV infection using IL28B and PD-1 genotyping. J.Hepatol. 2012; 56: 1230–8.
Xie JQ, Guo XY, Zhang XH, Lin BL, Xie DY, Gao ZL et al. Relationship between the genetic variation in interleukin 28B and response to antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Chin Med J 2012; 125: 2334–2338.
Derbala M, Rizk N, Shebl F, Alkaabi S, Eldweik N, John A et al. Interleukin-28 and hepatitis C virus genotype-4: treatment-induced clearance and liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18: 7003–7008.
Liu CH, Liang CC, Liu CJ, Tseng TC, Lin CL, Yang SS et al. Interleukin 28B genetic polymorphisms and viral factors help identify HCV genotype-1 patients who benefit from 24-week pegylated interferon plus ribavirin therapy. Antivir Ther 2012; 17: 477–484.
Bucci C, von Delft A, Christian A, Flemming VM, Harrison A, Halliday J et al. 'Favourable' IL28B polymorphisms are associated with a marked increase in baseline viral load in hepatitis C virus subtype 3a infection and do not predict a sustained virological response after 24 weeks of therapy. J Gen Virol 2013; 94: 1259–1265.
Del Campo JA, Ampuero J, Rojas L, Conde M, Rojas A, Maraver M et al. Insulin resistance predicts sustained virological response to treatment of chronic hepatitis C independently of the IL28b rs12979860 polymorphism. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013; 37: 74–80.
Grandi T, da Silva CM, Amaral KM, Picon PD, Costi C, da Fre NN et al. Response to treatment in Brazilian patients with chronic hepatitis C is associated with a single-nucleotide polymorphism near the interleukin-28B gene. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2013; 108: 48–53.
Jung YK, Kim JH, Ahn SM, Yang JW, Park SJ, Kim JW et al. Role of Interleukin 28B-related gene polymorphisms in chronic hepatitis C and the response to antiviral therapy in Koreans. J Clin Gastroenterol 2013; 47: 644–650.
Neukam K, Barreiro P, Rivero-Juarez A, Caruz A, Mira JA, Camacho A et al. Pegylated interferon plus ribavirin is suboptimal in IL28B CC carriers without rapid response. J Infect 2013; 67: 59–64.
Pasha HF, Radwan MI, Hagrass HA, Tantawy EA, Emara MH . Cytokines genes polymorphisms in chronic hepatitis C: impact on susceptibility to infection and response to therapy. Cytokine 2013; 61: 478–484.
Pavon-Castillero EJ, Munoz-de-Rueda P, Lopez-Segura R, Gila A, Quiles R, Munoz-Gamez JA et al. Importance of IL-10 and IL-6 during chronic hepatitis c genotype-1 treatment and their relation with IL28B. Cytokine 2013; 61: 595–601.
Seto WK, Tsang OT, Liu K, Chan JM, Wong DK, Fung J et al. Role of IL28B and inosine triphosphatase polymorphisms in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 6 infection. J Viral Hepat 2013; 20: 470–477.
Stenkvist J, Sonnerborg A, Weiland O . HCV RNA decline in chronic HCV genotype 2 and 3 during standard of care treatment according to IL28B polymorphism. J Viral Hepat 2013; 20: 193–199.
Sterne JAC, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JPA, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J . Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011; 342: d4002.
Cariani E, Villa E, Rota C, Critelli R, Trenti T . Translating pharmacogenetics into clinical practice: interleukin (IL)28B and inosine triphosphatase (ITPA) polymophisms in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin Chem Lab Med 2011; 49: 1247–1256.
Chen Y, Xu HX, Wang LJ, Liu XX, Mahato RI, Zhao YR . Meta-analysis: IL28B polymorphisms predict sustained viral response in HCV patients treated with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012; 36: 91–103.
Schreiber J, Moreno C, Garcia BG, Louvet A, Trepo E, Henrion J et al. Meta-analysis: the impact of IL28B polymorphisms on rapid and sustained virological response in HCV-2 and -3 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2012; 36: 353–362.
Jia Z, Ding Y, Tian S, Niu J, Jiang J . Test of IL28B polymorphisms in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with PegIFN and ribavirin depends on HCV genotypes: results from a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2012; 7: e45698.
Jiménez-Sousa MA, Fernández-Rodríguez A, Guzmán-Fulgencio M, García-Álvarez M, Resino S . Meta-analysis: implications of interleukin-28B polymorphisms in spontaneous and treatment-related clearance for patients with hepatitis C. BMC Med 2013; 11: 6.
Rangnekar AS, Fontana RJ . IL-28B polymorphisms and the response to antiviral therapy in HCV genotype 2 and 3 varies by ethnicity: a meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat 2013; 20: 377–384.
Lai M, Afdhal NH . Clinical utility of interleukin-28B testing in patients with genotype 1. Hepatology 2012; 56: 367–372.
Chou R, Hartung D, Rahman B, Wasson N, Cottrell EB, Fu R . Comparative effectiveness of antiviral treatment for hepatitis C virus infection in adults: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 2013; 158: 114–123.
Thompson AJ, McHutchison JG . Will IL28B polymorphism remain relevant in the era of direct-acting antiviral agents for hepatitis C virus? Hepatology 2012; 56: 373–81.
Liu S, Cipriano LE, Holodniy M, Owens DK, Goldhaber-Fiebert JD . New protease inhibitors for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann Intern Med 2012; 156: 279–290.
Cammà C, Petta S, Enea M, Bruno R, Bronte F, Capursi V et alWEF Study Group. Cost-effectiveness of boceprevir or telaprevir for untreated patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2012; 56: 850–860.
Lawitz E, Mangia A, Wyles D, Rodriguez-Torres M, Hassanein T, Gordon SC et al. Sofosbuvir for previously untreated chronic hepatitis C infection. N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 1878–1887.
Petta S, Cabibbo G, Enea M, Macaluso FS, Plaia A, Bruno R et alWEF Study Group. Cost-effectiveness of sofosbuvir-based triple therapy for untreated patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2014; 59: 1692–1705.
Jayasekera CR, Barry M, Roberts LR, Nguyen MH . Treating hepatitis C in lower-income countries. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 1869–1871.
Liang TJ, Ghany MG . Therapy of hepatitis C—Back to the future. N Engl J Med 2014; 370: 2043–2047.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Chiara Bassi (Area Governance della ricerca, Regione Emilia Romagna) for help and advice in literature search. This work was supported by Programma di Ricerca Regione-Università 2013—Area 2 ‘Ricerca per il Governo Clinico’ (Regione Emilia Romagna), code PRUa2-2013-00002033.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cariani, E., Roli, L., Missale, G. et al. Interleukin 28B polymorphisms as predictors of sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics J 16, 18–29 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2015.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2015.28
This article is cited by
-
Correlation between IL-28 polymorphism and spontaneous clearance in HCV patients: systematic review and meta-analysis
Archives of Virology (2021)
-
EGFR rs11506105 and IFNL3 SNPs but not rs8099917 are strongly associated with treatment responses in Iranian patients with chronic hepatitis C
Genes & Immunity (2017)