Abstract
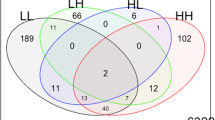
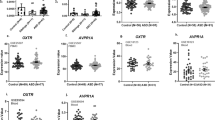
Children with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) often have severe behavioral problems. Not all children with these problems respond to atypical antipsychotic medications; therefore, we investigated whether peripheral blood gene expression before treatment with risperidone, an atypical antipsychotic, was associated with improvements in severe behavioral disturbances 8 weeks following risperidone treatment in 42 ASD subjects (age 112.7±51.2 months). Exon expression levels in blood before risperidone treatment were compared with pre–post risperidone change in Aberrant Behavior Checklist-Irritability (ABC-I) scores. Expression of exons within five genes was correlated with change in ABC-I scores across all risperidone-treated subjects: GBP6, RABL5, RNF213, NFKBID and RNF40 (α<0.001). RNF40 is located at 16p11.2, a region implicated in autism and schizophrenia. Thus, these genes expressed before treatment were associated with subsequent clinical response. Future studies will be needed to confirm these results and determine whether this expression profile is associated with risperidone response in other disorders, or alternative antipsychotic response within ASD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
des Portes V, Hagerman RJ, Hendren RL . Pharmacotherapy. In: Ozonoff S, Rogers SJ, Hendren RL (eds). Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Research Review for Practitioners. American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, 2003, pp 161–186.
Williams SK, Scahill L, Vitiello B, Aman MG, Arnold LE, McDougle CJ et al. Risperidone and adaptive behavior in children with autism. J Am Acad Child Adolescent Psychiatry 2006; 45: 431–439.
Bantick RA, Deakin JF, Grasby PM . The 5-HT1A receptor in schizophrenia: a promising target for novel atypical neuroleptics? J Psychopharmacol 2001; 15: 37–46.
Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY . Relationship between dopaminergic and serotonergic neuronal activity in the frontal cortex and the action of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 1999; 249 (Suppl 4): 90–98.
Swann AC . Neuroreceptor mechanisms of aggression and its treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 2003; 64 (Suppl 4): 26–35.
Tarazi FI, Zhang K, Baldessarini RJ . Long-term effects of olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine on dopamine receptor types in regions of rat brain: implications for antipsychotic drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 297: 711–717.
McDougle CJ, Hollway J, Scahill L, Koenig K, Aman MG, McGough JJ et al. Risperidone for the core symptom domains of autism: results from the study by the autism network of the research units on pediatric psychopharmacology. Am J Psychiatry 2005; 162: 1142–1148.
McCracken JT, McGough J, Shah B, Cronin P, Hong D, Aman MG et al. Risperidone in children with autism and serious behavioral problems. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: 314–321.
Shea S, Turgay A, Carroll A, Schulz M, Orlik H, Smith I et al. Risperidone in the treatment of disruptive behavioral symptoms in children with autistic and other pervasive developmental disorders. Pediatrics 2004; 114: E634–E641.
Pandina GJ, Bossie CA, Zhu Y, Flanders S . The aberrant behavior checklist: use in clinical trials of pediatric autism. J Child Adolescent Psychopharmacol 2006; 16: 661–662.
Posey DJ, McDougle CJ . The pharmacotherapy of target symptoms associated with autistic disorder and other pervasive developmental disorders. Harv Rev Psychiatry 2000; 8: 45–63.
Su KP, Wu PL, Pariante CM . A cross-over study on safety of lipid profiles associated with olanzapine and risperidone. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2005; 15: S463–S464.
Danielyan A, Kowatch RA . Management options for bipolar disorder in children and adolescents. Paediatr Drugs 2005; 7: 277–294.
Bottai T, Quintin P, Perrin E . Antipsychotics and the risk of diabetes: a general data review. Eur Psychiatry 2005; 20 (Suppl 4): S349–S357.
McKee JR, Bodfish JW, Mahorney SL, Heeth WL, Ball MP . Metabolic effects associated with atypical antipsychotic treatment in the developmentally disabled. J Clin Psychiatry 2005; 66: 1161–1168.
Erickson CA, Stigler KA, Posey DJ, McDougle CJ . Risperidone in pervasive developmental disorders. Expert Rev Neurother 2005; 5: 713–719.
Stamova B, Xu H, Jickling G, Bushnell C, Tian Y, Ander BP et al. Gene expression profiling of blood for the prediction of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2010; 41: 2171–2177.
Sollner T, Bennett MK, Whiteheart SW, Scheller RH, Rothman JE . A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell 1993; 75: 409–418.
Muller DJ, Klempan TA, De Luca V, Sicard T, Volavka J, Czobor P et al. The SNAP-25 gene may be associated with clinical response and weight gain in antipsychotic treatment of schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 2005; 379: 81–89.
Haase J, Killian AM, Magnani F, Williams C . Regulation of the serotonin transporter by interacting proteins. Biochem Soc Trans 2001; 29 (Part 6): 722–728.
Hanson E, Nasir RH, Fong A, Lian A, Hundley R, Shen Y et al. Cognitive and behavioral characterization of 16p11.2 deletion syndrome. J Dev Behav Pediatr 2010; 31: 649–657.
Shen Y, Dies KA, Holm IA, Bridgemohan C, Sobeih MM, Caronna EB et al. Clinical genetic testing for patients with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics 2010; 125: e727–e735.
Vassos E, Collier DA, Holden S, Patch C, Rujescu D, St Clair D et al. Penetrance for copy number variants associated with schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2010; 19: 3477–3481.
Borden KL, Freemont PS . The RING finger domain: a recent example of a sequence-structure family. Curr Opin Struct Biol 1996; 6: 395–401.
Sunderman Jr FW . The clinical biochemistry of 5′-nucleotidase. Ann Clin Lab Sci 1990; 20: 123–139.
Arnold LE, Farmer C, Kraemer HC, Davies M, Witwer A, Chuang S et al. Moderators, mediators, and other predictors of risperidone response in children with autistic disorder and irritability. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2010; 20: 83–93.
Correia CT, Almeida JP, Santos PE, Sequeira AF, Marques CE, Miguel TS et al. Pharmacogenetics of risperidone therapy in autism: association analysis of eight candidate genes with drug efficacy and adverse drug reactions. Pharmacogenomics J 2010; 10: 418–430.
Ikeda M, Tomita Y, Mouri A, Koga M, Okochi T, Yoshimura R et al. Identification of novel candidate genes for treatment response to risperidone and susceptibility for schizophrenia: integrated analysis among pharmacogenomics, mouse expression, and genetic case-control association approaches. Biol Psychiatry 2010; 67: 263–269.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the participation of study volunteers and their families. This study was supported by R21MH080026 (RLH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
Supplementary information
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lit, L., Sharp, F., Bertoglio, K. et al. Gene expression in blood is associated with risperidone response in children with autism spectrum disorders. Pharmacogenomics J 12, 368–371 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.23
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2011.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Meta-analysis of GWAS of over 16,000 individuals with autism spectrum disorder highlights a novel locus at 10q24.32 and a significant overlap with schizophrenia
Molecular Autism (2017)
-
Bridging Autism Spectrum Disorders and Schizophrenia through inflammation and biomarkers - pre-clinical and clinical investigations
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
-
Transcriptome analysis of microglia in a mouse model of Rett syndrome: differential expression of genes associated with microglia/macrophage activation and cellular stress
Molecular Autism (2017)
-
Prescription trends in children with pervasive developmental disorders: a claims data-based study in Japan
World Journal of Pediatrics (2016)
-
Pharmacogenomic Medicine in Autism: Challenges and Opportunities
Pediatric Drugs (2015)