Abstract
Cardiomyopathy is an important cause of heart failure in Sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for up to 30% of adult heart failure hospitalisations. This high prevalence poses a challenge in societies without access to resources and interventions essential for disease management. Over 80 genes have been implicated as a cause of cardiomyopathy. Mutations in the phospholamban (PLN) gene are associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and severe heart failure. In Africa, the prevalence of PLN mutations in cardiomyopathy patients is unknown. Our aim was to screen 315 patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (n = 111), DCM (n = 95), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (n = 40) and peripartum cardiomyopathy (n = 69) for disease-causing PLN mutations by high resolution melt analysis and DNA sequencing. We detected the previously reported PLN c.25C > T (p.R9C) mutation in a South African family with severe autosomal dominant DCM. Haplotype analysis revealed that this mutation occurred against a different haplotype background to that of the original North American family and was therefore unlikely to have been inherited from a common ancestor. No other mutations in PLN were detected (mutation prevalence = 0.2%). We conclude that PLN is a rare cause of cardiomyopathy in African patients. The PLN p.R9C mutation is not well-tolerated, emphasising the importance of this gene in cardiac function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Cardiomyopathy is defined as a myocardial disease in which the heart muscle is structurally and functionally abnormal, without hypertension, coronary artery disease, valvular disease or congenital heart disease which is sufficient to cause the observed myocardial abnormality1. It is a major cause of heart disease in Sub-Saharan Africa, accounting for 20–30% of adults hospitalised for acute heart failure in the region2. Cardiomyopathy poses a challenge in Africa because of its high prevalence in resource-poor societies, the difficulty of diagnosis, the limited access to effective interventions and the associated high mortality3. Cardiomyopathies can be primary (genetic, mixed or acquired) or secondary (infiltrative, toxic or inflammatory)4.
Cardiomyopathies are known to be caused by genes that have cytoskeletal, contractile and calcium regulatory functions5. One of the genes implicated in cardiomyopathy is phospholamban (PLN), which encodes the phospholamban protein that is involved in calcium signalling and muscle contraction. Mutations in PLN have been associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)6,7,8, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)9 and recently arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) in North America and Europe10, but the role of PLN in Africans with cardiomyopathy is unknown11. A PLN founder mutation, PLN p.R14del, was identified in large European cohorts, including 10–15% of Dutch patients with ARVC or DCM, and was associated with high mortality and poor prognosis10,12. As this mutation arose 575–825 years ago, the possibility exists that the PLN p.R14del founder mutation may be present in descendants of Dutch settlers and may cause cardiomyopathy in a subset of individuals of European descent in Southern Africa13. The aim of this study was to determine if PLN is a cause of cardiomyopathy in Africans, and explore the possibility of PLN founder mutations common between the African population and individuals with European ancestry.
Results
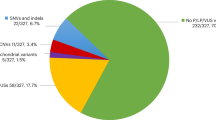
Mutation screening of PLN in 315 patients with cardiomyopathy (ARVC (n = 111)14, DCM (n = 95)15, HCM (n = 40)16, and peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM) (n = 69))17 revealed the previously reported c.25C > T (p.R9C) mutation in a proband of European descent with severe DCM (DCM 320.1; Individual II:2)6. This mutation results in the alteration of a conserved amino acid (Fig. 1A,B) from an arginine (R) to a cysteine (C) and was absent in 200 ethnically matched control chromosomes. No PLN mutations were detected in individuals with ARVC, HCM or PPCM.
(A) Electropherogram showing the c.25C > T sequence change. (B) Multiple species protein alignment of this sequence. (C) Pedigree of family DCM 320 showing variant c.25C > T and individuals with DCM. SB: Stillbirth; Gender (Square – Male; Circle – Female); Clinical Status (Black symbol – Affected; Clear symbol – Unaffected;? – Diagnosis uncertain); Mutation Status ( + – c.25C > T positive; – – c.25C > T negative).
Detailed investigations into the ancestry of individual DCM 320.1 pointed to an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern within this DCM family (Fig. 1C). The proband (DCM 320.1; II:2) had a heart transplant at the age of 35 years while her younger sister (DCM 320.5; II:3) was likewise affected with DCM and required a heart transplant at the age of 39 years. The proband’s son (DCM 320.3; III:1) developed DCM at the age of 24 years and underwent a heart transplant a year later. The echocardiogram showed features of DCM with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 20%. Coronary angiography showed patent epicardial coronary arteries, and left ventriculography displayed a dilated left ventricle with poor systolic function. The proband’s daughter (DCM 320.4; III:3) was asymptomatic but the echocardiogram showed borderline dilatation of the left ventricle (left ventricular end diastolic dimension of 5.3 cm) and left ventricular ejection fraction of 47%. Further enquiry also revealed that the proband’s mother had died of a heart condition at the age of 36 years. However, we were not able to confirm whether this individual was affected with DCM.
Subsequent mutation screening of PLN for the available members of this family found the c.25C > T (p.R9C) mutation in the proband’s affected son (DCM 320.3; Individual III:1) and daughter (DCM 320.4; Individual III:3) as well as the proband’s affected sister (DCM 320.6;Individual II:3), reflecting segregation of the c.25C > T mutation with DCM in this family.
Bioinformatic analysis tools MutationTaster, PolyPhen-2 and Align GVGD predicted the PLN c.25C > T (p.R9C) mutation to be disease-causing. Further, transgenic mice bearing the PLN p.R9C mutation developed severe DCM and underwent premature death, confirming the pathogenicity of this mutation6. Bioinformatic RNA tools mfold and RNAfold predicted this variant would change mRNA secondary structure whereas the ESEfinder tool predicted that this variant would alter serine/arginine-rich splicing factor (SRSF1 and SRSF5) exonic splice enhancer recognition sites.
As the PLN c.25C > T mutation was previously reported in a family of European descent by Schmitt and colleagues6, we wanted to ascertain if these mutations arose independently or if they were inherited from a common ancestor, possibly as early as the 17th century with the European colonisation of South Africa. Haplotypes were constructed using published microsatellite markers spanning 5.15 Mb across the PLN gene (D6S454, PLN −200 K, PLN +200 K and D6S412)13. In the DCM 320 family, the PLN c.25C > T mutation was found to be part of a disease-specific haplotype spanning this 5.15 Mb region (Fig. 2A). The PLN c.25C > T mutation was found to be part of a different haplotype spanning 1.85 Mb in the MDO DCM family described by Schmitt et al.6 (Fig. 2B).
Discussion
In the initial report of the PLN c.25C > T (p.R9C) mutation by Schmitt and colleagues6, the mutation was associated with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern in DCM which was characterised by increased cardiac chamber dimensions, decreased contractile function at 20–30 years of age and progression to heart failure within 5–10 years after symptom onset6, a phenotype remarkably similar to that observed in the DCM 320 family. Similarly, in the recent report by Truszkowska and others, the PLN p.R9C mutation was detected in an individual with acute onset of DCM at the age of 21 years, leading to heart transplantation at 22 years of age18.
Functional analysis of the effect of the PLN p.R9C mutation on the protein and its role in the development of DCM revealed significant consequences of this mutation. A transgenic mouse model harbouring the p.R9C mutation was shown to develop DCM6. Further evidence has suggested that PLN p.R9C results in decreased responsiveness to β-adrenergic stimulation secondary to reduced phosphorylation by protein kinase A6,19,20. This results in altered calcium kinetics and aberrant contractility. The presence of severe DCM in this family with PLN p.R9C reinforces the importance of this mutation in the pathogenesis of DCM.
We have established that the PLN c.25C > T mutation forms part of a disease-specific haplotype spanning 5.15 Mb across PLN in the DCM 320 family that differed from the 1.85 Mb haplotype observed in the MDO DCM family described by Schmitt et al.6. It is therefore unlikely that this mutation was inherited from a common ancestor. By contrast, the PLN p.R14del mutation, has been identified as a founder mutation in a large Dutch cohort of patients with ARVC, as well patients from Germany and Spain13,21. A mouse model with cardiac-specific overexpression of this mutation presented with DCM associated with arrhythmias, cardiac fibrosis and premature death8.
Although a total of 315 South African cardiomyopathy patients (ARVC, DCM, HCM, and PPCM) were screened in this study, only one disease-causing mutation was found in PLN (frequency of 0.2%) illustrating that PLN is not a common cause of cardiomyopathy in South Africa. The failure to detect PLN mutations in patients with PPCM is consistent with the findings of others22. To date, there are six PLN mutations (c.25C > T (p.R9C)6,18, c.26G > T (p.R9L)23,24, c.26G > A (p.R9H)24, c.40_42delAGA (p.R14del)8,10,13,25,26, c.73C > T (p.R25C)27 and c.116T > G (p.L39X)7) that are associated with DCM, one with ARVC (c.40_42delAGA (p.R14del)10) and three with HCM (c.116T > G (p.L39X)9,28, c.1-77A > G29 and c.1-42C > G30) (Table 1).
While the majority of these PLN mutations have been associated with severe cardiomyopathy, only PLN mutations associated with DCM meet the strict criteria to be called definitively pathogenic. These are nonsynonymous variants that alter a highly conserved amino acid residue across species, are absent from large numbers of healthy controls, demonstrate statistically significant co-segregation with affected members of a family, and are identified by an unbiased genetic approach. Important additional evidence comes from (1) the recapitulation of disease in animals engineered to express the variant, as exists for the PLN p.R9C mutation6 or (2) the same mutation is identified in unrelated individuals with the disease phenotype, as we have demonstrated herein for the PLN p.R9C mutation.
As far as we are aware, the three PLN mutations detected in patients with HCM are disease-associated and cannot be classified as definitely pathogenic for several reasons. First, the authors who reported the PLN c.116T > G (p.L39X) mutation in HCM provide evidence indicating the association of this mutation with HCM in a single proband31. There is no apparent familial segregation of this mutation with disease. The authors also provide no functional evidence demonstrating the role of this mutation in disease pathogenesis. Other authors provide evidence that this mutation is associated with disease in a single proband with HCM. The proband’s daughter carried the mutation but was unaffected with HCM, while the 3 year old granddaughter was affected with this disease28. The authors suggest that this may be due to incomplete penetrance associated with this mutation, but the fact that the affected granddaughter is so young calls this explanation into question. Also, no functional evidence is provided for the role of this mutation in DCM pathogenesis. Second, the PLN c.1-77A > G has been associated with HCM in a single proband29. No evidence for familial segregation or functional evidence suggesting a role of this mutation in HCM pathogenesis is provided. Finally, Medin et al. report the PLN c.1-42C > G variant as associated with disease in a family with HCM32. One of the proband’s sons was unaffected with HCM even though he carried the mutation, which may be explained by incomplete penetrance. However, no functional evidence suggesting the role of this variant in DCM pathogenesis is provided. For these reason, we classify these three variants as HCM-associated but not definitely pathogenic (Table 1).
In conclusion, we have identified the previously characterised c.25C > T PLN mutation that segregates with severe DCM in a South African kindred following the screening of 315 patients with different types of cardiomyopathy. No PLN mutations were identified in subjects with ARVC, HCM or PPCM. PLN mutations are a rare cause of cardiomyopathy in South Africans which should be added to screening panel for cardiomyopathy in the country.
Methods
The methods were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines of the University of Cape Town Human Research Ethics Committee, and they are presented in terms of samples, genetic screening, and bioinformatic analysis, and microsatellite analysis below.
Samples
South African patients with ARVC (n = 111; 46% of European descent), DCM (n = 95; 8% of European descent), HCM (n = 40; 33% of European descent) and PPCM (n = 69; 10% of European descent) were referred to the Cardiac Clinic in Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town for genetic evaluation. ARVC cases were enrolled in the Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Registry of South Africa. The diagnosis of ARVC was made according to the modified criteria set by the Task Force of the Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology33. DCM, PPCM and HCM patients were diagnosed on the basis of the definitions of the European Society of Cardiology1. The details on methods of clinical evaluation, demographics and clinical parameters of patients enrolled in this study have been described previously14,15,16,17.
Blood samples were collected for molecular genetic testing. The population controls were anonymous blood donors from the Western Province Blood Transfusion Service who provided blood samples for DNA isolation. The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the University of Cape Town, and informed consent was obtained from all participants. All ARVC cases included in this study had previously been screened for mutations in the desmosomal genes (DSP, PKP2, DSC2, DSG2 and JUP) known to cause ARVC but were found not to harbour any pathogenic mutations. In our screen we included 315 ARVC, DCM, HCM and PPCM cases with unidentified pathogenic mutations.
Genetic screening
Mutation screening of PLN included 111 ARVC, 95 DCM, 40 HCM, and 69 PPCM patients and was performed by high resolution melt analysis (HRM) and Sanger sequencing using the following primers: Forward – 5′-CCAGGCTACCTAAAAGAAGAC-3′; Reverse – 5′-TTCCTGTCTGCATGGGATG-3′. HRM is proven mutation screening method with a high sensitivity and specificity34. HRM reactions were prepared using 0.5U GoTaq® Flexi DNA Polymerase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 5X Colorless GoTaq® Flexi Buffer (Promega), 3 mM (final reaction concentration) MgCl2 (Promega), 0.8 μM dNTPs (final reaction concentration) (Bioline, London, United Kingdom), EvaGreen dye (Biotium, Hayward, CA, USA) and 0.4 μM of each primer (final reaction concentration). HRM reactions were conducted using the RotorGene 6000 (Corbett Life Sciences – Qiagen, Venlo, Limber, Netherlands) and conditions were 95 °C for 10 minutes, 50 cycles of 95 °C for 5 seconds, 55 °C for 10 seconds and 72 °C for 10 seconds, and a high resolution melt from 72 °C to 95 °C with 0.1 °C increases in temperature. Samples displaying changes in HRM profiles relative to controls were earmarked for purification and sequencing. HRM products were purified using Exonuclease I (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) and FastAPTM Thermosensitive Alkaline Phosphatase (Promega) using a Mastercycler® pro thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany); conditions were 37 °C for 1 hour and 75 °C for 15 minutes. Sequencing reactions were prepared using the BigDye® Direct Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems – Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Reaction conditions were 96 °C for 5 minutes and 25 cycles of 96 °C for 30 seconds, 50 °C for 15 seconds and 60 °C for 4 minutes. Sequencing products were analysed using capillary electrophoresis with the ABI PRISM® 3130 × l Genetic Analyser (Applied Biosystems) at the DNA Sequencing Unit (Department of Genetics, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town). The prevalence of variants of interest in the control population was determined by screening 200 ethnically matched control chromosomes by high resolution melt analysis and Sanger sequencing.
Bioinformatic analysis
Bioinformatic analysis of the PLN variants of interest was conducted using various bioinformatic tools [mfold (http://mfold.rna.albany.edu/?q=mfold/RNA-Folding-Form), RNAfold (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAfold.cgi), ESEFinder (http://rulai.cshl.edu/cgi-bin/tools/ESE3/esefinder.cgi?process=home), PolyPhen-2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/), SIFT (http://sift.jcvi.org/www/SIFT_seq_submit2.html), Align GVGD (http://agvgd.iarc.fr/agvgd_input.php) and MutationTaster (http://www.mutationtaster.org/)] to assess the impact of the variants on PLN structure and function at the mRNA and protein levels.
Microsatellite analysis
MDO DCM DNA samples for microsatellite analysis were obtained from Professor Christine Seidman (Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA). The D6S45413, PLN −200 K13, PLN +200 K13 and D6S41213 microsatellite markers were used to construct haplotypes for PLN. PCR products were run on a 2% agarose gel for verification of reaction success and product size and specificity. These products were then analysed using capillary electrophoresis with the ABI PRISM® 3130 × l Genetic Analyser (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) at the Division of Human Genetics, University of Cape Town. Results were analysed using GeneMapper® v4.1 software (Applied Biosystems) and haplotypes were constructed using Cyrillic v2.0 (Cyrillic Software, United Kingdom).
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Fish, M. et al. Mutation analysis of the phospholamban gene in 315 South Africans with dilated, hypertrophic, peripartum and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathies. Sci. Rep. 6, 22235; doi: 10.1038/srep22235 (2016).
Change history
18 May 2016
A correction has been published and is appended to both the HTML and PDF versions of this paper. The error has not been fixed in the paper.
References
Elliott, P. et al. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: a position statement from the european society of cardiology working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur Heart J 29, 270–276 (2008).
Damasceno, A. et al. The causes, treatment, and outcome of acute heart failure in 1006 Africans from 9 countries: Results of the sub-saharan africa survey of heart failure. Arch Int Med 172, 1386–1394, 10.1001/archinternmed.2012.3310 (2012).
Sliwa, K., Damasceno, A. & Mayosi, B. M. Epidemiology and etiology of cardiomyopathy in Africa. Circulation 112, 3577–3583, 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.542894 (2005).
Wexler, R. K., Elton, T., Pleister, A. & Feldman, D. Cardiomyopathy: an overview. Am Fam Physician 79, 778–784 (2009).
Watkins, H., Ashrafian, H. & Redwood, C. Inherited Cardiomyopathies. N Engl J Med 364, 1643–1656, 10.1056/NEJMra0902923 (2011).
Schmitt, J. P. et al. Dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure caused by a mutation in phospholamban. Science 299, 1410–1413, 10.1126/science.1081578 (2003).
Haghighi, K. et al. Human phospholamban null results in lethal dilated cardiomyopathy revealing a critical difference between mouse and human. J Clin Invest 111, 869–876, 10.1172/JCI17892 (2003).
Haghighi, K. et al. A mutation in the human phospholamban gene, deleting arginine 14, results in lethal, hereditary cardiomyopathy. PNAS 103, 1388–1393, 10.1073/pnas.0510519103 (2006).
Chiu, C. et al. Genetic screening of calcium regulation genes in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43, 337–343, 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.06.009 (2007).
van der Zwaag, P. A. et al. Phospholamban R14del mutation in patients diagnosed with dilated cardiomyopathy or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: evidence supporting the concept of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail 14, 1199–1207, 10.1093/eurjhf/hfs119 (2012).
Sliwa, K. & Mayosi, B. M. Recent advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and prognosis of acute heart failure and cardiomyopathy in Africa. Heart 99, 1317–1322, 10.1136/heartjnl-2013-303592 (2013).
van Rijsingen, I. A. et al. Outcome in phospholamban R14del carriers: results of a large multicentre cohort study. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 7, 455–465, 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000374 (2014).
van der Zwaag, P. A. et al. Recurrent and founder mutations in the Netherlands-Phospholamban p.Arg14del mutation causes arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy. Neth Heart J 21, 286–293, 10.1007/s12471-013-0401-3 (2013).
Watkins, D. A. et al. Clinical features, survival experience, and profile of plakophylin-2 gene mutations in participants of the Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Registry of South Africa. Heart Rhythm 6, S10–S17 (2009).
Ntusi, N. B. A., Badri, M., Gumedze, F., Wonkam, A. & Mayosi, B. M. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of familial and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy in Cape Town: A comparative study of 120 cases followed up over 14 years. S Afr Med J 101, 399–404 (2011).
Ntusi, N. A. B., Shaboodien, G., Badri, M., Gumedze, F. & Mayosi, B. M. Clinical features, spectrum of causal genetic mutations, and outcome of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in South Africans. Cardiovasc J Afr in press (2015).
Ntusi, N. B., Badri, M., Gumedze, F., Sliwa, K. & Mayosi, B. M. Pregnancy-Associated Heart Failure: A Comparison of Clinical Presentation and Outcome between Hypertensive Heart Failure of Pregnancy and Idiopathic Peripartum Cardiomyopathy. PLoS One 10, e0133466, 10.1371/journal.pone.0133466 (2015).
Truszkowska, G. T. et al. A study in Polish patients with cardiomyopathy emphasizes pathogenicity of phospholamban (PLN) mutations at amino acid position 9 and low penetrance of heterozygous null PLN mutations. BMC Med Genet 16, 21, 10.1186/s12881-015-0167-0 (2015).
Ha, K. N. et al. Lethal Arg9Cys phospholamban mutation hinders Ca2+ -ATPase regulation and phosphorylation by protein kinase A. PNAS 108, 2735–2740, 10.1073/pnas.1013987108 (2011).
Abrol, N., de Tombe, P. P. & Robia, S. L. Acute inotropic and lusitropic effects of cardiomyopathic R9C mutation of phospholamban. J Biol Chem 290, 7130–7140, 10.1074/jbc.M114.630319 (2015).
López-Ayala, J. M. et al. Phospholamban p.arg14del Mutation in a Spanish Family With Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Evidence for a European Founder Mutation. Rev Españ Cardiol (Engl Ed) 68, 346–349 (2015).
van Spaendonck-Zwarts, K. Y. et al. Titin gene mutations are common in families with both peripartum cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 35, 2165–2173, 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu050 (2014).
Truszkowska, G. et al. A study in Polish patients with cardiomyopathy emphasizes pathogenicity of phospholamban (PLN) mutations at amino acid position 9 and low penetrance of heterozygous null PLN mutations. BMC Med Genet 16, 21 (2015).
Medeiros, A. et al. Mutations in the human phospholamban gene in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J 162, 1088–1095.e1081, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2011.07.028 (2011).
DeWitt, M. M., MacLeod, H. M., Soliven, B. & McNally, E. M. Phospholamban R14 deletion results in late-onset, mild, hereditary dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 48, 1396–1398, 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.016 (2006).
Posch, M. G. et al. Genetic deletion of arginine 14 in phospholamban causes dilated cardiomyopathy with attenuated electrocardiographic R amplitudes. Heart Rhythm 6, 480–486, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.01.016 (2009).
Liu, G. S. et al. A novel human R25C-phospholamban mutation is associated with super-inhibition of calcium cycling and ventricular arrhythmia. Cardiovascular research 107, 164–174, 10.1093/cvr/cvv127 (2015).
Landstrom, A. P., Adekola, B. A., Bos, J. M., Ommen, S. R. & Ackerman, M. J. PLN-encoded phospholamban mutation in a large cohort of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy cases: summary of the literature and implications for genetic testing. Am Heart J 161, 165–171, 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.08.001 (2011).
Minamisawa, S. et al. Mutation of the phospholamban promoter associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304, 1–4 (2003).
Medin, M. et al. Mutational screening of phospholamban gene in hypertrophic and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and functional study of the PLN −42 C > G mutation. Eur J Heart Fail 9, 37–43, 10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.04.007 (2007).
Chiu, C. et al. Genetic screening of calcium regulation genes in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43, 337–343, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.06.009 (2007).
Medin, M. et al. Mutational screening of phospholamban gene in hypertrophic and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and functional study of the PLN –42 C > G mutation. Eur J Heart Fail 9, 37–43, 10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.04.007 (2007).
Marcus, F. I. et al. Diagnosis of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: proposed modification of the task force criteria. Circulation 121, 1533–1541, 10.1161/circulationaha.108.840827 (2010).
Liu, Y.-P. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of high resolution melting analysis for detection of KRAS mutations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 4, 7521, 10.1038/srep07521 (2014).
Ceholski, D. K., Trieber, C. A. & Young, H. S. Hydrophobic imbalance in the cytoplasmic domain of phospholamban is a determinant for lethal dilated cardiomyopathy. J Biol Chem 287, 16521–16529, 10.1074/jbc.M112.360859 (2012).
Ceholski, D. K., Trieber, C. A., Holmes, C. F. & Young, H. S. Lethal, hereditary mutants of phospholamban elude phosphorylation by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 287, 26596–26605, 10.1074/jbc.M112.382713 (2012).
Karakikes, I. et al. Correction of human phospholamban R14del mutation associated with cardiomyopathy using targeted nucleases and combination therapy. Nat Commun 6, 10.1038/ncomms7955 (2015).
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Nakita Laing and Ms Barbara McDonough for their assistance. The study was funded in part by grants from the Italian Government, the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, the South African Medical Research Council, the National Research Foundation of South Africa, and the Lily and Ernst Hausmann Research Trust, the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the National Institutes of Health, and the LaDue Memorial Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea for this analysis was conceived by B.M.M., L.C. and P.J.S. M.F., G.S. and B.M.M. designed the research. M.F. performed the research and analysed the data. S.K. conducted the phenotypic analysis of the South African family with the PLN mutation, and K.S. phenotyped the patients with peripartum cardiomyopathy. M.A.B. and C.E.S. contributed to the study comparing the haplotypes of the original family with the PLN mutation and the South African family. M.F., G.S. and B.M.M. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors have contributed to the final draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Fish, M., Shaboodien, G., Kraus, S. et al. Mutation analysis of the phospholamban gene in 315 South Africans with dilated, hypertrophic, peripartum and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathies. Sci Rep 6, 22235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22235
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22235
This article is cited by
-
The genetic basis for adult-onset idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy in people of African descent
Heart Failure Reviews (2023)
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy: a new insight into the rare but common cause of heart failure
Heart Failure Reviews (2022)
-
A bibliometric review of peripartum cardiomyopathy compared to other cardiomyopathies using artificial intelligence and machine learning
Biophysical Reviews (2022)
-
Peripartum cardiomyopathy: a global effort to find the cause and cure for the rare and little understood disease
Biophysical Reviews (2022)
-
Mutations of FAM111B gene are not associated with Systemic Sclerosis
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.