Abstract
Hair analysis for cannabinoids is extensively applied in workplace drug testing and in child protection cases, although valid data on incorporation of the main analytical targets, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC (THC-COOH), into human hair is widely missing. Furthermore, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCA-A), the biogenetic precursor of THC, is found in the hair of persons who solely handled cannabis material. In the light of the serious consequences of positive test results the mechanisms of drug incorporation into hair urgently need scientific evaluation. Here we show that neither THC nor THCA-A are incorporated into human hair in relevant amounts after systemic uptake. THC-COOH, which is considered an incontestable proof of THC uptake according to the current scientific doctrine, was found in hair, but was also present in older hair segments, which already grew before the oral THC intake and in sebum/sweat samples. Our studies show that all three cannabinoids can be present in hair of non-consuming individuals because of transfer through cannabis consumers, via their hands, their sebum/sweat, or cannabis smoke. This is of concern for e.g. child-custody cases as cannabinoid findings in a child’s hair may be caused by close contact to cannabis consumers rather than by inhalation of side-stream smoke.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Among illicit drugs cannabis is still the drug showing the highest prevalence, with an estimated 125–227 million consumers worldwide1. In hair analysis, the two main targets for cannabinoid analysis are the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and its metabolite 11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH)2. Typical models for incorporation of drugs into hair include passive diffusion from blood capillaries into matrix cells at the basement membrane of the hair follicle and diffusion from sweat or sebum into the completed hair shaft, but also the possibility of external contamination is an issue2,3. While presence of THC-COOH, which is only formed inside the body4, is considered a proof of ingestion/consumption according to the current scientific doctrine when detected in hair5,6,7,8, analysis for THC alone is still common laboratory practice, because THC-COOH hair concentrations are extremely low and afford the use of expensive instrumentation9,10. However, due to THC being present in cannabis smoke, there is a high probability of biased results caused by external contamination of the hair3,11 and the mechanism of incorporation for THC-COOH is still unknown.
Recently, in addition to THC, relatively high Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCA-A) concentrations were detected in forensic hair samples12,13. THCA-A is the non-psychoactive biosynthetic precursor of THC and the main cannabinoid in fresh cannabis plant material. When heated, e.g. during smoking or baking, THCA-A is decarboxylated yielding THC14 (Fig. 1). As relevant incorporation through the bloodstream could not be verified in previous investigations, the major part of this cannabinoid seems to originate from handling of cannabis material and subsequent transfer to the hair15. Furthermore, the chemical instability of THCA-A entails the risk of artifactually elevating the THC concentration during the analytical process, potentially leading to false positive findings12,13.
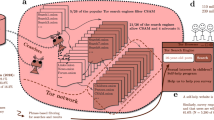
Potential incorporation pathways of cannabinoids into human hair.
Incorporation of ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCA-A), ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and its metabolite 11-nor-9-carboxy-THC (THC-COOH) into human hair can occur in the hair bulb via the bloodstream, by diffusion from sweat or sebum into the hair shaft, or by external contamination (e.g. contaminated fingers or side-stream smoke). The main metabolic pathway of THC and the molecular structures of the respective analytes are also given.
In this article, two studies are described in order to elucidate the main routes of incorporation for THC, THC-COOH and THCA-A into human hair and to provide a valid basis for correct interpretation of hair analysis results.
Results
Oral intake of THCA-A
To definitely exclude a relevant incorporation of THCA-A into hair via blood, sebum or sweat, a volunteer ingested 50 mg THCA-A daily over a 30 day period (cmax of THCA-A in serum was 2,120 ng/ml16, oral bioavailability of THCA-A: approximately 41%17). Despite a relatively high dose of 50 mg THCA-A per day (a heavy cannabis user may take up doses of several hundred mg of total THC daily and the proportion of THCA-A in cannabis smoke was found to be less than 1% by weight18), no THCA-A could be detected in any of the segmented hair samples obtained during the study. In accordance with the hair analysis results, no THCA-A could be detected in any of the sebum/sweat samples either.
Oral intake of dronabinol
In a second study, consisting of repeated oral intake of dronabinol (THC) by two volunteers over a 30 day period (2.5 mg, three times per day), the extent of THC incorporation via the bloodstream into hair was evaluated. No THC was detected at any time of sampling in all the head hair, beard hair or body hair samples (limit of detection: 1 pg/mg). From multiple serum samples taken within 8 hours (dosing interval) the estimated AUC0→24 h (THC) of the two participants ranged from 740–1,300 μg/L * min (n = 3 for each participant). Maximum serum concentrations of THC-COOH were 18 ng/mL (participant 1) and 40 ng/mL (participant 2), respectively (see Supplementary Tables S3 and S4 online). Considering the individual head hair growth rates (1.3 cm per month for both participants), THC-COOH was also detected in segments correlating to a time period located up to 2.3–3.1 months before the start of the THC intake (Fig. 2: Participant 2 showed THC-COOH positive results up to the segment 5–6 cm collected six weeks after the first intake, for participant 1 the most distal positive segment was 2–3 cm corresponding to maximum 3–4 weeks before start of THC intake; for full data see Supplementary Table S1 online). Analysing sebum/sweat samples of both participants revealed THC-COOH amounts of 4.3 to 82 pg/cm2 per day (Table 1). Analysis of hair samples from alternative sampling sites tended to show relatively high concentrations in beard, pubic and axillary hair (see Supplementary Table S2 online). In beard hair samples, THC-COOH could be detected up to 11 weeks after the last THC intake (Fig. 3).
THC-COOH concentration in beard hair after dronabinol intake.
11-nor-9-carboxy-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC-COOH) concentrations determined in the beard hair samples of two study participants before and after the intake of dronabinol (3 × 2.5 mg daily for 30 days). *For participant 1 only one sample was obtained covering weeks 8–10.
Discussion
The results strongly suggest that THCA-A is not incorporated into hair through the bloodstream or via sebum/sweat to a relevant extent. Although this was tested only in one individual, the daily dose of THCA-A was at least an order of magnitude higher than expected in excessive cannabis smokers. Therefore, the THCA-A detected in forensic hair samples (concentration range in hair samples of cannabis consumers: 46–4,700 pg/mg13) can only be explained by external contamination via handling of cannabis material15.
The incorporation rate of THC via the bloodstream into the hair seems to be negligible low as no THC could be detected in the hair samples of the participants after systemic dronabinol uptake. It follows from Fick’s law that the amount of analyte incorporated into hair should be proportional to the area under the analyte serum concentration over time curve (AUC). Given that the THC AUC0→24 h of the two participants was only less than five times lower than the AUC range found in the literature for occasional cannabis smokers after a single consumption (780–6,300 μg/L * min)19,20, it is obvious that also no relevant incorporation through the bloodstream into hair is expected to occur in cannabis users and THC detected in forensic hair samples does originate from external sources. To reach THC concentrations of 50 pg/mg (cut-off recommended by the Society of Hair Testing21) through incorporation via the bloodstream would require consumption of extremely high amounts of THC, which would certainly be associated with a several-fold higher amount of THC incorporated through contamination routes (cannabis smoke exposition and/or transfer by contaminated fingers). Consequently, THC findings in hair cannot be regarded as a proof of cannabis consumption. At the same time, oral uptake of THC or cannabis products does not necessarily lead to positive THC hair findings, which can be of interest in abstinence control.
Furthermore, the detection of THC-COOH in hair segments did not correlate to the period of THC intake and the presence of THC-COOH in sebum/sweat implicates a relevant contribution to the THC-COOH findings in hair samples by diffusion of the analyte from sebum into the hair matrix. The marked variations in the THC-COOH concentrations between body regions may be explained by differences in the physiology (e.g. presence of apocrine sweat glands in the axillary and pubic region), sampling particularities (e.g. regular shaving of beard hair vs. sampling of hair strands) and a possible transfer of the analyte due to contamination of hair with urine (pubic region). The fact, that THC-COOH was detectable up to 11 weeks past the intake period in beard hair further underlines a relevant incorporation via secretion of sebum which shows a physiological time shift, or by diffusion from surrounding tissues2.
At first glance, differentiation of the route of THC-COOH incorporation into hair seems irrelevant as long as positive THC-COOH findings in hair require THC uptake by the individual under investigation. However, considering the presence of THC-COOH in sebum/sweat, a transfer to other persons’ hair is possible. This is particularly true for young children or partners of cannabis consumers (close body contact, sleeping on the same pillow etc.). Comparing the maximum serum THC-COOH concentrations detected in persons massively exposed to cannabis smoke in a ‘coffee shop’ (0.5–1.7 ng/mL)22 to the maximum serum concentrations determined in our study (18 and 40 ng/mL), it seems very unlikely that passive smoke exposition can lead to similar THC-COOH concentrations in hair as chronic active consumption does. However, THC-COOH can be detected in hair of young children (age: <2 years)23 in concentrations similar to the concentrations detected in the hair after oral dronabinol intake. Therefore, it seems much more plausible that THC-COOH is transferred to the children’s hair by close contact to the cannabis consumers in the family context rather than by systemic uptake after exposition to cannabis smoke.
Limitations of the study
For the oral intake of THCA-A only one individual was tested. Although the extraordinary high serum concentrations reached should compensate for this, physiological characteristics of the individual may have led to THCA-A not being incorporated into hair to a measurable extent. In the study with oral intake of dronabinol a relatively low dose of THC was used, which may reflect THC uptake of moderate cannabis smokers, but not of heavy users. Therefore, measurable incorporation of THC from the blood stream cannot be excluded in the case of heavy cannabis smoking. Due to oral administration (slow resorption, first-pass effect) the maximum THC serum concentrations were lower than the maximum concentrations generally reached after smoking. Although – following from Fick’s law – incorporation should be proportional to the AUC, the diffusion coefficient may vary with the gradient. High concentration gradients as observed directly after smoking might therefore lead to a more efficient incorporation of THC. Furthermore, the number of individuals tested in this study was low (n = 2) and pharmacokinetic particularities may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusions
Knowing the main routes of cannabinoid incorporation into human hair, any interpretation of varying concentrations along the hair shaft in terms of time-resolved patterns of use may lead to false conclusions. Cases with high THC or THC-COOH concentrations in proximal hair segments are in particular critical as they may be interpreted as a recent increase of cannabis consumption. Not over-interpreting THC or THC-COOH findings in hair is of utmost importance in child protection cases, but also in the context of work place drug testing and any forensic application. Practitioners who work with results of hair analysis should be aware of these limitations and the severe consequences false conclusions could entail.
Although the results of our study cannot be transferred directly to other cannabinoids or other types of illicit drugs (in particular to less lipophilic and non-acidic compounds) the proportion of drugs incorporated into hair via the bloodstream is largely unknown and should be the focus of further research.
Methods
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Freiburg, Germany (EK-Freiburg 98/14) and the Federal Opium Agency (BfArM, Bonn, Germany) granted a permit for the intake of dronabinol. The study was registered in a World Health Organization primary register (German Clinical Trials Register; DRKS00006148, registered: 8th May 2014) and was conducted at the Institute of Forensic Medicine Freiburg, Germany, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki Principles and subsequent amendments. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Volunteers were recruited from the personal environment of the authors and affirmed that they neither consumed cannabis nor were exposed to cannabis via peers or family members prior to and during the study.
Oral intake of THCA-A
One male volunteer orally ingested 50 mg THCA-A daily over a 30 day period. Hair samples (head, chest, pubic, axillary and leg hair) were collected prior to the intake period and then on a weekly basis until three weeks after the last intake. The segmented hair samples (1 cm segments) were analysed for THCA-A applying a fully validated LC-MS/MS method24. See Supplementary Material for details.
Oral intake of dronabinol
Two male participants orally ingested 2.5 mg dronabinol (THC) three times daily over a 30 day period. Hair samples (head, beard and body hair) were collected prior to the intake period and then on a regular basis until several weeks after the last intake. Apart from hair samples, combined sebum/sweat samples were collected using Sebutapes®. All hair samples were analysed for THC and THC-COOH after alkaline hydrolysis applying a fully validated LC-MS3 method on a Shimadzu Nexera 2 UHPLC coupled to an ABSciex QTRAP 5500 linear ion-trap mass spectrometer. See Supplementary Material for details.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Moosmann, B. et al. Finding cannabinoids in hair does not prove cannabis consumption. Sci. Rep. 5, 14906; doi: 10.1038/srep14906 (2015).
References
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, World Drug Report 2014 (United Nations publication, Sales No. E.14.XI.7) (2014).
Pragst, F. & Balikova, M. A. State of the art in hair analysis for detection of drug and alcohol abuse. Clin. Chim. Acta 370, 17–49 (2006).
Thorspecken, J., Skopp, G. & Pötsch, L. In vitro contamination of hair by marijuana smoke. Clin. Chem. 50, 596–602 (2004).
Grotenhermen, F. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Cannabinoids. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 42, 327–360 (2003).
Thieme, D., Sachs, H. & Uhl, M. Proof of cannabis administration by sensitive detection of 11-nor-Delta (9)-tetrahydrocannabinol-9-carboxylic acid in hair using selective methylation and application of liquid chromatography-tandem and multistage mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 6, 112–8 (2014).
Uhl, M. & Sachs, H. Cannabinoids in hair: strategy to prove marijuana/hashish consumption. Forensic Sci. Int. 145, 143–7 (2004).
Dulaurent, S., Gaulier, J. M., Imbert, L., Morla, A. & Lachâtre, G. Simultaneous determination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, cannabinol and 11-nor-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-9-carboxylic acid in hair using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 236, 151–151 (2014).
Society of Hair Testing. Consensus on Hair Testing. http://soht.org/index.php/consensus (accessed: 30.06.2015).
Huestis, M. A. et al. Cannabinoid concentrations in hair from documented cannabis users. Forensic Sci. Int. 169, 129–136 (2007).
Sachs, H. & Dressler, U. Detection of THCCOOH in hair by MSD-NCI after HPLC clean-up. Forensic Sci. Int. 107, 239–247 (2000).
Moosmann, B., Roth, N. & Auwärter, V. Hair analysis for THCA-A, THC and CBN after passive in vivo exposure to marijuana smoke. Drug. Test. Anal. 6, 119–125 (2014).
Auwärter, V., Wohlfarth, A., Traber, J., Thieme, D. & Weinmann, W. Hair analysis for Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A - new insights into the mechanism of drug incorporation of cannabinoids into hair. Forensic Sci. Int. 196, 10–13 (2010).
Moosmann, B. et al. Cannabinoid findings in children hair – what do they really tell us? An assessment in the light of three different analytical methods with focus on interpretation of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A concentrations. Drug. Test. Anal. 7, 349–57 (2015).
Dussy, F. E., Hamberg, C., Luginbuhl, M., Schwerzmann, T. & Briellmann, T. A. Isolation of Δ9-THCA-A from hemp and analytical aspects concerning the determination of Δ9-THC in cannabis products. Forensic Sci. Int. 149, 3–10 (2005).
Moosmann, B., Roth, N. & Auwärter, V. Hair analysis for Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCA-A) and Δ9-tetrahydro-cannabinol (THC) after handling cannabis plant material. Drug Test. Anal. 10.1002/dta.1830.
Roth, N. Delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinolsäure A - Studien und Untersuchungen zur Anwendung als Cannabis-Konsummarker in der forensischen Toxikologie, PhD Thesis, University of Freiburg (2014).
Wohlfarth, A. Pharmakokinetik und Metabolismus von Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolsäure A im Menschen, PhD Thesis, University of Freiburg (2012).
Pomahacova, B., Van der Kooy, F. & Verpoorte, R. Cannabis smoke condensate III: The cannabinoid content of vaporised Cannabis sativa. Inhalation Toxicol. 21, 1108–1112 (2009).
Huestis, M. A., Henningfield, J. E. & Cone, E. J. Blood Cannabinoids. I. Absorption of THC and formation of 11-OH-THC and THCCOOH during and after smoking marijuana. J. Anal. Toxicol. 16, 276–282 (1992).
Toennes, S. W., Ramaekers, J. G., Theunissen, E. L., Moeller, M. R. & Kauert, G. F. Comparison of cannabinoid pharmacokinetic properties in occasional and heavy users smoking a marijuana or placebo joint. J. Anal. Toxicol. 32, 470–477 (2008).
Cooper, G. A. A., Kronstrand, R. & Kintz, P. Society of Hair Testing guidelines for drug testing in hair. Forensic Sci. Int. 218, 20–24 (2012).
Röhrich, J. et al. Concentrations of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and 11-nor-9-carboxytetrahydrocannabinol in blood and urine after passive exposure to cannabis smoke in a coffee shop. J. Anal. Toxicol. 34, 196–203 (2010).
Pragst, F., Broecker, S., Hastedt, M., Herre, S., Andresen-Streichert, H., Sachs, H. et al. Methadone and illegal drugs in hair from children with parents in maintenance treatment or suspected for drug abuse in a german community. Ther. Drug Monit. 35, 737–752 (2013).
Roth, N., Moosmann, B. & Auwärter, V. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for quantification of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A (THCA-A), THC, CBN and CBD in hair. J. Mass Spectrom. 48, 227–233 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for helpful comments and discussion to Leslie King (retired, Basingstoke, UK), Fritz Pragst (Institute of Legal Medicine, Charité-University Medicine Berlin, Germany), Annette Thierauf-Emberger and Stefan Pollak (both Institute of Forensic Medicine Freiburg, Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.A. and B.M. conceived and supervised the projects. B.M. and N.R. performed all experiments and analysed the data. All authors wrote the manuscript together and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Moosmann, B., Roth, N. & Auwärter, V. Finding cannabinoids in hair does not prove cannabis consumption. Sci Rep 5, 14906 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14906
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14906
This article is cited by
-
Associations between hair-derived cannabinoid levels, self-reported use, and cannabis-related problems
Psychopharmacology (2024)
-
Evidence for the transfer of methadone and EDDP by sweat to children’s hair
International Journal of Legal Medicine (2021)
-
Findings of illicit drugs in hair of children at different ages
International Journal of Legal Medicine (2021)
-
Detection of cannabinoids in hair after cosmetic application of hemp oil
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Surface Detection of THC Attributable to Vaporizer Use in the Indoor Environment
Scientific Reports (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.