Abstract
Pollination is important for both agriculture and biodiversity. For a significant number of plants, this process is highly and sometimes exclusively, dependent on the pollination activity of honeybees. The large numbers of honeybee colony losses reported in recent years have been attributed to colony collapse disorder. Various hypotheses, including pesticide overuse, have been suggested to explain the disorder. Using the Xenopus oocytes expression system and two microelectrode voltage-clamp, we report the functional expression and the molecular, biophysical and pharmacological characterization of the western honeybee’s sodium channel (Apis Mellifera NaV1). The NaV1 channel is the primary target for pyrethroid insecticides in insect pests. We further report that the honeybee’s channel is also sensitive to permethrin and fenvalerate, respectively type I and type II pyrethroid insecticides. Molecular docking of these insecticides revealed a binding site that is similar to sites previously identified in other insects. We describe in vitro and in silico tools that can be used to test chemical compounds. Our findings could be used to assess the risks that current and next generation pesticides pose to honeybee populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The pollination of various plants by bees is essential for biodiversity as well as for agriculture. The value of pollination services in the United States was estimated at US $14.6 billion in 20001. A more recent estimation has put the value of these services at approximately US $205 billion a year worldwide2. Despite the immense importance of honeybees for agriculture, reports of unusual colony losses continue to come in from the United States3 and elsewhere around the world4. These colony losses, which are characterized by the disappearance of adult bees from hives as well as abandoned food and brood, have been attributed to colony collapse disorder (CCD)5
Various hypotheses have been put forward to explain the cause of CCD, including insect-borne bacterial and fungal diseases, overuse of in-hive chemicals, overuse of agricultural pesticides and use of genetically modified crops5. Bacterial and fungal diseases can be ruled out as they preferentially affect larvae and pupae whereas CCD is characterized by the disappearance of adult bees6,7. The overuse of commonly used insecticides and the introduction of new chemicals thus appear to be the most reasonable explanation for CCD given that such practices may occur in the vicinity of large beekeeping operations.
While both the lethal and sub-lethal effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on honeybees have been the focus of many investigations recently (see Goulson 2013 for a review)8, few studies have focused on pyrethroid insecticides, which are the second most commonly used type of insecticide in agriculture today9 and are also widely used in combatting malaria and other insect-borne diseases10.
Pyrethroid insecticides target voltage gated sodium channels in mammals and insects11,12,13. Based on their homology with known sodium channels, two genes were identified as putative sodium channels in the Drosophila proteome, para and DSC114. Homologs of these proteins have also been predicted based on nucleotide sequences obtained from the Apis mellifera genome15.
Para stands for paralytic sodium channel because it was identified by locating the locus of mutations that induce temperature-sensitive paralysis phenotypes16. DSC1 stands for Drosophila sodium channel 1. The gene for this Drosophila channel was isolated based on its homology with a mammalian sodium channel DNA probe17. Recent experiments indicate that, while this channel resembles a sodium channel, the protein would be mainly permeable to calcium18,19. However, the para channel’s sequence and function would be more similar to known NaV channels. Thus, recent literature refers to this channel as NaV1. NaV1 is known as the principal target for sodium channel-specific pyrethroid insecticides20. In addition, mutations linked to knockdown resistance to pyrethroids have only been reported in the corresponding gene in other insects21 and in a gene coding for an enzyme that metabolizes such compounds22. In Drosophila, this channel is associated with a TipE and TipE homolog (TEH) regulatory subunit23,24. The original TipE subunit was named based on the location and phenotype induced by mutations in Drosophila (temperature-induced paralysis phenotype, locus E)25.
Sodium channels are responsible for the initiation of the action potential in many excitable cells. In mammals, they are essential for muscle contraction26, heart rhythmicity27 and neuronal firing28. However, in the presence of pyrethroid insecticides, the sodium channel deactivation and inactivation processes are disrupted29 leading to abnormal electrical activity, which has also been observed in honeybee antennal olfactory receptor neurons30. Moreover, sub-lethal doses have been shown to impair honeybee learning and memory31.
Mammalian sodium channels all feature four homologous domains32, each of which is composed of six transmembrane segments (S1–S6). The S1 to S4 segments of each domain form the voltage sensitive domain (VSD), which is responsible for driving the conformational changes of the protein. Upon depolarization, the VSDs activate, leading to the opening of the pore formed by the assembly of S5 and S6 of all the domains. Sodium ions then permeate and induce an inward current corresponding to the rising phase of the action potential.
Mammalian sodium channels are often co-expressed with one or more regulatory subunits (β1–4) whose function is to modulate the activity of the channels and increase expression levels33. The regulatory subunits for the NaV1 insect channels seem to have the same functions. However, the TipE and TipE homologous subunits (TEH) are quite different from the β1–4 subunits since they appear to feature two transmembrane segments24.
The functional characterization and molecular modeling of the Apis mellifera honeybee NaV1 channel (AmNaV1) reported here provides in vitro and in silico tools for assessing the toxicity of chemical compounds for honeybees. This could be an important step toward identifying the causes of CCD and designing new pesticides that are less toxic for honeybees.
Results
Sequence and molecular features of the AmNaV1 channel
A protein blast search revealed that the sodium channel sequence in the honeybee, as expected, features four homologous domains, which is characteristic of mammalian sodium and calcium channels. A protein profile analysis using hidden Markov models (HMMs) indicated that the AmNaV1 channel has a protein profile similar to the mammalian sodium and calcium channels. The hmmsearch algorithm using a protein profile inferred from manually curated sequences of mammalian sodium and calcium channels on the whole honeybee proteome as a query yielded a significant alignment with the AmNaV1 channel (e-value of 8.9E−24).
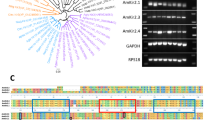
A comparison of the AmNaV1 channel minimum pore sequence as defined by Yu and Catterall34 to members of the voltage gated-like chanome (VGL-chanome) showed that the pore of the honeybee channel arose from the same ancestor as mammalian sodium channels (Fig. 1a–b). This comparison of the whole protein with mammalian sodium and calcium channels indicates that the honeybee NaV1 channel is a homolog of mammalian sodium channels which would have branched away from these channels early in evolution (Fig. 1c).
Phylogenetic classification of the AmNaV1 channel and its regulatory subunits.
The minimum pore sequence of the VGL-chanome protein was aligned with the minimum pore sequence of the AmNaV1 channel. (a) Consensus phylogenic tree generated with the maximum likelihood method (using PROML of the PHYLIP package) show that the pore of the AmNaV1 channel diverged in its evolution from the mammalian sodium channels. (b) The tree generated by an alignment of the whole channel with all manually curated sequences of the mammalian sodium and calcium channels shows that the whole sequence diverged early in its evolution. (c) The regulatory subunits of the AmNaV1 channel yielded a significant alignment with KCNMB family members (regulatory subunits of mammalian KCa channels). The resulting tree shows that the TEH family diverged from the KCNMB family members, establishing a family of its own. Based on the protein sequences, the TEH family can be divided in two subfamilies.
Five protein sequences homologous to the Drosophila melanogaster NaV1 channel regulatory subunits were found in the honeybee proteome. These proteins appeared to share a common ancestor with mammalian KCaβ subunits (KCNMB) (Fig. 1d). Further information on the protein sequences of these regulatory subunits can be found in the Supplemental Information section.
A sequence alignment of the four homologous domains with the domains of other voltage gated sodium channels showed that the honeybee NaV1 channel, like that of Drosophila, shares many features with mammalian sodium channels (Figure S1). Since it fits the protein profile of mammalian sodium and calcium channels, each domain of the NaV1 channel most likely features six transmembrane segments. The conserved residues highlighted in S1 to S3 show that the amino acids that form the VSD gating charge transfer center (GCTC)35 are completely conserved in each domain. Furthermore, the positively charged residues on the S4 segment that interact with the GCTC are also fully conserved, indicating that the topology of each VSD is similar to the topology described in our previously published model of the human NaV1.436.
The highlighted residues between the S5 and S6 segments in Figure S1 show that the selectivity filter of the AmNaV1 sodium channel is similar to that of mammalian sodium channels where two clusters of residues delimiting the ion conducting pore determine channel selectivity and sensitivity to tetrodotoxin (TTX)37,38. The clusters each consist of four conserved amino acids located in the re-entrant loop of the pore (DEKA and EEDD). In the honeybee NaV1 channel, the DEKA cluster is conserved while the EEDD cluster is substituted by EEQD (Figure S1a).
Alignments of the whole sequence indicated that the Apis mellifera NaV1 channel, like mammalian sodium channels, features a cluster of hydrophobic residues in the intracellular loop that links domains III and IV. In mammals, this cluster is involved in fast inactivation39. However, in insect channels, the MFMT sequence forms the inactivation particle. This sequence is similar to the IFMT sequence in mammalian channels (Figure S1b). The protein blast query also identified a putative site (the highly conserved serine S1581) for phosphorylation by PKC immediately after the hydrophobic cluster. (Figure S1b–c).
Alternative sequences for the NaV1 channel attributable to splice variants were also uncovered during our investigation (Figure S2a). They are the result of insertions or deletions of 9 to 11 residues in the large intracellular loops (DI/DII, DII/DIII and DIII/DIV linkers). The large intracellular loops of mammalian sodium channels are typically associated with phosphorylation sites32 and protein-protein interaction sites40,41. No RNA editing sites were found in the NaV1 sequence.
We did however find sequence variations for the TipE and TEH4 regulatory subunits which were attributable to RNA editing and genomic variations (Figure S2b). Indeed, three single amino acid substitutions encoded in the cDNA produced from honeybee heads were also found in the bee’s genomic DNA for TipE. One such substitution was found for TEH4. Those sequence variants were classified as genomic variations. Two single nucleotide substitutions coding for a change in the amino acid sequence of TipE were found in our cDNA banks. Since the corresponding variations could not be found in the bees’ genomic DNA, those were attributed to RNA edition.
Analysis of the AmNaV1 channel and the regulation of its regulatory subunits
An RT-PCR analysis showed that RNA corresponding to the AmNaV1 channel is expressed in all the honeybee tissues studied (brain, antenna, muscle, legs, gut and ganglion). AmNaV1 channel’s RNA was also present in the larvae (Fig. 2). This suggests that the AmNaV1 channel plays a major role in the physiological functions of the honeybee.
Expression of the AmNaV1 channel and its regulatory subunits in honeybee tissues.
The tissue-specific expression of proteins was assessed by RT-PCR. All the honeybee tissue samples underwent the same preparation steps from dissection to gel electrophoresis. The expected weights of the amplicons are displayed in base pairs (bp).
The regulatory subunits of the AmNaV1 channel were also widely expressed in these tissues, with the exception of TEH1, which was not expressed in the gut. TEH2 and TEH4 also appeared to be expressed at very low levels in the gut (Fig. 2).
Biophysical characterization
The regulatory subunits modulate the expression of the AmNaV1 channel
The co-expression of the regulatory subunits with the AmNaV1 channel was not required to record sodium currents in Xenopus oocytes, indicating that it is robustly expressed on the membrane (Fig. 3a). Raw data from standard pulse protocols showed that the honeybee TipE and TEH subunits affect the kinetics of the channel (Fig. 3a). In addition, the co-expression of the honeybee TipE and TEH subunits with the NaV1 channel increased the peak current (Fig. 3b). However, only the co-expression of the NaV1 channel with the TipE or TEH2 subunits yielded a statistically significant increase in expression levels.
Effect of the co-expression of the regulatory subunits on the expression of AmNaV1.
(a) Representative current traces from the pulse protocols applied to oocytes expressing either AmNaV1 alone or AmNaV1 and one of its regulatory subunits. The pulse protocols consisted of imposing−80 mV to +40 mV voltage steps in 5 mV increments. The oocytes were kept at the holding potential (−80 mV) for 1 s between voltage steps. (b) Relative amplitudes of the peak currents from oocytes expressing the AmNaV1 alone or with one regulatory subunit. The peak currents from 13–14 oocytes in response to a −80mV to −20 mV voltage step were measured for each bar. The mean was then normalized to the mean current amplitude measured in the presence of the TipE subunit. The differences between the means were then evaluated for statistical significance using a t-test with Bonferroni’s correction (***significant difference with AmNaV1 alone, p < 0.001). The oocytes came from the same batch and were tested the same day. (c) Representative current traces of an oocyte expressing AmNaV1 and TipE in response to a −80 mV to −20 mV voltage step. The current trace in orange was acquired in normal Ringer’s solution while the current trace in black was acquired in Ringer’s solution in which the sodium was replaced by choline.
As indicated by the sequence analysis, the AmNaV1 channel is selective for sodium ions. Indeed, removing sodium ions from the extracellular medium abolished the current produced by the AmNaV1 channel (Fig. 3c).
Voltage-dependence of activation of the AmNaV1 channel
Like its mammalian counterparts, the AmNaV1 channel is activated by membrane depolarizations. The conductance-voltage relationship (G–V curve) of the channel fits a Boltzmann function with a V1/2 of −31.7 ± 0.9 mV and a slope factor (k) of –2.9 ± 0.2 mV (n = 11).
An analysis of the activation properties of the AmNaV1 channel in the presence of the various regulatory subunits showed that the TEH2, TEH3 and TEH4 subunits shift the voltage-dependent activation of the channel to the right (Fig. 4a). When fitted to a Boltzmann function, this shift in the voltage-dependence of activation is represented by a shift of V1/2 toward more positive values (Fig. 4b). The TEH1, TEH3 and TEH4 subunits also had a significant effect on the slope factor of the Boltzmann curve (Fig. 4c), causing a less steep voltage-dependence of activation curve than the curve for the AmNaV1 channel alone. Overall, our data indicates that activation of the channel is slightly hindered in the presence of TEH2, TEH3 and TEH4 and is slightly facilitated in the presence of TEH1.
Effect of the different regulatory subunits on the biophysical properties of AmNaV1.
(a) The voltage-dependence of activation (G–V). Activation curves were derived from I–V curves (n = 7–14). The I–V curves were obtained using the protocol shown in the inset. The peak current measured at each potential was then divided by (V–Vrev), where V is the test potential and Vrev is the reversal potential. The conductances were then normalized and fitted to a standard Boltzmann equation (see Materials and Methods). (b–c) Plots of the fitted equation activation parameters (V1/2 and kv). Statistical differences were tested using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (d) The voltage-dependence of steady-state inactivation. The amplitude of the peak current was plotted as a function of the voltage imposed during the conditioning pulse (n = 8–14) using the protocol in the inset. The data was then fitted to a Boltzmann equation (see Materials and Methods). (e–f) Plots of the inactivation parameters (V1/2 and kv) of the fitted equation. Statistical differences were tested using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (g) Time constants of current decay. The protocol in (a) was used to generate transient sodium currents at different voltages. The decay of the transient current was fitted with a single exponential. For each condition, the time constant extracted from the fit was plotted as a function of the voltage imposed (n = 7–14). Typical raw data obtained as a result of a depolarization to −20 mV is shown in the inset to illustrate the different decay kinetics. (h) Recovery from inactivation. The amplitude of the peak current measured during the second pulse was divided by the amplitude measured during the first pulse and was then plotted against the time interval between the pulses (n = 8–14) using the protocol in the inset. (i) The resulting curves were fitted with a single exponential in order to compare the time constants. A statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction was performed to assess significant differences between the oocytes expressing regulatory subunits and oocytes expressing AmNaV1 alone. *p < 0.05 and ** and ***p < 0.01 and 0.001.
Voltage dependence of fast inactivation of the AmNaV1 channel
The voltage-dependence of fast inactivation of the AmNaV1 channel was also fitted with a Boltzmann function. The voltage of half-maximal inactivation (V1/2) in the absence of subunits was −52.1 ± 0.6 mV and the slope factor (k) was 4.3 ± 0.1 mV (n = 11).
The voltage-dependence of fast inactivation of the channel in the presence and absence of the regulatory subunits was evaluated using a standard two-pulse protocol. The current measured during the test pulse was plotted as a function of the voltage imposed during the conditioning pulse (Fig. 4d). Like the voltage-dependence of activation, the voltage-dependence of inactivation was fitted to a two-state Boltzmann function. A statistical analysis revealed a negative shift of the half-maximal voltage of inactivation (V1/2) in the presence of TEH1 and a positive shift in the presence of TEH4 (Fig. 4e). In addition, the slope factor (k) was higher in the presence of TEH3 and TEH4 (Fig. 4f). Overall, this means that TEH1 increases the steady-state inactivation of the channel while TEH4 decreases the steady-state inactivation. Differences in the time course of current decay were also observed (Fig. 4g). Fast inactivation was the main determinant of current decay. As illustrated by the raw data presented in Fig. 3a, the fast inactivation kinetics of the AmNaV1 channel were much slower in the presence of the TEH3 and TEH4 regulatory subunits, but were not affected by TipE, TEH1, or TEH2.
Recovery from inactivation
Recovery from inactivation was also evaluated using a two-pulse protocol. Briefly, the relative amplitude of the test pulse was plotted as a function of the Δt separating the conditioning and test pulses. The data points were fitted with a double exponential function. In the absence of the regulatory subunits, the faster exponential had a relative weight of 0.85 ± 0.05 and time constant (τ) of 8.2 ms ± 0.5 ms (n = 11). The slower exponential had a relative weight of 0.15 ± 0.05 and time constant (τ) of 80 ms ± 30 ms (n = 11). Despite slight apparent differences in the recovery from inactivation curves (Fig. 4h), no statistically significant differences were observed in the presence of the regulatory subunits (Fig. 4i).
Honeybee NaV1 single channel conductance
The single channel conductance of the honeybee NaV1 channel co-expressed with the TipE regulatory subunit was investigated using the patch clamp technique in the cell-attached configuration. Raw current traces were obtained at different voltages (Figure S4a). All-points histograms were then created in order to extract the mean single channel current amplitudes (Figure S4b). The extracted values were plotted as a function of the voltage imposed (Figure S4c). The data was fitted to a linear equation, yielding a slope value of 24.5 ± 0.2 pS for single channel conductance.
Pharmacological characterization
TTX sensitivity
Mammalian sodium channels are often divided into two groups that seem to have branched early in evolution: TTX-sensitive and TTX-insensitive channels42. The pharmacological characterization of uncharted sodium channels often begins with a determination of their TTX sensitivity. We evaluated the TTX sensitivity of the AmNaV1 channel and its TipE regulatory subunit. As expected, based on the high level of conservation of the DEKA and EEDD clusters, TTX inhibited sodium currents in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure S5a). Current inhibition expressed as the fraction of channels blocked as a function of TTX concentration was then plotted and fitted with the Hill equation (Figure S5b). This procedure resulted in a good-quality fit (R2 = 0.9992), with an evaluated half maximal inhibitory concentration of approximately 0.7 nM (IC50 = 0.7 nM), which is similar to that of the Drosophila NaV1 channel23, indicating that the honeybee channel was TTX sensitive. This was also predicted by the presence of an aromatic amino acid at position 449 (Y449). Other TTX-sensitive sodium channels usually feature an aromatic residue in the corresponding position. Substitution of the corresponding residue for an aromatic amino acid in TTX-resistant channels increases the sensitivity of the channels to TTX43,44.
Sensitivity to pyrethroids
To determine whether the honeybee NaV1 channel could be used to test the sensitivity of the honeybee for pyrethroid insecticides, we tested the effect of permethrin and fenvalerate, respectively type I and type II pyrethroid insecticides.
Adding 10 μM permethrin to the extracellular medium did not induce statistically significant shifts in activation, inactivation, or recovery from inactivation (Fig. 5a–c). Following conditioning pulses, extracellular permethrin induced a tail current that exhibited a linear voltage-dependence and an inversion at approximately +10 mV (Fig. 5d). A similar reversal potential was also observed for the transient current elicited in response to the pulse protocol used to create the G–V curve shown in Fig. 4a, indicating that the transient current and the tail current have similar selectivity and are most likely of the same nature.
Effect of permethrin on the honeybee NaV1 channel.
(a–c) The presence of 10 μM permethrin had no significant effect on the voltage-dependence of activation (a), the voltage-dependence of steady-state inactivation (b), or the recovery from inactivation (c) of AmNaV1 channels co-expressed with TipE. It did, however, induce a tail current. The maximal amplitude of the tail current after 200 conditioning pulses was recorded at different voltages (d). The normalized amplitude was plotted as a function of the voltage imposed during the recording (n = 9). The data was then fitted with a linear function (R2 = 0.98, y0 = −8.4%, slope = 1.0%/V).
Permethrin induced tail currents following activation, indicating that it traps the channel in its open state. The amplitude of the tail current increased as a function of the number of conditioning pulses (Fig. 6a) and the concentration of permethrin (Fig. 6b), indicating that this insecticide binds to the channel in its open state. In order to characterize the affinity of the channel for permethrin, we measured the amplitude of the tail current using varying numbers of conditioning pulses. Plotting the amplitude of the tail current as a function of the number of conditioning pulses showed that the maximal effect is reached after 200 pulses (Fig. 6c). Determining the number of pulses needed to reach the maximal effect made it possible to plot a dose-response curve (Fig. 6d). When fitted with the Hill equation, the curve yielded an R2 of 0.998, a Hill coefficient of 0.83 and an EC50 of 3.7 μM.
Permethrin induced tail currents in oocytes expressing AmNaV1.
The presence of 10 μM permethrin induced tail currents in oocytes co-expressing the AmNaV1 channel and the TipE regulatory subunit. (a) The amplitude of the tail current was highly dependent on the number of depolarizations imposed before the recording (pulses from −80 mV to −20 mV repeated at a frequency of 100 Hz). (b) The amplitude of the tail current was also dependent on the concentration of permethrin in the extracellular medium. The red dotted line represents the fit of the tail current at 10 μM. (c) The number of conditioning pulses (CP) required to attain the maximal amplitude of the tail current in the presence of 10 μM permethrin was then determined (n = 4). (d) The fraction of channels modified by permethrin (M) was calculated using equation 1 in the supplemental methods and plotted as a function of the dose applied using 200 conditioning pulses. The data was then fitted with a Hill curve in order to extract the Hill coefficient (h = 0.83) and the half maximal effective concentration (EC50 = 3.7 μM). The error bars represent the SEM.
Fenvalerate induced similar tail currents that depended on the number of conditioning pulses (Fig. 7a) and the concentration of this insecticide (Fig. 7b). Determining the number of conditioning pulses needed for maximal effect (Fig. 7c) was necessary in order to create a dose-response curve for fenvalerate (Fig. 7d). Fitting the data to the Hill curve yielded an R2 of 0.9987, a Hill coefficient of 1.18 and an EC50 of 290 nM.
Fenvalerate induced tail currents in oocytes expressing AmNaV1.
The presence of 10 μM fenvalerate induced a tail current in oocytes co-expressing AmNaV1 and its TipE regulatory subunit. (a) The amplitude of the tail current was highly dependent on the number of depolarizations imposed before the recording (pulses from −80 mV to −20 mV repeated at a frequency of 100 Hz). (b) The amplitude of the tail current was also dependent on the concentration of fenvalerate in the extracellular medium. The red dotted line represents the fit of the tail current at 10 μM. (c) The number of conditioning pulses (CP) required to attain the maximal amplitude of the tail current in the presence of 10 μM fenvalerate was then determined (n = 3). (d) The fraction of channels modified by fenvalerate (M) was calculated using equation 1 in the supplemental methods and plotted as a function of the dose applied using 1700 conditioning pulses. The data was then fitted with a Hill curve in order to extract the Hill coefficient (h = 1.18) and the half maximal effective concentration (EC50 = 290 nM). The error bars represent the SEM.
Comparing the results obtained from the application of permethrin and fenvalerate showed that more conditioning pulses were required to reach a maximal effect with fenvalerate. However, fenvalerate induced larger tail currents and had a higher affinity for the AmNaV1 channel than permethrin. In addition, the tail currents induced by fenvalerate took longer to deactivate (Figs 6b,7b). The deactivation of permethrin-induced tail currents was fitted to a single exponential with a time constant of 0.93 s ± 0.11 s. The deactivation of the fenvalerate-induced tail currents was better fitted to a double exponential. The relative weight of the slow component was 85.4% ± 3.6%. The time constants for both exponentials were 9.9 s ± 2.4 s and 31.8 s ± 1.8 s respectively.
Structural model and molecular docking
A structural model of the AmNaV1 channel was generated using Modeller45. The open-activated equilibrated structure of the NaVAb bacterial channel was used as a template46. This structure was preferred to the recently published partially activated crystal structure47 since our results indicated that pyrethroid insecticides bind to the activated/open channel. The homology model was then equilibrated for 20 ns using molecular dynamics simulations of the channel embedded in a solvated and ionized POPC model membrane.
The resulting structure was used for docking experiments to determine whether our model could be used for in silico compound screening. Since a binding site for pyrethroid insecticides was recently identified in the homologous Aedes aegypti NaV1 channel48 and since the amino acid sequence of the proposed binding site in the AmNaV1 is the same as that that of the A. aegypti channel, a suitable model for in silico compound screening should recapitulate this fact. The sensitivity of the channel to pyrethroid insecticides reported here also provided support for the existence of such a site.
Directed docking experiments using a large box (40 Å × 20 Å × 30 Å) centered on the proposed binding site revealed binding sites for permethrin and fenvalerate. Clustering all the poses obtained for permethrin (7799) and fenvalerate (7816) revealed that, in over 70% of the poses, the ligands would be in contact with residues that would induce knock-down resistance to pyrethroids if mutated (Fig. 8). This indicated that the model presented here can be used as an in silico tool to determine whether pyrethroid derivatives induce undesirable effects in honeybees.
Structural model and docking poses AmNaV1.
(a) Top view of one of the poses used for the docking calculations. The protein is in grey with the exception of the first domain, which is in blue. The residues involved in the binding site mapped by Du et al. in the A. aegypti channel are in purple. (b) A close-up view of the pore from the top, with the most populated docking pose for TTX. The most populated docking pose for TTX is in orange. The α-carbon of the residues involved in the DEKA motif of the selectivity filter are in green (D386, E989, K1496 and A1789). The residues located within 4.5 Å of the toxin which are known to contribute to TTX binding in mammalian sodium channels are displayed in yellow (Y387, W388, E389, G988, G1497 and D1792). The α-carbon of other residues known to contribute to TTX binding in mammalian sodium channels according to the model published by Tikhonov and Zhorov but not located within 4.5 Å of the TTX cluster are displayed in red (W990, E992, W1498, Q1500 and W1791). The α-carbon of the residues located within 4.5 Å of the TTX cluster but not considered to play a major role in TTX binding according to Tikhonov and Zhorov are shown in orange (D386, Y387, E389 E989, K1496, A1789 and D1792). (c) The most populated docking poses for permethrin are shown on a side view of the protein. (d) The most populated docking poses for fenvalerate are shown in the same view. The residues in purple in c and d are the residues involved in the binding site mapped by Du et al.
A directed docking experiment using a larger box (40 Å × 40 Å × 70 Å) centered on the pore of the channel was also performed to determine whether the model could account for the high TTX-sensitivity of the channel. We assessed the potential of residues of being implicated in the binding of TTX based on their proximity with the principal toxin conformation cluster, using a cutoff of 4.5 Å to discriminate between binding and non-binding residues. The model indicated that the residues of main selectivity filter (D386, E989, K1496 and A1789) are in close proximity of the most represented TTX conformation cluster (Fig. 8b). This was expected given that the binding site identified in mammalian sodium channels is also located in this vicinity38. Additionally, two of the four residues which constitute the secondary selectivity filter were close to the ligand, namely E389 and D1792. Again, the corresponding residues in mammalian sodium channels were shown to contribute to TTX binding by Terlau et al.. We also show that the Y387 seems to be implicated in TTX binding. This residue aligns with C373 in hNaV1.5. Interestingly, some mutations on the C373 residue are known to increases the sensitivity of the human channel to TTX43,44. Furthermore, the residues W388, G988 and G1497 were also in close proximity to TTX. The corresponding residues have been shown to contribute to TTX binding in other investigations on mammalian channels38,49. As could be expected, some differences existed between our docking experiments on insect channel compared to previous docking experiments on mammalian channels. Indeed, according to a model published by Tikhonov and Zhorov, the residues corresponding to the residues W990, E992, W1498, Q1500 and W1791 would contribute to TTX binding49. In our model, those residues were not within 4.5 Å of the ligand. Residues within 4.5 Å of the TTX cluster would rather include Q385, W402, Q1491, S1788, G1790 as well as the residues reported above (D386, Y387, E389 E989, K1496, A1789 and D1792). Although both models rely on docking experiments unconfirmed by mutagenesis, this could indicate that the TTX binding site could be slightly closer to the primary selectivity filter in AmNaV1, when compared to mammalian NaV1.
Discussion
The sequence of the Apis mellifera sodium channel (AmNaV1) features four homologous domains, a selectivity filter, a hydrophobic cluster in the DII/DIII linker and a putative phosphorylation site. Similar motifs are present in mammalian and other insect sodium channels. The sequence variations identified here are all located in the intracellular loops, which often feature protein-protein interaction or phosphorylation sites. Further investigations are warranted to determine the functional impacts and physiological implications of these splice variants.
The honeybee NaV1 channel shares striking similarities with other cloned insect sodium channels. A comparison with the NaV1 sequences of other pyrethroid-sensitive insects showed that the sequence reported here shares 78%, 80% and 82% identity with the amino acid sequences from Musca domestica (house fly), Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) and A. aegypti (yellow fever mosquito) (accession numbers NP_001188635.1, AAB47605.1 and ACB37024.1, respectively). Pyrethroids are used to control these three insects and the diseases they spread10.
Interestingly, the honeybee NaV1 channel only shares 58% identity with the Varroa destructor NaV1 channel (accession number AAP13992.1). This mite is a major vector of diseases affecting bees. Further investigations using both channels are required to determine whether there are any differences in the binding sites and affinities of these channels for pyrethroids. The results of these investigations could lead to the development of highly specific insecticides for in-hive use in order to control infections propagated by V. destructor.
Like the regulatory subunits of the D. melanogaster NaV1 channel24, the TipE and TEH subunits increased the expression of the honeybee NaV1 channel (Fig. 3).
The honeybee genome, like the D. melanogaster genome, codes for five regulatory subunits. While they share relatively low identity, the regulatory subunits of NaV1 channels appear to share a common ancestor with mammalian KCaβ regulatory subunits24. It would thus be interesting to determine whether the TipE and TEH subunits interact with honeybee KCaα channels.
RT-PCR experiments showed that the RNA corresponding to all the proteins investigated are expressed almost ubiquitously in honeybee tissues, indicating that the AmNaV1 channel may be involved in a wide variety of physiological functions in the honeybee. Curiously, earlier reports indicate that no sodium current were detectable in the honeybee’s muscle fibres50. Caution is warranted in the interpretation of RT-PCR results as we did not attempt to determine if the detection of RNA in those tissues is accompanied by the expression of proteins. Further experiments are warranted to determine if AmNaV1 proteins are expressed in all those tissues and whether they possess a significant physiological role.
We observed very few sequence variations for NaV1, TipE and TEH4. However, the sequence variations we mapped were seen in total RNA preparations from honeybee heads. Further investigations should focus on mapping all the sequence variations for the proteins reported here using other total RNA preparations. Examining the expression of sequence variants in specific tissues would be the first step toward determining their physiological roles.
The biophysical characterization of the Apis mellifera NaV1 channel with and without its regulatory subunits provided a brief overview of the basic properties of the channel. The regulatory subunits can be divided into two subfamilies based on their effect on the NaV1 channel. TipE, TEH1 and TEH2 did not change or increase steady-state inactivation while TEH3 and TEH4 hindered entry into the inactivated state. TEH3 and TEH4 also hindered activation of the channel and had a marked effect on current decay. The proposed division into two subfamilies is supported by the sequence analyses we performed. The phylogenetic tree indicated that the sequences of TEH3 and TEH4 are more similar to each another than to the other regulatory subunits. They are also the only proteins of the family to feature EGF-like domains.
The experiments reported here provide all the protocols and results required to test the toxicity of compounds for honeybees. Similar experiments could also be performed on other cloned insect channels and could be compared to the results from the honeybee channel to make sure that new insecticides are toxic for other insects, but not the honeybee.
The AmNaV1 channel was very sensitive to TTX. Similar affinities have been reported for other NaV1 channels23 and TTX-sensitive mammalian sodium channels (NaV1.1–1.4 and NaV1.6–1.7)51. The TTX sensitivity of the honeybee NaV1 channel was to be expected as most of the amino acid known to determine TTX sensitivity in mammalian channels are conserved in the AmNaV1 channel. Indeed, the secondary selectivity filter is mostly conserved, the primary DEKA filter is conserved and there is an aromatic residue at the position following the D of this filter (Y387). Moreover, other residues located between the filters which are known to contribute to TTX binding are also conserved. However, our docking experiments has shown that residues located outward of the secondary selectivity filter may not contribute to TTX binding in AmNaV1. Other residues located closer to the primary selectivity filter could be implicated in TTX binding. This displacement of the TTX binding site slightly closer to the DEKA cluster compared to TTX sensitive mammalian NaV1 channel could be a feature of insect NaV1 channels. Further mutagenesis experiments are required to confirm this hypothesis.
Permethrin and fenvalerate induced tail currents following activation. However, the EC50 for permethrin was shifted by more than an order of magnitude, indicating that type II pyrethroids may have higher affinities for the honeybee NaV1 channel. While we calculated an affinity of approximately 3.7 μM for AmNaV1, this does not mean that permethrin is not chronically or acutely toxic for the honeybee. Rather, it indicates that careful dosage may help minimize the impact on honeybees, although chronic exposure may still be deleterious31. The EC50 we measured is very close to the EC50 for permethrin on the sodium current of honeybee antennal olfactory receptor neurons (3.5 μM)30, indicating that the undesirable effect of permethrin on the olfactory functions of the honeybee may be exclusively due to the binding of the compound to the NaV1 channel. It also indicates that the in vitro technique proposed here replicates the results obtained from more complicated setups.
Fenvalerate had an EC50 of approximately 290 nM for AmNaV1. This higher affinity at lower concentrations than permethrin may make fenvalerate less suitable for agricultural uses. Fenvalerate also induced tail currents that decay less rapidly than the currents induced by permethrin, indicating that it could potentially be more toxic for honeybees. However, the LD50 of Apis mellifera reported for fenvalerate is twice that of permethrin52. The reason for this discrepancy might for instance be found either in detoxication capacities, in the existence of a more toxic metabolite or in the existence of a secondary target for permethrin. Therefore, although our model may be used as a precise and relatively fast way to assess the toxicity of chemical compounds for honeybees, this method would be complementary to in-vivo testing.
Interestingly, using similar protocols, other insect sodium channels were found to have similar susceptibility for pyrethroids53. However, the Drosophila NaV1 channel seems more affected by permethrin than the honeybee channel (EC50 = 12 nM for the Drosophila channel54 vs. 3.7 μM for the honeybee channel). This difference may be due in part to differences in the experimental procedures. Indeed, Vais et al. used ATX-II to inhibit inactivation while this toxin was not used in our study. In investigations where ATX-II was not used, the Drosophila channel displayed half maximal effective concentration superior to 0.01 μM55. Similarly, the EC50 reported for deltamethrin on the Drosophila’s channel in the presence of ATX-II is around 4.7 nM whereas no response was recorded at 100 nM in the absence of ATX-II56. Some key residues in the sequence of the honeybee NaV1 channel could also explain potential differences between the affinities of the honeybee and Drosophila channels. Rinkevich et al. summarized the state of knowledge about 38 mutations associated with knock-down resistance to pyrethroids in arthropods21. Five amino acids in the sequence of the honeybee NaV1 channel are suggestive of mutations associated with knock-down resistance to pyrethroids in arthropods. While these five amino acids are unlikely to account for the shift in sensitivity of the honeybee channel compared to the Drosophila channel, investigations focused on these residues are warranted. The E485K mutation (using M. domestica numbering) has been associated with knock-down resistance in Blattella germanica in the background of L1014F and L1014F+C785R57. The corresponding residue in the honeybee sequence is also negatively charged (D489). It is thus unlikely that this residue contributes significantly to a change in affinity for pyrethroids.
The L1596P mutation (using M. domestica numbering) in V. destructor induces a lower affinity for pyrethroids58. The corresponding residue in the honeybee is P1595. Interestingly, this residue is also a proline in other known insect NaV1 channels. This may explain potential differences in the affinity of the V. destructor NaV1 and the honeybee’s NaV1 for pyrethroids, but not between the honeybee and Drosophila channels since the proline residue is present in both these species.
The A1101T, A1215D and M1823I mutations (using M. domestica numbering) have also been associated with knock-down resistance phenotypes. However, one should be careful in drawing conclusions from these results since none of these mutations have been confirmed in vitro. Further information on these mutations and the corresponding residues in the AmNaV1 channel sequence can be found in the Supplemental Information section (Supplemental Table 1).
We also report here the creation of a structural model of the honeybee NaV1 sodium channel, which paves the way to in silico screening of compounds that can bind to the pore or to the pyrethroid binding site. This structural model may be used as a first step in the intelligent design of compounds intended either to target or to avoid targeting the honeybee NaV1 sodium channel. Our model indicated that the binding site for pyrethroids in the honeybee sodium channel is similar to the site recently identified in A. aegypti48. This may be an obstacle for the creation of insecticides that specifically target the NaV1 channels of insect pests but not the honeybee. However, given the low homology between the NaV1 channels of the honeybee and V. destructor, pyrethroid derivatives could be used to target this parasite which now invades the hives of both eastern and western honeybees59.
The binding poses showed pyrethroid insecticides in close proximity to the residues corresponding to those mapped by Du et al.48. The distance of docked compounds from these residues could thus be used as an objective criterion to predict potential interactions with the NaV1 channel.
We report the creation of new in vitro and in silico tools to test the toxicity of compounds for honeybees. These tools could be used to screen insecticides for agricultural and in-hive use. Compounds that induce statistically significant changes to the properties of the AmNaV1 channel at their recommended doses must be used with care. Efforts to reduce or eliminate toxic products from the environment should help alleviate pressure on honeybee colonies. Regardless of whether the cause of CCD is an infection, the overuse of chemicals, or a combination of these causes, taking the toxicity of certain compounds for honeybees into account should help in the fight against the disappearance of our principal pollinator.
Material and Methods
Solutions and reagents
The Ringer’s bath solution was composed of 116 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 2.9 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM HEPES. The pH was adjusted to 7.6 at 22 °C using 1 M NaOH.
The hyperosmotic solution used for single-channel recordings was composed of 200 mM K-aspartate, 20 mM KCl, 1 MgC12, 10 mM EGTA and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.5). For cell-attached experiments, the bath solution was composed of 100 mM K-aspartate, 50 mM KCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM glucose and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4). The pipette solution was composed of 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1.5 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 mM glucose and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4).
The OR3 solution was composed of a 1:2 dilution of Leibovitz’s L-15 medium supplemented with 15 mM HEPES and 50 mg/ml of gentamycin. The pH was adjusted to 7.6 at 22 °C using 1 M NaOH60.
The OR2 solution was composed of 82.5 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2 and 5 mM HEPES. The pH was adjusted to 7.6 at 22 °C using 1 M NaOH.
All the chemicals and drugs were from Sigma, except for tetrodotoxin, which was from Latoxan (France) and Leibovitz’s L-15 medium, which was purchased from Invitrogen (USA) in powder form. All the experiments were carried out at 22 °C.
Sequencing and cloning
The regulatory subunits were cloned in the pPol_Not1 vector. Two overlapping fragments of the AmNaV1 channel were cloned in the TOPO vector. Details about the generation of mRNA for oocyte injection and about the molecular cloning are available in the supplemental information section.
RT-PCR
Total RNA from honeybee tissues was extracted using Trizol kits (Sigma). cDNA preparations were then produced using Transcriptor first strand cDNA synthesis kits (Roche). cDNA preparations corresponding to the NaV1, TipE and TEH1-4 proteins were obtained by PCR amplification using oligonucleotide primers. The resulting cDNA preparations were run on agarose gels to determine whether the genes of interest were expressed in the tissues under investigation. Controls were performed with total RNA preparations using the same protocol but without reverse transcriptase. Primer sequences are available in the supplemental information section.
Xenopus oocytes
All experimental procedures involving Xenopus oocytes were approved by the Université Laval Institutional Animal Care Committee in line with the principles and guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care (Approval 2011155-1). They were prepared as described previously60. Briefly, oocytes were surgically removed from frogs anesthetized with MS-222. They were then treated with 2 mg/ml collagenase (Collagenase type 1A from Clostridium histolyticum, Sigma) in OR2 solution for 1 h. They were then incubated for at least 1 h at 18 °C in OR3 solution. Stage IV and V oocytes were microinjected with mRNA corresponding to AmNaV1 and the selected regulatory subunit (1 μg/μl for AmNaV1 and 0.3 μg/μl for regulatory subunits, 50 nl/oocyte). The injected oocytes were incubated at 18 °C in OR3 solution for at least 12 h before taking recordings.
Electrophysiology
Macroscopic currents from mRNA-injected oocytes were recorded in Ringer’s solution using the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique. The membrane potential for the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique was controlled using a Warner oocyte clamp (Warner Instrument Corp.). The currents were filtered at 5 kHz (−3 dB; four-pole Bessel filter). The headstage of the Warner amplifier was attached to a plastic pool containing a 3 M NaCl solution through a silver chloride wire connected to the bath solution using an agar bridge. The bridge contained 3% agar (w/v), 500 mM NMDG and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) and was threaded with a thin platinum/iridium wire to lower high-frequency impedance.
For the cell-attached patch experiments, the vitelline membrane was removed with forceps after briefly placing an oocyte in a hyperosmotic solution. Command pulses were generated and currents were recorded using pCLAMP software v10.3 and an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices). Patch electrodes (3–7 MΩ) fashioned from borosilicate glass (Corning 8161) were coated with HIPEC® (Dow Corning) to reduce capacitance and noise emissions. Single-channel currents were filtered at 2 KHz and were sampled at 100 kHz. Traces were low-pass filtered at 1.5 kHz using a digital filter included in the Clampfit software. Capacity transients were eliminated by averaging recordings without openings and subtracting this average from all recordings.
Data analysis and statistics
The electrophysiological data were analyzed using macros in Clampfit (pCLAMP v10.0; Molecular Devices) and custom scripts written using MATLAB (The MathWorks Inc.). The results are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed using a one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test in SigmaPlot (Systat Software). Differences were deemed significant at p < 0.05. The p values and number of measurements are indicated in the text or figure legends. Further information about the equations used for fits or to calculate the fraction of channels modified by pyrethroid insecticides are available in the supplemental information section.
Sequence alignments and homology modeling
The best template for building a model of the AmNaV1 channel transmembrane domains was identified by a PSI-BLAST search of the Protein Data Bank database. Since the NaVAb high-resolution structure released in 201147 bore the transmembrane domains with the highest max score, the recently published activated-open structure was used as a template for the homology model46.
The multiple sequence alignments were performed using the Clustal Omega web server61. Before building the model, the highly disordered intracellular loop regions between the four channel subunits were removed from the alignment because no structural template was available for them.
A standard MODELLER45 routine was used to build a comparative model of the AmNaV1 channel comprised of the pore domain and the four VSD. The homology model provided a low-resolution starting structure and, given the high structural similarity between the VSD of all the possible templates in the Protein Data Bank (KV1.2, KV1.2/2.1, NaVAb and NaVRh), the choice of the reference structure was not critical. Molecular dynamics simulations (see the following section) were used to relax the model in its membrane/solution environment.
Molecular dynamics simulations
The AmNaV1 channel model was then inserted in a fully hydrated POPC bilayer. The system was equilibrated under normal constant temperature and pressure conditions (298 °K, 1 atm) in a 116 mM NaCl solution. To ensure correct reorganization of the lipids and solution, the positions of the phosphates in the lipids and the positions of all of the atoms in the channel were constrained during the first nanosecond. The protein was constrained during the second step. The harmonic constraints on the protein were progressively removed over a period of 8 ns during the third step. Lastly, a 20-ns unrestrained MD simulation of the entire channel was conducted to relax the system.
The MD simulations were carried out using NAMD2.962. Langevin dynamics were applied to keep the temperature at 300 °K. The equations of motion were integrated using a multiple time-step algorithm63. Short- and long-range forces were calculated every first and second time-step, respectively, with 2.0-fs time-steps. Chemical bonds between hydrogen and heavy atoms were constrained to their equilibrium values. Long-range electrostatic forces were taken into account using the particle mesh Ewald approach64. The water molecules were described using the TIP3P model65. The simulation used the CHARMM27-CMAP force field with torsional cross-terms for the protein66 and CHARMM36 for the phospholipids67. A united-atom representation was adopted for the acyl chains of the POPC lipid molecules68. The simulations were performed on Temple University’s Owl’s Nest supercomputer.
Docking calculations
All the known enantiomers for each ligand were docked separately to the equilibrated model. Given that the conformational flexibility of the channel influences ligand binding, the compounds were docked against a family of ten equilibrium conformations of the channel structures. The conformations were sampled in the last 2 ns of the corresponding equilibrium MD simulations.
Ten independent docking calculations were performed for each ligand using AutoDock Vina 1.1.269. Each docking calculation yielded approximately 20 different docking poses. The ligand was docked on the receptor structure by considering a 40 × 20 × 30 Å3 grid for the proposed binding site of pyrethroid insecticides and a 40 × 40 × 70 Å3 grid for the binding site in the pore domain. The grid spacing used was 0.45 Å for both binding sites. A total of 7799, 7816 and 7996 docking solutions were recovered for permethrin, fenvalerate and TTX, respectively.
Clustering
A cluster analysis was used to identify the binding sites of the ligands. Clustering was performed using the GROMOS algorithm in g_cluster with a geometric distance cutoff of 0.5 Å. This algorithm is described in Daura et al.70 Clusters were ranked by population. The top cluster for each ligand was considered as being in the putative binding site. For permethrin and fenvalerate, the top 3 and top 5 clusters, respectively, contained over 70% of the docking solutions. These clusters were considered as being in the binding site since they were in contact with residues corresponding to the binding site identified by Du et al.48 (Supplemental Table 2) and displayed some overlap with the most populated cluster. The residues with at least one atom located within 4.5 Å of the ligand were considered as interacting candidates.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Gosselin-Badaroudine, P. et al. Characterization of the honeybee AmNaV1 channel and tools to assess the toxicity of insecticides. Sci. Rep. 5, 12475; doi: 10.1038/srep12475 (2015).
References
Morse, R. A. & Calderone, N. W. The value of honey bees as pollinators of U.S. crops in 2000. Bee Culture 128, 1–15 (2000).
Gallai, N., Salles, J.-M., Settele, J. & Vaissière, B. E. Economic valuation of the vulnerability of world agriculture confronted with pollinator decline. Ecol. Econ. 68, 810–821 (2009).
Van Engelsdorp, D., Hayes, J., Underwood, R. M. & Pettis, J. A survey of honey bee colony losses in the U.S., fall 2007 to spring 2008. PloS one 3, e4071–e4071, 10.1371/journal.pone.0004071 (2008).
Carreck, N. & Neumann, P. Honey bee colony losses. J. Apicult. Res. 49, 1–1, 10.3896/IBRA.1.49.1.01 (2010).
Oldroyd, B. P. What’s killing American honey bees? PLoS Biol. 5, e168–e168, 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050168 (2007).
Genersch, E. American Foulbrood in honeybees and its causative agent, Paenibacillus larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 103 Suppl, S10–19, 10.1016/j.jip.2009.06.015 (2010).
Aronstein, K. A. & Murray, K. D. Chalkbrood disease in honey bees. Journal of invertebrate pathology 103 Suppl, S20–29, 10.1016/j.jip.2009.06.018 (2010).
Goulson, D. REVIEW: An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Appl. Ecol. 50, 977–987, 10.1111/1365-2664.12111 (2013).
Casida, J. E. Pest toxicology: the primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 22, 609–619, 10.1021/tx8004949 (2009).
Ranson, H. et al. Pyrethroid resistance in African anopheline mosquitoes: what are the implications for malaria control? Trends Parasitol. 27, 91–98 (2011).
Tatebayashi, H. & Narahashi, T. Differential mechanism of action of the pyrethroid tetramethrin on tetrodotoxin-sensitive and tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 595–603 (1994).
Warmke, J. W. et al. Functional expression of Drosophila para sodium channels. Modulation by the membrane protein TipE and toxin pharmacology. J. Gen. Physiol. 110, 119–133 (1997).
Kadala, A. et al. Pyrethroids differentially alter voltage-gated sodium channels from the honeybee central olfactory neurons. PLoS One 9, e112194, 10.1371/journal.pone.0112194 (2014).
Littleton, J. T. & Ganetzky, B. Ion Channels and Synaptic Organization. Neuron 26, 35–43, 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81135-6 (2000).
The Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nature 443, 931–949, 10.1038/nature05260 (2006).
Loughney, K., Kreber, R. & Ganetzky, B. Molecular analysis of the para locus, a sodium channel gene in Drosophila. Cell 58, 1143–1154 (1989).
Salkoff, L. et al. Genomic organization and deduced amino acid sequence of a putative sodium channel gene in Drosophila. Science 237, 744–749, 10.1126/science.2441469 (1987).
Zhou, W., Chung, I., Liu, Z., Goldin, A. L. & Dong, K. A Voltage-Gated Calcium-Selective Channel Encoded by a Sodium Channel-like Gene. Neuron 42, 101–112, 10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00148-5 (2004).
Zhang, T., Liu, Z., Song, W., Du, Y. & Dong, K. Molecular characterization and functional expression of the DSC1 channel. Insect Biochem. Molec. 41, 451–458, 10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.04.010 (2011).
Narahashi, T. Neuronal ion channels as the target sites of insecticides. Pharmacol.Toxicol. 79, 1–14 (1996).
Rinkevich, F. D., Du, Y. & Dong, K. Diversity and Convergence of Sodium Channel Mutations Involved in Resistance to Pyrethroids. Pest. Biochem. Phys. 106, 93–100, 10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.02.007 (2013).
Riveron, J. M. et al. A single mutation in the GSTe2 gene allows tracking of metabolically-based insecticide resistance in a major malaria vector. Genome Biol. 15, R27–R27, 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r27 (2014).
Feng, G., Deak, P., Chopra, M. & Hall, L. M. Cloning and functional analysis of tipE, a novel membrane protein that enhances drosophila para sodium channel function. Cell 82, 1001–1011 (1995).
Derst, C., Walther, C., Veh, R. W., Wicher, D. & Heinemann, S. H. Four novel sequences in Drosophila melanogaster homologous to the auxiliary Para sodium channel subunit TipE. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 339, 939–948, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.096 (2006).
Kulkarni, S. J. & Padhye, A. Temperature-sensitive paralytic mutations on the second and third chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Res. 40, 191–191, 10.1017/S0016672300019054 (1982).
Jurkat-Rott, K. & Holzherr, B. Sodium channelopathies of skeletal muscle result from gain or loss of function. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 1, 239–248, 10.1007/s00424-010-0814-4 (2010).
Amin, A. S., Asghari-Roodsari, A. & Tan, H. L. Cardiac sodium channelopathies. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 460, 223–237, 10.1007/s00424-009-0761-0 (2010).
Mantegazza, M., Curia, G., Biagini, G., Ragsdale, D. S. & Avoli, M. Voltage-gated sodium channels as therapeutic targets in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Lancet neurology 9, 413–424, 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70059-4 (2010).
Soderlund, D. M. State-Dependent Modification of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by Pyrethroids. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 97, 78–86, 10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.06.010 (2010).
Kadala, A., Charreton, M., Jakob, I., Le Conte, Y. & Collet, C. A use-dependent sodium current modification induced by type I pyrethroid insecticides in honeybee antennal olfactory receptor neurons. Neurotoxicology 32, 320–330, 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.02.007 (2011).
Taylor, K. S., Waller, G. D. & Crowder, L. A. Impairment of a classical conditioned response of the honey bee (Apis mellifera l.) by sublethal doses of synthetic pyrethroid insecticides. Apidologie 18, 243–252, 10.1051/apido:19870304 (1987).
Yu, F. H. & Catterall, W. A. Overview of the voltage-gated sodium channel family. Genome Biol 4, 207–207 (2003).
Zhao, J., O’Leary, M. E. & Chahine, M. Regulation of Nav1.6 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve Na+ channels by auxiliary β-subunits. J. Neurophysiol. 106, 608–619, 10.1152/jn.00107.2011 (2011).
Yu, F. H. & Catterall, W. A. The VGL-chanome: a protein superfamily specialized for electrical signaling and ionic homeostasis. Sci. STKE 2004, re15–re15, 10.1126/stke.2532004re15 (2004).
Tao, X., Lee, A., Limapichat, W., Dougherty, D. A. & MacKinnon, R. A gating charge transfer center in voltage sensors. Science 328, 67–73 (2010).
Gosselin-Badaroudine, P., Delemotte, L., Moreau, A., Klein, M. L. & Chahine, M. Gating pore currents and the resting state of Nav1.4 voltage sensor domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 10.1073/pnas.1217990109 (2012).
Heinemann, S. H., Terlau, H., Stühmer, W., Imoto, K. & Numa, S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature 356, 441–443, 10.1038/356441a0 (1992).
Terlau, H. et al. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Letters 293, 93–96 (1991).
West, J. W. et al. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89, 10910–10914 (1992).
Schultz, J. et al. Specific interactions between the syntrophin PDZ domain and voltage-gated sodium channels. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 5, 19–24, 10.1038/nsb0198-19 (1998).
Garrido, J. J. et al. A targeting motif involved in sodium channel clustering at the axonal initial segment. Science 300, 2091–2094, 10.1126/science.1085167 (2003).
Goldin, A. L. et al. Nomenclature of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Neuron 28, 365–368 (2000).
Satin, J. et al. A Mutant of TTX-Resistant Cardiac Sodium Channels with TTX-Sensitive Properties. Science 256, 1202–1205, 10.1126/science.256.5060.1202 (1992).
Chen, L. Q., Chahine, M., Kallen, R. G., Barchi, R. L. & Horn, R. Chimeric study of sodium channels from rat skeletal and cardiac muscle. FEBS Letters 309, 253–257, 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80783-D (1992).
Eswar, N. et al. Comparative protein structure modeling using Modeller. Current protocols in bioinformatics Chapter 5, Unit 5.6–Unit 5.6 (2006).
Amaral, C., Carnevale, V., Klein, M. L. & Treptow, W. Exploring conformational states of the bacterial voltage-gated sodium channel NavAb via molecular dynamics simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 109, 21336–21341, 10.1073/pnas.1218087109 (2012).
Payandeh, J., Scheuer, T., Zheng, N. & Catterall, W. A. The crystal structure of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Nature 475, 353–358 (2011).
Du, Y. et al. Molecular evidence for dual pyrethroid-receptor sites on a mosquito sodium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 110, 11785–11790, 10.1073/pnas.1305118110 (2013).
Tikhonov, D. B. & Zhorov, B. S. Modeling P-loops domain of sodium channel: homology with potassium channels and interaction with ligands. Biophys J 88, 184–197, 10.1529/biophysj.104.048173 (2005).
Collet, C. & Belzunces, L. Excitable properties of adult skeletal muscle fibres from the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Exp Biol 210, 454–464, 10.1242/jeb.02667 (2007).
Catterall, W. A., Goldin, A. L. & Waxman, S. G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 397–409, 10.1124/pr.57.4.4 (2005).
Hardstone, M. C. & Scott, J. G. Is Apis mellifera more sensitive to insecticides than other insects? Pest. Manag. Sci. 66, 1171–1180, 10.1002/ps.2001 (2010).
Liu, Z., Tan, J., Valles, S. M. & Dong, K. Synergistic interaction between two cockroach sodium channel mutations and a tobacco budworm sodium channel mutation in reducing channel sensitivity to a pyrethroid insecticide. Insect. Biochem. Molec. 32, 397–404, 10.1016/S0965-1748(01)00116-3 (2002).
Vais, H. et al. Mutations of the para sodium channel of Drosophila melanogaster identify putative binding sites for pyrethroids. Mol. Pharmacol. 64, 914–922, 10.1124/mol.64.4.914 (2003).
Zhao, Y., Park, Y. & Adams, M. E. Functional and evolutionary consequences of pyrethroid resistance mutations in S6 transmembrane segments of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co 278, 516–521, 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3832 (2000).
Vais, H. et al. Activation of Drosophila sodium channels promotes modification by deltamethrin. Reductions in affinity caused by knock-down resistance mutations. J. Gen. Physiol. 115, 305–318, 10.1085/jgp.115.3.305 (2000).
Tan, J. et al. Novel sodium channel gene mutations in Blattella germanica reduce the sensitivity of expressed channels to deltamethrin. Insect. Biochem. Molec. 32, 445–454, 10.1016/S0965-1748(01)00122-9 (2002).
Liu, Z., Tan, J., Huang, Z. Y. & Dong, K. Effect of a fluvalinate-resistance-associated sodium channel mutation from varroa mites on cockroach sodium channel sensitivity to fluvalinate, a pyrethroid insecticide. Insect. Biochem. Molec. 36, 885–889, 10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.08.006 (2006).
Rosenkranz, P., Aumeier, P. & Ziegelmann, B. Biology and control of Varroa destructor. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 103 Suppl, S96–119, 10.1016/j.jip.2009.07.016 (2010).
Chahine, M., Chen, L. Q., Barchi, R. L., Kallen, R. G. & Horn, R. Lidocaine block of human heart sodium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 24, 1231–1236, 10.1016/0022-2828(92)93090-7 (1992).
Sievers, F. et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7, 539–539, 10.1038/msb.2011.75 (2011).
Phillips, J. C. et al. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 26, 1781–1802 (2005).
Izaguirre, J. A., Reich, S. & Skeel, R. D. Longer time steps for molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 110, 9853–9864 (1999).
Darden, T., York, D. & Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 98, 10089–10089, 10.1063/1.464397 (1993).
Jorgensen, W. L., Chandrasekhar, J., Madura, J. D., Impey, R. W. & Klein, M. L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 926–926 (1983).
Mackerell, A. D., Feig, M. & Brooks, C. L. Extending the treatment of backbone energetics in protein force fields: limitations of gas-phase quantum mechanics in reproducing protein conformational distributions in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1400–1415 (2004).
Klauda, J. B. et al. Update of the CHARMM all-atom additive force field for lipids: validation on six lipid types. J. Phys. Chem. B. 114, 7830–7843, 10.1021/jp101759q (2010).
Hénin, J., Shinoda, W. & Klein, M. L. United-atom acyl chains for CHARMM phospholipids. J. Phys. Chem. B. 112, 7008–7015 (2008).
Trott, O. & Olson, A. J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 455–461, 10.1002/jcc.21334 (2010).
Daura, X. et al. Peptide Folding: When Simulation Meets Experiment. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 38, 236–240, 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990115)38:1/2<236::AID-ANIE236>3.0.CO;2-M (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank Valérie Pouliot and Karine Drapeau technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Pierre Giovenazzo for providing bees during the course of this study. This study was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC Discovery Grant). Gosselin-Badaroudine was supported by Postgraduate Scholarship from NSERC. This research was also supported in part by the National Science Foundation through major research instrumentation grant number CNS-09-58854. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute for General Medical Sciences (grant P01 GM55876 to M.L. Klein). L. Delemotte receives funding from European Union Seventh Framework Program “Voltsens” (grant PIOF-GA-2012-329534). This work was also supported by ANR, grant bee-channel N° ANR-13-BSV7-0010-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Designed the experiments: P.G.B., P.C., M.R., T.C., C.C. and M.C. Performed the experiments and analyzed the results: P.G.B., A.M., L.D., M.L.K. and M.C. Wrote the paper: P.G.B., L.D., M.L.K. and M.C.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Gosselin-Badaroudine, P., Moreau, A., Delemotte, L. et al. Characterization of the honeybee AmNaV1 channel and tools to assess the toxicity of insecticides. Sci Rep 5, 12475 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12475
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12475
This article is cited by
-
Voltage-gated sodium channels from the bees Apis mellifera and Bombus terrestris are differentially modulated by pyrethroid insecticides
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Honey bees long-lasting locomotor deficits after exposure to the diamide chlorantraniliprole are accompanied by brain and muscular calcium channels alterations
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Honeybee locomotion is impaired by Am-CaV3 low voltage-activated Ca2+ channel antagonist
Scientific Reports (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.