Abstract
Graphene-decorated V2O5 nanobelts (GVNBs) were synthesized via a low-temperature hydrothermal method in a single step. V2O5 nanobelts (VNBs) were formed in the presence of graphene oxide, a mild oxidant, which also enhanced the conductivity of GVNBs. From the electron energy loss spectroscopy analysis, the reduced graphene oxide (rGO) are inserted into the layered crystal structure of V2O5 nanobelts, which further confirmed the enhanced conductivity of the nanobelts. The electrochemical energy-storage capacity of GVNBs was investigated for supercapacitor applications. The specific capacitance of GVNBs was evaluated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and charge/discharge (CD) studies. The GVNBs having V2O5-rich composite, namely, V3G1 (VO/GO = 3:1), showed superior specific capacitance in comparison to the other composites (V1G1 and V1G3) and the pure materials. Moreover, the V3G1 composite showed excellent cyclic stability and the capacitance retention of about 82% was observed even after 5000 cycles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Ensuring the availability of energy is a serious concern faced worldwide and therefore, alternative energy-conversion systems based on renewable energy sources have been in the focus of research. The transportation of that kind of sustainable energy from the point of generation to the end user is yet another challenging task that involves power grids for large-distance and high-capacity energy-storage devices for small-scale and mobile applications1. For small-scale applications, batteries have been developed with high energy density that, however, are limited by a low power density. Traditional capacitors are best known for their high power density, but have a fundamental flaw in their low energy density. By combining the figure of merit of these two systems, supercapacitors (also known as ultracapacitors or electrochemical double-layer capacitors, EDLCs) are being developed, resulting in higher power density and energy density than conventional batteries and traditional capacitors, respectively2. Basically, carbon materials are best known for their double layer capacitance behaviour, which provides the high power density to the capacitors. To enhance the energy density of supercapacitors, suitable pseudocapacitance materials have been combined with the carbon-based materials. Various carbon materials, such as activated carbon, graphite, carbon nanotubes, or graphene have been used. Among these, graphene, a new class of carbon material has attracted great interest due to its high surface area and excellent electrical, mechanical, chemical and thermal properties3,4. In case of pseudocapacitance materials, conducting polymers and transition-metal oxides are primarily used in order to enhance the energy density of supercapacitors5. Among the various transition-metal oxides, V2O5 (VO) has widely been investigated as a high-potential candidate material because of the following merits: low cost, abundant resources, layered structure, high energy density and wide potential window arising from its multivalent oxidation states6,7. Although VO-based materials have achieved remarkable benchmark properties in various fields, such as in lithium-ion batteries, field-effect transistors, gas sensors and supercapacitors, their poor electronic conductivity and bulk material properties prevent enhanced device performance8,9,10,11,12. In this regard, a large number of VO nanostructures, such as nanowires, nanotubes and nanobelts have recently been fabricated in order to obtain a high surface area13,14. Moreover, the combination of commercially available carbon allotropes and their derivatives with metal-oxide materials enhances the electronic conductivity of the composites and also prevents agglomeration of metal-oxide nanoparticles during cycling tests15,16,17. Enhanced electrochemical energy storage using nanostructured VO/graphene composites have been reported recently18,19,20,21. However, the preparation of nanostructures of VO/graphene composites commonly followed two-step processes in which reduced graphene oxide (rGO) was usually prepared either by chemical reduction or by a thermal treatment in order to obtain higher conductivity22,23,24,25. Further, very recently, our group synthesized graphene decorated nanostructured VO by simple mixing of VO particles and graphene oxide (GO) in DI water. However, this process takes a long time (approximately eight weeks) to fabricate nanostructure26. In this paper, we have reported a facile low-temperature hydrothermal process for the rapid synthesis of graphene-decorated VO nanobelts (GVNBs) without any harmful oxidizing or reducing chemical agents and surfactants. During the synthesis of GVNBs, VO particles were converted into uniformly distributed nanobelts with simultaneous reduction of GO into rGO, even at low temperature. GO played a vital role in this study. Initially, GO might act as a mild oxidizing agent to synthesize V2O5 nanobelts in DI water under hydrothermal conditions, in which GO is converted into rGO (generally, oxidizing agents reduce themselves while chemical reaction occurs). Once the GVNBs are synthesized, the highly conducting reduced GO provides double layer capacitance (in turn high power density) to the supercapacitors. Overall, the nanostructured VO involves in the faradaic reaction (psuedocapacitance), which provides high energy density and the highly conducting rGO having large surface area implicates double layer capacitance, which delivers high power density to the supercapacitors. The as prepared GVNBs having vanadium rich composition showed the enhanced specific capacitance of 288 F g−1 due to the combination of pseudocapacitance and double-layer capacitance behaviour.
Results and Discussion
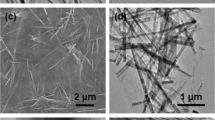
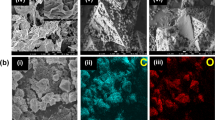
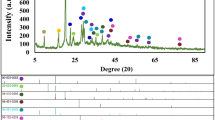
Figure 1 illustrates the role of the different precursors on the synthesis of GVNBs by the low-temperature hydrothermal process. The mixing of VO suspension and rGO precursors did not induce the formation of nanobelts (Scheme a). However, the mixing of GO precursors with the VO dispersion under the same experimental conditions (scheme c) leads to the formation of GVNBs. In order to confirm the role of GO on the nanobelts formation, only VO dispersion was subjected to the low-temperature hydrothermal process at identical experimental conditions (scheme b), but no noticeable morphological change could be observed. Figure 2 presents the field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images of pristine VO, VO after the hydrothermal treatment, the composite of VO with rGO and GVNBs synthesized via the low-temperature hydrothermal process with different ratios of VO and GO (V3G1, V1G1 and V1G3, here V3G1 indicates the ratio of VO/GO = 3:1). On the basis of FE-SEM images, the transformation into nanobelts have been observed only in case GO was added into the VO suspension, whereas the absence of GO or the use of rGO at the same conditions did not induce the formation of GVNBs. The structure of pristine VO, GVNBs and rGO have been investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), as shown in Figure 3. The peaks of pristine VO well matched the corresponding standard pattern (JCPDS Card No. 89-0612). The XRD patterns of different composites (V3G1, V1G1 and V1G3) of GVNBs contain peaks of GO, rGO and VO nanobelts (VNBs). The peaks at 6.32°, 25.9°, 28.5°, 32.7° and 41.7° correspond to the (001), (110), (111), (004) and (005) planes of VNBs, respectively27,28. The interlayer distance of GVNBs at the (001) reflection is calculated to be 1.40 nm, which is larger than the interlayer distance of pure V2O5 nanowires (1.15 nm) reported previously for the same (001) planes29,30. The peaks at 17.2°, 24.6° are assigned to partially reduced GO and rGO respectively31. Usually, GO is reduced to rGO via a high-temperature heat treatment or by strong reducing agents. In this experiment, partially reduced GO (prGO) was synthesized using the hydrothermal method under identical conditions for all samples to enable a quantitative comparison of the performance32,33,34. GO shows (001) reflection at the peak position of 10.72° (8.25 Å)35. When GO is reduced by external factors like a heat treatment or reducing chemical agents, etc., the peak position of the GO sheet shifts toward higher scattering angles, according to the degree of reduction. prGO synthesized by the hydrothermal method shows the (002) reflection at the peak position of 16° (5.54 Å). The new peak appeared the (002) plane at 24° (3.71 Å) is the characteristic of rGO. Most interestingly, the GVNBs show a very sharp characteristic rGO peak of the (002) plane at 24° (3.71 Å) and, simultaneously, the (002) reflection of prGO at the peak position of 17.5° (5.07 Å), which confirms that the mixing of V2O5 with GO under the identical hydrothermal conditions leads to the pronounced reduction of GO to rGO (shift of the (002) peak from 16 to 17.5°)31,36,37 Figure 4a shows a bright-field transmission electron microscopy (BF-TEM) image of a GVNB with a width of ~200 nm and the corresponding selective area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern. Orthorhombic crystal structure with a lattice parameter of a = 12.30 Å, b = 3.81 Å, c = 13.98 Å is confirmed by the indexing of diffraction spots, which are larger than the pure VNBs lattice parameter values (a = 11.722 Å, b = 3.570 Å, c = 11.520 Å)38. The GVNB preferentially grows along the [010] direction. In order to identify the existence of carbon element inside the GVNBs, we employed scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) technique. As shown in EELS, elemental mapping of figure 4c and d, carbon is detected at the whole GVNB region, but the distribution is uneven. Moreover, the point EELS spectrum (see Figure 4e) clearly shows the strong carbon signal at the marked region of figure 4d. The bright contrast of STEM image, strong carbon signal and increased lattice parameter may be due to the distribution of nano-sized rGO sheets between the V2O5 layers. Figure S1 (a) shows the Raman spectrum of V3G1, which reflects the interaction of VO and GO. The peak at 990 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching mode related to the vanadium-oxygen bond V = O39. The peaks at 519 cm−1 and 688 cm−1 are assigned to the bending vibrations of V3-O (triply coordinated oxygen) and V2-O (doubly coordinated oxygen) bonds, respectively40. The peaks centered at 283 cm−1 and 403 cm−1 are attributed to the modes originating from y- and x-displacements of O1 atoms, respectively41. High-frequency Raman peaks at 1352 cm−1 and 1590 cm−1 matched the D and G band of GO, respectively. The G band of GVNBs shows a little shift of up to 10 cm−1 compared to that of rGO, which may be due to the interaction between the GO and VO interfaces (Figure S1 (b))42,43. As evident from the V2p X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectrum shown in Figure S2, the peaks located at 515.8 eV and 517.5 eV correspond to the +4 and +5 oxidation states of vanadium ions, respectively. The ratio of the two V2p peaks represents the quantitative information of two different vanadium ions (+4 and +5) in the composites. If VO and GO are mixed in DI water, after 1day, a significant amount of V4+ ions is oxidized and the seeding is initiated in a direction, which is confirmed by the reduction in the ratio of V4+/V5+ from 0.096 to 0.055. Following the hydrothermal reaction, the increase in the ratio of V4+/V5+ (from 0.055 to 0.2524) was observed, which could be ascribed to the metastable state of vanadium oxide. The higher value of V4+/V5+ (0.2524) compared to the previous report (0.153)26 might be due to the effect of external forces such as high pressure and temperature during the hydrothermal reaction. Therefore, the mechanism of the nanobelts formation can be assumed as follows: The oxygen-containing functional groups present at the GO surface interact with the vanadium pentoxide surface. GO acts like an oxidizing agent, which oxidizes the vanadium ions from the partially existing V4+ to the V5+ soluble state during the reaction with GO. This intermediate compound is unstable and turns back into the stable +4 oxidation state (formation of VO seeds by trapping electrons from water molecules) and forms nanobelts26,44. As suggested by Li et al., seeded V2O5 pieces gather together in the existence of rGO, gradually grows in a direction to form a nanobelt composite45,46,47,48,49. Figure S3 presents C1s XPS spectra of GO before and after the hydrothermal treatment and mixture of GO and V2O5 (V3G1) after the hydrothermal treatment. Compared to pristine GO (GO before the hydrothermal treatment, Figure S3 (a)), a lower amount of oxygen-containing functional groups at the surface of GO and a higher portion of C-C bonding is observed in Figures S3 (b) and (c), which shows that even the low-temperature hydrothermal treatment leads to the partial reduction of GO to rGO. Interestingly, a higher portion of C-C bonding (284.6 eV) is observed in Figure S3 (c), which may originate from the interaction of V2O5 with GO, in addition to the hydrothermal treatment32,36,37,44,50. The width and thickness of a single nanobelt has been measured using atomic force microscopy (AFM), the measured values are 330 ± 20 nm and 25 ± 5 nm, respectively (Figure S4).
The electrochemical performance of VO, rGO and GVNBs was measured in 1 M Na2SO4 electrolyte and the specific capacitance Cs (in F g−1) of the electro-active materials was calculated using CV, as well as galvanostatic charge/discharge curves. CV of the electro-active materials was carried out at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 in the potential window of 0.0 to 0.8 V (Figure 5 (a)). All curves retain their quasi-rectangular shape, which confirms ideal EDLC of the materials. The vanadium-rich composite (V3G1) shows a broad redox peak with retention of quasi-rectangular shape. The calculated Cs value of the electro-active materials V3G1, V1G1, V1G3, rGO and VO are 288, 244, 135, 28.8 and 24.8 F g−1 respectively. As expected, the three different composites of VxGy material (V3G1, V1G1 and V1G3) possess higher Cs values than rGO and VO. The enhanced capacitance of the VxGy materials is attributed to the combination of non-faradaic (EDLC) and faradaic (redox) electrochemical processes. The intercalated rGO sheets provide high electrical conductivity and the addition of rGO with VO provides larger surface area, which further enhances the EDLC (non-faradaic process) of the VxGy materials. Moreover, the V2O5 nanobelts have high surface area, layered crystal structure and multivalent oxidation states of vanadium ions. These properties facilitate the insertion and extraction of alkali-metal ions (Li+, Na+ K+ etc.,) near the surface of the electro-active material. The electrochemical sodium-ion insertion process can be expressed as follows51:

From Equation (1), the charge/discharge processes involve the reversible intercalation of sodium ions into the layered V2O5 crystal structure with simultaneous electron transfer. This redox reaction leads to the partial reduction of V+5 to V+4 (and vice versa during oxidation) and thus provides the pseudocapacitance to the VxGy composites. Among the VxGy group of electro-active materials, the vanadium-rich composite V3G1 showed the highest Cs value of around 288 F g−1 (at the scan rate of 10 mV s−1), which is higher than the previously reported capacitances in the works of Fu et al19. (graphene/vanadium-oxide nanotubes, 225 F g−1 @10 mV s−1 in 1 M Na2SO4 solution) and Bonso et al52. (composite of exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets and V2O5 nanotubes, 35 F g−1 @ 10 mV s−1 in 2 M KCl, 226 F g−1 @ 10 mV s−1 in LiTFSI electrolyte). The rGO-dominated composite V1G3 has a low content of V2O5 nanobelts and also the porosity is limited by the existence of excess rGO (see SEM image Figure 2 (f)). Noticeably, the presently investigated rGO has a lower capacitance than the values reported in the literature19,53,54. The lower Cs value of rGO is ascribed to the low conductivity, which arises from the partial reduction of GO to rGO. Since the low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis was adopted and furthermore, no reducing chemical reagents are added in this work, the degree of reduction of GO to rGO is less compared to other methods19,51,55,56. From the XRD analysis, the intensity of the rGO peak is smaller than that of the GO peak, which confirms the partial reduction of GO to rGO. In general, GO has lower conductivity than rGO due to the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups in the sp3-hybridized orbital31,33. The lower Cs value of pristine V2O5 particles may arise from the smaller surface area and lower conductivity in comparison to V2O5 nanostructures19,57. If the VxGy materials are synthesized hydrothermally at low temperature, the interaction between oxygen-containing functional groups (present in GO) and the V2O5 crystallites is significant, which leads to the pronounced conversion of GO to rGO (refer also to the XRD section and the mechanism for nanobelt formation). Therefore, all VxGy composites possess higher conductivity and capacitance than the individual components. Moreover, the presence of V2O5 nanobelts between the graphene sheets prohibits the re-stacking of graphene sheets, which further enhances the conductivity of graphene54. To further understand the electrochemical reversibility of the V3G1 composite, additional CV studies were performed at different scan rates (5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 125 mV s−1) in 1 M Na2SO4 electrolyte solution. All CV curves retain their ideal quasi-rectangular shape even at higher scan rates (Figure 5 (b)), which is an indication of ideal capacitive behavior with excellent reversibility of this electrode material51. Figure 5 (c) shows the relationship between the specific capacitance of the electrode materials and the scan rate. By increasing the scan rate, the Cs value drops, which is a common phenomenon arising from the mass-transport limitation of sodium ions at high scan rates58. In detail, the interior (bulk part) of the electrode cannot sustain the redox transition due to the diffusion limitation of ions within the electrode. Therefore, the part of the electrode surface is inaccessible for electrochemical reaction at higher scan rates, which leads to a lower capacitance. Figure 6 (a) shows the galvanostatic charge-discharge (CD) curves of rGO, pristine VO particles and the three different VxGy composites obtained using 1 M Na2SO4 solution at a current density of 0.5 A g−1. The Cs values of the electro-active materials V3G1, V1G1, V1G3, rGO and VO are 128.8, 111.9, 117.5, 8.2 and 6.3 F g−1 respectively. Consistent with the CV curves, the discharge time and the specific capacitance of the VxGy materials are higher than those of pristine V2O5 particles and rGO sheets. The CD profiles of the V3G1 and V1G1 composites are symmetric and resemble an equilateral triangle, which is an indication of a high rate capability during the CD process. The CD curve of the V1G3 composite deviates from the ideal linear relationship due to the poor conductivity of this material, which further limits its pseudocapacitance19. Figure 6 (b) presents the CD profiles of the V3G1 composite at various CD rates. All CD curves exhibit a nearly linear CD rate from low to high current densities, which is an indication of balanced faradaic and non-faradaic processes. At very low discharge current density of 0.25 A g−1, the pseudocapacitance behavior is clearly visible, reflected in the non-linear shape of the CD curve and the specific capacitance of 134 F g−1 was observed. For higher current densities such as 0.5, 0.75 and 1 A g−1, the respective specific capacitance values are calculated as 128.8, 108 and 103.9 F g−1. Further the calculated specific capacitance values of V1G1 at various current densities (0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1 A g−1) are as follows: 128, 111.9, 105 and 97.5 F g−1. The graphene rich composition V1G3 has specific capacitance values of 121, 117.5, 88.1 and 55 F g−1 at the same descending order of current density values. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is an ideal tool to analyze the internal resistance and capacitance of electrode materials. EIS experiments were carried out in the frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 100 KHz in aqueous 1 M Na2SO4 solution. Figure 6 (c) represents the Nyquist plots of rGO, pristine V2O5 particles and three different composites of VxGy electro-active materials. Each Nyquist plot shows a semicircle at high-to-medium frequencies and an inclined line at low frequency, which represent the charge-transfer and diffusion resistance, respectively. In the high-frequency region, the first intersection point with the real axis represents the total impedance of the bulk solution (Rs), electrodes (Re) and the contact resistance (Rc) between electrode and current collector. At medium frequencies, the second intersection point of the semicircle with the real axis indicates the combination of the double-layer capacitance (Cdl) inparallel with the charge-transfer resistance (Rct). The inclined line in the low-frequency region represents the Warburg impedance (Ws) corresponding to the diffusive resistance of the electrolyte in the interior part of the electrode surface. The Rct values of VO, rGO, V1G3, V1G1 and V3G1 are 27.5, 20.2, 13.6, 9.2 and 5.7 Ω respectively. The charge-transfer resistance of the VxGy materials is lower than in case of VO and rGO. The lower Rct value of the VxGy materials leads to improved charge transfer and enhanced capacitance due to the following reasons: (i) V2O5 nanobelts having high surface area enhances the pseudocapacitance of the electrode material, (ii) VxGy materials possess highly conducting rGO sheets with high surface area improved the electronic conductivity of the GVNB composite and also enhance the electrochemical double-layer capacitance of the working electrode and (iii) the incorporation of V2O5 nanobelts between the graphene sheets prevents the agglomeration of graphene sheets which also enhances the conductivity. Electrochemical cycling stability is one of the key factors that determines the applicability of this material to commercial supercapacitors. The cyclic stability of the V3G1 composite was measured by CV in the potential window of 0 to 0.8 V at a high scan rate of 200 mV s−1 for 5000 cycles. According to previous reports, the capacitance retention of pure vanadium oxide in aqueous electrolyte is very poor due to the structural damage caused by the insertion and desertion of electrolyte ions19,59. In the present case, the V3G1 material retains 93% of its initial capacitance value after 1000 cycles and, further, 82% capacitance retention is observed even after 5000 cycles which demonstrates excellent stability of the material with superior reversibility during the cycling test (Figure 7 (a)). This capacitance retention is much higher than that previously reported by Fu et al19. (48% retention after 5000 cycles @ 100 mV s−1 scan rate) and the best among vanadium oxide-based composite materials51,52. EIS was measured after 5000 cycles for the post analysis of the electrode material. The shape of the EIS spectrum was similar to the initial spectrum, which comprises a semicircular arc in the high-frequency region and an inclined line in the low-frequency region. The Rct value increased from 2.3 to 6.32 Ω after 5000 cycles (see Figure 7 (b)). This might be induced by the adhesion loss between the electro-active material and the current collector or due to the dissolution of a small amount of V2O5 in aqueous medium at a high scan rate (the change in color of the solution from white to yellow is an indication)53,60,61. From the electrochemical performance described above, we conclude that GVNBs could be a potential candidate for practical supercapacitor applications. Moreover, the electrical conductance affects the intrinsic performance of GVNBs, hence we measured the current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of a single GVNB synthesized by hydrothermal method as shown in Fig. S5, the values are much higher than a single GVNB grown by spontaneous method and V2O5 nanowire (VON) synthesized by sol-gel method26. The superior current was observed in the I-V curve of GVNB synthesized by hydrothermal method which may be the reason for the enhancement of the specific capacitance.
(a) CV curves of rGO, pristineVO particles, V1G3, V1G1 and V3G1 electro-active materials measured at a scan rate of 10 mV s−1 in 1 M Na2SO4 solution. (b) CV curves of the V3G1 electrode measured at different scan rates ranging from 5 to 125 mV s−1. (c) Specific capacitance calculated from the CV curves of Figure 1(b) of the V3G1 electrode at various scan rates.
(a) Galvanostatic charge-discharge curves of rGO, pristine VO particles, V1G3, V1G1 and V3G1 electro-active materials measured at a constant current density of 0.5 A g−1 in 1 M Na2SO4 solution. (b) Galvanostatic charge-discharge curves of V3G1 electrode material measured at various current densities. (c) Electrochemical impedance spectra of rGO pristine V2O5 particles, V1G3, V1G1 and V3G1 electro-active materials measured in 1 M Na2SO4 solution. The inset shows an enhanced view of the high-to-medium frequency region.
In summary, we have reported a facile method for the synthesis of GVNBs using a low-temperature hydrothermal process. GO played a vital role as a mild oxidizing agent for the formation of nanowires, as well as enhanced the conductivity of GVNBs. The insertion of rGO into the layered V2O5 crystal structure is confirmed by EELS analysis. The high surface area and pseudocapacitive nature of VNBs along with the enhanced conductivity of GVNBs upon addition of graphene resulted in an improved specific capacitance. Among various GVNBs, the V2O5-rich composition, V3G1 showed the highest capacitance and long-term cycle life with the capacitance retention of 82% even after 5000 cycles.
Methods
Preparation of GO and rGO
GO was prepared from natural graphite powder according to the modified Hummer's method62. 12 g of graphite powder (SP-1, Bay carbon), 10 g of K2S2O8 (Sigma Aldrich, ≥99.0%) and 10 g of P2O5 (Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%) were added to 50 mL of concentrated H2SO4 solution and heated to 80°C. The resultant mixture was kept overnight with 2 L of DI water. The mixture was then filtered and washed with DI water several times. The suspension was dried in vacuum under ambient conditions. This pretreated flake-like graphite was mixed with 460 mL of H2SO4 at 0°C and then 60 g of KMnO4 (Sigma Aldrich, ≥99.0%) was added slowly for further oxidation. The mixture was stirred for 2 h at 35°C and, subsequently, 920 mL of DI water was added. Shortly afterwards, 2.8 L of DI water and 50 mL of 30% H2O2 (SAMCHUN pure chemical) were added into the concentrated H2SO4 solution. The GO suspension was centrifuged and washed with 5 L of 10% HCl (SAMCHUN pure chemical) solution and, repeatedly, with 5 L of DI water, followed by filtering of the graphite-oxide solution through dialysis (dialysis membrane: Spectrum Laboratories, MWCO-12-14,000) for 2 weeks. Finally, GO sheets were prepared through drying the resulting suspension at 50°C for 3 days. In this work, two kinds of rGO were separately prepared by different methods. The first type of rGO was prepared by pyrolysis of GO in a quartz tube furnace at 1100°C for 2 h under Ar flow63 for comparison purpose with GO used for the synthesis of GVNBs. The other type of rGO was obtained via the hydrothermal route32 and annealed in a vacuum furnace to investigate the characteristics of supercapacitors under the same conditions like those of GVNBs.
Synthesis of graphene decorated V2O5 nanobelts composites (GVNBs)
Different ratios (3:1, 1:1, 1:3) of pristine V2O5 (VO) particles (Aldrich) and of as-synthesized GO were dispersed in 30 mL of DI water and then stirred vigorously for 2 h at room temperature. The obtained yellow/brownish slurry was transferred into a 50 mL Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave and maintained at 120°C for 24 h in a muffle furnace. Then, the autoclave was cooled naturally to room temperature inside the muffle furnace. The resulting material was freeze-dried for 72 h to obtain GVNBs with high surface area. The final product was transferred into a vacuum furnace and annealed at 400°C for 2 h under Ar gas in order to improve the crystallinity of the GVNBs.
Materials Characterization
The crystalline structure of the as-prepared samples was characterized using XRD (Bruker D8 Advance with Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å). The morphologies of the samples were observed by FE-SEM (Nano230, FEI co.). XPS (Thermo Fisher, UK) measurements were performed with monochromatic Al Kα radiation as X-ray source for the investigation of the surface states. To gain further insight into the structure of the products, they were additionally investigated by Raman spectroscopy (Alpha 300S, WITec) using a He-Ne laser with 532 nm in wavelength. The thickness of a single GVNB on SiO2 substrate was measured using AFM (Multimode V, Veeco). BF-TEM, electron diffraction pattern and EELS were performed with an image-side aberration-corrected TEM (Titan3 G2 60-300, FEI) which was operated at 80 kV. High-angle annular dark field (HAADF) scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) was carried out using a probe-side aberration-corrected TEM (JEOL 2100F, JEOL) operated at 200 kV.
Electrochemical Characterization
Electrochemical experiments were carried out in the typical three-electrode-cell setup using a potentiostat/galvanostat (Biologic/VSP) at room temperature. The working-electrode paste was prepared by mixing the corresponding electro-active materials (rGO, V2O5, V1G3, V1G1 and V3G1), conducting acetylene black and a polymeric binder (polyvinylidene difluoride) in the mass ratio of 80:10:10 and ground in a mortar using an N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP) solvent. The paste was then coated on nickel-foam substrate (mass loading ~3.5 mg/cm2) using the spatula and then dried at 120°C for 12 h in a vacuum oven. A large surface area platinum mesh was used as counter electrode, Ag/AgCl (std. KCl) was used as reference electrode and 1 M Na2SO4 solution was used as electrolyte. Cyclic voltammograms (CV) were obtained at various scan rates (5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 125 mV s−1) in the potential window of 0 to 0.8 V (Vs Ag/AgCl [std. KCl]). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were carried out over the frequency range of 0.1 Hz to 100 kHz with the AC amplitude of 10 mV. Galvanostatic charge/discharge curves were recorded at different current densities (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1 A g−1) in the potential window of 0 to 0.8 V (Vs Ag/AgCl [std. KCl]).
References
Wang, H. & Dai, H. Strongly coupled inorganic-nano-carbon hybrid materials for energy storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 3088–3113 (2013).
Ellis, B. L., Knauth, P. & Djenizian, T. Three-dimensional self-supported metal oxides for advanced energy storage. Adv. Mater. 26, 3368–3397 (2014).
Geim, A. K. Graphene: Status and prospects. Science 324, 1530–1534 (2009).
Geim, A. K. & Novoselov, K. S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183–191 (2007).
Yan, J., Wang, Q., Wei, T. & Fan, Z. Recent advances in design and fabrication of electrochemical supercapacitors with high energy densities. Adv. Energy Mater. 4 (2014).
Wang, W. Y., Takahashi, K., Lee, K. & Cao, G. Nanostructured vanadium oxide electrodes for enhanced lithium-ion intercalation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 1133–1144 (2006).
Wang, Y. & Cao, G. Developments in nanostructured cathode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 20, 2251–2269 (2008).
Cao, A. M., Hu, J. S., Liang, H. P. & Wan, L. J. Self-assembled vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) hollow microspheres from nanorods and their application in lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 4391–4395 (2005).
Liu, J., Xia, H., Xue, D. & Lu, L. Double-shelled nanocapsules of V2O5-based composites as high-performance anode and cathode materials for Li ion batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 12086–12087 (2009).
Dexmer, J. et al. Vanadium oxide-PANI nanocomposite-based macroscopic fibers: 1D alcohol sensors bearing enhanced toughness. Chem. Mater. 20, 5541–5549 (2008).
Kim, G. T. et al. Field-effect transistor made of individual V2O5 nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1875–1877 (2000).
Wee, G., Soh, H. Z., Cheah, Y. L., Mhaisalkar, S. G. & Srinivasan, M. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of electrospun V2O5 nanofibers as supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 6720–6725 (2010).
Aricò, A. S., Bruce, P., Scrosati, B., Tarascon, J. M. & Van Schalkwijk, W. Nanostructured materials for advanced energy conversion and storage devices. Nat. Mater. 4, 366–377 (2005).
Bruce, P. G., Scrosati, B. & Tarascon, J. M. Nanomaterials for rechargeable lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 2930–2946 (2008).
Lee, J. W. et al. Extremely stable cycling of ultra-thin V2O5 nanowire-graphene electrodes for lithium rechargeable battery cathodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 9889–9894 (2012).
Sathiya, M., Prakash, A. S., Ramesha, K., Tarascon, J. M. & Shukla, A. K. V2O5-anchored carbon nanotubes for enhanced electrochemical energy storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 16291–16299 (2011).
Perera, S. D. et al. Vanadium oxide nanowire-carbon nanotube binder-free flexible electrodes for supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 1, 936–945 (2011).
Wang, Y. & Cao, G. Synthesis and enhanced intercalation properties of nanostructured vanadium oxides. Chem. Mater. 18, 2787–2804 (2006).
Fu, M. et al. Graphene/vanadium oxide nanotubes composite as electrode material for electrochemical capacitors. Physica B 421, 77–82 (2013).
Zhao, H., Pan, L., Xing, S., Luo, J. & Xu, J. Vanadium oxidesereduced graphene oxide composite for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors with improved electrochemical performance. J. Power Sources 222, 21–31 (2013).
Perera, S. D. et al. Vanadium oxide nanowire-Graphene binder free nanocomposite paper electrodes for supercapacitors: A facile green approach. J. Power Sources 230, 130–137 (2013).
Stankovich, S. et al. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45, 1558–1565 (2007).
Li, D., Müller, M. B., Gilje, S., Kaner, R. B. & Wallace, G. G. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105 (2008).
Shin, H. J. et al. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1987–1992 (2009).
Becerril, H. A. et al. Evaluation of solution-processed reduced graphene oxide films as transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2, 463–470 (2008).
Lee, M. et al. Graphene oxide assisted spontaneous growth of V2O5 nanowires at room temperature. Nanoscale 6, 11066–11071 (2014).
Yu, J., Yu, J. C., Ho, W., Wu, L. & Wang, X. A Simple and General Method for the Synthesis of Multicomponent Na 2V6O16·3H2O Single-Crystal Nanobelts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 3422–3423 (2004).
Avansi Jr, W., Ribeiro, C., Leite, E. R. & Mastelaro, V. R. Vanadium pentoxide nanostructures: An effective control of morphology and crystal structure in hydrothermal conditions. Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 3626–3631 (2009).
Xiong, C., Aliev, A. E., Gnade, B. & Balkus Jr, K. J. Fabrication of silver vanadium oxide and V2O5 nanowires for electrochromics. ACS Nano 2, 293–301 (2008).
Kim, B. H. et al. Hydrogen spillover in Pd-doped V2O5 nanowires at room temperature. Chem. Asian J. 7, 684–687 (2012).
Kim, B. H. et al. Investigation on the existence of optimum interlayer distance for H 2 uptake using pillared-graphene oxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 14217–14222 (2012).
Zhou, Y., Bao, Q., Tang, L. A. L., Zhong, Y. & Loh, K. P. Hydrothermal dehydration for the “green” reduction of exfoliated graphene oxide to graphene and demonstration of tunable optical limiting properties. Chem. Mater. 21, 2950–2956 (2009).
Dreyer, D. R., Park, S., Bielawski, C. W. & Ruoff, R. S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 228–240 (2010).
Nethravathi, C. & Rajamathi, M. Chemically modified graphene sheets produced by the solvothermal reduction of colloidal dispersions of graphite oxide. Carbon 46, 1994–1998 (2008).
Hong, W. G. et al. Agent-free synthesis of graphene oxide/transition metal oxide composites and its application for hydrogen storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 7594–7599 (2012).
Rout, C. S. et al. Synthesis and characterization of patronite form of vanadium sulfide on graphitic layer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 8720–8725 (2013).
Nam, I., Kim, N. D., Kim, G. P., Park, J. & Yi, J. One step preparation of Mn3O4/graphene composites for use as an anode in Li ion batteries. J. Power Sources 244, 56–62 (2013).
Petkov, V. et al. Structure of V2O5·nH2O xerogel solved by the atomic pair distribution function technique. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 10157–10162 (2002).
Fang, W. C. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of vanadium oxide/carbon nanotube composites for supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 11552–11555 (2008).
Yan, B. et al. Single-crystalline v2O5 ultralong nanoribbon waveguides. Adv. Mater. 21, 2436–2440 (2009).
Baddour-Hadjean, R., Pereira-Ramos, J. P., Navone, C. & Smirnov, M. Raman microspectrometry study of electrochemical lithium intercalation into sputtered crystalline v2O5 thin films. Chem. Mater. 20, 1916–1923 (2008).
Tsukamoto, T., Yamazaki, K., Komurasaki, H. & Ogino, T. Effects of surface chemistry of substrates on Raman spectra in graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 4732–4737 (2012).
Das, A., Chakraborty, B. & Sood, A. K. Raman spectroscopy of graphene on different substrates and influence of defects. Bull. of Mater. Sci. 31, 579–584 (2008).
Liu, H. & Yang, W. Ultralong single crystalline V2O5 nanowire/graphene composite fabricated by a facile green approach and its lithium storage behavior. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 4000–4008 (2011).
Ren, X., Jiang, Y., Zhang, P., Liu, J. & Zhang, Q. Preparation and electrochemical properties of V2O5 submicron-belts synthesized by a sol-gel H2O2 route. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 51, 133–138 (2009).
Zhou, F., Zhao, X., Yuan, C., Li, L. & Xu, H. Low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of orthorhombic vanadium pentoxide nanowires. Chem. Lett. 36, 310–311 (2007).
Zhou, F., Zhao, X., Liu, Y., Yuan, C. & Li, L. Synthesis of millimeter-range orthorhombic V2O5 nanowires and impact of thermodynamic and kinetic properties of the oxidant on the synthetic process. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 16, 2506–2509 (2008).
Livage, J. Vanadium pentoxide gels. Chem. Mater. 3, 578–593 (1991).
Li, M., Kong, F., Wang, H. & Li, G. Synthesis of vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) ultralong nanobelts via an oriented attachment growth mechanism. CrystEngComm 13, 5317–5320 (2011).
Xu, L. et al. Spontaneous redox synthesis of Prussian blue/graphene nanocomposite as a non-precious metal catalyst for efficient four-electron oxygen reduction in acidic medium. J. Power Sources 240, 101–108 (2013).
Perera, S. D. et al. Vanadium oxide nanowire – Graphene binder free nanocomposite paper electrodes for supercapacitors: A facile green approach. J. Power Sources 230, 130–137 (2013).
Bonso, J. S. et al. Exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets–V2O5 nanotube composite electrodes for supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 203, 227–232 (2012).
Ramadoss, A. & Kim, S. J. Improved activity of a graphene–TiO2 hybrid electrode in an electrochemical supercapacitor. Carbon 63, 434–445 (2013).
Ramadoss, A., Kim, G.-S. & Kim, S. J. Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide/TiO2 nanorod/reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanostructures as electrode materials for supercapacitor applications. CrystEngComm 15, 10222–10229 (2013).
Yang, S. et al. Bottom-up Approach toward Single-Crystalline VO2-Graphene Ribbons as Cathodes for Ultrafast Lithium Storage. Nano Lett. 13, 1596–1601 (2013).
Zhao, H., Pan, L., Xing, S., Luo, J. & Xu, J. Vanadium oxides–reduced graphene oxide composite for lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors with improved electrochemical performance. J. Power Sources 222, 21–31 (2013).
Qu, Q., Zhu, Y., Gao, X. & Wu, Y. Core–Shell Structure of Polypyrrole Grown on V2O5 Nanoribbon as High Performance Anode Material for Supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2, 950–955 (2012).
Liu, W.-w., Yan, X.-b. & Xue, Q.-j. Multilayer hybrid films consisting of alternating graphene and titanium dioxide for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 1413–1422 (2013).
Reddy, R. N. & Reddy, R. G. Porous structured vanadium oxide electrode material for electrochemical capacitors. J. Power Sources 156, 700–704 (2006).
Yan, J. et al. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of graphene nanosheet/Co3O4 composite for supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 55, 6973–6978 (2010).
Yan, J. et al. Fast and reversible surface redox reaction of graphene–MnO2 composites as supercapacitor electrodes. Carbon 48, 3825–3833 (2010).
Tung, V. C., Allen, M. J., Yang, Y. & Kaner, R. B. High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 25–29 (2009).
Wang, X., Zhi, L. & Müllen, K. Transparent, conductive graphene electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nano Lett. 8, 323–327 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government, MSIP (2013R1A1A2059244). B.H.K. and H.-B.-R. L. were supported by the Incheon National University Research Grant in 20141308. We would like to thank Mr. R. Ananthakumar, Jeju National University, Republic of Korea for the assistance of specific capacitance calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.L. and S.K.B. designed the study, performed experiments, collected and analysed data and wrote the paper. H.Y.J. performed and analysed the TEM study. W.G.H. provided graphene oxide and analysed the data. H.-B.-R.L. performed electrical measurement and analysed data. B.H.K. and Y.J. supervised the study and wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder in order to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Balasingam, S., Jeong, H. et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of graphene decorated V2O5 nanobelts for enhanced electrochemical energy storage. Sci Rep 5, 8151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08151
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08151
This article is cited by
-
A review on the electrochemical behavior of graphene–transition metal oxide nanocomposites for energy storage applications
Journal of Materials Science (2023)
-
Polyaniline/vanadium pentoxide/lead tetroxide ternary composite for LPG sensing
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2023)
-
Investigations of flexible pseudocapacitive electrodes consisting of ternary V2O5/PEDOT/rGO hybrids in Li-ion containing aqueous and organic electrolytes
Journal of Materials Science (2023)
-
NiS/Cu7S4 composites as high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2023)
-
Mesoporous V2O5/g-C3N4 Nanocomposites for Promoted Mercury (II) Ions Reduction Under Visible Light
Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.