Abstract
Landslides are frequently triggered by extreme meteorological events which has led to concern and debate about their activity in a future greenhouse climate. It is also hypothesized that dry spells preceding triggering rainfall may increase slope predisposition to sliding, especially in the case of clay-rich soils. Here we combined dendrogeomorphic time series of landslides and climatic records to test the possible role of dry spells and extreme downpours on process activity in the Outer Western Carpathians (Central Europe). To this end, we tested time series of past frequencies and return periods of landslide reactivations at the regional scale with a Generalized Linear Mixed (GLM) model to explore linkages between landslide occurrences and triggering climate variables. Results show that landslide reactivations are concentrated during years in which spring and summer precipitation sums were significantly higher than usual, and that triggering mechanisms vary between different types of landslides (i.e. complex, shallow or flow-like). The GLM model also points to the susceptibility of landslide bodies to the combined occurrence of long, dry spells followed by large precipitation. Such situations are likely to increase in frequency in the future as climate models predict an enhancement of heatwaves and dry spells in future summers, that would be interrupted by less frequent, yet more intense storms, especially also in mountain regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Landslides represent global natural hazards causing thousands of fatalities every year and heavy devastation of infrastructure1. In the most affected areas, financial costs and countermeasures are in the order of billions of dollars2,3. Whereas lithology, slope morphology, land-use changes, climate warming, and/or anthropogenic pressure can predispose slope stability4,5,6,7,8, it is extreme rainfall, rapid snowmelt or earthquakes that will ultimately trigger landslide events9. In addition, the timing and velocity of slowly/persistently moving earthflows can be driven by internal conditions within the landslide body (such as soil swelling) and less so climatic triggers10. A proper understanding of the interactions and interdependencies of these factors and how climatic events influence the occurrence of landslides is crucial to understand landslide frequencies and magnitudes, even more so in a context of climate change where triggering conditions are likely to change.
Landslide research has recently focused on the monitoring of their movement using either in-situ11 or remotely sensed techniques12, calculation of rainfall intensity-duration thresholds for the initiation of mass movement activity13, landscape modelling and surface roughness dating14, and geochronological approaches to determine the age of landslide bodies or their activity. If combined with historical sources, geochronological data and palaeoclimatic proxies have repeatedly evidenced linkages between climate and landslide activity15. It was shown that both long-lasting16,17,18,19 and short-term, yet intense rainfalls19,20,21,22 are key drivers of landsliding, along with rapid snowmelt episodes or rain-on-snow events23,24,25. Besides, the combined effect of dry spells and extreme rainfall has been linked to landslide activity due to shrinking-swelling effects of clayey minerals in the weathered bedrock of landslide bodies10,26. In this context, the current understanding is that macropores of clay-rich soils would enlarge during dry spells which would then facilitate water transport into the landslide body during subsequent, high-magnitude rainfall26.
An improved understanding of how the consecutive occurrence of dry spells and downpours impacts on landslide dynamics are quite central because IPCC scenarios27 across Europe project an increase in the intensity and duration of dry spells/heatwaves and an increase in the intensity of heavy rainfall events. The combined occurrence of both phenomena – dry spell duration and precipitation intensity – is referred to as hydroclimatic intensity and shown to have increased in response to global warming over the second half of the 20th century28.
The actual triggering of landslides also depends on the structural setting and lithology which in turn may differ among different landslide types: deep-seated landslides are generally thought to respond to excessive monthly and/or seasonal rainfall sums, whereas shallow landsliding would depend mainly on intense, yet short-lived rainfall peaks5,29.
To test the hypotheses of changes in hydroclimatic intensity and differences in triggers, robust, long-term records of landslide activity are critically needed. In reality, however, assessments are often hampered by fairly incomplete, descriptive records of historical activity on one hand, or short periods covered by systematic monitoring limiting the number of recorded landslides on the other hand, as well as by the absence of systematic, long-term meteorological data6. The extension of times series of landslides and the accurate dating of landslide activity is thus crucial for any analysis of climate factors triggering events. Besides the application of surface roughness dating14 and satellite imagery interpretation29, dendrogeomorphology (i.e. the dating of geomorphic processes using tree-ring records30) can overcome this shortcoming by dating past landslide activity in forested regions16,23,31,32. The resulting chronologies may be used as a basis for the comparison of climate records with years or decades with enhanced mass movement activity33,34. In addition, by modelling the combined effect of climate variables, one may also gain deeper understanding of mass movement triggering mechanisms23,35.
In the past, however, research on climate–landslide relations focused at the local or catchment scales32,36,37,38,39 whereas regional, tree-ring based chronologies of past landsliding have remained scarce. First promising attempts towards regional analysis were realized on seven landslide bodies in the Pyrenees and French Alps to reveal common mechanisms of landslide triggering16,23.
Here, we use a comprehensive regional, dendrogeomorphic landslide reconstruction40 from the Outer Western Carpathians (Central Europe) to test whether the successive occurrence of dry spells and extreme precipitation has had a negative effect on landslide activity in the past. To this end, we combine reconstructed time series from 26 landslide bodies with climate variables using a Generalized Linear Mixed (GLM) model, and will put observed, past climate-landslide drivers into perspective by comparing outcomes with projections of future climate change.
Landslide region
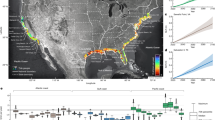
The Hostýnsko-Vsetínská hornatina Mts. represent a mid-mountain part of the Outer Western Carpathians (Central Europe) and are centred around 49.4°N and 18.0°E (Fig. 1). The area is composed of Palaeogene flysch (predominantly sandstone, claystone, and shale) thrusted to nappe structures with evidence of multiple, past tectonic, but without tectonic seismic activity in modern times. The presence of montmorillonitic clays (e.g., smectite) favours the shrinking and swelling of weathered bedrock, thereby the cohesion and friction angle41. This lithological setting and mineralogical composition has favoured the evolution of different landslide types in the region (i.e. shallow, flow-like, and complex landslides) and the formation of very distinct morphological features (Supplementary Figs S1, S2). In fact, the density and variety of different, active landslides is considered unique for Central Europe42.
Location of landslide sites and meteorological stations. Map (a) shows the location of the study region within Central Europe. Map (b) shows the distribution of known landslides and tectonic features75,76: 1 – active landslides; 2 – non-active landslides; 3 – normal fault; 4 – thrust fault; 5 – fold nappe. Maps were created and modified in the ArcMap 10.1 software (ESRI; https://www.esri.com/en-us/home). Source of base maps: images of SRTM 1 Arc-Second Global77 available from USGS Earth Explorer (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov).
The area of interest (c. 600 km2; 40 × 15 km) is characterized by fully humid temperate climate. Mean annual temperature ranges from 5 °C at the summits to 8 °C in the valleys. Precipitation increases in zonal direction with the lowest annual precipitation in the western part (700–800 mm) and highest values in the eastern part (900–1200 mm) of the study region. Summers normally receive the largest amounts of rainfall (Fig. S3) when 24-h rainfall sums may exceed 100 mm in extreme cases. Snow covers the surface between December and April and lasts on the ground for 60 days at the foothills to 140 days at summits43.
The region suffered from intense deforestation for pasturing during the Wallachian colonisation in the 15th to 17th centuries. Nowadays, forest stands cover the slopes again, and are composed predominantly of introduced Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) with occasional silver fir (Abies alba Mill.), European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) and European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) trees.
The presence of non-permeable, plastic claystone and extreme precipitation during springs and summers favours the release of frequent landslide activity over the entire region. Documentary sources44,45,46 report on landslide calamites in 1919, 1940, and 1997 as a result of extreme rainfall episodes.
Results
Precipitation triggers of the landslide activity
Dendrogeomorphic reconstruction of past process activity provides evidence of 237 landslide events over the 26 landslide bodies for the period 1920–2017 (Fig. 2). Landslides occurred in 66 different years of which 51.5% were characterized by above-average annual precipitation. Years with landslide reactivations show significantly higher annual precipitation sums than those without landslide activity (p = 0.02), and even more so when summer (p = 0.01) or spring (p = 0.04) precipitation sums are taken into consideration. By contrast, autumn and winter precipitation do not significantly differ between event and non-event years (p = 0.66 and 0.08, respectively; Fig. 3). The annual values of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI; calculated for the period 1936–2017; Fig. 2) point to eleven landslide reactivations that would have occurred during moderately or extremely wet years (e.g. 1941, 1981, 1997), whereas seven landslide events occurred during moderately or extremely dry years (e.g. 1942, 1959, 1973). In addition, monthly SPI allowed identification of wetting and drying cycles during particular years (Fig. S4). We observed the occurrence of drying cycles in winter and/or spring followed by extreme rainfall event in summer and/or autumn in 50% of the years (e.g. 1939–40, 1956–57, 1970–72, 1982, 1994, 1996–97) in 50% of the landslides for which the It index >10% and/or the ratio of landslides exceeded 10%. The remaining events were either associated to rainfall accumulation over the course of the year, possible rain-on-snow events, or could not be associated to any specific pattern (Fig. S4).
Chronology of landslide activity, annual precipitation totals in the study region, annual Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and number of wet/dry months according to the monthly SPI. The ratio of active landslides and value of average It index (i.e. number of disturbed trees in a particular year divided by the number of all sampled trees living in that particular year; in %) of all landslide events40 is denoted for each event year. Grey dashed lines show the event years with more than 20% of active landslides and exceeding the 10% value of It index.
Slight differences in triggering conditions also exist between shallow, flow-like, and complex landslides. Not only do complex landslides occur less frequently (recurrence interval: 12.9 yrs) than their flow-like and shallow counterparts (8.3 and 7.5 yrs, respectively; Fig. S5), we also observe significantly larger annual precipitation sums in years with reconstructed shallow and flow-like landslide activity (p = 0.01 and 0.02, respectively). In the case of complex landslides, differences between event and non-event years are not significant (p = 0.09). Above-average spring precipitation has the largest effect on shallow landslides (p = 0.02), whereas larger-than-normal summer precipitation seems to be the main driver of activity in complex landslide bodies (p = 0.03). Spring and summer precipitation seems to be equally important for the release of flow-like landslides (Fig. 4). In addition, landslides of the western part of the study region are most likely triggered during spring precipitation events. Interestingly, activity in its central parts probably responds to higher winter precipitation (p = 0.01), whereas no significant differences are observed during spring and summer. The eastern region shows the best correspondence with significantly higher summer precipitation sums (p = 0.03), but also with significantly lower autumn precipitation (p = 0.01; Fig. 4).
P-values of Mann-Whitney U test showing differences between years with and without landslide activity based on annual (ANN) and seasonal (DJF = winter; MAM = spring; JJA = summer; SON = autumn) precipitation totals, regions and landslide types. Red up = significantly higher precipitation during event years; yellow up = higher precipitation, but no significant difference: 0.05 < p < 0.10; equal sign = no significant difference; red down = significantly lower precipitation sums in event years.
Precipitation trends and landslide frequencies
Precipitation did not change significantly over the last ~100 yrs, neither in terms of annual nor seasonal sums – and only a slightly positive trend is discernible for winter (p = 0.06, Kendal’s τ = 0.13) and spring precipitation (p = 0.09, τ = 0.11). By contrast, decadal variability is quite remarkable both in terms of annual and seasonal precipitation totals (Figs 5, S6–S8). Periods of increased landslide activity correlate with periods of enhanced summer rainfall, especially if the latter occurs after drier years/summers. As such, dry periods during the 1930s and 1950s were followed by enhanced landslide activity in wet periods of the 1940s and 1960s. The same pattern cannot, however, be found during the intense landsliding of the 1990s. During the first half of the 1990s, a positive linear trend is observed in winter and spring precipitation, but also a significantly negative trend in summer precipitation. The strong increase in summer rainfall after 1995 converted the negative trend to positive, even in terms of annual precipitation sums. Despite negative decadal trends of summer precipitation observed from 1985 to 1995, landslide activity has increased, thereby pointing to the complexity of climate-landslide linkages.
Comparison of precipitation trends with frequency of landslide activity. Decadal trends of spring (A) and summer precipitation (B) with significance levels based on the Mann-Kendal trend test (black-bordered polygons show the most significant drying or wetting periods); (C) decadal frequency of landslide activity based on landslide types.
Dry spells and extreme precipitation enhance landslide activity
We hypothesized that increasing air temperatures have an influence on the drying rate of soils, which in turn results in the spreading of tension cracks (Fig. S2) and a weakening of soil anchorage, especially in the case where the soil is then affected by important rainfall, and ultimately favor landslide triggering. To test the hypothesis that dry spells and subsequent rainfall episodes can explain regional landslide activity over the course of the 20th century, we applied a Generalized Linear Mixed (GLM) models (see methods). The GLM model suggests that the probability of landsliding increases in years with long dry spells and maximum precipitation sums (Fig. 6). The Akaike Information Criterion (AIC, see Methods) supports the statistical model accounting for the combined effect with a first-order autoregressive parameter AIC = 12175.49 against the null hypothesis (AIC = 12313.19). When compared to the individual effects of the dry spell (model parameter = −0.110; p-value = 0.328) and maximum precipitation (model parameter = 1.009; p-value < 0.000), the combined effect of both covariates is highly significant with a larger weight in model outcome (model parameter = 1.219, p-value < 0.000; number of observation = 1999; degrees of freedom = 1970; Fig. 6). Thus, our results support the positive role of maximum precipitation sums at the annual scale in triggering landslides, and that dry spells play a role in predisposing process activity by changing soil properties.
Predicted tree-ring disturbance induced by regional landslide activity is shown here as a function of maximum annual precipitation rate and dry spells by using a generalized linear mixed (GLM) model. The colour ramp indicates the predicted response of tree-growth disturbances to landslides activity. The labelled dots indicate landslide signals during specific years. The units for the maximum annual precipitation rate and dry spells have been standardized and are shown with Z-scores.
Discussion
The spatio-temporal occurrence of landslides mainly depends on the frequency and intensity of triggers, with the latter often being site-specific and dependent on climate as well as changes thereof6. The significant influence of heavy precipitation on landslide reactivations has been documented repeatedly, even at regional scales13,16,46. Several studies also pointed to the crucial role of antecedent rainfall in triggering mass movement activity18,47. In the region analysed here, a stark inter-decadal variability of landslide activity can be observed over the last century, but no clear long-term trends. This is in contrast to reconstructions from the European Alps where an increasing trend of debris flows and shallow landslides has been observed over the last 100 years, mostly as a result of complex interactions between changing weather patterns triggering events, enhanced glacial retreat and permafrost degradation7,23,48.
Peaks in landslide activity in the study region (1940–41, 1961, 1965, 1967, and 1985) correspond with generally wet years, and most of these years were also known from historical annals46. Furthermore, the increased frequency of landslides recorded from 1996 to 2010 corresponds to the wet episode recorded across Central Europe. During this period, frequent floods and enhanced landsliding were reportedly caused by long-term, intense precipitation (1997, 2002, 2010)18,46,49.
The combined role of increased air temperatures and prolonged dry spells has been identified mostly in Alpine region where it is an important driver of rockfall occurrences50. By contrast, a direct link between the two parameters has not been investigated for landslide activity yet. The statistical model employed in this study supports the importance of dry spells in triggering landslide activity, at least in the study region and can be explained by the regional lithological settings. In the Outer Western Carpathians, soils and weathered bedrock contain ample amounts of smectite minerals characterised by a high sorptive and swelling capacity on the one hand and very low permeability on the other hand41,51. During dry spells, the amount and size of preferential flow paths (such as through tension cracks and fissures) may increase due to a shrinking of the smectite-rich soils. These new and enlarged transport conduits will then allow infiltration of water during subsequent rainfall episodes. Pore water pressure will increase rapidly in these materials and ultimately induce surface movements. Wetting/drying cycles are considered important in cracking, even in deep-seated failure movements and despite the fact that preferential flow paths will only influence the soil mantle52. It has also been shown that soil swelling, continuous opening/closing of the fissures, and compaction/compression forces of upslope material will result in increased pore-fluid pressure and thereby act as important drivers of activity in clay-rich, slow moving earthflows10,53,54. Despite the fact that forested slopes are somewhat less susceptible to occurrence of desiccation cracks than bare surfaces, the enlargement of tension cracks (Fig. S2) and fissures in specific parts of landslide bodies may increase water infiltration as well. In addition, even if trees are considered slope stabilizing agents, they may also facilitate the creation of new preferential flow paths due to the spreading of the root system (both living and decayed roots)55. However, mechanisms of water infiltration into a landslide body and the evolution of preferential flow paths has not been understood fully so far52.
According to our results, drying/wetting cycles would have favoured the initial reactivation of multiple landslides in the study area in 1939, 1940, 1972, 1985 and 1994. Landslide chronology also points to the occurrence of events during generally drier years but with concurrent extreme, yet short-lived summer precipitation (>50 mm), for instance in the years 1942, 1946, 1982, and 1988. Moreover, the extremely long dry spells in 1953–54 and 1964 were followed by extremely wet periods in 1955 and 1965, and thus point to a possible influence of longer-than-annual drying/wetting cycles (Fig. S4). In addition, results of GLM confirmed the positive anomalies of annual rainfall and dry spells in 1930, 1981, and 1997. Furthermore, during these years, long dry spells in winter/spring were followed by intense rainfall during the summer months. The 1990s were the most active period in terms of landsliding and characterised by drier summers and more humid winters/springs, first of all until 1995. Frequent alternations of dry and wet months in 1990–94 as well as the concurrent occurrence of maximum daily rainfall between 30–60 mm seem to be important factors of incipient landslide activity. In addition, the dry winter 1996/1997, in combination with slopes that have been destabilised by preceding landslide activity should thus be considered as complex preparatory factors of the enhanced landsliding in 1997 (Figs 6, S4).
In addition, we also observed an influence of above-average precipitation sums during winter and spring on landslide activity. Based on the reconstructed time series of landslides, we expect massive winter snowpack and its rapid melting in spring to be a trigger not only of shallow landslides located predominantly in the central part, but also of complex landslides located predominantly in the western part of the study region. The influence of rain-on-snow events on landslide reactivations was documented in the areas surrounding our study region45,56, but cannot be confirmed in this study and with the approaches used. Dry spells appear to be more important in complex landslides as differences in precipitation vary less than for the other landslide types between years with and without landsliding (Figs 4, S9). In California, such a depth-dependent response of persistently moving earthflows has been observed above all as enhanced activity of shallow landslides, but less so in deeper landslides29. We assume that the drying/wetting cycles in the Flysch Carpathians can be more effective in parts with abundant tension cracks and fissures. As complex landslides may represent various morphological features that are commonly observed in shallow and deep-seated landslides, the probability for the occurrence of such mechanisms could increase in the future. However, the interacting movement mechanisms of individual landslide zones can also strongly affect the timing of their reactivations57.
To improve linkages between landslides and climate further, it would be desirable to go beyond the construction of annually-resolved landslide chronologies by adding field monitoring to the time series of process activity58. In addition, radar data could improve the assessment of precipitation intensity and sums and therefore reduce uncertainties inherent to the assessment local rainfall events causing local landslide reactivations with a more regional weather station network13 with stations located mostly at the foothills meaning the possible underestimation of precipitation in the mountainous parts caused by orographic enhancement34,59,60. As the analysis presented here was performed at the regional scale and as more than half of the landslide sites are located at the foothills of the Outer Western Carpathians, errors related to the choice of stations has, however, been minimized as much as possible.
Conclusions and Implications
The analysis of tree-ring based landslide chronologies in terms of climatic triggers and variation thereof can not only further our understanding of long-term process dynamics and the evolution of triggers, but thereby also and unambiguously help the prediction of landslide behaviour in a future greenhouse climate. In this paper, we demonstrate that mass movements are not only triggered by precipitation, but that dry spells have a significant influence on landsliding as well in the Outer Western Carpathians. This combined effect has recently been considered in persistently moving clayey landslides over the western U.S. In addition, landslide reactivations vary quite significantly between landslide types and exhibit contrasting climate-landslide linkages. In view of the anticipated increase in the frequency, intensity and duration of dry spells as well as the possibility of having more intense rainfall events, one might expect significant changes in landslide activity to occur in the study region.
Material and Methods
Landslide activity in the study region was analysed from documentary sources (available papers, landslide database of the Czech Geological Survey, LiDAR-derived digital elevation model with a resolution of 2 × 2 m), and field survey focusing on the morphology of the landslide body with open tension cracks, visible scarps and tilted tree stems. All selected landslides (26 sites) were then divided into groups based on the type of landslide movement (flow-like, shallow, and complex landslides) and regional settings (western, central, and eastern parts of the mountain range; see Supplementary Table S1). All conifer trees (1322 tree individuals of P. abies, L. decidua, and A. alba) with evidence of past landslide activity (i.e. stem tilting, stem bends, exposure of root system near scarps) were sampled following standard approaches40,61. Two cores (one from the tilted side and one from the opposite side) were extracted from each tree with a Pressler increment borer (40 × 0.5 cm) and stored in plastic boxes. Tree position was recorded with a GPS device and supplementary information about external disturbances and social position of trees were noted. In addition, samples from reference trees (i.e. trees growing nearby the landslide sites showing no signs of geomorphic disturbances) were extracted perpendicularly to the slope at breast height.
All sampled trees were subjected to tree-ring counting and measuring with a TimeTable measuring device and PAST4 software62. The reference chronologies were built with Arstan63 using a standard double detrending procedure (with a negative exponential function, or linear regression, in the first step and a cubic spline function in the second step). Reference curves were cross-dated with disturbed samples to (i) identify pointer years, (ii) to eliminate false and missing rings in disturbed samples, and (iii) to avoid any misinterpretation related to climate-related growth signals. The onset of compression wood and abrupt growth suppression were identified as two common growth disturbances caused by landslide activity39,64,65. Criteria used for the consideration of growth disturbances as a result of landslide activity are described in Supplementary Table S2. Identification of event years was based on the event-response index (It)66 with defined thresholds at 5 and 10%, and final chronologies were compiled for (i) each landslide site separately, (ii) groups of landslide types, (iii) groups based on zonal settings, and for the (iv) whole region (Fig. S5)40. The beginning of each chronology was determined by the year when at least 10 trees were available for analysis. The recurrence interval of landslide reactivations was then calculated as the quotient of the length of the landslide chronology and the number of reconstructed landslide events40.
Data series from nine meteorological stations covering the landslide region were used for the climate–landslide analysis. Stations were carefully selected based on their position, length and continuity of the data series (Fig. S3 and Table S3). Precipitation data were quality controlled based on standard methods67 and homogenized using the Craddock test68. Monthly values of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) were calculated to analyse wet and dry periods69,70. The SPI calculation is based on long-term precipitation records which are fitted to a probability distribution before being transformed to the normal distribution. Therefore, the normal SPI is zero, negative values indicate wet months, and positive values indicate dry months. The wetting and/or drying events end as soon as the SPI becomes positive (in the case of drying events) or negative (in the case of wetting events)70. The combination of drying and wetting events was then compared with landslide activity. Annual and seasonal precipitation values from all stations were used to test differences between years with and without landslide activity33,34. Firstly, precipitation data were averaged from all stations to analyse years coming from the overall landslide chronology and chronologies based on the landslide types (under the assumption of a randomly distribution of complex, flow-like, and shallow landslides). Secondly, precipitation data were regionally averaged from stations belonging to a particular zone (western, central, and eastern) to analyse years coming from the chronologies based on zonal settings67. Finally, a non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test was applied to identify significant differences between precipitation during years with and without landslide activity at a significance level α = 0.05.
For trend analysis, we used the Mann-Kendall (MK) test for climate variables at different seasons, previously standardized using Z-score. The purpose of the Mann-Kendall (MK) test71,72 is to statistically assess if a monotonic upward or downward trend exists for the variable of interest. A monotonic upward (downward) trend means that a variable consistently increases (decreases) through time, but the trend may or may not be linear. The MK test can be used in place of a parametric linear regression analysis, which can be used to test if the slope of the estimated linear regression line is different from zero. The regression analysis requires that the residuals from the fitted regression line be normally distributed; an assumption not required by the MK test, that is, the MK test is a non-parametric (distribution-free) test.
Then we used a Generalized Linear Mixed (GLM) model to investigate linkages between tree-ring response to landslides and climate variables (i.e. dry spell and maximum precipitation) at the annual scale. In the model, tree-ring signals induced by landslide activity have been grouped by geographic zone to account for potential random effects. We also considered an autocorrelation term to account for potential long-medium-memory effects. Model selection was based on the Akaike Information Criterion corrected for small sample sizes (AICc)73,74. The alternative hypotheses were tested by using the delta AICc between each alternative hypothesis and the null hypothesis (i.e. AICc of the null model minus AICc of each model). To evaluate residuals in the selected model, we plotted standardized residuals against quantiles of the standard normal of the selected model and for each site analysed (see Fig. S9).All predictor variables were standardized before model fitting using a Z-score.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Froude, M. J. & Petley, D. N. Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 18, 2161–2181, https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-2161-2018 (2018).
Petley, D. Landslide hazards. In Geomorphological hazards and disaster prevention (eds Petley, D. N., Alcantara-Ayala, I. & Goudie, A). 63–74 (Cambridge University Press, 2010).
Klose, M., Maurischat, P. & Damm, B. Landslide impacts in Germany: a historical and socioeconomic perspective. Landslides 13(1), 183–199 (2016).
Jakob, M. & Lambert, S. Climate change effects on landslides along the southwest coast of British Columbia. Geomorphology 107(3–4), 275–284 (2009).
Crozier, M. J. Deciphering the effect of climate change on landslide activity: A review. Geomorphology 124(3–4), 260–267 (2010).
Gariano, S. L. & Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a changing climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 162, 227–252 (2016).
Stoffel, M. & Huggel, C. Effects of climate change on mass movements in mountain environments. Prog. Phys. Geog. 36(3), 421–439 (2012).
Stoffel, M., Tiranti, D. & Huggel, C. Climate change impacts on mass movements – case studies from the European Alps. Sci. Total Environ. 493, 1255–1266 (2014).
Crozier, M. J. Landslides: causes, consequences & environment (Taylor & Francis, 1986).
Schulz, W. H., Smith, J. B., Wang, G., Jiang, Y. & Roering, J. J. Clayey landslide initiation and acceleration strongly modulated by soil swelling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 45(4), 1888–1896 (2018).
Prokešová, R. et al. Kinematic behaviour of a large earthflow defined by surface displacement monitoring, DEM differencing, and ERT imaging. Geomorphology 224, 86–101 (2014).
Metternicht, G., Hurni, L. & Gogu, R. Remote sensing of landslides: An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote sens. Environ. 98(2–3), 284–303 (2005).
Guzzetti, F., Peruccacci, S., Rossi, M. & Stark, C. P. The rainfall intensity–duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: an update. Landslides 5(1), 3–17 (2008).
LaHusen, S. R., Duvall, A. R., Booth, A. M. & Montgomery, D. R. Surface roughness dating of long-runout landslides near Oso, Washington (USA), reveals persistent postglacial hillslope instability. Geology 44(2), 111–114 (2016).
Pánek, T. Landslides and Quaternary climate changes – The state of the art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 196, 102871 (2019).
Corominas, J. & Moya, J. Reconstructing recent landslide activity in relation to rainfall in the Llobregat River basin, Eastern Pyrenees, Spain. Geomorphology 30(1–2), 79–93 (1999).
Zêzere, J. L., Trigo, R. M. & Trigo, I. F. Shallow and deep landslides induced by rainfall in the Lisbon region (Portugal): assessment of relationships with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Nat Hazard Earth Sys. 5(3), 331–344 (2005).
Pánek, T. et al. Rainfall-induced landslide event of May 2010 in the eastern part of the Czech Republic. Landslides 8(4), 507–516 (2011).
Raška, P., Zábranský, V., Brázdil, R. & Lamková, J. The late Little Ice Age landslide calamity in North Bohemia: Triggers, impacts and post-landslide development reconstructed from documentary data (case study of the Kozí vrch Hill landslide). Geomorphology 255, 95–107 (2016).
Lopez Saez, J. et al. Dendrogeomorphic reconstruction of past landslide reactivation with seasonal precision: the Bois Noir landslide, southeast French Alps. Landslides 9(2), 189–203 (2012).
Beniston, M. August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33(5), L05701, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL025573 (2006).
Jemec, M. & Komac, M. Rainfall patterns for shallow landsliding in perialpine Slovenia. Nat. Hazards 67(3), 1011–1023 (2013).
Lopez Saez, J., Corona, C., Stoffel, M. & Berger, F. Climate change increases frequency of shallow spring landslides in the French Alps. Geology 41(5), 619–622 (2013).
Raška, P., Klimeš, J. & Dubišar, J. Using local archive sources to reconstruct historical landslide occurrence in selected urban regions of the Czech Republic: examples from regions with different historical development. Land Degrad. Dev. 26(2), 142–157 (2015).
Stoffel, M. & Corona, C. Future winters glimpsed in the Alps. Nat. Geosci. 11(7), 458–460 (2018).
Cockburn, J. M., Vetta, M. & Garver, J. I. Tree-ring evidence linking late twentieth century changes in precipitation to slope instability, central New York state, USA. Phys. Geogr. 37(2), 153–168 (2016).
Stocker, T. F. et al. IPCC, 2013: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1535 pp (2013).
Giorgi, F. et al. Higher hydroclimatic intensity with global warming. J. Climate 24(20), 5309–5324 (2011).
Bennett, G. L. et al. Historic drought puts the brakes on earthflows in Northern California. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43(11), 5725–5731 (2016).
Alestalo, J. Dendrochronological interpretation of geomorphic processes. Fennia 105, 1–140 (1971).
Stoffel, M., Butler, D. R. & Corona, C. Mass movements and tree rings: A guide to dendrogeomorphic field sampling and dating. Geomorphology 200, 106–120 (2013).
Šilhán, K. et al. The dating of bedrock landslide reactivations using dendrogeomorphic techniques: The Mazák landslide, Outer Western Carpathians (Czech Republic). Catena 104, 1–13 (2013).
Tichavský, R., Šilhán, K. & Tolasz, R. Tree ring-based chronology of hydro-geomorphic processes as a fundament for identification of hydro-meteorological triggers in the Hrubý Jeseník Mountains (Central Europe). Sci. Total Environ. 579, 1904–1917 (2017).
Paolini, L., Villalba, R. & Grau, H. R. Precipitation variability and landslide occurrence in a subtropical mountain ecosystem of NW Argentina. Dendrochronologia 22(3), 175–180 (2005).
Ballesteros-Cánovas, J. A., Trappmann, D., Madrigal-González, J., Eckert, N. & Stoffel, M. Climate warming enhances snow avalanche risk in the Western Himalayas. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115(13), 3410–3415 (2018).
Stefanini, M. C. Spatio-temporal analysis of a complex landslide in the Northern Apennines (Italy) by means of dendrochronology. Geomorphology 63(3–4), 191–202 (2004).
Fantucci, R. & Sorriso-Valvo, M. Dendrogeomorphological analysis of a slope near Lago, Calabria (Italy). Geomorphology 30(1–2), 165–174 (1999).
Van Den Eeckhaut, M., Muys, B., Van Loy, K., Poesen, J. & Beeckman, H. Evidence for repeated re‐activation of old landslides under forest. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 34(3), 352–365 (2009).
Lopez Saez, J., Corona, C., Stoffel, M. & Berger, F. High-resolution fingerprints of past landsliding and spatially explicit, probabilistic assessment of future reactivations: Aiguettes landslide, Southeastern French Alps. Tectonophysics 602, 355–369 (2013).
Šilhán, K., Tichavský, R., Škarpich, V., Břežný, M. & Stoffel, M. Regional, tree-ring based chronology of landslides in the Outer Western Carpathians. Geomorphology 321, 33–44 (2018).
Baroň, I., Cílek, V., Krejčí, O., Melichar, R. & Hubatka, F. Structure and dynamics of deep-seated slope failures in the Magura Flysch Nappe, outer Western Carpathians (Czech Republic). Nat. Hazard Earth Sys. 4(4), 549–562 (2004).
Klimeš, J. Analýza podmínek vzniku svahových deforamcí ve Vsetínských vrších. PhD thesis. in Czech (Charles University in Prague, 2007).
Tolasz, R. et al. Climate Atlas of Czechia. In Czech (ČHMÚ, 2007).
Záruba, Q. Studie o sesuvných terénech na Vsatsku a Valašsku. Časopis Moravského musea zemského 20–21 in Czech (1922).
Rybář, J. et al. Hodnocení svahových deformací v oblasti Vsetínska. (MS Úst. struktury a mech. hornin Akad. věd Čes. republ., In Czech (2000).
Bíl, M. et al. A chronology of landsliding and its Impacts on the Village of Halenkovice, Outer Western Carpathians. Geografie 4, 342–363 (2014).
Hong, Y. et al. The influence of intense rainfall on the activity of large-scale crystalline schist landslides in Shikoku Island, Japan. Landslides 2(2), 97–105 (2005).
Wood, J. L., Harrison, S., Turkington, T. A. R. & Reinhardt, L. Landslides and synoptic weather trends in the European Alps. Climatic Change 136(2), 297–308 (2016).
Kundzewicz, Z. W. et al. Summer floods in Central. Europe–climate change track? Nat. Hazards 36(1–2), 165–189 (2005).
Ravanel, L. & Deline, P. Climate influence on rockfalls in high-Alpine steep rockwalls: The north side of the Aiguilles de Chamonix (Mont Blanc massif) since the end of the ‘Little Ice. Age’. The Holocene 21(2), 357–365 (2011).
Murray, H. H. Structure and composition of the clay minerals and their physical and chemical properties. Dev. Clay Sci. 2, 7–31 (2006).
Sidle, R. C. & Bogaard, T. A. Dynamic earth system and ecological controls of rainfall-initiated landslides. Earth-Sci. Rev. 159, 275–291 (2016).
Krzeminska, D. M., Bogaard, T. A., Malet, J. P. & Van Beek, L. P. H. A model of hydrological and mechanical feedbacks of preferential fissure flow in a slow-moving landslide. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 17(3), 947–959 (2013).
Handwerger, A. L. et al. A shift from drought to extreme rainfall drives a stable landslide to catastrophic failure. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1569, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38300-0 (2019).
Ghestem, M., Sidle, R. C. & Stokes, A. The influence of plant root systems on subsurface flow: implications for slope stability. Bioscience 61(11), 869–879 (2011).
Bíl, M. & Müller, I. The origin of shallow landslides in Moravia (Czech Republic) in the spring of 2006. Geomorphology 99(1–4), 246–253 (2008).
Šilhán, K. et al. Understanding complex slope deformation through tree-ring analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 665, 1083–1094 (2019).
Šilhán, K., Prokešová, R., Medveďová, A. & Tichavský, R. The effectiveness of dendrogeomorphic methods for reconstruction of past spatio-temporal landslide behaviour. Catena 147, 325–333 (2016).
Stoffel, M., Bollschweiler, M. & Beniston, M. Rainfall characteristics for periglacial debris flows in the Swiss Alps: past incidences – potential future evolutions. Climatic Change 105, 263–280 (2011).
Schneuwly-Bollschweiler, M. & Stoffel, M. Hydrometeorological triggers of periglacial debris flows – a reconstruction dating back to 1864. J. Geophys. Res. – Earth Surface 117; https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JF002262 (2012).
Stoffel, M. & Bollschweiler, M. Tree-ring analysis in natural hazards research? an overview. Nat. Hazard Earth Sys. 8(2), 187–202 (2008).
VIAS. Time Table. Installation and instruction manual. (Vienna, 2005).
Cook, E. R. A Time Series Analysis Approach to Tree-ring Standardization. PhD thesis. (Tucson, 1985).
Westing, A. H. Formation and function of compression wood in gymnosperms II. Bot.Rev. 34, 51–78 (1965).
Stoffel, M. & Corona, C. Dendroecological dating of geomorphic disturbance in trees. Tree-ring Res. 70(1), 3–20 (2014).
Shroder, J. F. Dendrogeomorphological analysis of mass movement on Table Cliffs Plateau, Utah. Quaternary Res. 9(2), 168–185 (1978).
Brunetti, M., Maugeri, M., Nanni, T. & Navarra, A. Droughts and extreme events in regional daily Italian precipitation series. Int. J. Climatol. 22(5), 543–558 (2002).
Craddock, J. M. Methods for comparing annual rainfall records for climatic purposes. Weather 34, 332–346 (1979).
McKee, T. B., Doesken, N. J. & Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology 17(22), 179–183. Boston, MA: American Meteorological Society (1993).
World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Standardized precipitation index user guide (2012).
Mann, H. B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 245–259 (1945).
Kendall, K. Thin-film peeling-the elastic term. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 8(13), 1449–1452 (1975).
Madrigal-González, J. et al. Forest productivity in southwestern Europe is controlled by coupled North Atlantic and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillations. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 2222, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02319-0 (2017).
Ballesteros‐Cánovas, J. A. et al. On the extraordinary winter flood episode over the North Atlantic Basin in 1936. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1436, 206–216, https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13911 (2018).
Geological Map 1: 25,000. Praha, Czech Geological Survey. Available from: http://mapy.geology.cz/geocr_25/.
Ground Instabilities, Geohazards. Praha, Czech Geological Survey. Available from: https://mapy.geology.cz/svahove_nestability/.
USGS. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global. US Geological Survey, https://doi.org/10.5066/F7PR7TFT. (2015).
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (Project no. 19-01866 S) and the project of the University of Ostrava (SGS02/Přf/2019-2020). Václav Škarpich and students are warmly acknowledged for their help during fieldworks. Tomáš Pánek is acknowledged for the discussion about the landslide mechanisms. The authors acknowledge Georgina Bennett and an two other anonymous reviewers for insightful and constructive feedback on an earlier version of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.Tich., J.A.B.C. and K.S. designed the research. R.Tich. and K.S. performed the fieldwork. R. Tol. prepared the climate data. R.Tich. and K.S. performed the dendrogeomorphic analysis. R.Tich. and J.A.B.C. performed the climate analyses. R.Tich., J.A.B.C., K.S. and M.S. performed the results interpretation. All wrote and reviewed the manuscript and prepared figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tichavský, R., Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A., Šilhán, K. et al. Dry Spells and Extreme Precipitation are The Main Trigger of Landslides in Central Europe. Sci Rep 9, 14560 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51148-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51148-2
This article is cited by
-
Using distributed root soil moisture data to enhance the performance of rainfall thresholds for landslide warning
Natural Hazards (2023)
-
Extreme precipitation events and landslide activity in the Kashmir Himalaya
Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment (2023)
-
Mountain surface processes and regulation
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Machine learning for landslides prevention: a survey
Neural Computing and Applications (2021)
-
A comparative machine learning approach to identify landslide triggering factors in northern Chilean Patagonia
Landslides (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.