Abstract
The plant Dysosma versipellis is known for its antimicrobial and anticancer properties but is a rare and vulnerable perennial herb that is endemic to China. In this study, 224 isolates were isolated from various tissues of D. versipellis, and were classified into 53 different morphotypes according to culture characteristics and were identified by sequence analyses of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of the rRNA gene. Although nine strains were not assignable at the phylum level, 44 belonged to at least 29 genera of 15 orders of Ascomycota (93%), Basidiomycota (6%), and Zygomycota (1%). Subsequent assays revealed antimicrobial activities of 19% of endophytic extracts against at least one pathogenic bacterium or fungus. Antimicrobial activity was also determined using the agar diffusion method and was most prominent in extracts from four isolates. Moreover, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry analyses (UPLC–QTOF MS) showed the presence of podophyllotoxin in two Fusarium strains, with the highest yield of 277 μg/g in Fusarium sp. (WB5121). Taken together, the present data suggest that various endophytic fungi of D. versipellis could be exploited as sources of novel natural antimicrobial or anticancer agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Resistance to antibiotics and drugs in pathogenic bacteria and fungi and overuse of antibiotics are the major challenges for researchers all over the world1. Thus, safer and novel antimicrobial drugs are eagerly awaited2, and natural secondary metabolites from endophytic fungi are increasingly considered due to their diverse structural classes and various bioactivities. These include antifungal3, antibacterial4, anticancer, anti-HIV5, and other promising bioactivities6,7. In addition, endophytic fungi are nontoxic and, thus, provide a promising source of novel drugs8.
Endophytic fungi inhabit living plant tissues without causing apparent disease or injury to the host9 and are ubiquitous in vascular plant species10,11. Currently, less than 10% of the approximately one million known terrestrial endophytes have been investigated12. However, several rare medicinal plants produce important bioactive compounds to survive in unique environments and may host novel and diverse fungal endophytes7,13, and these have rarely been isolated and characterized.
Dysosma versipellis (Hance) M. Cheng ex Ying (Fig. 1a) is commonly referred to as podophyllum, hemipilia, fatsia, or octagonal lotus, and is a rare and vulnerable perennial herb of the Berberidaceae family14. This plant species is endemic to China and is mainly distributed in high altitudes ranging from 200–2400 m above sea level in disjunct stands of warm-temperate, deciduous, montane forests (Fig. 1b) across central and eastern China15. Dysosma species including D. aurantiocaulis, D. difformis, D. majorensis, D. pleiantha, D. tsayuensis, D. veitchii, and D. versipellis have been identified in previous studies and six of these are endemic to China16. As a traditional Chinese medicine, extracts from the rhizomes of this plant has been used as antibacterial treatments for syphilis and an antidote for snake bites17. In recent decades, D. versipellis has attracted increasing pharmaceutical attention due to the discovery of podophyllotoxin (PTOX), which is a pivotal lignan and is used as a natural source of various anticancer PTOX derivatives18. Recent studies show antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties of the flavonoids quercitrin and kaempferol from this plant19. However, due to overexploitation and slow growth, all Dysosma species have been under the threat of extinction20. Therefore, to protect these valuable medicinal plants and maintain the supply of PTOX for anticancer drugs, alternative sources are eagerly sought. Among these, endophytic fungi have the potential to produce PTOX21 for the production of podophyllotoxin21. However, to date, only a few PTOX-producing fungi associated with Berberidaceae plants have been reported22,23. In the present study, we investigated the diversity of culturable fungal endophytes of D. versipellis and screened the endophytic fungi for antimicrobial activities and PTOX-producing fungal isolates using HPLC and UPLC–QTOF MS analyses.
Results and Discussion
Isolation, sequencing data, and diversity of culturable endophytic fungi
In this study, a total of 224 fungal colonies (isolation rate, 41.2%) were isolated from 544 tissue segments of D. versipellis plants and included 62 (32.6%), 104 (42.3%), 33 (73.3%), and 25 (39.7%) strains from root, rhizome, stem, and leaf tissue segments, respectively (Table 1). The 224 isolates were assigned to 53 representative morphotypes (19, 22, 6, and 6 strains from roots, rhizomes, stems, and leaves, respectively) according to culture characteristics on potato dextrose agar (PDA; Fig. 1c), and all culturable morphotypes were identified according to ITS rDNA sequence analyses. Subsequently, 44 isolates were categorized at the genus level based on sequence similarity analyses, and the other nine isolates remained unidentified due to low sequence homology in the GenBank database.
According to diversity and sequence data of 53 isolates recovered from D. versipellis plants, at least 29 fungal genera were identified (Table 2). Among these, 25 belong to the Ascomycota and the isolates matched to 32 different species. The isolates WB5104 and WB5105 were identified only at the phylum level, and belonged to Ascomycota. Four (7.5%) isolates were classified as Basidiomycota, comprising the genera Phyllosticta (WB5139), Psathyrella (WB5140) and Rhizoctonia (WB5145 and WB5146). One (1.9%) isolate (WB5130) was classified as Zygomycota, and the genus Mucor. Shannon–Wiener diversity indices (H′; Table 1) show that D. versipellis host various fungal species, and that their rhizome tissues have the highest endophytic community diversity (2.728), followed by their roots (2.433), stems (1.330), and leaves (1.242).
In further analyses, 49 representative morphotypes belonged to four classes of the Ascomycota phylum, including Dothideomycetes, Eurotiomycetes, Leotiomycetes, and Sordariomycetes. Most of the isolates (n = 28) from D. versipellis belonged to Sordariomycetes class in this study. This class was represented by seven orders: Glomerellales (7 isolates), Hypocreales (13 isolates), Diaporthales (2 isolates), Xylariales (4 isolates), Magnaporthales (1 isolate), Ophiostomales (1 isolate), Sordariales (1 isolate); and 13 genera: Acremonium, Arthrinium, Colletotrichum, Cylindrocarpon, Dactylonectria, Diaporthe, Fusarium, Hypoxylon, Ilyonectria, Pestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis, Volutella and Xenocremonium. Six isolates (WB5119, WB5133, WB5147, WB5148, WB5149 and WB5150) had no sequence similarities with any reference species from the GenBank database.
Ten isolates were assigned to Dothideomycetes class, comprising three orders: Pleosporales (6 isolates), Capnodiales (3 isolates) and Venturiales (1 isolate) and eight genera (Alternaria, Cladosporium, Ochroconis, Microsphaeropsis, Phoma, Pseudocercospora, Pyrenochaeta and Ramichloridium). Three isolates were assigned to Eurotiomycetes class and Chaetothyriales order, representing the genera Exophiala, Minimelanolocus and Phialophora. Finally, two isolates were assigned to Letiomycetes class. One (WB5144) was classified as Rhexocercosporidium genus of the Helotiales order. No sequence similarity with any reference species was detected in GenBank for the WB5128 isolate.
The present data show that D. versipellis roots and rhizomes contain a rich diversity of endophytic fungi, and we found that the most ubiquitous phylum of fungi is Ascomycota, which is reportedly among the most prevalent group of eukaryotes globally24,25. In addition, Sordariomycetes was the most prevalent class of endophytic species in the present study, followed by Dothideomycetes, Eurotiomycetes, and Leotiomycetes, as shown previously. We also found that 77.4% of endophytic fungi are present in roots and rhizomes of D. versipellis, and only 22.6% of fungal isolates were found in stems and leaves. Colletotrichum is a common fungal genus26 and was abundant in the stems and leaves, but was absent in roots and rhizomes. Cylindrocarpon, Fusarium, Ilyonectria, and Rhizoctonia only colonized roots and rhizomes, whereas Alternaria, Arthrinium, Mucor, Pestalotiopsis, Phialophora, Phoma, Rhizoctonia were exclusively detected in roots. Another 19 isolates only colonized rhizomes, and Acremonium and Ochroconis were exclusively present in leaves. Pseudocercospora, Ramichloridium only colonized stems. Based on these varying spatial distributions of endophyte communities in D. versipellis, we suggested that these microbiotas have adapted to distinct tissue microenvironments, resulting in clear tissue specificity among endophytic fungi in D. versipellis, as indicated in a previous study of Indian medicinal plants27,28.
Additionally, the isolates WB5143 (Ramichloridium sp., Fig. 1c), WB5104 (Ascomycota) and WB5136 (Cadophora sp.) have darkly pigmented and septate hyphae of thick walls. These are referred to as dark septate fungi (DSE) and were isolated from roots. Jumpponen & Trappe suggested that DSE frequently colonize roots of mycorrhizal or nonmycorrhizal plants and play unique roles in terrestrial ecosystems29. However, in contrast with the common root tissue habitat of DSE, Ramichloridium sp. (WB5143) was isolated from stems of plants.
Antimicrobial activity of ethanolic fraction of culture supernatants of endophytic fungal species
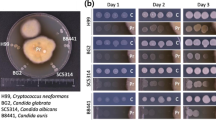
In this study, antimicrobial-producing fungi belonged to the genera Fusarium, Cladosporium, Ilyonectria, Microsphaeropsis, Cadophora, Phoma, Rhizoctonia, Virgaria. In addition, the ethanolic extracts of two unidentified isolates also inhibited the microbial growth (Table 3).
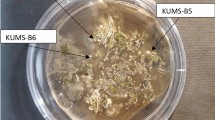
Endophytic strains of Fusarium are well-known producers of various metabolites screened in the host plants30; the commercially important drug precursor PTOX was originally found in the endangered genus Dysosma21 but is also produced by the endophytic F. oxysporum from Juniperus recurva plants23. Other natural agents include Taxol which was originally found in Taxus plants and was produced by endophytic F. proliferatum from Taxus x media31. Additionally, 2-methylbutyraldehyde-substituted α-pyrone, beauvericin, and subglutinol A and B are dominant antimicrobial compounds that are produced by endophytic Fusarium spp. isolated from medicinal plants32,33,34. Most members of the genus Cladosporium also produce antimicrobial compounds, and C. uredinicola from Tinospora cordifolia was found to possess anti-insect properties, potentially protecting plants against insect pests35. In the present study, Cladosporium sp. (WB5106) exhibited high antimicrobial activity against S. aureus, E. coli, B. subtilis, and C. tropicalis, but did not show any activity against A. fumigatus.
Interestingly, all of the present endophytic fungal strains that produce antimicrobial compounds were isolated from roots or rhizomes of D. versipellis. Similar studies had also showed medicinal plants with antifungal, antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant activities may provide more feasible opportunities to isolate and culture endophytic fungal producers6,36. However, further studies are required to characterize dynamic changes of endophytic communities6 and uncultured fungi30 and to confirm fungal tissue specificity in D. versipellis.
Screening of PTOX-producing fungi
Crude extracts of endophytic fungi were screened for fungal PTOX using HPLC and UPLC–QTOF MS analyses. In these analyses, PTOX from Fusarium sp. WB5121 and WB5122 had retention times that corresponded with the standard PTOX (Fig. 2) and corresponding yields were 277 and 1.25 µg/g (wet weight of crude extracts), respectively, after culture in 200 mL of potato dextrose broth (PDB) at 26 °C ± 2 °C with shaking at 125 rpm for 10 days. Associated MS spectra showed the same peak MH+ at m/z 459.12 for standard and fungal PTOX from Fusarium sp. WB5122, and that of the fungal PTOX from Fusarium sp. WB5121 yielded a peak MH+ at m/z 459.13 (Fig. 3), indicating the presence of endogenous PTOX in isolates of Fusarium sp. WB5122 and WB5121 strains.
In conclusion, D. versipellis harbors a rich and diverse range of endophytic fungi and provides a fungal resource for the study of PTOX and other unique secondary metabolites. Among the present endophytic fungi, 18.9% and 3.7% of strains produced antimicrobial and anticancer metabolites, respectively. Hence, future studies of metabolic pathways, mutual relationships, and fungal species identification are warranted.
Materials and Methods
Collection of plant material
The wild plant samples of D. versipellis were collected from Yongfu county, Guangxi province of China (109°36′E; 24°37′N). Samples were placed in polyethylene bags, labeled, transported to the laboratory, and refrigerated at 4 °C, as described previously37. Plant specimens were identified by Dr. Tan and were preserved in the herbarium of the Guangxi Botanical Garden of Medicinal Plants.
Fungal isolation and cultivation
Endophytic fungi were isolated from stems, leaves, and roots of plants. Procedures for surface sterilization of plant tissues and isolation and cultivation of fungi are described by Tan et al.38. Briefly, stems, leaves, and roots were separated from plants, were washed thoroughly in running tap water, and were surface-sterilized in a sequence of 70% ethanol (v/v) for 30 s and sodium hypochlorite solution (2.5%, v/v) for 5 min. All tissues were then rinsed three times with sterile distilled water and were surface-dried with sterile filter paper. Subsequently, 0.5 × 0.5-cm pieces were excised using a sterile blade and were placed on PDA containing 50-µg/mL oxytetracycline and 50-µg/mL streptomycin. Nine segments were plated per Petri dish (90-mm diameter). Petri dishes were then wrapped in parafilm and were incubated at 25 °C in the dark for more than one week. Samples were checked daily and colonies were routinely isolated, purified, and maintained in PDA for identification and antimicrobial assays. Pure endophytic fungi were finally photographed and preserved in the laboratory of Mycology, Guangxi Botanical Garden of Medicinal Plants.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification, sequencing, and molecular identification
To produce fungal mycelia, all strains were grown on PDA plates at 25 °C for 10 days. Mycelia were scraped using sterile pipette tips and were then freeze-dried, and DNA from endophytic fungi were then extracted using E.Z.N.A.TM Fungal DNA Mini Kits (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, USA) according to the manufacturers’ instructions for use as templates in polymerase chain reactions (PCR). The primers ITS1 (5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′) and ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′) were constructed for molecular phylogenetic studies and were used to amplify ribosomal internal transcribed spacers (ITS)39. The PCR mixture (50 µL) contained 25 µL of Taq PCR Master Mix (Qiagen, Bejing), 2 µL of each primer at 5 µM, 19 µL of H2O, and 2 µL of genomic DNA. PCR were performed using a thermal cycler (BioRAD) with an initial denaturation step at 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 1 min, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min, and then a final extension step at 72 °C for 7 min. Subsequently, 5-µL PCR products were analyzed electrophoretically in 1% (w/v) agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide. After visual inspection under UV light, 45-µL aliquots of PCR products were purified and sequenced at the Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Technology & Services Co. Ltd. Sequences were then compared with ITS sequences from reliable isolates listed in the NCBI database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Only sequence matches with high similarity to those published in previous studies were included in analyses. All identified isolates were categorized at genus or family levels according to the ownership criterion as follows: species of the same genera have sequence similarity (SS) of >95% and those of the same families had SS of <95%6,40. The sequences obtained in this study were previously submitted to the GenBank database with accession numbers from KY940469 to KY940519.
Crude extract preparation of fungal fermentation broth
Fifty-three strains were precultured on PDA (potato extract, 200 g/L; dextrose, 20 g/L) for 7 days, and five plugs (6 mm of diameter) of each fungus were then pre-inoculated into 500-mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 200-mL PDB containing 200 g/L potato extract and 20 g/L dextrose. All cultures were incubated on a rotary shaker (125 rpm) at 26 °C ± 2 °C in the dark for 10 days. Cultures were then filtered to collect fermentation broth and wet mycelia were discarded. Fermentation broth was extracted with four volumes of ethanol for one day and filtrates were further concentrated in vacuo to remove organic solvent41. Concentrates were then volatilized in a water bath at 60 °C and dried residues and were finally stored at −20 °C. Crude extracts were diluted with 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to 10 mg/mL and were sterilized by filtration using a Millipore filter (0.22 µm) prior to antimicrobial assays.
Antimicrobial activity
Five pathogens, including the fungi A. fumigatus and C. albicans and bacteria E. coli, B. subtilis, and S. aureus, were used to test antimicrobial activities of 53 crude fungal EtOH extracts, and inhibitory effects were assayed using the agar diffusion method with 10-mg/mL extracts at 100 µg/disk. Ampicillin sodium (100 µg/disk) and fluconazole (25 µg/disk) were used as positive antimicrobial controls and 10% DMSO was used as a negative control. Antimicrobial activities were determined according to diameters of inhibition zones (ZI) and experiments were repeated three times.
Determination of PTOX-producing fungi
PTOX-producing endophytic fungi were screened using HPLC22,23 analyses and the agent was identified using UPLC–QTOF MS. In these experiments, crude extracts of fungal isolates were dissolved in 1 mL of 80% methanol (v/v) and were filtered through 0.22-µm syringe filters prior to HPLC analyses (Agilent 1260, USA), which were performed using a Zorbax SB-C18 column (5 µm, 4.6 mm × 250 mm; Agilent, USA). Gradient elution was then performed with acetonitrile/H2O binary solvent-delivery gradient elution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min as follows: 0–20 min, 20% acetonitrile; 20–25 min, 60% acetonitrile; 25–30 min, acetonitrile; volume fraction. Analytes were detected at 207 nm and injection volumes for all fungal methanol extracts and PTOX standard were 20 and 5 µL, respectively. PTOX standard was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Corporation (St. Louis, Missouri, USA).
Fungal PTOX was further identified using a UPLC–QTOF MS system (Waters, USA) as described previously42. Briefly, chromatographic separation was performed with an Acquity UPLC HSS T3 C18 column (1.8 μm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) with an injection volume of 0.3 µL and a binary gradient elution mixture comprising water with 0.1% formic acid (A) and 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile (B) as follows: 0–3.5 min, 10–35% B; 3.5–5.5 min, 35–40% B; 5.5–6.5 min, 40–60% B; 6.5–8.0 min, 60–90% B; 8.1–10 min, 10% B. The mobile phase was applied at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min and the temperature of the column oven was set to 35 °C.
The MS was operated in negative ion mode and was set to total ion chromatogram mode with the following mass conditions: capillary voltage = 2500 V, cone voltage = 40 V, low collision energy = 6 V, source temperature = 100 °C, desolvation temperature = 400 °C, and desolvation gas flow = 800 L/h. Data acquisition and processing were conducted using MassLynx version 4.1 (Waters, Manchester, UK).
Statistical analyses
Colonization rates (CR%) of fungal strains isolated from D. versipellis were calculated as follows: CR% = (Nsc/Nss) × 100, where Nsc represents the number of segments infected by fungi and the Nss represents the total number of segments investigated43. Isolation rates (IR%) of the strains were calculated as follows: IR% = (Ni/Nt) × 100, where Ni represents the number of segments from which fungal species were isolated and Nt is the total number of segments incubated44. The diversity of fungal species from D. versipellis was evaluated using the Shannon–Weiner Index (H′) with the following formulas:
where ni represents the numbers of individuals and N represents the total number of individuals45. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Change history
20 August 2018
A correction to this article has been published and is linked from the HTML and PDF versions of this paper. The error has been fixed in the paper.
References
Aksoy, D. Y. & Unal, S. New antimicrobial agents for the treatment of Gram-positive bacterial infections. Clin Microbiol Infect 14, 411–420 (2008).
Katoch, M. et al. Diversity, phylogeny, anticancer and antimicrobial potential of fungal endophytes associated with Monarda citriodora L. BMC Microbiology 17, 44 (2017).
Silva-Hughes, S. A. F. et al. Diversity and antifungal activity of the endophytic fungi associated with the native medicinal cactus Opuntia humifusa (Cactaceae) from the United States. Microbiological Research 175, 67–77 (2015).
Salam, N. et al. Endophytic actinobacteria associated with Dracaena cochinchinensis Lour.: isolation, diversity, and their cytotoxic activities. BioMed Research International 10.1155/2017/1308563 (2017).
Zhang, D. W. et al. A novel assay for screening inhibitors targeting HIV-1 integrase dimerization based on Ni-NTA magnetic agarose beads. Scientific Reports 6, 25375 (2016).
Cui, J. L. et al. Diversity and antioxidant activity of culturable endophytic fungi from alpine plants of Rhodiola crenulata, R. angusta, and R. sachalinensis. PLoS ONE 10(3), e0118204 (2015).
Strobel, G. A. Endophytes as sources of bioactive products. Microbes infect. 5, 535–544 (2003).
Pupo, M. T. et al. Microbial natural products: a promising source of bioactive compounds. (In: Taft CA, editor Modern Biotechnology in Medicinal Chemistry and Industry. Kerala: Research Signpost, p 51–78, 2006).
Petrini, O. et al. Ecology, metabolite production, and substrate utilization in endophytic fungi. Nat Toxins 1, 185–196 (1992).
Arnold, A. E., Maynard, Z. & Gilbert, G. S. Fungal endophytes in dicotyledonous neotropical trees: patterns of abundance and diversity. Mycol. Res. 105, 1502–1507 (2001).
Hawksworth, D. L. The variety of fungal-algal symbioses, their evolutionary significance, and the nature of lichens. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 96, 3–20 (1988).
Ganley, R. J., Brunsfeld, S. J. & Newcombe, G. A community of unknown, endophytic fungi in western white pine. PNAS 101, 10107–10112 (2004).
Pupo, M. T. et al. Microbial natural products: a promising source of bioactive compounds. (In: Taft CA, editor. Modern Biotechnology in Medicinal Chemistry and Industry. Kerala: Research Signpost, p 51-78, 2006).
Wang, S. & Xie, Y. China species red list (Vol.1). (Beijing: Higher Education Press, p 324, 2004).
Ying, T. S., Zhang, Y. L. & Boufford, D. E.. The endemic genera of seed plants of China. (Beijing: Science Press, 1993).
Editorial Board of Flora of China. Flora of China (Vol. 29). (Beijing: Science Press, p 254-260, 2001).
Jiangsu New Medical College. Dictionary of Chinese Traditional Medicine. (Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1986).
Canel, C. et al. Molecules of interest: podophyllotoxin. Phytochemistry 54, 115–120 (2000).
Chen, R. D. et al. Flavonoid glycosides from callus cultures of Dysosma versipellis. China. Journal of Chinese Material Medica 41(1), 87–91 (2016).
Chaurasia, O. P. et al. Podophyllum L.: an endangered and anticancerous medicinal plant-an overview. Indian J. Tradit. Know. 11, 234–241 (2012).
Vasundhara, M. et al. Molecular Approaches to screen bioactive compounds from endophytic fungi. Front. Microbiol. 7, 1774 (2016).
Eyberger, A. L. et al. Endophyte fungal isolates from Podophyllum peltatum produce podophyllotoxin. J. Nat. Prod. 69, 1121–1124 (2006).
Kour, A. et al. Isolation and identification of an endophytic strain of Fusarium oxysporum producing podophyllotoxin from Juniperus recurva. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 1115–1121 (2008).
Zare, R. et al. Gibellulopsis, a suitable genus for Verticillium nigrescens, and Musicillium, a new genus for V. theobromae. Nova Hedwigia 85(3-4), 463–489 (2007).
Pereiro, M. et al. Cutaneous infection caused by Alternaria in patients receiving tacrolimus. Med. Mycol. 42(3), 277–282 (2004).
Ko K T. W., et al. From morphology to molecular biology: can we use sequence data to identify fungal endophytes? Fungal Diversity https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-011-0130-0 (2011).
Kaul, S. et al. Prospecting endophytic fungal assemblage of Digitalis lanata Ehrh. (Foxglove) as a novel source of digoxin: a cardiac glycoside. Biotech. 3, 335–340 (2013).
Mishra, A. et al. Season and tissue type affect fungal endophyte communities of the Indian medicinal plant Tinospora cordifolia more strongly than geographic location. Microb. Ecol. 64, 388–398 (2012).
Jumpponen, A. & Trappe, J. M. Dark septate endophytes: a review of facultative biotrophic root-colonizing fungi. New Phytologist 140, 295–310 (1998).
Tejesvi, M. V. et al. Bioactivity and genetic diversity of endophytic fungi in Rhododendron tomentosum Harmaja. Fungal Diversity 47, 97–107 (2011).
Xiong, zQ. et al. Diversity of endophytic fungi and screening of fungal paclitaxel producer from Anglojap yew, Taxus x media. BMC Microbiology 13, 71 (2013).
Lee, J. C. et al. Subglutinols A and B: immunosuppressive compounds from the endophytic fungus Fusarium subglutinans. J. Org. Chem. 60, 7076–7077 (1995).
Sean, F. B. & Jon, C. CR377, a new pentaketide antifungal agent isolated from an endophytic fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 3, 1447–1448 (2000).
Wang, Q. X. et al. Chemical constituents from endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Fitoterapia 82, 777–781 (2011).
Thakur A. et al. Insecticidal potential of an endophytic fungus, Cladosporium uredinicola, against Spodoptera litura. Phytoparasitica https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-013-0298-9 (2013).
Strobel, G. et al. Natural products from endophytic microorganisms. J. Nat. Prod. 67, 257–268 (2004).
Tan, X. M. et al. In vitro seed germination and seedling growth of an endangeredepiphytic orchid, Dendrobium officinale, endemic to China using mycorrhizal fungi (Tulasnella sp.). Scientia Horticulturae 165, 62–68 (2014).
Tan, X. M. et al. Isolation and identification of endophytic fungi in roots of nine Holcoglossum plants (Orchidaceae) collected from Yunnan, Guangxi, and Hainan provinces of China. Curr. Microbiol. 64, 140–147 (2012).
White, T. J. et al. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications. (Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) Academic Press, New York. p 315-322, 1990).
Bosshard, P. P. et al. Ribosomal DNA sequencing for identification of aerobic Gram-positive rods in the clinical laboratory (an 18-month evaluation). Journal of Clinical Microbiology 41, 4134-4140. PMID: 12958237 (2003).
Xing, Y. M. et al. Antimicrobial activity and biodiversity of endophytic fungi in Dendrobium devonianum and Dendrobium thyrsiflorum from Vietman. Curr. Microbiol https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9848-2 (1997).
Fu, Y. J. et al. An analytical pipeline to compare and characterise the anthocyanin antioxidant activities of purple sweet potato cultivars. Food Chemistry 194, 46–54 (2016).
Hata, K. & Futai, K. Endophytic fungi associated with healthy pine needles and needles infested by the pine needle gall midge. Thecodiplosis Japonensis. Can. J. Bot. 73, 384–390 (1995).
Sun, Y. et al. Endophytic fungi associated with two Sauaeda species growing in alkaline soil in China. Mycosphere 2, 239–248 (2011).
Grafenhan, T. et al. An overview of the taxonomy, phylogeny, and typification of nectriaceous fungi in Cosmospora, Acremonium, Fusarium, Stilbella, and Volutella. Stud. Mycol 68, 79–113 (2011).
Crous, P. W. & Groenewald, J. Z. A. Phylogenetic re-evaluation of Arthrinium. IMA Fungus 4(1), 133–154 (2013).
Bussaban, B. et al. Molecular and morphological characterization of Pyricularia and allied genera. Mycologia 97(5), 1002–1011 (2005).
Cantrell, S. A. et al. Fungal communities of young and mature hypersaline microbial mats. Mycologia 105(4), 827–836 (2013).
Braun, U. et al. Phylogeny and taxonomy of Cladosporium-like hyphomycetes, including Davidiella gen. nov., the teleomorph of Cladosporium s. str. Mycol. Prog. 2(1), 3–18 (2003).
Tao, G. et al. Endophytic Colletotrichum species from Bletilla ochracea (Orchidaceae), with descriptions of seven new speices. Fungal Divers. 61(1), 139–164 (2013).
Glynou,K. et al.The local environment determines the assembly of root endophytic fungi at a continental scale. Environ. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13112 (2015).
Weir, B. S. et al. The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud. Mycol. 73(1), 115–180 (2012).
Alvarez, E. et al. Diversity and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum species isolated from soursop in Colombia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 139(2), 319–332 (2014).
Halleen, F. et al. Neonectria liriodendri sp. nov., the main causal agent of black foot disease of grapevines. Studies in Mycology 55, 227–234 (2006).
Cabral, A. et al. Cylindrocarpon root rot: multi-gene analysis reveals novel species within the Ilyonectria radicicola species complex. Mycol. Prog. 11(3), 655–688 (2012).
Miao, C. P. et al. Rhizospheric fungi of Panax notoginseng: diversity and antagonism to host phytopathogens. J. Ginseng. Res. 40(2), 127–134 (2016).
Tesitelova, T. et al. Symbiotic germination capability of four Epipactis species (Orchidaceae) is broader than expected from adult ecology. Am. J. Bot. 99(6), 1020–1032 (2012).
Gomes, R. R. et al. Diaporthe: a genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia 31, 1–41 (2013).
Li, Q. & Wang, G. Diversity of fungal isolates from three Hawaiian marine sponges. Microbiol. Res. 164(2), 233–241 (2009).
Hirose, D. et al. Microfungi associated with withering willow wood in ground contact near Syowa Station, East Antarctica for 40 years. Polar Biol. 36, 919–924 (2013).
Zhao, J. et al. Endophytic fungi from pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) produce antioxidant Cajaninstilbene acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(17), 4314–4319 (2012).
Khot, P. D. et al. Sequencing and analysis of fungal rRNA operons for development of broad-range fungal PCR assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75(6), 1559–1565 (2009).
Wu, L. et al. Geographic and tissue influences on endophytic fungal communities of Taxus chinensis var. mairei in China. Curr. Microbiol. 66(1), 40–48 (2013).
Gao, Y. et al. Characterization of five fungal endophytes producing Cajaninstilbene acid isolated from pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. PLoS ONE 6(11), E27589 (2011).
U’Ren, J. M. et al. Host and geographic structure of endophytic and endolichenic fungi at a continental scale. Am. J. Bot. 99(5), 898–914 (2012).
Liu, X. Y. et al. Backbone tree for Chaetothyriales with four new species of Minimelanolocus from aquatic habitats. Fungal Biol. 119(11), 1046–1062 (2015).
Rodrigues, A. et al. Ecology of microfungal communities in gardens of fungus-growing ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): a year-long survey of three species of attine ants in Central Texas. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 78(2), 244–255 (2011).
Lian, X. & de Hoog, G. S. Indoor wet cells harbour melanized agents of cutaneous infection. Med. Mycol. 48(4), 622–628 (2010).
Del Olmo-Ruiz, M. & Arnold, A. E. Community structure of fern-affiliated endophytes in three neotropical forests. J. Trop. Ecol. 33(1), 60–73 (2017).
Micalizzi, E. W. et al. Microbial inhibitors of the fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the causal agent of white-nose syndrome in bats. PLoS one 12(6), E0179770 (2017).
Maharachchikumbura, S. S. et al. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 79, 121–186 (2014).
Ban, Y. et al. The response of dark septate endophytes (DSE) to heavy metals in pure culture. PLoS one 7(10), E47968 (2012).
Aveskamp, M. M. et al. Highlights of the Didymellaceae: a polyphasic approach to characterise Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Stud. Mycol. 65, 1–60 (2010).
Motohashi, K. et al. Phylogenetic analyses of Japanese species of Phyllosticta sensu stricto. Mycoscience 50, 291–302 (2009).
Vasutova, M. et al. Phylogenetic studies in Psathyrella focusing on sections Pennatae and Spadiceae-new evidence for the paraphyly of the genus. Mycol. Res. 112 (PT 10, 1153–1164 (2008).
Crous, P. W. et al. Phylogenetic lineages in the Capnodiales. Stud. Mycol 64, 17–47S7 (2009).
Quaedvlieg, W. et al. Sizing up Septoria. Stud. Mycol 75(1), 307–390 (2013).
Diaz Arias, M. M. et al. Diversity and biogeography of sooty blotch and flyspeck fungi on apple in the eastern and midwestern United States. Phytopathology 100(4), 345–355 (2010).
Ruifen Zhang et al. Diosgenin production of Dioscorea zingiberensis cultures stimulated by its endophytic fungi. Journal of Biotechnology 136S, 151 (2008).
Kelderer, M. et al. Planting in the inter-row to overcome replant disease in apple orchards: a study on the effectiveness of the practice based on microbial indicators. Plant Soil 357(1-2), 381–393 (2012).
Manici, L. M. & Bonora, P. Molecular genetic variability of Italian binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. isolates from strawberry. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 118(1), 31–42 (2007).
Knapp, D. G. The dark side is not fastidious-dark septate endophytic fungi of native and invasive plants of semiarid sandy areas. PLoS ONE 7(2), E32570 (2012).
Nonaka, K. et al. Virgaria boninensis, a new hyphomycete (Xylariaceae) from soils in the Bonin Islands, Japan. Mycoscience 54, 394–399 (2013).
Lombard, L. et al. Generic concepts in Nectriaceae. Stud. Mycol. 80, 189–245 (2015).
Herrera, J. et al. Shifting fungal endophyte communities colonize Bouteloua gracilis: effect of host tissue and geographical distribution. Mycologia 102(5), 1012–1026 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Project No. 81360682), the Scientific Research Foundation of Introduced Doctor of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine (Project No. B170032), the Guangxi Science Foundation (Project No. 2016GXNSFBA380088; Project No. 2015GXNSFDA139012), and the Key Laboratory Project of Guangxi University (Project No. J17008). The authors give great thanks to Dr. Gang Zhang (Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, China) and Dr. Jin-long Cui (Shanxi University, China) for proof-read of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.M.T. and Y.Q.Z. conceived and designed the experiments. X.M.T., L.L.H., H.Z.T. and Y.W. performed the experiments. X.M.T., X.L.Z., X.H.X. and L.Y.Y. analyzed the data. X.M.T. and Y.Q.Z. wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Xm., Zhou, Yq., Zhou, Xl. et al. Diversity and bioactive potential of culturable fungal endophytes of Dysosma versipellis; a rare medicinal plant endemic to China. Sci Rep 8, 5929 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24313-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24313-2
This article is cited by
-
The anticancer and antibacterial potential of bioactive secondary metabolites derived From bacterial endophytes in association with Artemisia absinthium
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Enhanced podophyllotoxin production of endophyte Fusarium proliferatum TQN5T by host extract and phenylalanine
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Glomus mosseae on the Growth and Medicinal Components of Dysosma versipellis Under Copper Stress
Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology (2021)
-
Diversity and Spatiotemporal Distribution of Fungal Endophytes Associated with Salvia multicaulis
Current Microbiology (2021)
-
Bioactive Molecules of Endophytic Fungi and Their Potential in Anticancer Drug Development
Current Pharmacology Reports (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.