Abstract
Zero-dimensional MoS2 quantum dots (QDs) possess distinct physical and chemical properties, which have garnered them considerable attention and facilitates their use in a broad range of applications. In this study, we prepared monolayer MoS2 QDs using temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water. The morphology, crystal structures, chemical, and optical properties of the MoS2 QDs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, UV–vis absorption spectra, and photoluminescence spectra. The analysis results show that highly pure, uniform, and monolayer MoS2 QDs can be successfully prepared. Moreover, by temporally shaping a conventional single pulse into a two-subpulse train, the production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials (including nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs) and the ratio of small size MoS2 QDs can be substantially improved. The underlying mechanism is a combination of multilevel photoexfoliation of monolayer MoS2 and water photoionization–enhanced light absorption. The as-prepared MoS2 QDs exhibit excellent electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reactions because of the abundant active edge sites, high specific surface area, and excellent electrical conductivity. Thus, this study provides a simple and green alternative strategy for the preparation of monolayer QDs of transition metal dichalcogenides or other layered materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Recently, graphene-like layered transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) have attracted substantial research attention because of their distinct physical and chemical properties1, 2. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a typical TMD with a sizable intrinsic bandgap, comprises layered S–Mo–S sandwiched structures held by relatively weak Van der Waals forces; therefore, MoS2 can be readily cleaved along the layer surface3, 4. As a structure changes from a thin layer to a monolayer, MoS2 transforms from an indirect-bandgap semiconductor (1.2 eV for bulk material) to a direct-bandgap semiconductor (1.9 eV for monolayer)4,5,6. This unique structure and properties enable MoS2 to be applied in many fields, including biomedicine, energy storage, gas sensing, catalysis, and electronics engineering7. Monolayer MoS2 quantum dots (QDs), which possess strong quantum confinement, edge effects8, and direct-bandgap properties, are important MoS2-based nanostructures that have attracted considerable research attention in recent years. The abundant active edge sites, high specific surface area, and excellent electrical conductivity, together with the strong hydrogen adsorption properties9,10,11,12,13, have made monolayer QDs efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reactions (HERs). Because the small size particles posses strong optical nonlinearity properties14, 15, the QDs are a promising photoluminescence (PL) material for biomedical and optical-imaging applications16, 17. In addition, the more uniform the size distribution of the monolayer QDs is, the more stable the quantum size confinement effects and the stronger the PL properties of the QDs are. Thus, there is tremendous demand to elucidate an effective method for preparing uniform-size monolayer MoS2 QDs.
To date, several strategies for preparing MoS2 QDs have been proposed, including sonication combined with solvothermal treatment synthesis18, lithium intercalation19, liquid exfoliation in organic solvents20, hydrothermal synthesis21, electrochemical etching22, electro-Fenton reaction processing23, and grinding exfoliation9. These methods all have their own advantages; for example, liquid exfoliation can provide a high yield of MoS2 QDs, chemical intercalation can yield 1T-phase MoS2 QDs with excellent HERs catalytic reactivity, and one-pot hydrothermal synthesis can yield heterostructures in a single step. However, all of these methods also have drawbacks: chemical intercalation may introduce metallic heteroatoms in MoS2, resulting in structural destruction and loss of the pristine semiconducting properties of MoS2; liquid exfoliation may be time consuming and requires the use of hazardous organic solvents; electrochemical etching may require harsh conditions, complex chemical reactions, and multiple steps as well as an intricate post-treatment process to remove byproducts; and grinding exfoliation may result in large size distributions and multilayer MoS2 nanoparticles. In short, the production of monolayer MoS2 QDs with uniform size distribution through a fast, simple, green, and one-step method remains a challenge.
Here, we propose the temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water as a novel approach for the fast, green, and one-step preparation of uniform monolayer MoS2 QDs. Femtosecond lasers with ultrahigh peak power densities (typically > 1013 W cm−2) and ultrashort pulse durations have unique characteristics, such as nonthermal effect and nonlinear nonequilibrium processing24,25,26, giving rise to the possibility of monolayer photoexfoliation of two-dimensional materials27, 28. Furthermore, through temporal shaping of a conventional single pulse into a two-subpulse train, we can improve the production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials (including nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs) and the ratio of uniform, small-size MoS2 QDs. The underlying mechanism is a combination of multilevel photoexfoliation of monolayer MoS2 and water photoionization–enhanced light absorption; this mechanism can be induced and well controlled using temporally shaped femtosecond lasers. The proposed method has the following major advantages over current strategies: (1) the preparation time is considerably reduced; (2) the method is environmentally-friendly; the bulk MoS2 targets are ablated in water; hence, high-purity MoS2 QDs can be obtained without the use of metallic heteroatoms or chemical reagents. Thus, the as-prepared MoS2 QDs can be directly used for further characterization and applications without intricate post-treatment processing. In particular, the use of the temporally shaped femtosecond laser has the following advantages: (1) uniform monolayer MoS2 QDs with a size distribution of 1–5 nm can be prepared; (2) small monolayer MoS2 QDs can be prepared in high yield (36.73 wt%); these QDs have numerous active edges and excellent electrocatalytic activity for HERs (low onset potential of approximately 140 mV, small Tafel slope of approximately 66 mV dec−1). Moreover, the temporally shaped femtosecond laser has the potential to be a fast, uniform, green, and alternative strategy to facilely and efficiently prepare QDs of TMDs or other layered materials for abroad applications in biomedical, optical imaging, energy storage, and catalysis areas.
Results and Discussion
A novel fast, green, and one-step method was proposed to prepare high-purity, uniform, and small (size distribution of 1–5 nm) monolayer MoS2 QDs through temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water. The experimental setup for the temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation is shown in Supplementary Figure S1, wherein a conventional femtosecond pulse is temporally shaped into two subpulses (energy ratio 1:1, total laser fluence 0.77 J cm−2) with time delays ranging from 0 to 10 ps. The underlying mechanism is a combination of multilevel photoexfoliation of monolayer MoS2 and water photoionization–enhanced light absorption; this mechanism can be induced and well controlled using a temporally shaped femtosecond laser, as shown in Fig. 1. As the first subpulse (with fluence slightly higher than the ablation threshold of 0.24 J cm−2 for bulk MoS2)29 irradiates on the MoS2 surface, the heated electrons spill out. Therefore, the MoS2 interlayer interactions are reduced by Coulomb repulsion28, which can trigger first-level photoexfoliation (detachment of the multilayer MoS2 QDs/nanosheets from bulk materials) within the femtosecond time scale. The electron and hole recombination in the MoS2 surface lasts from 2 to 100 ps after the first subpulse30. As the second subpulse with 10 ps time delay irradiates, the enhanced Coulomb repulsion due to enhanced ionization–induced charge accumulation results in the MoS2 QDs/nanosheets or bulk MoS2 surface achieving second-level photoexfoliation (small monolayer MoS2 QDs preparation). Meanwhile, the first subpulse can ionize the water molecules within the hydrogen-bond associated time from 200 fs to 13 ps31. The increase in electron density due to the ionization of water molecules via the first subpulse enhances the light absorption for the second subpulse, which is responsible for the high yield of MoS2 QDs. While in the case of femtosecond laser single pulse ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water, the laser pulse has a total fluence of 0.77 J cm−2, which is much greater than the ablation threshold of bulk MoS2. Therefore, when the femtosecond laser single pulse irradiates on the MoS2 surface, it can induce a localized transient free-electron density that is much higher than the critical density. This leads to thermal phase-change mechanisms (e.g. melting and evaporation) dominating the ablation process, thereby resulting in more large size nanosheets/nanoparticles and a wide size distribution. In short, through temporally shaping of a conventional single pulse into a two-subpulse train, we can improve the production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials (including nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs) and the ratio of uniform, small-size MoS2 QDs, a finding which corroborates previous reported results32,33,34.
Details about the synthesis and experimental setup of this study are reported in the Experimental Section. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of the surface of the original bulk MoS2 targets before and after temporally shaped femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation in water are shown in Supplementary Figure S2. After ablation, the dark-brown MoS2 aqueous solution with concentration of 166.02 μg/mL (Fig. 2b) was allowed to settle for 2–4 hours, following which it was centrifuged for 10 minutes at 8000 rpm to obtain a transparent light-yellow supernatant solution with concentration of 60.98 μg/mL (Fig. 2c). The yield of MoS2 QDs—defined as the concentration of the transparent light-yellow supernatant solution that mainly consists of QDs obtained after concentration relative to the concentration of the dark-brown MoS2 aqueous solution comprising nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs before concentration—was approximately 36.73 wt%. For comparison, a photograph of the MoS2 aqueous solution prepared using a femtosecond laser single pulse before centrifugation is shown in Fig. 2a. The concentration of this MoS2 aqueous solution with concentration of 79.06 μg/mL was obviously smaller than that of the solution prepared through temporally shaped femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation. The ablation time was 2 hours and the production rate for femtosecond laser single pulse and temporally shaped pulse train was 3.29 and 6.92 μg/min, respectively. Thus, we improved the production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials (including nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs) by 2.1 times through temporally shaping a conventional single pulse into a two-subpulse train.
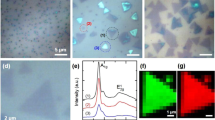
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to characterize the size, morphology, and lattice structure of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. Figure 3a reveals that the as-prepared MoS2 QDs obtained after centrifugation were homogeneously dispersed, with little aggregation. Figure 3c and d show that the as-prepared MoS2 QDs were monodispersed crystalline. Additionally, the inset of Fig. 3b shows the size distribution of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs, exhibiting a relatively narrow size distribution of approximately 1–5 nm and an average lateral dimension of approximately 2.6 nm. Before centrifugation, however, the nanomaterials prepared through femtosecond laser single-pulse ablation exhibited a broad distribution of approximately 1–120 nm and an average lateral dimension of approximately 36.3 nm; additionally, the ratio of the QDs that were smaller than 10 nm was only 16.7% (Supplementary Figure S3a). By contrast, the ratio of the small QDs prepared using the temporally shaped femtosecond laser two-subpulse train, and which were variously sized from approximately 1–10 nm, was more than 50% (Supplementary Figure S3(b–d)). These results revealed that temporally shaping a conventional single pulse into a two-subpulse train and then optimizing the delay between the two ultrashort subpulses greatly improves the ratio of uniform small-size MoS2 QDs. This improvement is due to the multilevel photoexfoliation of MoS2 that is triggered by an increase in the localized transient free-electron density to slightly higher than the critical density, and then foster the nonthermal phase-change mechanism (Coulomb repulsion)28 to dominate the ablation process, resulting in a high photon absorption efficiency and narrow size distribution25, 35. In the case of femtosecond laser single pulse with the same total energy, a localized transient free-electron density that is much higher than critical density can be induced; this leads to the thermal phase-change mechanisms (e.g. melting and evaporation) dominating the ablation process and thereby results in more large-size nanosheets/nanoparticles and a broad distribution36, 37. The high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image in the inset of Fig. 3d clearly shows that the as-prepared MoS2 QDs have parallel and ordered lattice fringes, indicating that the QDs are well crystallized. The d-spacing of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs is 0.19 nm, which is assigned to the (105) face of the MoS2 crystal. The corresponding fast Fourier transform (FFT) pattern similarly revealed the hexagonal lattice structure of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements were also performed to confirm the morphology and thickness of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. As shown in the AFM height profile (Fig. 3f), the thickness of most of the QDs was less than 1 nm, indicating that most of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs were monolayer, in accordance with previous reported results18, 21, 38, 39.
TEM images (a–d) at different scale bars: (a) 100 nm, (b) 20 nm, (c) 10 nm, and (d) 5 nm, and AFM image (e) 250 nm. Inset image in (b) shows the size distribution. Inset images in (d) show the HRTEM images (upper panel) and FFT pattern (lower panel) of the crystal of MoS2 QDs. (f) Height profile corresponding with the line in (e).
To confirm that the temporally shaped femtosecond laser method has universality (i.e., can produce QDs of other TMDs and other layered materials), WS2 QDs and graphene QDs (GQDs) were also prepared using this method, as shown in Supplementary Figures S4 and S5. After 2 hours of femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation of the bulk WS2 targets in water and then 10 minutes of centrifugation at 8000 rpm, we obtained WS2 QDs that were homogeneously dispersed with little aggregation (Supplementary Figure S4a) and highly crystalline (Supplementary Figure S4c). The inset of Supplementary Figure S4b shows the size distribution of the as-prepared WS2 QDs, and indicates that they had a relatively narrow size distribution that varied from approximately 1–8 nm and an average lateral dimension of approximately 4.1 nm. Similarly, we have also preliminary attempted to prepare GQDs by temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of graphene oxide (GO) dispersions. After 1 hour of femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation, we obtained GQDs that were homogeneously dispersed with little aggregation and were almost smaller than 5 nm (Supplementary Figure S5). However, this was a preliminary experiment, and additional research should be conducted to verify the ability of our method to prepare GQDs.
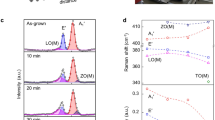
The crystal structure of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs was systematically characterized through X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy. As shown in Fig. 4a, the original bulk MoS2 target had an obviously strong diffraction peak at 2θ = 14.4° corresponding to the (002) face, indicating that the original materials had a multilayer structure. In addition, several lower peaks located at 2θ = 29°, 2θ = 39.6°, 2θ = 44.2°, 2θ = 49.8°, and 2θ = 60.2° can be observed, which are assigned to the (004), (103), (006), (105), and (008) faces, respectively (JCPDF (37–1492)). If the materials are thin or monolayer, no signals or peaks exist on the XRD patterns because there is no constructive interference from the aligned crystal planes18. After femtosecond laser ablation, the (002) peak of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs almost disappeared, confirming that the QDs were thinned to monolayer or few layers, which was in accordance with the AFM results. Further, the small peak at 2θ = 28.4°, corresponding to the (004) face, probably resulted from the partial restacking of QDs during the drying process18, 40.
Raman spectra are a common and facile measurement to investigate the layers of MoS2 materials. In Fig. 4b, the bulk MoS2 target shows two characteristic Raman peaks at 384.3 and 410 cm−1, corresponding to E2g 1 (in-plane optical vibration of the Mo−S bond in opposite directions) and A1g (out-of-plane optical vibration of S atoms) active modes, respectively. By contrast, the A1g and E2g 1 modes of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs had a red-shift of 1.8 cm−1 and blue-shift of 2.5 cm−1, respectively. In other words, the frequency difference between the A1g and E2g 1 modes reduced from 25.7 cm−1 for bulk MoS2 to 21.4 cm−1 for QDs, indicating that the as-prepared MoS2 QDs were thinned to mono- or bi-layers, which was consistent with previous reports41. As shown in Supplementary Figure S4d, the bulk WS2 also shows two characteristic Raman peaks at 351.0 and 420.6 cm−1 corresponding to E2g and A1g active modes, respectively. By contrast, the E2g and A1g active modes of the as-prepared WS2 QDs were at 353.0 and 420.4 cm−1 and had a blue-shift of 2 cm−1 and red-shift of 0.2 cm−1, respectively. These results indicated that the thickness of the as-prepared WS2 QDs was thinned to a few layers.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements were performed to investigate the chemical composition and phase state of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. The high-resolution XPS spectra of original bulk MoS2 (Fig. 5a) exhibits two obvious peaks at 229.4 and 232.6 eV, which belong to the Mo4+3d5/2 and Mo4+3d3/2 components of 2H-MoS2, respectively. Another small peak at 226.6 eV is the S 2 s of MoS2 and other peaks observed at 162.3 and 163.5 eV are assigned to S2−2p3/2 and S2−2p1/2 in 2H-MoS2, respectively (Fig. 5b). The Binding energies of Mo 3d and S 2p regions reveal that the original bulk MoS2 has a strong trigonal prismatic structure. In the Mo 3d spectra of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs, the Mo4+ doublet and S 2 s peak were observed at 231.6, 228.3, and 225.3 eV (Fig. 5c). In addition, a new small peak located at a higher binding energy (235.3 eV) is ascribed to Mo6+, demonstrating that the Mo edges in MoS2 QDs are slightly oxidated during the transition from the Mo4+ state to the Mo6+ state. Similarly, the S 2p spectra shows the S2− doublet at 162.3 and 163.7 eV (Fig. 5d). Further, a peak at a higher binding energy (168.6 eV) is observed, which corresponds to the presence of an S–O bond42, indicating partial oxidation of the S edges in MoS2 QDs. The oxidation percentage of Mo and S edges were 6.6% and 14.5%, respectively. This slight oxidation can be attributed to femtosecond laser ablation process, in which the femtosecond laser–induced transient high temperatures at the centre of the focal point focused on the MoS2–water interface. Although such oxidation can somewhat modify the electronic properties of the original 2H-MoS2 12, 43, this can also generate more active surface sites with high catalytic properties, thus improving the HERs22, 44. The full spectrum of the XPS survey of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs is shown in Supplementary Figure S6. Here, except for the XPS peaks of Si that come from the substrate, there are only C, O, Mo, and S elements in the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. These results demonstrate that the MoS2 QDs prepared through the temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water exhibited high purity, with no metallic heteroatoms or chemical reagents. Thus, they can be directly used for further characterization and applications.
To further investigate the optical properties of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs, UV–vis absorption spectra were investigated (Fig. 6a). The peaks appearing at 340, 430, 590, and 650 nm are the characteristic absorption bands of the original bulk MoS2. The obvious peaks at 590 and 650 nm were assigned to the K point of the Brillouin zone, and the peaks at 340 and 430 nm were attributed to the direct transition from the deep valence band to the conduction band18, 20, 45. However, these four characteristic absorption bands disappear in the spectra of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. Only one peak is observed in the near-UV region (λ < 300 nm), which was attributed to the excitonic features of MoS2 QDs46. Moreover, the strong blue-shift during optical absorption of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs was attributed to the quantum confinement and edge effects11 when the lateral size of the MoS2 QDs is reduced to <50 nm. According to the TEM results, the majority of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs are in the range of 1–5 nm and a strong blue shift is observed; this is similar to findings reported elsewhere18, 21, 39, 47, 48.
(a) UV–vis spectra of the bulk MoS2 and as-prepared MoS2 QDs. (b) Excitation and emission PL spectra of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs prepared in NMP. (c) Emission PL spectra of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs under different excitation wavelengths prepared in NMP. (d) Emission PL spectra of the NMP aqueous solution without MoS2 materials.
Apart from in water, we explored the temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in other aqueous media, such as N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP). The PL spectra of the MoS2 QDs prepared in NMP exhibit a strong emission peak at 340 nm under an excitation wavelength of 290 nm (Fig. 6b). The origin of PL from the present MoS2 QDs may be because of the exciton recombination at the electron (hole) trap constituted by the uncompensated positive (negative) charge at the dangling bonds22. In addition, the PL spectra of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs suspensions were measured at various excitation wavelengths. With an increase in the excitation wavelength from 290 to 370 nm, the PL emission peaks shift to longer wavelengths, namely from 340 to 450 nm (Fig. 6c). This phenomenon of excitation-dependent PL property confirmed the polydispersity of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. This phenomenon may also be due to the presence of several trap states, as observed in GQDs48,49,50. Moreover, we characterized the emission PL spectra of the NMP aqueous solution without MoS2 materials (Fig. 6d). The PL intensity of all the emission peaks of the NMP solution is much lower than that of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. In addition, the shape and position of the PL emission peaks of the NMP solution are visibly different from those of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. Furthermore, to determine whether the NMP solution can be transformed into carbon dots by temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation and then enhance the PL intensity of the MoS2, we performed the same experiments in the NMP solution without MoS2 materials. According to the resulting Raman spectra, no obvious Raman peaks are assigned to the carbon materials; this indicates that no carbon dots were decomposed to enhance the PL intensity of the MoS2 QDs (Supplementary Figure S7). Therefore, we suppose that femtosecond laser ablation of a NMP aqueous solution (which comprises nitrogen-containing organic solvents) causes nitrogen-containing functional groups to be adsorbed on the surface of the as-prepared MoS2 QDs. This may result in a substantial enhancement of PL, as was observed elsewhere in GQDs51.
The as-prepared MoS2 materials were used as efficient electrocatalysts for HERs. The HERs activity of these materials was explored in an N2-saturated 0.5 M H2SO4 electrolyte in a typical three-electrode electrochemical workstation by using a standard rotating-disk glassy carbon electrode (GCE, 5 mm diameter) as the working electrode. A Pt wire electrode and a Ag/AgCl electrode were used as the counter and reference electrodes, respectively. The GCE was modified using MoS2 composites (10 ps) (composite of nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs prepared using temporally shaped femtosecond laser) for linear sweep voltammetry measurements at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1. For comparison, similar measurements were also conducted on a bare GCE, a GCE modified using bulk MoS2, a GCE modified using MoS2 composites (0 ps) (composite of nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs prepared using femtosecond laser single pulse), and a commercial Pt electrode (20 wt% Pt/C). The obtained polarization curve of the Pt catalyst displays extremely high HERs catalytic activity with a near-zero onset overpotential (Fig. 7a). However, the bare GCE and bulk MoS2 exhibit extremely low HERs catalytic activity with a high onset overpotential of approximately 350 and 320 mV, respectively. Moreover, their cathodic current density is very weak, hardly increasing with the negative potential. By contrast, the MoS2 composites (0 ps) show a slightly lower onset overpotential of approximately 260 mV. While the MoS2 composites (10 ps) exhibit a relatively high HERs catalytic activity with a low onset overpotential of approximately 140 mV, and the cathodic current density increases rapidly with an increase in the negative overpotential. At approximately 400 mV, the as-prepared MoS2 composites (10 ps) display an extremely large cathodic current density of 36 mA cm−2. Whereas the MoS2 composites (0 ps) display a cathodic current density of 2.2 mA cm−2. Notably, the HERs catalytic activity of the as-prepared MoS2 composites (10 ps) is comparable with that in other recent reports21, 22.
HERs activity of the as-prepared MoS2 materials. (a) Polarization curves. (b) Corresponding Tafel plots of bulk MoS2, MoS2 composites (0 ps), MoS2 composites (10 ps), and Pt electrodes at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 in 0.5 M H2SO4. (c) EIS Nyquist plots of bulk MoS2, MoS2 composites (0 ps), and MoS2 composites (10 ps). (d) Stability test of MoS2 composites (10 ps).
The Tafel slope is another key parameter in evaluating the HERs catalytic activity of catalysts; it reflects the intrinsic property of the electrocatalytic materials and is determined by the rate-limiting step of the HERs. The smaller the Tafel slope is, the faster is the hydrogen generation rate obtained at the applied negative overpotential. The Tafel slope is obtained by fitting the linear portions of the Tafel plots to the Tafel equation (η = b log |j| + a, where j is the current density and b is the Tafel slope). As shown in Fig. 7b, the Tafel plots derived from the polarization curves indicate that the commercial Pt has a Tafel slope of approximately 36 mV dec−1, which is close to that identified by other previous reports18, 21, 52. For MoS2 composites (10 ps), the slope is approximately 66 mV dec−1, which is much smaller than that of the MoS2 composites (0 ps) (approximately 102 mV dec−1) and bulk MoS2 (approximately 131 mV dec−1). This demonstrates that the HERs catalytic activity is determined by the Volmer-Heyrovsky reaction9. Considerable improvement was seen between bulk MoS2 and MoS2 composites (10 ps). Indeed, the Tafel slope of the MoS2 composites prepared through temporally shaped femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation is comparable to or smaller than that of the composites prepared through either a hydrothermal approach21, sonication combined with solvothermal treatment synthesis18, or electrochemical etching22. Nevertheless, the slope is poorer than that of 1 T phase MoS2 nanosheets prepared through chemical exfoliation12, 53, 54 or MoS2 heterostructures on reduced graphene oxide55. A comparison of the HERs catalytic activity of the MoS2 composites prepared using a femtosecond laser with the MoS2-based HERs catalysts prepared using other typical synthesis methods is presented in Supplementary Table S1.
Compared with the MoS2 composites prepared using a femtosecond laser single pulse, an obvious improvement in the HERs catalytic activity can be obtained using MoS2 composites prepared by a temporally shaped femtosecond laser. This may be attributed to several reasons. First, there is a much higher ratio of small-size QDs prepared and a reduction of the lateral and vertical dimensions to monolayer ultrasmall QDs when suing a temporally shaped femtosecond laser (see the TEM images in Fig. 3 and Figure S3). This produces more available edge sites for hydrogen adsorption. Second, there is a much higher production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials prepared that can be estimated from the concentration of the as-prepared MoS2 aqueous solutions (see Fig. 2) when using a temporally shaped femtosecond laser. Finally, more MoS2 materials were thinned to monolayer zero-dimensional QDs when using a temporally shaped femtosecond laser, which resulted in a high edge-to-basal plane ratio. Notably, this results in considerable improvement of the carrier mobility, which further enhances the efficiency of electron transfer between the active edge sites and the underlying electrode18, 56; and is revealed through electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. As shown in Fig. 7c, the Nyquist plots demonstrate that the electron transfer resistance considerably reduces from bulk MoS2 (1500 Ω) to MoS2 composites (0 ps) (500 Ω) and MoS2 composites (10 ps) (180 Ω), resulting in a faster electron transfer between the MoS2 composite catalysts and the electrode.
Finally, we measured the stability and durability of the MoS2 composite (10 ps) catalysts under continuous operation. As shown in Fig. 7d, the HERs catalytic activity of these MoS2 composites (10 ps) had no obvious change even after 1000 continuous cycles. This stability is comparable to that reported in prior research9, 44, 45, 52, 57, 58. Moreover, there is only an approximately 20% loss of cathodic current when a potential of −300 mV vs. reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) is applied for 5000 seconds of continuous operation (Supplementary Figure S8), an outcome which reflects results elsewhere21.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we reported a novel, fast, green, and one-step approach to prepare monolayer MoS2 QDs using the temporally shaped femtosecond laser ablation of bulk MoS2 targets in water. We achieved a uniform size distribution monolayer and a high production rate of MoS2 QDs by simply adjusting the laser power and the two-subpulse delay within a pulse train. The as-prepared MoS2 QDs possess abundant active edge sites, high carrier mobility, and a large specific surface area; consequently, the QDs exhibit excellent electrocatalytic activity for the HERs with an onset overpotential of approximately 140 mV, a Tafel slope of approximately 66 mV dec−1, long-term durability, and high stability. In addition, MoS2 QDs possess strong quantum confinement and edge effects that, when combined with the direct bandgap property, afford them with unique PL features. Thus, MoS2 QDs have great potential in the biomedical and optical-imaging applications. Furthermore, the production rate of MoS2 nanomaterials might be further enhanced through multi-beam parallel processing or optimization of other laser parameters, such as scan speed, laser wavelength, and pulse delay, etc. In short, this study provided a novel, simple, green, and one-step approach to facilely and efficiently produce QDs of TMDs or other layered materials for broad potential applications.
Methods
Materials
Original bulk 2H-MoS2 and WS2 targets (10 × 10 × 5 mm3) were purchased from Jiangxi Ketai Advanced Materials Co. Ltd, Jiangxi, China. Original GO dispersions were purchased from Nanjing XFNANO Materials TECH Co.,Ltd, China. NMP and H2SO4 (98%) were acquired from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. Nafion solution (5%) was purchased from Dupont China Holding Co. Ltd. N2 with a purity of 99.9% was purchased from Beijing Hairui Tongda Gas Technology Co. Ltd. All reagents were of analytical grade and used without further purification.
Preparation of MoS2 Quantum Dots
An amplified Ti:sapphire laser system (Spectra Physics Inc.) was used to generate linearly polarized laser pulses of 50 fs (FWHM) pulse duration at 800 nm central wavelength with a repetition rate of 1 kHz. Collinear two-subpulse irradiation was obtained using a Michelson interferometer, which splits each pulse into two temporally separated subpulses with nearly identical pulse characters. The temporal separation (τs), which ranges from 100 fs to tens of picoseconds, was adjusted using a computer-controlled linear translation stage with a micrometer resolution. Before laser ablation, the bulk MoS2 targets were dipped into ethanol and then water for ultrasonic cleaning for 10 minutes using a sonicator (KQ3200DB). Then, the bulk MoS2 targets were placed at the bottom of a glass vessel filled with 5 mL of distilled water. The typical thickness of the liquid above the targets were approximately 3 mm. The glass vessel was mounted on a computer-controlled six-axis positioning system (M-840.5DG, PI, Inc.), and the targets were continuously moved during laser irradiation to obtain a fresh surface for ablation. The laser beam was focused normally on the surface of the target by using a plano-convex lens (f = 100 mm). The MoS2 QDs were prepared using a temporally shaped femtosecond laser two-subpulse train with a total energy of 3.5 μJ (0.77 J cm−2), and the intensity of the two subpulses was approximately 1:1. The pulse delay between the two subpulses was 10 ps. When using a conventional femtosecond laser single pulse, the pulse delay between the two subpulses was 0 ps. The pulse energy was finely controlled using a half-wave plate combined with a polarizer and was mounted prior to the interferometer entrance. The preparation was performed in air at ambient pressure and temperature. After ablation for 2 hours, the MoS2 aqueous solution was allowed to settle for 2–4 hours and was then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain the transparent light-yellow supernatant solution. Subsequently, the supernatant solution was sonicated for 1 hour in an ice bath to avoid the agglomeration of QDs, which can be directly applied for further characterization. For HERs, we used MoS2 composites that comprised MoS2 nanosheets, nanoparticles, and QDs before centrifugation. In addition to water, the proposed methodology can be applied to other aqueous media such as NMP; the other experimental parameters and procedures are the same as those applied in the preparation of QDs in water. The WS2 QDs were prepared using the same experimental setup and process as that for the preparation of MoS2 QDs. However, the pulse energy and pulse delay were changed to 2 μJ (0.44 J cm−2) and 2 ps, respectively. The concentration of the original GO dispersions was 2 mg/mL, which we diluted to 0.5 mg/mL using deionised water. The total power (density) of the temporally shaped femtosecond laser pulse two-subpulse train was 200 mW (44 J/cm2) and the pulse delay between the two subpulses was 10 ps. After 1 hour of femtosecond laser two-subpulse train ablation of the GO dispersions, we obtained GQDs.
Electrochemical Measurements
The HERs catalytic activity of the as-prepared MoS2 composites (composite of nanosheets and QDs) was evaluated using a computer-controlled electrochemical workstation (CHI 760D) in a standard three-electrode system. The rotating-disc GCE was used as the working electrode while a Ag/AgCl (in 3.5 M KCl solution) electrode was used as the reference electrode; a Pt wire was used as the counter electrode. The MoS2 composites working electrode was prepared as follows: (1) 10 μL of MoS2 composites solution was dropped onto a GCE with 5 mm diameter using a pipettor and dried at room temperature; (2) the process of (1) was repeated five times; (3) 5 μL of Nafion solution (5%) was coated on the GCE. All the measurements were performed in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. Before the experiments, the electrolyte was degassed in bubbling N2 for 30 minutes. Subsequently, the GCE was pre-conditioned (prior to collecting polarization curves) through cyclic voltammetry (CV) at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 for 200 cycles while the GCE was rotated at 1600 rpm. After the CV, linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) was performed at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 while the working electrode was rotated at 1600 rpm. iR compensation was performed for all the polarization curves of all catalysts. All the potentials obtained in our study were through RHE calibration against the RHE. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was performed using the same configuration at an overpotential η = −0.35 V vs RHE from 106 to 1 Hz at an alternating current voltage of 5 mV. The stability and durability of the MoS2 composites were evaluated through CV for 1000 cycles with a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 and continuous operation of 5000 s at an overpotential η = −0.3 V vs. RHE while rotating the working electrode at 1600 rpm, respectively.
Characterization
The SEM images were obtained using a field emission environmental scanning electron microscope (QUANTA 200 FEG). The concentration of MoS2 aqueous solutions were characterized using an optical emission spectroscope with inductively coupled plasma (Varian Vista-MPX). The TEM images were captured with a JEM2010 at an accelerating voltage of 200 KV. AFM images were obtained using a Bruker Multimode 8 in the tapping mode after the samples were deposited on a freshly cleaved mica surface through the drop-casting method. XRD data were obtained using D8 ADVANCE (Bruker) with Cu–Kα radiation (40 kV, 40 mA). Raman spectra were acquired through inVia-reflex microconfocal laser Raman spectroscopy (Renishaw) with the excitation laser line at 633 nm. XPS analysis was performed on a ESCALAB 250Xi spectrometer (Thermo Fisher) with an Al Kα X-ray source. UV–vis spectra were obtained using a U-3900 spectrophotometer. Fluorescence spectroscopy was performed using a F-7000 FL spectrophotometer.
References
Huang, X., Zeng, Z. & Zhang, H. Metal dichalcogenide nanosheets: preparation, properties and a pplications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 1934–1946 (2013).
Kim, E. et al. Site Selective Doping of Ultrathin Metal Dichalcogenides by Laser-Assisted Reaction. Adv. Mater. 28, 341–346, doi:10.1002/adma.201503945 (2016).
Mattheiss, L. Band structures of transition-metal-dichalcogenide layer compounds. Phys. Rev. B 8, 3719 (1973).
Eda, G. et al. Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett 11, 5111–5116 (2011).
Mak, K. F., Lee, C., Hone, J., Shan, J. & Heinz, T. F. Atomically thin MoS 2: a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 136805 (2010).
Bang, G. S. et al. Effective liquid-phase exfoliation and sodium ion battery application of MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 7084–7089 (2014).
Shi, Y. et al. van der Waals epitaxy of MoS2 layers using graphene as growth templates. Nano Lett. 12, 2784–2791 (2012).
Wilcoxon, J. & Samara, G. Strong quantum-size effects in a layered semiconductor: MoS2 nanoclusters. Phys. Rev. B 51, 7299 (1995).
Benson, J., Li, M., Wang, S., Wang, P. & Papakonstantinou, P. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Edges of a Few Layer Molybdenum Disulfide Nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 14113–14122 (2015).
Bonde, J., Moses, P. G., Jaramillo, T. F., Nørskov, J. K. & Chorkendorff, I. Hydrogen evolution on nano-particulate transition metal sulfides. Faraday Discuss. 140, 219–231 (2009).
Jaramillo, T. F. et al. Identification of active edge sites for electrochemical H2 evolution from MoS2 nanocatalysts. Science 317, 100–102 (2007).
Voiry, D. et al. Conducting MoS2 nanosheets as catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Lett. 13, 6222–6227 (2013).
Sun, X. et al. Semimetallic molybdenum disulfide ultrathin nanosheets as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Nanoscale 6, 8359–8367 (2014).
Chen, L. et al. A frozen matrix hybrid optical nonlinear system enhanced by a particle lens. Nanoscale 7, 14982–14988 (2015).
Zhou, Y. et al. Tunable optical nonlinearity of silicon nanoparticles in solid state organic matrix. Opt. Mater. Express 5, 1606–1612 (2015).
Yang, Z.-C. et al. Intrinsically fluorescent carbon dots with tunable emission derived from hydrothermal treatment of glucose in the presence of monopotassium phosphate. Chem. Commun. 47, 11615–11617 (2011).
Yang, Y. et al. One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan. Chem. Commun. 48, 380–382 (2012).
Xu, S., Li, D. & Wu, P. One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 1127–1136 (2015).
Ha, H. D., Han, D. J., Choi, J. S., Park, M. & Seo, T. S. Dual role of blue luminescent MoS2 quantum dots in fluorescence resonance energy transfer phenomenon. Small 10, 3858–3862 (2014).
Gopalakrishnan, D., Damien, D. & Shaijumon, M. M. MoS2 quantum dot-interspersed exfoliated MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Nano 8, 5297–5303 (2014).
Ren, X. et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of monolayer MoS2 quantum dots for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 10693–10697 (2015).
Gopalakrishnan, D. et al. Electrochemical synthesis of luminescent MoS2 quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 51, 6293–6296 (2015).
Li, B. L. et al. Electrochemically induced Fenton reaction of few-layer MoS2 nanosheets: preparation of luminescent quantum dots via a transition of nanoporous morphology. Nanoscale 6, 9831–9838 (2014).
Lenzner, M. et al. Femtosecond optical breakdown in dielectrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4076 (1998).
Jiang, L. & Tsai, H.-L. Repeatable nanostructures in dielectrics by femtosecond laser pulse trains. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 151104 (2005).
Joglekar, A. P., Liu, H.-h, Meyhöfer, E., Mourou, G. & Hunt, A. J. Optics at critical intensity: Applications to nanomorphing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 5856–5861 (2004).
Jeschke, H. O., Garcia, M. E. & Bennemann, K. Theory for the ultrafast ablation of graphite films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 015003 (2001).
Miyamoto, Y., Zhang, H. & Tománek, D. Photoexfoliation of graphene from graphite: an Ab initio study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 208302 (2010).
Paradisanos, I., Kymakis, E., Fotakis, C., Kioseoglou, G. & Stratakis, E. Intense femtosecond photoexcitation of bulk and monolayer MoS2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 041108, doi:10.1063/1.4891679 (2014).
Wang, H., Zhang, C. & Rana, F. Ultrafast Dynamics of Defect-Assisted Electron-Hole Recombination in Monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 15, 339–345, doi:10.1021/nl503636c (2015).
Woutersen, S., Emmerichs, U. & Bakker, H. J. Femtosecond Mid-IR Pump-Probe Spectroscopy of Liquid Water: Evidence for a Two-Component Structure. Science 278, 658–660, doi:10.1126/science.278.5338.658 (1997).
Li, X. et al. Production rate enhancement of size-tunable silicon nanoparticles by temporally shaping femtosecond laser pulses in ethanol. Opt. Express 23, 4226–4232, doi:10.1364/OE.23.004226 (2015).
Axente, E. et al. Size distribution of Au NPs generated by laser ablation of a gold target in liquid with time-delayed femtosecond pulses. arXiv preprint arXiv:1008.0374 (2010).
Zhao, X. & Shin, Y. C. Ablation enhancement of silicon by ultrashort double-pulse laser ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 111907 (2014).
Jiang, L. & Tsai, H. L. Energy transport and material removal in wide bandgap materials by a femtosecond laser pulse. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 48, 487–499, doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2004.09.016 (2005).
Amendola, V. & Meneghetti, M. Laser ablation synthesis in solution and size manipulation of noble metal nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3805–3821, doi:10.1039/B900654K (2009).
Chichkov, B. N., Momma, C., Nolte, S., Von Alvensleben, F. & Tünnermann, A. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 63, 109–115 (1996).
Yin, Z. et al. Single-layer MoS2 phototransistors. ACS Nano 6, 74–80 (2011).
Dai, W. et al. Tunable fabrication of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for intracellular microRNA detection and multiphoton bioimaging. Small 11, 4158–4164 (2015).
Lin, L. et al. Fabrication of luminescent monolayered tungsten dichalcogenides quantum dots with giant spin-valley coupling. ACS Nano 7, 8214–8223 (2013).
Lee, C. et al. Anomalous lattice vibrations of single-and few-layer MoS2. ACS Nano 4, 2695–2700 (2010).
Lv, X.-J., She, G.-W., Zhou, S.-X. & Li, Y.-M. Highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen production by nickel promoted molybdenum sulfide microspheres catalysts. RSC Adv. 3, 21231–21236 (2013).
Jaegermann, W. & Schmeisser, D. Reactivity of layer type transition metal chalcogenides towards oxidation. Surf. Sci. 165, 143–160 (1986).
Wu, Z. et al. MoS2 nanosheets: a designed structure with high active site density for the hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal. 3, 2101–2107 (2013).
Wang, T. et al. Enhanced electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reaction from self-assembled monodispersed molybdenum sulfide nanoparticles on an Au electrode. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 625–633 (2013).
Chikan, V. & Kelley, D. Size-dependent spectroscopy of MoS2 nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 3794–3804 (2002).
Liu, N. et al. Large-area atomically thin MoS2 nanosheets prepared using electrochemical exfoliation. ACS Nano 8, 6902–6910 (2014).
Štengl, V. & Henych, J. Strongly luminescent monolayered MoS2 prepared by effective ultrasound exfoliation. Nanoscale 5, 3387–3394 (2013).
Shinde, D. B. & Pillai, V. K. Electrochemical preparation of luminescent graphene quantum dots from multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chem.–Eur. J. 18, 12522–12528 (2012).
Bao, L. et al. Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: from preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv. Mater. 23, 5801–5806 (2011).
Zhang, M. et al. Facile synthesis of water-soluble, highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a robust biological label for stem cells. J J. Mater. Chem. 22, 7461–7467 (2012).
Li, F. et al. MoS2 quantum dot decorated RGO: a designed electrocatalyst with high active site density for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 21772–21778, doi:10.1039/C5TA05219J (2015).
Lukowski, M. A. et al. Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution Catalysis from Chemically Exfoliated Metallic MoS2 Nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 10274–10277, doi:10.1021/ja404523s (2013).
Voiry, D. et al. Enhanced catalytic activity in strained chemically exfoliated WS2 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution. Nat Mater 12, 850–855, doi:10.1038/nmat3700 http://www.nature.com/nmat/journal/v12/n9/abs/nmat3700.html#supplementary-information (2013).
Chang, Y. H. et al. Highly Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Production by MoSx Grown on Graphene-Protected 3D Ni Foams. Adv. Mater. 25, 756–760 (2013).
Xie, J. et al. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 25, 5807–5813 (2013).
Wang, T. et al. Size-Dependent Enhancement of Electrocatalytic Oxygen‐Reduction and Hydrogen-Evolution Performance of MoS2 Particles. Chem.–Eur. J. 19, 11939–11948 (2013).
Li, Y. et al. MoS2 nanoparticles grown on graphene: an advanced catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 7296–7299 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 91323301 and 51575053), National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB1104300), and the 863 Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2015AA043504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.L., L.J. and X.L. conceived and designed the experiments. B.L., L.J. and X.L. wrote the paper with input from all of the authors. All of the experiments were conducted by B.L. with P.R., P.Z., A.W., and Z.C. The experimental datas were analysed by B.L. with P.R., P.Z., Z.C., and the manuscript was reviewed by all of the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Jiang, L., Li, X. et al. Preparation of Monolayer MoS2 Quantum Dots using Temporally Shaped Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Bulk MoS2 Targets in Water. Sci Rep 7, 11182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10632-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10632-3
This article is cited by
-
Light-Responsive Organic-Inorganic Hydrogel Functionalized with MoO3 Composites of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Choline Chloride-Based Polymeric Deep Eutectic Solvent
Chemistry Africa (2024)
-
Hierarchical 3D flowers of 1T@2H-MoS2 assembled with an array of ultrathin nano-petals for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2024)
-
Fabrication of sub-20 nm MoS2 horizontal nanowire on silicon substrates by inclusion of precursors into polystyrene-b-polyethylene oxide nanopatterns: Detailed structural investigation
Nano Research (2024)
-
Photocatalytic Activity Enhancement of Au-Decorated Polythiophene/CeO2 Ternary Visible Light Photocatalyst Fabricated by Facile Hydrothermal and Photoreduction Routes
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering (2024)
-
Ternary Composite-Enabled Photocatalytic Degradation of Multi-class Pollutants: Case Study of Congo Red, Diclofenac Sodium, and Pendimethalin
Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.