Abstract
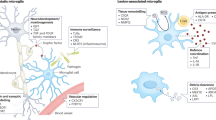
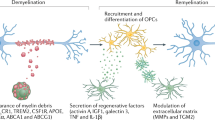
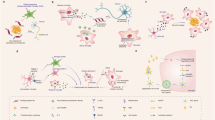
The neuroimmune system is involved in development, normal functioning, aging, and injury of the central nervous system. Microglia, first described a century ago, are the main neuroimmune cells and have three essential functions: a sentinel function involved in constant sensing of changes in their environment, a housekeeping function that promotes neuronal well-being and normal operation, and a defense function necessary for responding to such changes and providing neuroprotection. Microglia use a defined armamentarium of genes to perform these tasks. In response to specific stimuli, or with neuroinflammation, microglia also have the capacity to damage and kill neurons. Injury to neurons in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, and prion diseases, as well as in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal dementia, and chronic traumatic encephalopathy, results from disruption of the sentinel or housekeeping functions and dysregulation of the defense function and neuroinflammation. Pathways associated with such injury include several sensing and housekeeping pathways, such as the Trem2, Cx3cr1 and progranulin pathways, which act as immune checkpoints to keep the microglial inflammatory response under control, and the scavenger receptor pathways, which promote clearance of injurious stimuli. Peripheral interference from systemic inflammation or the gut microbiome can also alter progression of such injury. Initiation or exacerbation of neurodegeneration results from an imbalance between these microglial functions; correcting such imbalance may be a potential mode for therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Río Hortega, P. Noticia de un nuevo y fácil método para la coloración de la neuroglia y el tejido conjuntivo. Trab. Lab. Invest. Biol. 15, 367–378 (1918).
Giulian, D. & Baker, T. J. Characterization of ameboid microglia isolated from developing mammalian brain. J. Neurosci. 6, 2163–2178 (1986).
Jung, S. et al. Analysis of fractalkine receptor CX(3)CR1 function by targeted deletion and green fluorescent protein reporter gene insertion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4106–4114 (2000).
Haynes, S. E. et al. The P2Y12 receptor regulates microglial activation by extracellular nucleotides. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 1512–1519 (2006).
Yang, G., Parkhurst, C. N., Hayes, S. & Gan, W. B. Peripheral elevation of TNF-α leads to early synaptic abnormalities in the mouse somatosensory cortex in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 10306–10311 (2013).
Hickman, S. E., Allison, E. K. & El Khoury, J. Microglial dysfunction and defective beta-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Neurosci. 28, 8354–8360 (2008).
Hickman, S. E. et al. The microglial sensome revealed by direct RNA sequencing. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 1896–1905 (2013).
Keren-Shaul, H. et al. A unique microglia type associated with restricting development of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 169, 1276–1290.e17 (2017).
Lawson, L. J., Perry, V. H., Dri, P. & Gordon, S. Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 39, 151–170 (1990).
El Khoury, J. Neurodegeneration and the neuroimmune system. Nat. Med. 16, 1369–1370 (2010).
Ransohoff, R. M. & El Khoury, J. Microglia in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 8, a020560 (2015).
Kierdorf, K. et al. Microglia emerge from erythromyeloid precursors via Pu.1- and Irf8-dependent pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 273–280 (2013).
Tay, T. L. et al. A new fate mapping system reveals context-dependent random or clonal expansion of microglia. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 793–803 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia. Nat. Immunol. 13, 753–760 (2012).
Abud, E. M. et al. iPSC-derived human microglia-like cells to study neurological diseases. Neuron 94, 278–293.e9 (2017).
Muffat, J. et al. Efficient derivation of microglia-like cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Med. 22, 1358–1367 (2016).
Ryan, K. J. et al. A human microglia-like cellular model for assessing the effects of neurodegenerative disease gene variants. Sci. Transl. Med. 9, eaai7635 (2017).
Gosselin, D. et al. An environment-dependent transcriptional network specifies human microglia identity. Science 356, eaal3222 (2017).
Fourgeaud, L. et al. TAM receptors regulate multiple features of microglial physiology. Nature 532, 240–244 (2016).
Vasek, M. J. et al. A complement-microglial axis drives synapse loss during virus-induced memory impairment. Nature 534, 538–543 (2016).
Lui, H. et al. Progranulin deficiency promotes circuit-specific synaptic pruning by microglia via complement activation. Cell 165, 921–935 (2016).
Zhan, Y. et al. Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 400–406 (2014).
Fuhrmann, M. et al. Microglial Cx3cr1 knockout prevents neuron loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 411–413 (2010).
Krasemann, S. et al. The TREM2-APOE pathway drives the transcriptional phenotype of dysfunctional microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunity 47, 566–581.e9 (2017).
Healy, L. M. et al. MerTK is a functional regulator of myelin phagocytosis by human myeloid cells. J. Immunol. 196, 3375–3384 (2016).
Liddelow, S. A. et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541, 481–487 (2017).
El Khoury, J. B. et al. CD36 mediates the innate host response to beta-amyloid. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1657–1666 (2003).
El Khoury, J. et al. Ccr2 deficiency impairs microglial accumulation and accelerates progression of Alzheimer-like disease. Nat. Med. 13, 432–438 (2007).
Selkoe, D. J. & Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 8, 595–608 (2016).
Frautschy, S. A. et al. Microglial response to amyloid plaques in APPsw transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 152, 307–317 (1998).
D’Andrea, M. R., Cole, G. M. & Ard, M. D. The microglial phagocytic role with specific plaque types in the Alzheimer disease brain. Neurobiol. Aging 25, 675–683 (2004).
Tooyama, I., Kimura, H., Akiyama, H. & McGeer, P. L. Reactive microglia express class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 523, 273–280 (1990).
Martin, E., Boucher, C., Fontaine, B. & Delarasse, C. Distinct inflammatory phenotypes of microglia and monocyte-derived macrophages in Alzheimer’s disease models: effects of aging and amyloid pathology. Aging Cell 16, 27–38 (2017).
Lambert, J. C. et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 45, 1452–1458 (2013).
Jonsson, T. et al. Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 368, 107–116 (2013).
El Khoury, J. & Hickman, S.E. Mechanisms of amyloid-beta clearance in Alzheimer’s disease. in Research Progress in Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia, vol. 4. (ed. Sun, M.-K.) 37–66 (Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009).
Frenkel, D. et al. Scara1 deficiency impairs clearance of soluble amyloid-β by mononuclear phagocytes and accelerates Alzheimer’s-like disease progression. Nat. Commun. 4, 2030 (2013).
El Khoury, J. et al. Scavenger receptor-mediated adhesion of microglia to beta-amyloid fibrils. Nature 382, 716–719 (1996).
Hong, S. et al. Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models. Science 352, 712–716 (2016).
Coraci, I. S. et al. CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer’s disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to beta-amyloid fibrils. Am. J. Pathol. 160, 101–112 (2002).
Gold, M. & El Khoury, J. β-amyloid, microglia, and the inflammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 37, 607–611 (2015).
Venegas, C. et al. Microglia-derived ASC specks cross-seed amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 552, 355–361 (2017).
Hickman, S. E. & El Khoury, J. The neuroimmune system in Alzheimer’s disease: the glass is half full. J. Alzheimers Dis. 33(Suppl 1), S295–S302 (2013).
Oddo, S., Caccamo, A., Kitazawa, M., Tseng, B. P. & LaFerla, F. M. Amyloid deposition precedes tangle formation in a triple transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 24, 1063–1070 (2003).
Villemagne, V. L. et al. Aβ-amyloid and tau imaging in dementia. Semin. Nucl. Med. 47, 75–88 (2017).
Bisht, K. et al. Dark microglia: a new phenotype predominantly associated with pathological states. Glia 64, 826–839 (2016).
Ferrer, I. et al. Glial and neuronal tau pathology in tauopathies: characterization of disease-specific phenotypes and tau pathology progression. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73, 81–97 (2014).
Asai, H. et al. Depletion of microglia and inhibition of exosome synthesis halt tau propagation. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1584–1593 (2015).
Bolós, M. et al. Direct evidence of internalization of tau by microglia in vitro and in vivo. J. Alzheimers Dis. 50, 77–87 (2016).
Lee, D. C. et al. LPS- induced inflammation exacerbates phospho-tau pathology in rTg4510 mice. J. Neuroinflammation 7, 56 (2010).
Saman, S. et al. Exosome-associated tau is secreted in tauopathy models and is selectively phosphorylated in cerebrospinal fluid in early Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 3842–3849 (2012).
Fiandaca, M. S. et al. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: a case-control study. Alzheimers Dement. 11, 600–7.e1 (2015).
Cherry, J. D. et al. Microglial neuroinflammation contributes to tau accumulation in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 4, 112 (2016).
Yoshiyama, Y. et al. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 53, 337–351 (2007).
Bhaskar, K. et al. Regulation of tau pathology by the microglial fractalkine receptor. Neuron 68, 19–31 (2010).
Nash, K. R. et al. Fractalkine overexpression suppresses tau pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Neurobiol. Aging 34, 1540–1548 (2013).
Bemiller, S. M. et al. TREM2 deficiency exacerbates tau pathology through dysregulated kinase signaling in a mouse model of tauopathy. Mol. Neurodegener. 12, 74 (2017).
Deng, H., Wang, P. & Jankovic, J. The genetics of Parkinson disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 42, 72–85 (2018).
Dickson, D. W. Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 46(Suppl 1), S30–S33 (2018).
McGeer, P. L., Itagaki, S., Boyes, B. E. & McGeer, E. G. Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38, 1285–1291 (1988).
Gerhard, A. et al. In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 21, 404–412 (2006).
Halliday, G. M. & Stevens, C. H. Glia: initiators and progressors of pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 26, 6–17 (2011).
Croisier, E., Moran, L. B., Dexter, D. T., Pearce, R. K. & Graeber, M. B. Microglial inflammation in the parkinsonian substantia nigra: relationship to alpha-synuclein deposition. J. Neuroinflammation 2, 14 (2005).
Su, X. et al. Synuclein activates microglia in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 29, 1690–1701 (2008).
Kim, C. et al. Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat. Commun. 4, 1562 (2013).
Kuhlmann, T. et al. An updated histological classification system for multiple sclerosis lesions. Acta Neuropathol. 133, 13–24 (2017).
Yamasaki, R. et al. Differential roles of microglia and monocytes in the inflamed central nervous system. J. Exp. Med. 211, 1533–1549 (2014).
Zrzavy, T. et al. Loss of ‘homeostatic’ microglia and patterns of their activation in active multiple sclerosis. Brain 140, 1900–1913 (2017).
Ghosh, R. & Tabrizi, S. J. Huntington disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 147, 255–278 (2018).
Tai, Y. F. et al. Microglial activation in presymptomatic Huntington’s disease gene carriers. Brain 130, 1759–1766 (2007).
Pavese, N. et al. Microglial activation correlates with severity in Huntington disease: a clinical and PET study. Neurology 66, 1638–1643 (2006).
Sapp, E. et al. Early and progressive accumulation of reactive microglia in the Huntington disease brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 161–172 (2001).
Crotti, A. et al. Mutant huntingtin promotes autonomous microglia activation via myeloid lineage-determining factors. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 513–521 (2014).
Lall, D. & Baloh, R. H. Microglia and C9orf72 in neuroinflammation and ALS and frontotemporal dementia. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 3250–3258 (2017).
Henkel, J. S. et al. Presence of dendritic cells, MCP-1, and activated microglia/macrophages in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord tissue. Ann. Neurol. 55, 221–235 (2004).
Turner, M. R. et al. Evidence of widespread cerebral microglial activation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an [11C](R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography study. Neurobiol. Dis. 15, 601–609 (2004).
Gurney, M. E. et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264, 1772–1775 (1994).
Yamanaka, K. et al. Mutant SOD1 in cell types other than motor neurons and oligodendrocytes accelerates onset of disease in ALS mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 7594–7599 (2008).
Apolloni, S., Amadio, S., Montilli, C., Volonté, C. & D’Ambrosi, N. Ablation of P2X7 receptor exacerbates gliosis and motoneuron death in the SOD1-G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 4102–4116 (2013).
Hall, E. D., Oostveen, J. A. & Gurney, M. E. Relationship of microglial and astrocytic activation to disease onset and progression in a transgenic model of familial ALS. Glia 23, 249–256 (1998).
Liao, B., Zhao, W., Beers, D. R., Henkel, J. S. & Appel, S. H. Transformation from a neuroprotective to a neurotoxic microglial phenotype in a mouse model of ALS. Exp. Neurol. 237, 147–152 (2012).
Frakes, A. E. et al. Microglia induce motor neuron death via the classical NF-κB pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron 81, 1009–1023 (2014).
Meissner, F., Molawi, K. & Zychlinsky, A. Mutant superoxide dismutase 1-induced IL-1beta accelerates ALS pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 13046–13050 (2010).
Harraz, M. M. et al. SOD1 mutations disrupt redox-sensitive Rac regulation of NADPH oxidase in a familial ALS model. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 659–670 (2008).
Zhao, W. et al. Extracellular mutant SOD1 induces microglial-mediated motoneuron injury. Glia 58, 231–243 (2010).
O’Rourke, J. G. et al. C9orf72 BAC transgenic mice display typical pathologic features of ALS/FTD. Neuron 88, 892–901 (2015).
O’Rourke, J. G. et al. C9orf72 is required for proper macrophage and microglial function in mice. Science 351, 1324–1329 (2016).
Spiller, K. J. et al. Microglia-mediated recovery from ALS-relevant motor neuron degeneration in a mouse model of TDP-43 proteinopathy. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 329–340 (2018).
Paolicelli, R. C. et al. TDP-43 depletion in microglia promotes amyloid clearance but also induces synapse loss. Neuron 95, 297–308.e6 (2017).
Iaccarino, L. et al. An in vivo 11C-(R)-PK11195 PET and in vitro pathology study of microglia activation in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 2856–2868 (2018).
Yamasaki, T., Suzuki, A., Hasebe, R. & Horiuchi, M. Flow cytometric detection of PrPSc in neurons and glial cells from prion-infected mouse brains. J. Virol. 92, e01457–17 (2017).
Falsig, J. et al. A versatile prion replication assay in organotypic brain slices. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 109–117 (2008).
Sorce, S. et al. The role of the NADPH oxidase NOX2 in prion pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1004531 (2014).
Aguzzi, A. & Zhu, C. Microglia in prion diseases. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 3230–3239 (2017).
Hafner-Bratkovič, I., Benčina, M., Fitzgerald, K. A., Golenbock, D. & Jerala, R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophage cell lines by prion protein fibrils as the source of IL-1β and neuronal toxicity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 4215–4228 (2012).
Xie, W. L. et al. Abnormal activation of microglia accompanied with disrupted CX3CR1/CX3CL1 pathway in the brains of the hamsters infected with scrapie agent 263K. J. Mol. Neurosci. 51, 919–932 (2013).
Hughes, M. M., Field, R. H., Perry, V. H., Murray, C. L. & Cunningham, C. Microglia in the degenerating brain are capable of phagocytosis of beads and of apoptotic cells, but do not efficiently remove PrPSc, even upon LPS stimulation. Glia 58, 2017–2030 (2010).
Sakai, K. et al. Absence of CD14 delays progression of prion diseases accompanied by increased microglial activation. J. Virol. 87, 13433–13445 (2013).
Kouadir, M. et al. CD36 participates in PrP(106-126)-induced activation of microglia. PLoS One 7, e30756 (2012).
Simonian, N. A. & Coyle, J. T. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36, 83–106 (1996).
Brown, G. C. & Vilalta, A. How microglia kill neurons. Brain Res. 1628(Pt B), 288–297 (2015).
Maezawa, I. & Jin, L. W. Rett syndrome microglia damage dendrites and synapses by the elevated release of glutamate. J. Neurosci. 30, 5346–5356 (2010).
Gan, L. et al. Identification of cathepsin B as a mediator of neuronal death induced by Abeta-activated microglial cells using a functional genomics approach. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 5565–5572 (2004).
Leonardo, C. C., Hall, A. A., Collier, L. A., Gottschall, P. E. & Pennypacker, K. R. Inhibition of gelatinase activity reduces neural injury in an ex vivo model of hypoxia-ischemia. Neuroscience 160, 755–766 (2009).
Hickman, S. E. & El Khoury, J. TREM2 and the neuroimmunology of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 88, 495–498 (2014).
Yeh, F. L., Wang, Y., Tom, I., Gonzalez, L. C. & Sheng, M. TREM2 Binds to apolipoproteins, including APOE and CLU/APOJ, and thereby facilitates uptake of amyloid-beta by microglia. Neuron 91, 328–340 (2016).
Wang, Y. et al. TREM2 lipid sensing sustains the microglial response in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Cell 160, 1061–1071 (2015).
Zhao, Y. et al. TREM2 is a receptor for β-amyloid that mediates microglial function. Neuron 97, 1023–1031.e7 (2018).
Suárez-Calvet, M. et al. Early changes in CSF sTREM2 in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease occur after amyloid deposition and neuronal injury. Sci. Transl. Med. 8, 369ra178 (2016).
Takahashi, K., Rochford, C. D. & Neumann, H. Clearance of apoptotic neurons without inflammation by microglial triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2. J. Exp. Med. 201, 647–657 (2005).
Wang, Y. et al. TREM2-mediated early microglial response limits diffusion and toxicity of amyloid plaques. J. Exp. Med. 213, 667–675 (2016).
Ulland, T. K. et al. TREM2 maintains microglial metabolic fitness in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 170, 649–663.e13 (2017).
Condello, C., Yuan, P., Schain, A. & Grutzendler, J. Microglia constitute a barrier that prevents neurotoxic protofibrillar Aβ42 hotspots around plaques. Nat. Commun. 6, 6176 (2015).
Jay, T. R., von Saucken, V. E. & Landreth, G. E. TREM2 in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 12, 56 (2017).
Song, W. M. et al. Humanized TREM2 mice reveal microglia-intrinsic and -extrinsic effects of R47H polymorphism. J. Exp. Med. 215, 745–760 (2018).
Paloneva, J. et al. DAP12/TREM2 deficiency results in impaired osteoclast differentiation and osteoporotic features. J. Exp. Med. 198, 669–675 (2003).
Satoh, J. et al. Immunohistochemical characterization of microglia in Nasu-Hakola disease brains. Neuropathology 31, 363–375 (2011).
Suárez-Calvet, M. et al. sTREM2 cerebrospinal fluid levels are a potential biomarker for microglia activity in early-stage Alzheimer’s disease and associate with neuronal injury markers. EMBO Mol. Med. 8, 466–476 (2016).
Lue, L. F. et al. TREM2 protein expression changes correlate with Alzheimer’s disease neurodegenerative pathologies in post-mortem temporal cortices. Brain Pathol. 25, 469–480 (2015).
Lill, C. M. et al. The role of TREM2 R47H as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 11, 1407–1416 (2015).
Cady, J. et al. TREM2 variant p.R47H as a risk factor for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 71, 449–453 (2014).
Jiang, T. et al. Silencing of TREM2 exacerbates tau pathology, neurodegenerative changes, and spatial learning deficits in P301S tau transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Aging 36, 3176–3186 (2015).
Leyns, C. E. G. et al. TREM2 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation and protects against neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, 11524–11529 (2017).
Hickman, S. E. & El Khoury, J. Mechanisms of mononuclear phagocyte recruitment in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 9, 168–173 (2010).
Zujovic, V., Schussler, N., Jourdain, D., Duverger, D. & Taupin, V. In vivo neutralization of endogenous brain fractalkine increases hippocampal TNFalpha and 8-isoprostane production induced by intracerebroventricular injection of LPS. J. Neuroimmunol. 115, 135–143 (2001).
Liu, Z., Condello, C., Schain, A., Harb, R. & Grutzendler, J. CX3CR1 in microglia regulates brain amyloid deposition through selective protofibrillar amyloid-β phagocytosis. J. Neurosci. 30, 17091–17101 (2010).
Morganti, J. M. et al. The soluble isoform of CX3CL1 is necessary for neuroprotection in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 32, 14592–14601 (2012).
Cardona, A. E. et al. Control of microglial neurotoxicity by the fractalkine receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 917–924 (2006).
Thome, A. D., Standaert, D. G. & Harms, A. S. Fractalkine signaling regulates the inflammatory response in an α-synuclein model of Parkinson disease. PLoS One 10, e0140566 (2015).
Martin, I. et al. Ribosomal protein s15 phosphorylation mediates LRRK2 neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Cell 157, 472–485 (2014).
Lopez-Lopez, A. et al. CX3CR1 is a modifying gene of survival and progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 9, e96528 (2014).
Calvo, A. et al. Common polymorphisms of chemokine (C-X3-C motif) receptor 1 gene modify amyotrophic lateral sclerosis outcome: a population-based study. Muscle Nerve 57, 212–216 (2018).
Grizenkova, J., Akhtar, S., Brandner, S., Collinge, J. & Lloyd, S. E. Microglial Cx3cr1 knockout reduces prion disease incubation time in mice. BMC Neurosci. 15, 44 (2014).
Striebel, J. F., Race, B., Carroll, J. A., Phillips, K. & Chesebro, B. Knockout of fractalkine receptor Cx3cr1 does not alter disease or microglial activation in prion-infected mice. J. Gen. Virol. 97, 1481–1487 (2016).
PrabhuDas, M. R. et al. A consensus definitive classification of scavenger receptors and their roles in health and disease. J. Immunol. 198, 3775–3789 (2017).
Cornejo, F. et al. Scavenger receptor-A deficiency impairs immune response of microglia and astrocytes potentiating Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Brain Behav. Immun. 69, 336–350 (2018).
Šerý, O. et al. CD36 gene polymorphism is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Biochimie 135, 46–53 (2017).
Wilkinson, K., Boyd, J. D., Glicksman, M., Moore, K. J. & El Khoury, J. A high content drug screen identifies ursolic acid as an inhibitor of amyloid beta protein interactions with its receptor CD36. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 34914–34922 (2011).
Origlia, N. et al. Microglial receptor for advanced glycation end product-dependent signal pathway drives beta-amyloid-induced synaptic depression and long-term depression impairment in entorhinal cortex. J. Neurosci. 30, 11414–11425 (2010).
Vodopivec, I. et al. RAGE does not affect amyloid pathology in transgenic ArcAbeta mice. Neurodegener. Dis. 6, 270–280 (2009).
Chitramuthu, B. P., Bennett, H. P. J. & Bateman, A. Progranulin: a new avenue towards the understanding and treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Brain 140, 3081–3104 (2017).
Gong, Y. et al. Microglial dysfunction as a key pathological change in adrenomyeloneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 82, 813–827 (2017).
Chen, Y. et al. Association of progranulin polymorphism rs5848 with neurodegenerative diseases: a meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 262, 814–822 (2015).
Minami, S. S. et al. Progranulin protects against amyloid β deposition and toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nat. Med. 20, 1157–1164 (2014).
Van Kampen, J. M., Baranowski, D. & Kay, D. G. Progranulin gene delivery protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 9, e97032 (2014).
Sleegers, K. et al. Progranulin genetic variability contributes to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 71, 253–259 (2008).
Erny, D. et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 965–977 (2015).
Vogt, N. M. et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 7, 13537 (2017).
Minter, M. R. et al. Antibiotic-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity influences neuro-inflammation and amyloidosis in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 6, 30028 (2016).
Sampson, T. R. et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell 167, 1469–1480.e12 (2016).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grant RF1 AG051506 to J.E.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table 1
Trem2 variants associated with neurodegenerative diseases.
Supplementary Video 1
This is a video taken using two photon microscopy from a Cx3cr1-GFP mouse with a cranial window clearly showing how the microglia processes are constantly moving. When focal injury is induced with a laser in the middle of the field of vision these processes move from the individual cells towards the site of the injury.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickman, S., Izzy, S., Sen, P. et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 21, 1359–1369 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0242-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0242-x
This article is cited by
-
Understanding immune microenvironment alterations in the brain to improve the diagnosis and treatment of diverse brain diseases
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α regulates microglial innate immune memory and the pathology of Parkinson’s disease
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2024)
-
Taming microglia: the promise of engineered microglia in treating neurological diseases
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2024)
-
A P2RY12 deficiency results in sex-specific cellular perturbations and sexually dimorphic behavioral anomalies
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2024)
-
Differential contribution of THIK-1 K+ channels and P2X7 receptors to ATP-mediated neuroinflammation by human microglia
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2024)