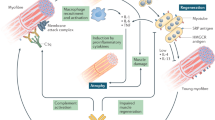
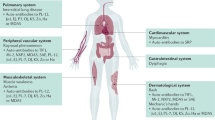
Abstract
Since the discovery of an acute monophasic paralysis, later coined Guillain–Barré syndrome, almost 100 years ago, and the discovery of chronic, steroid-responsive polyneuropathy 50 years ago, the spectrum of immune-mediated polyneuropathies has broadened, with various subtypes continuing to be identified, including chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) and multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN). In general, these disorders are speculated to be caused by autoimmunity to proteins located at the node of Ranvier or components of myelin of peripheral nerves, although disease-associated autoantibodies have not been identified for all disorders. Owing to the numerous subtypes of the immune-mediated neuropathies, making the right diagnosis in daily clinical practice is complicated. Moreover, treating these disorders, particularly their chronic variants, such as CIDP and MMN, poses a challenge. In general, management of these disorders includes immunotherapies, such as corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulin or plasma exchange. Improvements in clinical criteria and the emergence of more disease-specific immunotherapies should broaden the therapeutic options for these disabling diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 1 digital issues and online access to articles
$99.00 per year
only $99.00 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodfellow, J. A. & Willison, H. J. Guillain-Barré syndrome: a century of progress. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 12, 723–731 (2016).This article provides an excellent review on the clinical and scientific developments in a dynamic field in neuroimmunology.
Vallat, J. M., Sommer, C. & Magy, L. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges for a treatable condition. Lancet Neurol. 9, 402–412 (2010). This comprehensive overview of CIDP discusses how this disorder can be diagnosed and treated.
Latov, N. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 10, 435–446 (2014). This extensive summary of the current knowledge on immune-mediated neuropathies describes how to approach these heterogeneous disorders in clinical practice.
Sejvar, J. J., Baughman, A. L., Wise, M. & Morgan, O. W. Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 36, 123–133 (2011).
McGrogan, A., Madle, G. C., Seaman, H. E. & de Vries, C. S. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome worldwide — a systematic literature review. Neuroepidemiology 32, 150–163 (2009).
Suryapranata, F. S. et al. Epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in Aruba. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 94, 1380–1384 (2016).
Blum, S., Reddel, S., Spies, J. & McCombe, P. Clinical features of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome at seven hospitals on the east coast of Australia. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 18, 316–320 (2013).
Nachamkin, I. et al. Patterns of Guillain-Barré syndrome in children: results from a Mexican population. Neurology 69, 1665–1671 (2007).
Bae, J. S. et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome in Asia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 85, 907–913 (2014).
Uncini, A., Manzoli, C., Notturno, F. & Capasso, M. Pitfalls in electrodiagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome subtypes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 81, 1157–1163 (2010).
Mitsui, Y. et al. A multicentre prospective study of Guillain-Barré syndrome in Japan: a focus on the incidence of subtypes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 110–114 (2015).
Hauck, L. J. et al. Incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome in Alberta, Canada: an administrative data study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 318–320 (2008).
Yuki, N. & Hartung, H. P. Guillain-Barré syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 2294–2304 (2012).
Kuitwaard, K., van Koningsveld, R., Ruts, L., Jacobs, B. C. & van Doorn, P. A. Recurrent Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 80, 56–59 (2009).
Jacobs, B. C. et al. The spectrum of antecedent infections in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a case-control study. Neurology 51, 1110–1115 (1998).
van den Berg, B. et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome: pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 10, 469–482 (2014).
Cao-Lormeau, V. M. et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: a case-control study. Lancet 387, 1531–1539 (2016).
Nascimento, O. J. M. & da Silva, I. R. F. Guillain-Barré syndrome and Zika virus outbreaks. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 30, 500–507 (2017).
Martin Arias, L. H., Sanz, R., Sainz, M., Treceno, C. & Carvajal, A. Guillain-Barré syndrome and influenza vaccines: a meta-analysis. Vaccine 33, 3773–3778 (2015).
Poland, G. A. & Jacobsen, S. J. Influenza vaccine, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and chasing zero. Vaccine 30, 5801–5803 (2012).
Hocker, S., Nagarajan, E., Rubin, M. & Wijdicks, E. F. M. Clinical factors associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome following surgery. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 8, 201–206 (2018).
Stübgen, J. P. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 37, 281–292 (2008).
Blum, S. & McCombe, P. A. Genetics of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP): current knowledge and future directions. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 19, 88–103 (2014).
Mevorach, D. et al. Therapy with eculizumab for patients with CD59 p.Cys89Tyr mutation. Ann. Neurol. 80, 708–717 (2016).
Mahdi-Rogers, M. & Hughes, R. A. Epidemiology of chronic inflammatory neuropathies in southeast England. Eur. J. Neurol. 21, 28–33 (2014).
Cats, E. A. et al. Correlates of outcome and response to IVIg in 88 patients with multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurology 75, 818–825 (2010).
Miyashiro, A. et al. Are multifocal motor neuropathy patients underdiagnosed? An epidemiological survey in Japan. Muscle Nerve 49, 357–361 (2014).
Nobile-Orazio, E., Bianco, M. & Nozza, A. Advances in the treatment of paraproteinemic neuropathy. Curr. Treat Options Neurol. 19, 43 (2017).
Mygland, A. & Monstad, P. Chronic polyneuropathies in Vest-Agder, Norway. Eur. J. Neurol. 8, 157–165 (2001).
Raheja, D., Specht, C. & Simmons, Z. Paraproteinemic neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 51, 1–13 (2015).
Mathey, E. K. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: from pathology to phenotype. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 973–985 (2015). This excellent review on the immunopathogenesis of immune-mediated neuropathies emphasizes the role of humoral immune responses in these disorders.
Meyer zu Horste, G., Hartung, H. P. & Kieseier, B. C. From bench to bedside — experimental rationale for immune-specific therapies in the inflamed peripheral nerve. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 3, 198–211 (2007). This comprehensive overview on existing animal models for studying immune-mediated neuropathies discusses how insights from these model systems help our understanding for translational medicine in this disease entity.
Mäurer, M. & Gold, R. Animal models of immune-mediated neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 15, 617–622 (2002).
Meyer zu Horste, G. et al. Thymic epithelium determines a spontaneous chronic neuritis in Icam1(tm1Jcgr)NOD mice. J. Immunol. 193, 2678–2690 (2014).
de Seze, J. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a new animal model for new therapeutic targets. Rev. Neurol. 172, 767–769 (2016).
Zautner, A. E. et al. Seroprevalence of campylobacteriosis and relevant post-infectious sequelae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 33, 1019–1027 (2014).
Ho, T. W. et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome in northern China. Relationship to Campylobacter jejuni infection and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain 118, 597–605 (1995).
Hughes, R. A. & Cornblath, D. R. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 366, 1653–1666 (2005).
Godschalk, P. C. et al. The crucial role of Campylobacter jejuni genes in anti-ganglioside antibody induction in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 1659–1665 (2004).
Sheikh, K. A., Deerinck, T. J., Ellisman, M. H. & Griffin, J. W. The distribution of ganglioside-like moieties in peripheral nerves. Brain 122, 449–460 (1999).
Yuki, N. et al. Carbohydrate mimicry between human ganglioside GM1 and Campylobacter jejuni lipooligosaccharide causes Guillain-Barré syndrome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 11404–11409 (2004).
McGonigal, R. et al. Anti-GD1a antibodies activate complement and calpain to injure distal motor nodes of Ranvier in mice. Brain 133, 1944–1960 (2010).
Rupp, A. et al. Motor nerve terminal destruction and regeneration following anti-ganglioside antibody and complement-mediated injury: an in and ex vivo imaging study in the mouse. Exp. Neurol. 233, 836–848 (2012).
He, L., Zhang, G., Liu, W., Gao, T. & Sheikh, K. A. Anti-ganglioside antibodies induce nodal and axonal injury via Fcgamma receptor-mediated inflammation. J. Neurosci. 35, 6770–6785 (2015).
Clark, A. J. et al. Co-cultures with stem cell-derived human sensory neurons reveal regulators of peripheral myelination. Brain 140, 898–913 (2017).
Hafer-Macko, C. E. et al. Immune attack on the Schwann cell surface in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 39, 625–635 (1996).
Griffin, J. W. et al. Early nodal changes in the acute motor axonal neuropathy pattern of the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurocytol. 25, 33–51 (1996).
Vural, A., Doppler, K. & Meinl, E. Autoantibodies against the node of Ranvier in seropositive chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: diagnostic, pathogenic, and therapeutic relevance. Front. Immunol. 9, 1029 (2018).
Uncini, A. & Kuwabara, S. Nodopathies of the peripheral nerve: an emerging concept. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 1186–1195 (2015). This article provides an excellent review on the emerging concept of various clinical subclasses of chronic neuropathies defined by the presence of different autoantibodies.
Shahrizaila, N. et al. Antibodies to single glycolipids and glycolipid complexes in Guillain-Barré syndrome subtypes. Neurology 83, 118–124 (2014).
Rinaldi, S. et al. Antibodies to heteromeric glycolipid complexes in Guillain-Barré syndrome. PLOS ONE 8, e82337 (2013). This excellent summary of a complex topic deciphers the broad spectrum of potential autoantibodies in GBS.
Uncini, A. & Kuwabara, S. Electrodiagnostic criteria for Guillain-Barré syndrome: a critical revision and the need for an update. Clin. Neurophysiol. 123, 1487–1495 (2012).
Samukawa, M. et al. Electrophysiological assessment of Guillain-Barré syndrome with both Gal-C and ganglioside antibodies; tendency for demyelinating type. J. Neuroimmunol. 301, 61–64 (2016).
Goodfellow, J. A. & Willison, H. J. Antiganglioside, antiganglioside-complex, and antiglycolipid-complex antibodies in immune-mediated neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 29, 572–580 (2016).
Makowska, A. et al. Immune responses to myelin proteins in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 664–671 (2008).
Kwa, M. S., van Schaik, I. N., Brand, A., Baas, F. & Vermeulen, M. Investigation of serum response to PMP22, connexin 32 and P(0) in inflammatory neuropathies. J. Neuroimmunol. 116, 220–225 (2001).
Sawai, S. et al. Moesin is a possible target molecule for cytomegalovirus-related Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 83, 113–117 (2014).
Miyaji, K., Devaux, J. & Yuki, N. Moesin is a possible target molecule for cytomegalovirus-related Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 83, 2314 (2014).
Kwa, M. S. et al. Autoimmunoreactivity to Schwann cells in patients with inflammatory neuropathies. Brain 126, 361–375 (2003).
Devaux, J. J., Odaka, M. & Yuki, N. Nodal proteins are target antigens in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 17, 62–71 (2012).
Doppler, K. et al. Auto-antibodies to contactin-associated protein 1 (Caspr) in two patients with painful inflammatory neuropathy. Brain 139, 2617–2630 (2016).
Kiefer, R., Kieseier, B. C., Bruck, W., Hartung, H. P. & Toyka, K. V. Macrophage differentiation antigens in acute and chronic autoimmune polyneuropathies. Brain 121, 469–479 (1998).
Kuwabara, S., Nakajima, M., Matsuda, S. & Hattori, T. Magnetic resonance imaging at the demyelinative foci in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 48, 874–877 (1997).
Duggins, A. J. et al. Spinal root and plexus hypertrophy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain 122, 1383–1390 (1999).
Kiefer, R., Kieseier, B. C., Stoll, G. & Hartung, H. P. The role of macrophages in immune-mediated damage to the peripheral nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 64, 109–127 (2001).
Vital, A. et al. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with dysglobulinemia: a peripheral nerve biopsy study in 18 cases. Acta Neuropathol. 100, 63–68 (2000).
Van den Berg, L. H., Mollee, I., Wokke, J. H. & Logtenberg, T. Increased frequencies of HPRT mutant T lymphocytes in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: further evidence for a role of T cells in the etiopathogenesis of peripheral demyelinating diseases. J. Neuroimmunol. 58, 37–42 (1995).
Chi, L. J. et al. Distribution of Th17 cells and Th1 cells in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 345–356 (2010).
Staudt, M., Diederich, J. M., Meisel, C., Meisel, A. & Klehmet, J. Differences in peripheral myelin antigen-specific T cell responses and T memory subsets in atypical versus typical CIDP. BMC Neurol. 17, 81 (2017).
Sanvito, L., Makowska, A., Gregson, N., Nemni, R. & Hughes, R. A. Circulating subsets and CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cell function in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Autoimmunity 42, 667–677 (2009).
Sanvito, L. et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses to myelin protein peptides in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 80, 333–338 (2009).
Schneider-Hohendorf, T. et al. CD8+ T cell immunity in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 78, 402–408 (2012).
Klehmet, J. et al. Circulating lymphocyte and T memory subsets in glucocorticosteroid versus IVIG treated patients with CIDP. J. Neuroimmunol. 283, 17–22 (2015).
Pollard, J. D., McCombe, P. A., Baverstock, J., Gatenby, P. A. & McLeod, J. G. Class II antigen expression and T lymphocyte subsets in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 13, 123–134 (1986).
Meyer zu Horste, G. et al. Mouse Schwann cells activate MHC class I and II restricted T cell responses, but require external peptide processing for MHC class II presentation. Neurobiol. Dis. 37, 483–490 (2010).
Mausberg, A. K. et al. Recovery of the T cell repertoire in CIDP by IV immunoglobulins. Neurology 80, 296–303 (2013).
Lim, J. P., Devaux, J. & Yuki, N. Peripheral nerve proteins as potential autoantigens in acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies. Autoimmun. Rev. 13, 1070–1078 (2014).
Yan, W. X., Taylor, J., Andrias-Kauba, S. & Pollard, J. D. Passive transfer of demyelination by serum or IgG from chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy patients. Ann. Neurol. 47, 765–775 (2000).
Doppler, K. et al. Destruction of paranodal architecture in inflammatory neuropathy with anti-contactin-1 autoantibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 720–728 (2015).
Querol, L., Devaux, J., Rojas-Garcia, R. & Illa, I. Autoantibodies in chronic inflammatory neuropathies: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 13, 533–547 (2017). This extensive summary on the role of autoantibodies in immune-mediated neuropathies describes how to utilize this information in clinical practice.
Uncini, A., Zappasodi, F. & Notturno, F. Electrodiagnosis of GBS subtypes by a single study: not yet the squaring of the circle. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 5–8 (2015).
Cifuentes-Diaz, C. et al. Nodes of Ranvier and paranodes in chronic acquired neuropathies. PLOS ONE 6, e14533 (2011).
Lonigro, A. & Devaux, J. J. Disruption of neurofascin and gliomedin at nodes of Ranvier precedes demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Brain 132, 260–273 (2009).
Koike, H. et al. Paranodal dissection in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with anti-neurofascin-155 and anti-contactin-1 antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 88, 465–473 (2017).
Vallat, J. M. et al. Paranodal lesions in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy associated with anti-neurofascin 155 antibodies. Neuromuscul. Disord. 27, 290–293 (2017).
Kuwahara, M. et al. Clinical features of CIDP with LM1-associated antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 84, 573–575 (2013).
Delmont, E. et al. Autoantibodies to nodal isoforms of neurofascin in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain 140, 1851–1858 (2017).
Pestronk, A. et al. A treatable multifocal motor neuropathy with antibodies to GM1 ganglioside. Ann. Neurol. 24, 73–78 (1988).
Cats, E. A. et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy: association of anti-GM1 IgM antibodies with clinical features. Neurology 75, 1961–1967 (2010).
Susuki, K. et al. Anti-GM1 antibodies cause complement-mediated disruption of sodium channel clusters in peripheral motor nerve fibers. J. Neurosci. 27, 3956–3967 (2007).
Piepers, S. et al. IVIg inhibits classical pathway activity and anti-GM1 IgM-mediated complement deposition in MMN. J. Neuroimmunol. 229, 256–262 (2010).
Yuki, N., Watanabe, H., Nakajima, T. & Spath, P. J. IVIG blocks complement deposition mediated by anti-GM1 antibodies in multifocal motor neuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 82, 87–91 (2011).
Vlam, L. et al. Complement activity is associated with disease severity in multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2, e119 (2015).
Harschnitz, O. et al. Autoantibody pathogenicity in a multifocal motor neuropathy induced pluripotent stem cell-derived model. Ann. Neurol. 80, 71–88 (2016).
Taylor, B. V. et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy: pathologic alterations at the site of conduction block. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 63, 129–137 (2004).
Garg, N. et al. Motor unit remodelling in multifocal motor neuropathy: the importance of axonal loss. Clin. Neurophysiol. 128, 2022–2028 (2017).
Kaji, R. et al. Pathological findings at the site of conduction block in multifocal motor neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 33, 152–158 (1993).
Oh, S. J., Claussen, G. C., Odabasi, Z. & Palmer, C. P. Multifocal demyelinating motor neuropathy: pathologic evidence of ‘inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy’. Neurology 45, 1828–1832 (1995).
Shimizu, F. et al. Sera from patients with multifocal motor neuropathy disrupt the blood-nerve barrier. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 85, 526–537 (2014).
Priori, A. et al. Distinctive abnormalities of motor axonal strength-duration properties in multifocal motor neuropathy and in motor neurone disease. Brain 125, 2481–2490 (2002).
Kiernan, M. C., Guglielmi, J. M., Kaji, R., Murray, N. M. & Bostock, H. Evidence for axonal membrane hyperpolarization in multifocal motor neuropathy with conduction block. Brain 125, 664–675 (2002).
Latov, N. et al. Plasma-cell dyscrasia and peripheral neuropathy with a monoclonal antibody to peripheral-nerve myelin. N. Engl. J. Med. 303, 618–621 (1980).
Nobile-Orazio, E. et al. Frequency and clinical correlates of anti-neural IgM antibodies in neuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Ann. Neurol. 36, 416–424 (1994).
Takatsu, M. et al. Immunofluorescence study of patients with neuropathy and IgM M proteins. Ann. Neurol. 18, 173–181 (1985).
Vital, C. et al. Myelin modifications in 8 cases of peripheral neuropathy with Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia and anti-MAG activity. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 21, 509–516 (1997).
Hays, A. P., Lee, S. S. & Latov, N. Immune reactive C3d on the surface of myelin sheaths in neuropathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 18, 231–244 (1988).
Jacobs, J. M. Morphological changes at paranodes in IgM paraproteinaemic neuropathy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 34, 544–553 (1996).
Stalder, A. K. et al. Immunoglobulin M deposition in cutaneous nerves of anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein polyneuropathy patients correlates with axonal degeneration. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 68, 148–158 (2009).
Hays, A. P., Latov, N., Takatsu, M. & Sherman, W. H. Experimental demyelination of nerve induced by serum of patients with neuropathy and an anti-MAG IgM M-protein. Neurology 37, 242–256 (1987).
Tatum, A. H. Experimental paraprotein neuropathy, demyelination by passive transfer of human IgM anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein. Ann. Neurol. 33, 502–506 (1993).
Ilyas, A. A., Quarles, R. H., Dalakas, M. C. & Brady, R. O. Polyneuropathy with monoclonal gammopathy: glycolipids are frequently antigens for IgM paraproteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 6697–6700 (1985).
Kuwabara, S. et al. Hyperreflexia in axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome subsequent to Campylobacter jejuni enteritis. J. Neurol. Sci. 199, 89–92 (2002).
Wakerley, B. R. & Yuki, N. Pharyngeal-cervical-brachial variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 85, 339–344 (2014).
Wakerley, B. R. & Yuki, N. Mimics and chameleons in Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes. Pract. Neurol. 15, 90–99 (2014).
Asbury, A. K. & Cornblath, D. R. Assessment of current diagnostic criteria for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 27, S21–S24 (1990).
Sejvar, J. J. et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome and Fisher syndrome: case definitions and guidelines for collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data. Vaccine 29, 599–612 (2011).
Fokke, C. et al. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome and validation of Brighton criteria. Brain 137, 33–43 (2014).
Hadden, R. D. et al. Electrophysiological classification of Guillain-Barré syndrome: clinical associations and outcome. Plasma Exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain-Barré Syndrome Trial Group. Ann. Neurol. 44, 780–788 (1998).
Albers, J. W., Donofrio, P. D. & McGonagle, T. K. Sequential electrodiagnostic abnormalities in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 8, 528–539 (1985).
Orlikowski, D. et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome following primary cytomegalovirus infection: a prospective cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 52, 837–844 (2011).
Hadden, R. D. et al. Preceding infections, immune factors, and outcome in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 56, 758–765 (2001).
Willison, H. J., Jacobs, B. C. & van Doorn, P. A. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 388, 717–727 (2016).
Kaida, K. et al. Ganglioside complexes as new target antigens in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 56, 567–571 (2004).
Galazky, I. et al. Guillain-Barré/CIDP-like neuropathy in two parkinsonian patients following intestinal levodopa/carbidopa treatment. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 20, 125–127 (2014).
Prommel, P., Pilgram-Pastor, S., Sitter, H., Buhk, J. H. & Strik, H. Neoplastic meningitis: how MRI and CSF cytology are influenced by CSF cell count and tumor type. ScientificWorldJournal 2013, 248072 (2013).
van Koningsveld, R. et al. A clinical prognostic scoring system for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 6, 589–594 (2007). This study is one of the first promising attempts to introduce clinical predictive markers in a potentially life-threatening disease.
Walgaard, C. et al. Prediction of respiratory insufficiency in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 67, 781–787 (2010).
Yamagishi, Y. et al. Markers for Guillain-Barré syndrome with poor prognosis: a multi-center study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 22, 433–439 (2017).
Koski, C. L. et al. Derivation and validation of diagnostic criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 277, 1–8 (2009).
Barohn, R. J., Kissel, J. T., Warmolts, J. R. & Mendell, J. R. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy — clinical characteristics, course, and recommendations for diagnostic criteria. Arch. Neurol. 46, 878–884 (1989).
Boukhris, S., Magy, L., Khalil, M., Sindou, P. & Vallat, J. M. Pain as the presenting symptom of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP). J. Neurol. Sci. 254, 33–38 (2007).
Kuitwaard, K., Bos-Eyssen, M. E., Blomkwist-Markens, P. H. & van Doorn, P. A. Recurrences, vaccinations and long-term symptoms in GBS and CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 14, 310–315 (2009).
Mendell, J. R. et al. Evidence for central nervous system demyelination in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 37, 1291–1294 (1987).
Pineda, A. A. et al. A distinct subgroup of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with CNS demyelination and a favorable response to immunotherapy. J. Neurol. Sci. 255, 1–6 (2007).
Rotta, F. T. et al. The spectrum of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 173, 129–139 (2000).
Saperstein, D. S., Katz, J. S., Amato, A. A. & Barohn, R. J. Clinical spectrum of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Muscle Nerve 24, 311–324 (2001).
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society — first revision. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 1–9 (2010).
Lewis, R. A., Sumner, A. J., Brown, M. J. & Asbury, A. K. Multifocal demyelinating neuropathy with persistent conduction block. Neurology 32, 958–964 (1982).
Breiner, A. & Brannagan, T. H. 3rd. Comparison of sensitivity and specificity among 15 criteria for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 50, 40–46 (2014).
Latov, N. et al. Timing and course of clinical response to intravenous immunoglobulin in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 67, 802–807 (2010).
Tackenberg, B. et al. Classifications and treatment responses in chronic immune-mediated demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 68, 1622–1629 (2007).
French CIDP Study Group. Recommendations on diagnostic strategies for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 115–118 (2008).
Capek, S., Amrami, K. K., Dyck, P. J. & Spinner, R. J. Targeted fascicular biopsy of the sciatic nerve and its major branches: rationale and operative technique. Neurosurg. Focus 39, E12 (2015).
Stettner, M. et al. Corneal confocal microscopy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann. Clin. Transl Neurol. 3, 88–100 (2016).
Ruts, L., Drenthen, J., Jacobs, B. C. & van Doorn, P. A. Distinguishing acute-onset CIDP from fluctuating Guillain-Barré syndrome: a prospective study. Neurology 74, 1680–1686 (2010).
Alessandro, L. et al. Differences between acute-onset chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (A-CIDP) and acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP) in adult patients. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 23, 154–158 (2018).
Markowitz, J. A., Jeste, S. S. & Kang, P. B. Child neurology: chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy in children. Neurology 71, e74–e78 (2008).
Rajabally, Y. A., Stettner, M., Kieseier, B. C., Hartung, H. P. & Malik, R. A. CIDP and other inflammatory neuropathies in diabetes — diagnosis and management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 13, 599–611 (2017).
Mohamed, A., Davies, L. & Pollard, J. D. Conduction block in vasculitic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 21, 1084–1088 (1998).
Mathis, S., Magy, L., Diallo, L., Boukhris, S. & Vallat, J. M. Amyloid neuropathy mimicking chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 45, 26–31 (2012).
Cortese, A. et al. Misdiagnoses of transthyretin amyloidosis: a clinical and electrodiagnostic study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 10, O13 (2015).
Manji, H. Drug-induced neuropathies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 115, 729–742 (2013).
Oh, S. J., Kurokawa, K., de Almeida, D. F., Ryan, H. F. Jr & Claussen, G. C. Subacute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 61, 1507–1512 (2003).
Vlam, L. et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 8, 48–58 (2012).
Stangel, M. et al. Treatment of patients with multifocal motor neuropathy with immunoglobulins in clinical practice: the SIGNS registry. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 9, 165–179 (2016).
Lambrecq, V., Krim, E., Rouanet-Larriviere, M. & Lagueny, A. Sensory loss in multifocal motor neuropathy: a clinical and electrophysiological study. Muscle Nerve 39, 131–136 (2009).
Van den Berg-Vos, R. M. et al. Multifocal inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy: a distinct clinical entity? Neurology 54, 26–32 (2000).
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of multifocal motor neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society — first revision. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 295–301 (2010).
Delmont, E. et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy with and without conduction block: a single entity? Neurology 67, 592–596 (2006).
Meuth, S. G. & Kleinschnitz, C. Multifocal motor neuropathy: update on clinical characteristics, pathophysiological concepts and therapeutic options. Eur. Neurol. 63, 193–204 (2010).
Kyle, R. A. et al. Long-term follow-up of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 241–249 (2018).
Hoffman, E. M. et al. Impairments and comorbidities of polyneuropathy revealed by population-based analyses. Neurology 84, 1644–1651 (2015).
Zis, P., Sarrigiannis, P. G., Rao, D. G., Hewamadduma, C. & Hadjivassiliou, M. Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy: a systematic review. J. Neurol. 263, 1903–1910 (2016).
Kuijf, M. L. et al. Detection of anti-MAG antibodies in polyneuropathy associated with IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 73, 688–695 (2009).
Trojaborg, W., Hays, A. P., van den Berg, L., Younger, D. S. & Latov, N. Motor conduction parameters in neuropathies associated with anti-MAG antibodies and other types of demyelinating and axonal neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 18, 730–735 (1995).
Nobile-Orazio, E. IgM paraproteinaemic neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 17, 599–605 (2004).
Willison, H. J. et al. The clinical and laboratory features of chronic sensory ataxic neuropathy with anti-disialosyl IgM antibodies. Brain 124, 1968–1977 (2001).
Steck, A., Yuki, N. & Graus, F. Antibody testing in peripheral nerve disorders. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 115, 189–212 (2013).
Kieseier, B. C. et al. Advances in understanding and treatment of immune-mediated disorders of the peripheral nervous system. Muscle Nerve 30, 131–156 (2004).
Hughes, R. A., Swan, A. V. & van Doorn, P. A. Intravenous immunoglobulin for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 9, CD002063 (2004).
The French Cooperative Group on Plasma Exchange in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Appropriate number of plasma exchanges in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 41, 298–306 (1997).
Hughes, R. A. Treatment of peripheral nerve disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 18, 554–556 (2005).
van Doorn, P. A., Kuitwaard, K. & Jacobs, B. C. Serum IgG levels as biomarkers for optimizing IVIg therapy in CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 16 (Suppl. 1), 38–40 (2011).
Hughes, R. A., Brassington, R., Gunn, A. A. & van Doorn, P. A. Corticosteroids for Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10, CD001446 (2016).
Davidson, A. I. et al. Inhibition of complement in Guillain-Barré syndrome: the ICA-GBS study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 22, 4–12 (2017).
Misawa, S. et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 17, 519–529 (2018).
Koller, H., Kieseier, B. C., Jander, S. & Hartung, H. P. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1343–1356 (2005).
Dyck, P. J. et al. Chronic inflammatory polyradiculoneuropathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 50, 621–637 (1975).
Dyck, P. J. et al. Prednisone improves chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy more than no treatment. Ann. Neurol. 11, 136–141 (1982).
Hughes, R. A., Mehndiratta, M. M. & Rajabally, Y. A. Corticosteroids for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 11, CD002062 (2017).
Gold, R. & Kieseier, B. C. Therapy of immune neuropathies with intravenous immunoglobulins. J. Neurol. 253(Suppl. 5), V59–V63 (2006).
Hughes, R. A. et al. Intravenous immune globulin (10% caprylate-chromatography purified) for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (ICE study): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 7, 136–144 (2008). This article presents the first and largest conducted trial in CIDP demonstrating long-term effects of IVIG in patients with this disorder.
Lopate, G., Pestronk, A. & Al-Lozi, M. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with high-dose intermittent intravenous methylprednisolone. Arch. Neurol. 62, 249–254 (2005).
Nobile-Orazio, E. et al. Frequency and time to relapse after discontinuing 6-month therapy with IVIg or pulsed methylprednisolone in CIDP. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 86, 729–734 (2015).
Nobile-Orazio, E. et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin versus intravenous methylprednisolone for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 11, 493–502 (2012).
Vrancken, A. F., Notermans, N. C., Jansen, G. H., Wokke, J. H. & Said, G. Progressive idiopathic axonal neuropathy—a comparative clinical and histopathological study with vasculitic neuropathy. J. Neurol. 251, 269–278 (2004).
Markvardsen, L. H. et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in responders to intravenous therapy with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 20, 836–842 (2013).
RMC Trial Group. Randomised controlled trial of methotrexate for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (RMC trial): a pilot, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 8, 158–164 (2009).
van Schaik, I. N. et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin for maintenance treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (PATH): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 17, 35–46 (2018).
Cocito, D. et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in CIDP and MMN: a different long-term clinical response? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 87, 791–793 (2015).
Leussink, V. I., Hartung, H. P., Kieseier, B. C. & Stettner, M. Subcutaneous immunoglobulins in the treatment of chronic immune-mediated neuropathies. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 9, 336–343 (2016).
Hughes, R. A. et al. Intramuscular interferon beta-1a in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Neurology 74, 651–657 (2010).
Fialho, D., Chan, Y. C., Allen, D. C., Reilly, M. M. & Hughes, R. A. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy with methotrexate. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 77, 544–547 (2006).
Mahattanakul, W., Crawford, T. O., Griffin, J. W., Goldstein, J. M. & Cornblath, D. R. Treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with cyclosporin-A. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 60, 185–187 (1996).
Matsuda, M., Hoshi, K., Gono, T., Morita, H. & Ikeda, S. Cyclosporin A in treatment of refractory patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 224, 29–35 (2004).
Gorson, K. C., Amato, A. A. & Ropper, A. H. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in patients with chronic immune demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 63, 715–717 (2004).
Mahdi-Rogers, M., Brassington, R., Gunn, A. A., van Doorn, P. A. & Hughes, R. A. C. Immunomodulatory treatment other than corticosteroids, immunoglobulin and plasma exchange for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 5, CD003280 (2017).
Gladstone, D. E., Prestrud, A. A. & Brannagan, T. H. 3rd. High-dose cyclophosphamide results in long-term disease remission with restoration of a normal quality of life in patients with severe refractory chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 10, 11–16 (2005).
McHutchison, J. G. et al. Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 1485–1492 (1998).
Leitch, M. M., Sherman, W. H. & Brannagan, T. H. 3rd. Fludarabine in the treatment of refractory chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathies. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 17, 1–5 (2015).
Dyck, P. J., O’Brien, P., Swanson, C., Low, P. & Daube, J. Combined azathioprine and prednisone in chronic inflammatory-demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 35, 1173–1176 (1985).
Kieseier, B. C. & Stuve, O. A critical appraisal of treatment decisions in multiple sclerosis — old versus new. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 7, 255–262 (2011).
Hirst, C., Raasch, S., Llewelyn, G. & Robertson, N. Remission of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy after alemtuzumab (Campath 1H). J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 77, 800–802 (2006).
Marsh, E. A. et al. Alemtuzumab in the treatment of IVIG-dependent chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 257, 913–919 (2010).
Engelhardt, B. & Ransohoff, R. M. The ins and outs of T-lymphocyte trafficking to the CNS: anatomical sites and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol. 26, 485–495 (2005).
Vallat, J. M. et al. Natalizumab as a disease-modifying therapy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy — a report of three cases. Eur. Neurol. 73, 294–302 (2015).
Wolf, C. et al. Natalizumab treatment in a patient with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Arch. Neurol. 67, 881–883 (2010).
Leger, J. M., Guimaraes-Costa, R. & Muntean, C. Immunotherapy in peripheral neuropathies. Neurotherapeutics 13, 96–107 (2016).
Koski, C. L. Initial and long-term management of autoimmune neuropathies. CNS Drugs 19, 1033–1048 (2005).
Umapathi, T., Hughes, R. A., Nobile-Orazio, E. & Leger, J. M. Immunosuppressive treatment for multifocal motor neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2, CD003217 (2002).
Kieseier, B. C., Dalakas, M. C. & Hartung, H. P. Immune mechanisms in chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy. Neurology 59, S7–S12 (2002).
Nobile-Orazio, E., Cappellari, A. & Priori, A. Multifocal motor neuropathy: current concepts and controversies. Muscle Nerve 31, 663–680 (2005).
Federico, P., Zochodne, D. W., Hahn, A. F., Brown, W. F. & Feasby, T. E. Multifocal motor neuropathy improved by IVIg: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 55, 1256–1262 (2000).
Harbo, T. et al. Subcutaneous versus intravenous immunoglobulin in multifocal motor neuropathy: a randomized, single-blinded cross-over trial. Eur. J. Neurol. 16, 631–638 (2009).
Harbo, T., Andersen, H. & Jakobsen, J. Long-term therapy with high doses of subcutaneous immunoglobulin in multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurology 75, 1377–1380 (2010).
Cocito, D. et al. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in CIDP and MMN: a short-term nationwide study. J. Neurol. 261, 2159–2164 (2014).
Chaudhry, V. & Cornblath, D. R. An open-label trial of rituximab (Rituxan®) in multifocal motor neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 196–201 (2010).
Niermeijer, J. M. et al. Intermittent cyclophosphamide with prednisone versus placebo for polyneuropathy with IgM monoclonal gammopathy. Neurology 69, 50–59 (2007).
Renaud, S. et al. Rituximab in the treatment of polyneuropathy associated with anti-MAG antibodies. Muscle Nerve 27, 611–615 (2003).
Renaud, S. et al. High-dose rituximab and anti-MAG-associated polyneuropathy. Neurology 66, 742–744 (2006).
Svahn, J. et al. Anti-MAG antibodies in 202 patients: clinicopathological and therapeutic features. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 89, 499–505 (2017).
Gono, T. et al. Rituximab therapy in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy with anti-SGPG IgM antibody. J. Clin. Neurosci. 13, 683–687 (2006).
Graham, R. C., Hughes, R. A. & White, C. M. A prospective study of physiotherapist prescribed community based exercise in inflammatory peripheral neuropathy. J. Neurol. 254, 228–235 (2007).
Khan, F. et al. Outcomes of high- and low-intensity rehabilitation programme for persons in chronic phase after Guillain-Barré syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 43, 638–646 (2011).
Markvardsen, L. H. et al. Resistance training and aerobic training improve muscle strength and aerobic capacity in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 57, 70–76 (2017).
Garssen, M. P. et al. Physical training and fatigue, fitness, and quality of life in Guillain-Barré syndrome and CIDP. Neurology 63, 2393–2395 (2004).
Cocito, D. et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy during treatment with infliximab. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 10, 386–387 (2005).
Wilson, J. R., Conwit, R. A., Eidelman, B. H., Starzl, T. & Abu-Elmagd, K. Sensorimotor neuropathy resembling CIDP in patients receiving FK506. Muscle Nerve 17, 528–532 (1994).
Merkies, I. S. et al. Understanding the consequences of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy from impairments to activity and participation restrictions and reduced quality of life: the ICE study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 15, 208–215 (2010).
Forsberg, A., Press, R. & Holmqvist, L. W. Residual disability 10 years after falling ill in Guillain-Barré syndrome: a prospective follow-up study. J. Neurol. Sci. 317, 74–79 (2012).
White, C. M., Hadden, R. D., Robert-Lewis, S. F., McCrone, P. R. & Petty, J. L. Observer blind randomised controlled trial of a tailored home exercise programme versus usual care in people with stable inflammatory immune mediated neuropathy. BMC Neurol. 15, 147 (2015).
Merkies, I. S. & Kieseier, B. C. Fatigue, pain, anxiety and depression in Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Eur. Neurol. 75, 199–206 (2016).
Merkies, I. S., Schmitz, P. I., Samijn, J. P., van der Meche, F. G. & van Doorn, P. A. Fatigue in immune-mediated polyneuropathies. European Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Group. Neurology 53, 1648–1654 (1999).
Drory, V. E., Bronipolsky, T., Bluvshtein, V., Catz, A. & Korczyn, A. D. Occurrence of fatigue over 20 years after recovery from Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 316, 72–75 (2012).
Renoir, T., Hasebe, K. & Gray, L. Mind and body: how the health of the body impacts on neuropsychiatry. Front. Pharmacol. 4, 158 (2013).
Kuitwaard, K., Ruts, L., van Doorn, P. A. & van der Pol, W. L. Individual patients who experienced both Guillain-Barré syndrome and CIDP. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 14, 66–68 (2009).
Draak, T. H. P., Faber, C. G. & Merkies, I. S. J. Quality of life in inflammatory neuropathies: the IN-QoL. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 89, 256–262 (2018).
Mahdi-Rogers, M., McCrone, P. & Hughes, R. A. Economic costs and quality of life in chronic inflammatory neuropathies in southeast England. Eur. J. Neurol. 21, 34–39 (2014).
Forsberg, A., de Pedro-Cuesta, J. & Widen Holmqvist, L. Use of healthcare, patient satisfaction and burden of care in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Rehabil. Med. 38, 230–236 (2006).
Merkies, I. S. et al. Health-related quality-of-life improvements in CIDP with immune globulin IV 10%: the ICE Study. Neurology 72, 1337–1344 (2009).
Appeltshauser, L., Weishaupt, A., Sommer, C. & Doppler, K. Complement deposition induced by binding of anti-contactin-1 auto-antibodies is modified by immunoglobulins. Exp. Neurol. 287, 84–90 (2017).
Querol, L. et al. Rituximab in treatment-resistant CIDP with antibodies against paranodal proteins. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2, e149 (2015).
Querol, L. et al. Neurofascin IgG4 antibodies in CIDP associate with disabling tremor and poor response to IVIg. Neurology 82, 879–886 (2014).
Ogata, H. et al. Characterization of IgG4 anti-neurofascin 155 antibody-positive polyneuropathy. Ann. Clin. Transl Neurol. 2, 960–971 (2015).
Chan, Y. C., Allen, D. C., Fialho, D., Mills, K. R. & Hughes, R. A. Predicting response to treatment in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 77, 114–116 (2006).
Ng, J. K. et al. Neurofascin as a target for autoantibodies in peripheral neuropathies. Neurology 79, 2241–2248 (2012).
Uncini, A. & Vallat, J. M. Autoimmune nodo-paranodopathies of peripheral nerve: the concept is gaining ground. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 89, 627–635 (2017).
Misawa, S. et al. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 56, 666–669 (2001).
Hartung, H. P., Reiners, K., Schmidt, B., Stoll, G. & Toyka, K. V. Serum interleukin-2 concentrations in Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic idiopathic demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: comparison with other neurological diseases of presumed immunopathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 30, 48–53 (1991).
Willison, H. J. & Yuki, N. Peripheral neuropathies and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain 125, 2591–2625 (2002).
Wakerley, B. R., Uncini, A. & Yuki, N. Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes — new diagnostic classification. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 10, 537–544 (2014).
Harschnitz, O. et al. MMN: from immunological cross-talk to conduction block. J. Clin. Immunol. 34, S112–S119 (2014).
Kuwabara, S. et al. IgG anti-GM1 antibody is associated with reversible conduction failure and axonal degeneration in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 44, 202–208 (1998).
Ho, T. W. et al. Anti-GD1a antibody is associated with axonal but not demyelinating forms of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 45, 168–173 (1999).
Yuki, N., Kuwabara, S., Koga, M. & Hirata, K. Acute motor axonal neuropathy and acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy share a common immunological profile. J. Neurol. Sci. 168, 121–126 (1999).
Nagashima, T., Koga, M., Odaka, M., Hirata, K. & Yuki, N. Continuous spectrum of pharyngeal-cervical-brachial variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 64, 1519–1523 (2007).
van Schaik, I. N., Bossuyt, P. M., Brand, A. & Vermeulen, M. Diagnostic value of GM1 antibodies in motor neuron disorders and neuropathies: a meta-analysis. Neurology 45, 1570–1577 (1995).
Garcia-Santibanez, R. et al. CANOMAD and other chronic ataxic neuropathies with disialosyl antibodies (CANDA). J. Neurol. 265, 1402–1409 (2018).
Querol, L. et al. Antibodies to contactin-1 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 73, 370–380 (2013).
Miura, Y. et al. Contactin 1 IgG4 associates to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy with sensory ataxia. Brain 138, 1484–1491 (2015).
Devaux, J. J. et al. Neurofascin-155 IgG4 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Neurology 86, 800–807 (2016).
Hiraga, A. et al. Patterns and serial changes in electrodiagnostic abnormalities of axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology 64, 856–860 (2005).
Berciano, J. et al. Severe Guillain-Barré syndrome: sorting out the pathological hallmark in an electrophysiological axonal case. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 14, 54–63 (2009).
Grimm, A. et al. Ultrasound and electrophysiologic findings in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome at disease onset and over a period of six months. Clin. Neurophysiol. 127, 1657–1663 (2016).
Adachi, Y. et al. Brachial and lumbar plexuses in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: MRI assessment including apparent diffusion coefficient. Neuroradiology 53, 3–11 (2011).
Sugimoto, T. et al. Ultrasonographic nerve enlargement of the median and ulnar nerves and the cervical nerve roots in patients with demyelinating Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: distinction from patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 260, 2580–2587 (2013).
Zaidman, C. M. & Pestronk, A. Nerve size in chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy varies with disease activity and therapy response over time: a retrospective ultrasound study. Muscle Nerve 50, 733–738 (2014).
Corse, A. M. et al. Sensory nerve pathology in multifocal motor neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 39, 319–325 (1996).
Gordon, P. H. & Wilbourn, A. J. Early electrodiagnostic findings in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 58, 913–917 (2001).
Reviewer information
Nature Reviews Disease Primers thanks G. Lauria, E. Nobile-Orazio, A. Uncini, J. Vallat and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Introduction (B.C.K. and H.-P.H.); Epidemiology (B.C.K., E.K.M. and C.S.); Mechanisms/pathophysiology (B.C.K., E.K.M. and H.-P.H.); Diagnosis, screening and prevention (B.C.K. and C.S.); Management (B.C.K., E.K.M., C.S. and H.-P.H.); Quality of life (B.C.K.); Outlook (B.C.K. and H.-P.H.); Overview of Primer (B.C.K.).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
B.C.K. reports receiving personal fees for consulting for Grifols and UCB. E.K.M. reports receiving funding from the GBS/CIDP Foundation International and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and is a member of the Scientific Committee of the Trish Multiple Sclerosis Research Foundation. C.S. reports receiving personal fees for educational talks for Alnylam, CSL Behring, Grifols, Kedrion, Sanofi-Genzyme, Shire and Pfizer; personal fees for consulting for Air Liquide, Alnylam, Astellas, Baxalta and UCB; and research support to the institution from Kedrion. H.-P.H. reports CSL Behring fees for serving on a steering committee and from UCB for participating on advisory boards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kieseier, B.C., Mathey, E.K., Sommer, C. et al. Immune-mediated neuropathies. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4, 31 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0027-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0027-2
This article is cited by
-
Introducing electronic monitoring of disease activity in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (EMDA CIDP): trial protocol of a proof of concept study
Neurological Research and Practice (2023)
-
Orbital inflammatory pseudotumor: new advances in diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
Single-cell analysis reveals novel clonally expanded monocytes associated with IL1β–IL1R2 pair in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Versorgungssituation von CIDP-Patienten in neun deutschen Zentren des Neuritis Netzes
Der Nervenarzt (2023)
-
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and psoriasis comorbidity with significantly alleviated in symptoms after secukinumab: case report
BMC Neurology (2022)