Abstract
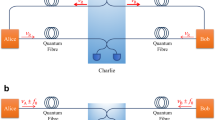
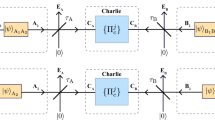
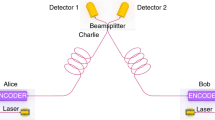
Twin-field (TF) quantum key distribution (QKD) fundamentally alters the rate-distance relationship of QKD, offering the scaling of a single-node quantum repeater. Although recent experiments have demonstrated the new opportunities for secure long-distance communications allowed by TF-QKD, formidable challenges remain to unlock its true potential. Previous demonstrations have required intense stabilization signals at the same wavelength as the quantum signals, thereby unavoidably generating Rayleigh scattering noise that limits the distance and bit rate. Here, we introduce a dual-band stabilization scheme that overcomes past limitations and can be adapted to other phase-sensitive single-photon applications. Using two different optical wavelengths multiplexed together for channel stabilization and protocol encoding, we develop a setup that provides repeater-like key rates over communication distances of 555 km and 605 km in the finite-size and asymptotic regimes respectively and increases the secure key rate at long distance by two orders of magnitude to values of practical relevance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Code availability
The codes used to process the data for this paper are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Bennett, C. H. & Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014).
Ekert, A. K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991).
Pirandola, S., Laurenza, R., Ottaviani, C. & Banchi, L. Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 8, 15043 (2017).
Takeoka, M., Guha, S. & Wilde, M. M. Fundamental rate-loss tradeoff for optical quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 5235 (2014).
Briegel, H.-J., Dür, W., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Quantum repeaters: the role of imperfect local operations in quantum communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5932–5935 (1998).
Duan, L.-M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–418 (2001).
Sangouard, N., Simon, C., de Riedmatten, H. & Gisin, N. Quantum repeaters based on atomic ensembles and linear optics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 33–80 (2011).
Guha, S. et al. Rate-loss analysis of an efficient quantum repeater architecture. Phys. Rev. A 92, 022357 (2015).
Bhaskar, M. K. et al. Experimental demonstration of memory-enhanced quantum communication. Nature 580, 60–64 (2020).
Lo, H.-K., Curty, M. & Qi, B. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012).
Braunstein, S. L. & Pirandola, S. Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012).
Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z. L., Dynes, J. F. & Shields, A. J. Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 557, 400–403 (2018).
Minder, M. et al. Experimental quantum key distribution beyond the repeaterless secret key capacity. Nat. Photonics 13, 334–338 (2019).
Wang, S. et al. Beating the fundamental rate-distance limit in a proof-of-principle quantum key distribution system. Phys. Rev. X 9, 021046 (2019).
Liu, Y. et al. Experimental twin-field quantum key distribution through sending or not sending. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 100505 (2019).
Zhong, X., Hu, J., Curty, M., Qian, L. & Lo, H.-K. Proof-of-principle experimental demonstration of twin-field type quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 100506 (2019).
Fang, X.-T. et al. Implementation of quantum key distribution surpassing the linear rate-transmittance bound. Nat. Photonics 14, 422–425 (2020).
Chen, J.-P. et al. Sending-or-not-sending with independent lasers: secure twin-field quantum key distribution over 509 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 070501 (2020).
Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K., Wang, W. & Lucamarini, M. Information theoretic security of quantum key distribution overcoming the repeaterless secret key capacity bound. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.05511 (2018).
Ma, X., Zeng, P. & Zhou, H. Phase-matching quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 8, 031043 (2018).
Lin, J. & Lütkenhaus, N. Simple security analysis of phase-matching measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 98, 042332 (2018).
Curty, M., Azuma, K. & Lo, H.-K. Simple security proof of twin-field type quantum key distribution protocol. npj Quantum Inf. 5, 64 (2019).
Cui, C. et al. Twin-field quantum key distribution without phase postselection. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 034053 (2019).
Wang, X.-B., Yu, Z.-W. & Hu, X.-L. Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 98, 062323 (2018).
Jiang, C., Yu, Z.-W., Hu, X.-L. & Wang, X.-B. Unconditional security of sending or not sending twin-field quantum key distribution with finite pulses. Phys. Rev. Appl. 12, 024061 (2019).
Yu, Z.-W., Hu, X.-L., Jiang, C., Xu, H. & Wang, X.-B. Sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution in practice. Sci. Rep. 9, 3080 (2019).
Gottesman, D. & Hoi-Kwong, L. Proof of security of quantum key distribution with two-way classical communications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 49, 457–475 (2003).
Chau, H. F. Practical scheme to share a secret key through a quantum channel with a 27.6% bit error rate. Phys. Rev. A 66, 802 (2002).
Xu, H., Yu, Z.-W., Jiang, C., Hu, X.-L. & Wang, X.-B. Sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution: breaking the direct transmission key rate. Phys. Rev. A 101, 042330 (2020).
Boaron, A. et al. Secure quantum key distribution over 421 km of optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 190502 (2018).
Gottesman, D., Jennewein, T. & Croke, S. Longer-baseline telescopes using quantum repeaters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 070503 (2012).
Arrazola, J. M. & Lütkenhaus, N. Quantum fingerprinting with coherent states and a constant mean number of photons. Phys. Rev. A 89, 062305 (2014).
Xu, F. et al. Experimental quantum fingerprinting with weak coherent pulses. Nat. Commun. 6, 8735 (2015).
Zhong, X., Xu, F., Lo, H.-K. & Qian, L. Efficient experimental quantum fingerprinting with wavelength division multiplexing. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.06049v1 (2020).
Kimble, H. J. The quantum internet. Nature 453, 1023–1030 (2008).
Jiang, C., Hu, X.-L., Yu, Z.-w. & Wang, X.-b. Composable security for practical quantum key distribution with two way classical communication. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.00739v1 (2021).
Lo, H.-K., Ma, X. & Chen, K. Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005).
Wang, X.-B. Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank X.-B. Wang and H. Xu for their useful feedback on the TWCC protocol. We acknowledge funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the grant agreement number 857156 ‘OPENQKD’ and under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement number 675662. M.M. acknowledges financial support from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and Toshiba Europe Limited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.P. and M.M. developed the experimental setup, performed the measurements and analysed the data. M.S. and R.I.W. supported the experimental work. M.-J.L. provided the ultralow-loss fibres. Z.Y., M.L. and A.J.S. guided the work. M.L., M.P. and M.M. provided the simulations and wrote the manuscript, with contributions from all the authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Photonics thanks Guilherme B. Xavier and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary discussion, Figs. 1–3 and Tables 1–9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pittaluga, M., Minder, M., Lucamarini, M. et al. 600-km repeater-like quantum communications with dual-band stabilization. Nat. Photon. 15, 530–535 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00811-0
This article is cited by
-
Electrical tuning of quantum light emitters in hBN for free space and telecom optical bands
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Forty thousand kilometers under quantum protection
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Twin-field quantum key distribution without optical frequency dissemination
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Experimental demonstration of multiparty quantum secret sharing and conference key agreement
npj Quantum Information (2023)
-
Tight finite-key analysis for mode-pairing quantum key distribution
Communications Physics (2023)