Abstract
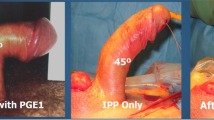
Peyronie’s disease, or fibrous transformations of the tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa that cause penile curvature, is estimated to affect 3.2–8.9% of the male population. Treatment options for PD are based on the severity of the penile deformity and erectile function; of which surgical options include manual modeling during penile prosthesis implantation, plication, plaque incision, and grafting. Multiple approaches may be employed; each with its own advantages, limitations, and risk/benefit ratios. In this regard, we sought to review and highlight the current approaches for the management of residual curvature, optimal patient selection, and preoperative planning.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De la Peyronie F. Sur quelques obstacles qui s’ opposent à l'éjaculation nautrelle de la semence. Mem Acad R Chir. 1743;1:337–42.
Levine LA, Burnett AL. Standard operating procedures for Peyronie's disease. J Sex Med. 2013;10:230–44.
El-Khatib FM, Towe M, Yafi FA. Management of Peyronie's disease with collagenase clostridium histolyticum in the acute phase. World J Urol. 2019; e-pub ahead of print 15 May 2019; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02791-x.
Bilgutay AN, Pastuszak AW. Peyronie’s disease: a review of etiology, diagnosis, and management. Curr Sex Health Rep. 2015;7:117–31.
Moreland RB, Nehra A. Pathophysiology of Peyronie's disease. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:406–10.
Zargooshi J. Trauma as the cause of Peyronie's Disease: penile fracture as a model of trauma. J Urol. 2004;172:186–8.
Herati AS, Pastuszak AW. The genetic basis of peyronie disease: a review. Sex Med Rev. 2016;4:85–94.
Nelson CJ, Diblasio C, Kendirci M, Hellstrom W, Guhring P, Mulhall JP. The chronology of depression and distress in men with Peyronie's disease. J Sex Med. 2008;5:1985–90.
Nelson CJ, Mulhall JP. Psychological impact of Peyronie's disease: a review. J Sex Med. 2013;10:653–60.
Mulhall JP, Schiff J, Guhring P. An analysis of the natural history of Peyronie's disease. J Urol. 2006;175:2115–8.
Chung E. Diagnosis and management of Peyronie's disease: an evidence‐based review. Trends Urol Men Health. 2015;6:18–22.
Devine CJ Jr, Somers KD, Jordan SG, Schlossberg SM. Proposal: trauma as the cause of the Peyronie's lesion. J Urol. 1997;157:285–90.
Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Rajfer J. Mechanisms of disease: new insights into the cellular and molecular pathology of Peyronie's Disease. Nat Clin Pr Urol. 2005;2:291–7.
Ralph D, Gonzalez-Cadavid N, Mirone V, Perovic S, Sohn M, Usta M, et al. The management of Peyronie's disease: evidence-based 2010 guidelines. J Sex Med. 2010;7:2359–74.
Antonini G, De Berardinis E, Del Giudice F, Busetto GM, Lauretti S, Fragas R, et al. Inflatable penile prosthesis placement, scratch technique and postoperative vacuum therapy as a combined approach to definitive treatment of Peyronie's disease. J Urol. 2018;200:642–7.
Müller A, Mulhall JP. Peyronie's disease intervention trials: methodological challenges and issues. J Sex Med. 2009;6:848–61.
Hellstrom WJ, Bivalacqua TJ. Peyronie's disease: etiology, medical, and surgical therapy. J Androl. 2000;21:347–54.
Anaissie J, Yafi FA. A review of surgical strategies for penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie's disease. Transl Androl Urol. 2016;5:342–50.
Hatzichristodoulou G. The PICS technique: a novel approach for residual curvature correction during penile prosthesis implantation in patients with severe Peyronie's disease using the collagen fleece TachoSil. J Sex Med. 2018;15:416–21.
Mulhall JP, Ahmed A, Anderson M. Penile prosthetic surgery for peyronie's disease: defining the need for intraoperative adjuvant maneuvers. J Sex Med. 2004;1:318–21.
Mulcahy JJ, Wilson SK. Management of Peyronie's disease with penile prostheses. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:384–8.
Carson CC. Penile prosthesis implantation in the treatment of Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2000;4:S122–6.
Montorsi F, Guazzoni G, Barbieri L, Maga T, Rigatti P, Graziottin A, et al. AMS 700 CX inflatable penile implants for Peyronie's disease: functional results, morbidity and patient-partner satisfaction. Int J Impot Res. 1996;8:85–6.
Wilson SK, Cleves MA, Delk JR 2nd. Long-term followup of treatment for peyronie's disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 2001;165:825–9.
Hakim LS, Kulaksizoglu H, Hamill BK, Udelson D, Goldstein I. A guide to safe corporotomy incisions in the presence of underlying inflatable penile cylinders: results of in vitro and in vivo studies. J Urol. 1996;155:918–23.
Levine LA, Dimitriou RJ. A surgical algorithm for penile prosthesis placement in men with erectile failure and Peyronie's disease. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12:147–51.
Garaffa G, Minervini A, Christopher NA, Minhas S, Ralph DJ. The management of residual curvature after penile prosthesis implantation in men with Peyronie's disease. BJU Int. 2011;108:1152–6.
Yafi FA, Sangkum P, McCaslin IR, Hellstrom WJ. Strategies for penile prosthesis placement in Peyronie's disease and corporal fibrosis. Curr Urol Rep. 2015;16:21.
Serefoglu EC, Hellstrom WJ. Treatment of Peyronie's disease: 2012 update. Curr Urol Rep. 2011;12:444–52.
Wilson SK, Cleves MA, Delk JR,2nd. Long-term followup of treatment for Peyronie's disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol. 1994;152:1121–3.
Kadioglu A, Akman T, Sanli O, Gurkan L, Cakan M, Celtik M. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease: a critical analysis. Eur Urol. 2006;50:235–48.
Raz S, Dekernion JB, Kaufman JJ. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease: a new approach. J Urol. 1977;117:598–601.
Lyons MD, Carson CC 3rd, Coward RM. Special considerations for placement of an inflatable penile prosthesis for the patient with Peyronie's disease: techniques and patient preference. Med Devices. 2015;8:331–40.
Adibi M, Hudak SJ, Morey AF. Penile plication without degloving enables effective correction of complex Peyronie's deformities. Urology. 2012;79:831–5.
Hudak SJ, Morey AF, Adibi M, Bagrodia A. Favorable patient reported outcomes after penile plication for wide array of Peyronie disease abnormalities. J Urol. 2013;189:1019–24.
Rahman NU, Carrion RE, Bochinski D, Lue TF. Combined penile plication surgery and insertion of penile prosthesis for severe penile curvature and erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 2004;171:2346–9.
Shindel AW, Bullock TL, Brandes S. Urologist practice patterns in the management of Peyronie's disease: a nationwide survey. J Sex Med. 2008;5:954–64.
Chung PH, Scott JF, Morey AF. High patient satisfaction of inflatable penile prosthesis insertion with synchronous penile plication for erectile dysfunction and Peyronie's disease. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1593–1588.
Puri K, Hellstrom WJ. Long-term follow-up of the indications for manual modeling vs plaque excision/ grafting in men undergoing placement of inflatable penile prostheses for peyronie’s disease. J Urol. 2004;171:331.
Djordjevic ML, Kojovic V. Penile prosthesis implantation and Tunica Albuginea incision without grafting in the treatment of Peyronie's disease with erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:391–4.
Kim DH, Lesser TF, Aboseif SR. Subjective patient-reported experiences after surgery for Peyronie's disease: corporeal plication versus plaque incision with vein graft. Urology. 2008;71:698–702.
Levine LA, Benson J, Hoover C. Inflatable penile prosthesis placement in men with Peyronie's disease and drug-resistant erectile dysfunction: a single-center study. J Sex Med. 2010;7:3775–83.
Mulhall JP, Anderson M, Parker M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction: functional and satisfaction outcomes. J Sex Med. 2005;2:132–8.
Lentz AC, Carson CC 3rd. Peyronie's surgery: graft choices and outcomes. Curr Urol Rep. 2009;10:460–7.
Garcia-Gomez B, Ralph D, Levine L, Moncada-Iribarren I, Djinovic R, Albersen M, et al. Grafts for Peyronie's disease: a comprehensive review. Andrology. 2018;6:117–26.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Sansalone S. Penile length and girth restoration in severe Peyronie's disease using circular and longitudinal grafting. BJU Int. 2013;111:213–9.
Rolle L, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Sedigh O, Destefanis P, Galletto E, et al. A new, innovative, lengthening surgical procedure for Peyronie's disease by penile prosthesis implantation with double dorsal-ventral patch graft: the ‘sliding technique. J Sex Med. 2012;9:2389–95.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE. Penile lengthening and widening without grafting according to a modified ‘sliding' technique. BJU Int. 2015;116:965–72.
Wilson SK, Mora-Estaves C, Egydio P, Ralph D, Habous M, Love C, et al. Glans necrosis following penile prosthesis implantation. Prev Treat Suggest. 2017;107:144–8.
Kaufman JL, Chang BB, Shah DM, Koslow AR, Leather RP. Acute arterial insufficiency of the male genitalia. Ann Vasc Surg. 1991;5:370–4.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Valenzuela RJ. Modified Sliding Technique (MoST) for penile lengthening with insertion of inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med. 2015;12:1100–4.
Fakhoury MQ, Halpern J, Bennett N. Recent advancements penile prosthet. F100 Res.2019;8:193.
Fang A, Wang R. Nondegloving technique for Peyronie's disease with penile prosthesis implantation and double dorsal-ventral patch graft. Asian J Androl. 2018;20:90–2.
Hatzichristodoulou G, Gschwend JE, Lahme S. Surgical therapy of Peyronie's disease by partial plaque excision and grafting with collagen fleece: feasibility study of a new technique. Int J Impot Res. 2013;25:183–7.
Hatzichristodoulou G. Surgical therapy of Peyronie’s disease by partial plaque excision and Sealing of tunical defect with collagen fleece: the Sealing technique. Video J Prosth Urol. 2016;2:76.
Hatzichristodoulou G, Tsambarlis P, Kübler H, Levine LA. Peyronie's graft surgery-tips and tricks from the masters in andrologic surgery. Transl Androl Urol. 2017;6:645–56.
Falcone M, Preto M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Garaffa G, Sedigh O, et al. A comparative study between 2 different grafts used as patches after plaque incision and inflatable penile prosthesis implantation for end-stage Peyronie's disease. J Sex Med. 2018;15:848–52.
Hatzichristodoulou Georgios. Partial plaque excision and grafting with collagen fleece in Peyronie disease. J Sex Med. 2016;13:277–81.
Hatzichristodoulou G. Introducing the ventral sealing technique using collagen fleece for surgical therapy of patients with ventral Peyronie's curvature: initial experience. Int J Impot Res. 2018;30:306–11.
Shaeer O. Trans-corporal incision of Peyronie's plaques. J Sex Med. 2011;8:589–93.
Perito P, Wilson S. The Peyronie’s plaque ‘scratch’: an adjunct to modeling. J Sex Med. 2013;10:1194–7.
Bella AJ, Beasley KA, Obied A, Brock GB. Minimally invasive intracorporeal incision of Peyronie's plaque: initial experiences with a new technique. Urology. 2006;68:852–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Khatib, F.M., Huynh, L.M. & Yafi, F.A. Intraoperative methods for residual curvature correction during penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease and refractory erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 32, 43–51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0215-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-019-0215-y
This article is cited by
-
Comment on “Comparison of patient-reported outcomes after penile prosthesis placement in men with and without Peyronie’s disease”
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Residual penile curvature correction by modeling during penile prosthesis implantation in Peyronie’s disease patients
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Surgical tips in difficult penile prosthetic surgery: a narrative review
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)