Abstract
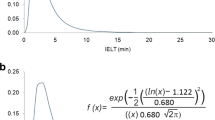
As lifelong premature ejaculation (PE) and subjective PE are two different PE subtypes, the measurement of their characteristic features requires different objective measures. In this article, we address the differences between lifelong PE and subjective PE, in terms of the extent of variation of sexual performance and propose a new objective measure for research of subjective PE. By considering lifelong PE as a mainly “male” sex disorder and subjective PE as a mainly “man” sex disorder, we show that stopwatch-mediated intravaginal ejaculation latency time (IELT) measurement is most adequate for research of lifelong PE, but inadequate for research of subjective PE. Subjective PE needs another objective measure to capture its key characteristics. Arguments are provided to show that the characteristics of subjective PE are different from the key features of lifelong PE. The core issue in lifelong PE is the very short IELT with a very small variation in sexual performance. Subjective PE is characterized by a higher variation of sexual performance. Stopwatch-mediated IELT measurement is essential in case of small variation of sexual performance. In contrast, measurement of various parameters of penile intravaginal thrusting is suggested to be more appropriate in case of high variation of sexual performance observed in subjective PE. In conclusion, research of lifelong PE should be performed by stopwatch measurement of the IELT whereas research of subjective PE should be performed by movement tracker devices, designed to be bound to the males body and/or inserted into the women’s vagina with robust software to measure intravaginal thrusting variation performance. Future studies are warranted to provide scientific data to support this hypothesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schapiro B. Premature ejaculation: a review of 1130 cases. J Urol. 1943;50:374–9.
Godpodinoff ML. Premature ejaculation: clinical subgroups and etiology. J Sex Marital Ther. 1989;15:130.
Serefoglu EC, McMahon CG, Waldinger MD, Althof SE, Shindel A, Adaikan G, et al. An evidence-based unified definition of lifelong and acquired premature ejaculation: report of the second international society for sexual medicine ad hoc committee for the definition of premature ejaculation. J Sex Med. 2014;11:1423–41.
Waldinger MD. Ejaculatio praecox, erectio praecox, and detumescentia praecox as symptoms of a hypertonic state in lifelong premature ejaculation: a new hypothesis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2014;121:189–94.
Waldinger MD, Rietschel M, Nothen MM, Hengeveld MW, Olivier B. Familial occurrence of primary premature ejaculation. Psychiatr Genet. 1998;8:37–40.
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fifth Edition (DSM-5). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. p. 443–6.
Waldinger MD, Schweitzer DH. Changing paradigms from an historical DSM-III and DSM-IV view towards an evidence based definition of premature ejaculation. Part I: validity of DSM-IV-TR. J Sex Med. 2006;3:682–92.
Waldinger MD, Schweitzer DH. Changing paradigms from an historical DSM-III and DSM-IV view towards an evidence based definition of premature ejaculation. Part II: proposals for DSM-V and ICD-11. J Sex Med. 2006;3:693–705.
Waldinger MD. Toward evidence-based genetic research on lifelong premature ejaculation: a critical evaluation of methodology. Korean J Urol. 2011;52:1–8.
Schapiro B. Präjaculin. Kombiniertes Epiphysen-Präparat gegen Reizzustände am Genitale und Hypererotismus.. Hamburg: Chemische Farbrik Promonta G.m.b.H.; 1932.
Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW, Zwinderman AH. Paroxetine treatment of premature ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry. 1994;151:1377–9.
Waldinger MD, Zwinderman AH, Schweitzer DH, Olivier B. Relevance of methodological design for the interpretation of efficacy of drug treatment of premature ejaculation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Impot Res. 2004;16:369–81.
Waldinger MD. Drug treatment options for premature ejaculation. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19:1077–85.
Waldinger MD, Berendsen HHG, Blok BFM, Olivier B, Holstege G. Premature ejaculation and serotonergic antidepressants-induced delayed ejaculation: the involvement of the serotonergic system. Behav Brain Res. 1998;92:111–8.
Waldinger MD. Towards evidence-based drug treatment research on premature ejaculation: a critical evaluation of methodology. J Impot Res. 2003;15:309–13.
McMahon CG, Touma K. Treatment of premature ejaculation with paroxetine hydrochloride. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:241–5.
McMahon CG. Treatment of premature ejaculation with sertraline hydrochloride: a single-blind placebo controlled crossover study. J Urol. 1998;159:1935–8.
Tanner BA. Two case reports on the modification of the ejaculatory response with the squeeze technique. Psychother Res Practice. 1973;297:297.
Cooper AJ, Magnus RV. A clinical trial of the beta blocker propranolol in premature ejaculation. J Psychosom Res. 1984;28:331–6.
Althof SE, Levine SB, Corty EW, Risen CB, Stern EB. A double-blind crossover trial of clomipramine for rapid ejaculation in 15 couples. J Clin Psychiatry. 1995;56:402–7.
Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW, Zwinderman AH, Olivier B. An empirical operationalization study of DSM-IV diagnostic criteria for premature ejaculation. Intern J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 1998;2:287–93.
Waldinger MD, Quinn P, Dilleen M, Mundayat R, Schweitzer DH, Boolell M. A Multi-national population survey of Intravaginal Ejaculation Latency Time. J Sex Med. 2005;2:492–7.
Waldinger MD, McIntosh J, Schweitzer DH. A five-nation survey to assess the distribution of the intravaginal ejaculatory latency time among the general male population. J Sex Med. 2009;6:2888–95.
Fanciullacci F, Colpi GM, Beretta G, Zanollo A. Cortical evoked potentials in subjects with true premature ejaculation. Andrologia. 1988;20:326–30.
Colpi GM, Fanciullacci F, Beretta G, Negri L, Zanollo A. Evoked sacral potentials in subjects with true premature ejaculation. Andrologia. 1986;18:583–6.
Segraves RT, Saran A, Segraves K, Maguire E. Clomipramine vs placebo in the treatment of premature ejaculation. Prague, Czechoslovakia: Paper presented at the meeting of the International Academy of Sex Research; 1992.
Mackenzie A, Reynolds JD, Sutherland W. “Variation in Male Mating Success on Leks”. Am Nat. 1995;145:633–52.
Flamingo Maring Dance: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CUb0evFZbNM
Doyal L. Sex and gender: the challenges for epidemiologists. Int J Health Serv. 2003;33:569–79.
Payne S. “Smoke like a man die like a man”? A review of the relationship between gender, sex and lung cancer. Soc Sci Med. 2001;53:1067–80.
Mos J, Olivier B, Bloetjes K, Poth M. Drug-induced facilitation of sexual behavior in the male rat: Behavioral and pharmacological integration. In: Slob AK, Baum MJ, editors. Psychoneuroendocrinology of growth and development. Bussum, The Netherlands: Medicom Europe; 1990. p. 221–32.
Olivier B, Mos J. Animal psychobiology. In: Archer T, Hansen S, editors, Behavioral Biology: Neuroendocrine Axis. Hillsdale, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1991.
Agmo A, Fernandeze H. Dopamine and sexual behavior in the male rat: a reevaluation. J Neural Transm. 1989;77:21–37.
Ahlenius S, Larsson K, Svensson L. Further evidence for an inhibitory role of central 5-HT in male rat sexual behavior. Psychopharmacology. 1980;68:217–20.
Pattij T, de Jong T, Uitterdijk A, Waldinger MD, Veening JG, van der Graaf PH, et al. Individual differences in male rat ejaculatory behavior: searching for models to study ejaculation disorders. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22:724–34.
Pattij T, Olivier B, Waldinger MD. Animal models of ejaculatory behaviour. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:4069–77.
Patrick DL, Althof SE, Pryor JL, Rosen R, Rowland DL, Ho KF, et al. Premature ejaculation: an observational study of men and their partners. J Sex Med. 2005;2:358–67.
Giuliano F, Patrick DL, Porst H, La Pera G, Kokoszka A, Merchant S, et al. Premature ejaculation: results from a Five-country European observational study. Eur Urol. 2008;53:1048–57.
Janssen PKC, Waldinger MD. The mathematical formula of the intravaginale ejaculation latency time (IELT) distribution of lifelong premature ejaculation differs from the IELT distribution formula of men in the general male population. Investig Clin Urol. 2016;57:119–28.
Mos J, Mollet I, JTBM Tolboom, Waldinger MD, Olivier B. A comparison of the effects of different serotonin reuptake blockers on sexual behaviour of the male rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;9:123–35.
de Jong TR, Pattij T, Veening JG, Waldinger MD, Cools AR, Olivier B. Effects of chronic selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on 8-OH-DPAT-induced facilitation of ejaculation in rats: comparison of fluvoxamine and paroxetine. Psychopharmacology. 2005;179:509–15.
Olivier JD, de Jong TR, Jos Dederen P, van Oorschot T, Heeren D, Pattij T, et al. Effects of acute and chronic apomorphine on sex behaviour and copulation-induced neural activation in the male rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;576:61–76.
Olivier B, Chan JS, Snoeren EM, Olivier JD, Veening JG, Vinkers CH, et al. Differences in sexual behaviour in male and female rodents: role of serotonin. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2011;8:15–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Waldinger is an adviser of Emotional Brain B.V. and Sapphire Pharmaceuticals
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldinger, M.D., Schweitzer, D.H. Method and design of drug treatment research of subjective premature ejaculation in men differs from that of lifelong premature ejaculation in males: proposal for a new objective measure (part 1). Int J Impot Res 31, 328–333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0107-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0107-6
This article is cited by
-
Current and emerging treatment options for premature ejaculation
Nature Reviews Urology (2022)
-
Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation: a continuum movens supporting couple sexual dysfunction
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2022)
-
Redefining a sexual medicine paradigm: subclinical premature ejaculation as a new taxonomic entity
Nature Reviews Urology (2021)
-
Use of a confirmed mathematical method for back-analysis of IELT distributions: ejaculation time differences between two continents and between continents and men with lifelong premature ejaculation (Part 1)
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)
-
Men with subjective premature ejaculation have a similar lognormal IELT distribution as men in the general male population and differ mathematically from males with lifelong premature ejaculation after an IELT of 1.5 minutes (Part 2)
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)