Abstract
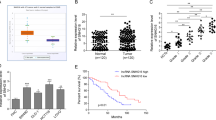
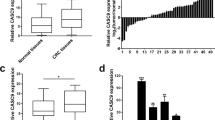
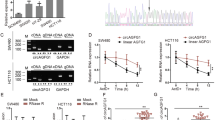
Recent researches have reported that long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) five prime to Xist (FTX) plays a crucial role in the initiation and progression of cancers. In the current study, the clinical significance and functional roles of lncRNA FTX in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression were investigated. A significant increase of lncRNA FTX expression in CRC tissue and cell lines was observed. Overexpression of lncRNA FTX was significantly associated with the bigger tumor diameter, the advanced TNM stage, the lymph node, and distant metastasis, and also predicted poor prognosis of patients with CRC. Functional analyses demonstrated that knockdown of lncRNA FTX markedly inhibited CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro. Mechanistically, FTX directly interacted with miR-215 and suppressed miR-215 expression. FTX also bind to vimentin and reduced its phosphorylation level on Ser83 in CRC cells. Finally, using siRNAs against lncRNA FTX could dramatically inhibit CRC growth and distant metastasis in vivo. Taken together, our data demonstrated an oncogenic role of lncRNA FTX in CRC tumorigenesis and progression via interaction with miR-215 and vimentin. Then, a promising therapeutic target for CRC was provided.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:104–17.
Day LW, Velayos F. Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance in the elderly: updates and controversies. Gut Liver. 2015;9:143–51.
Flynn RA, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cell-fate programming and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:752–61.
Chen S, Zhu J, Wang F, Guan Z, Ge Y, Yang X, et al. LncRNAs and their role in cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:110685–92.
Wangyang Z, Daolin J, Yi X, Zhenglong L, Lining H, Yunfu C, et al. NcRNAs and Cholangiocarcinoma. J Cancer. 2018;9:100–7.
Slaby O, Laga R, Sedlacek O. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J. 2017;474:4219–51.
Huang W, Tian Y, Dong S, Cha Y, Li J, Guo X, et al. The long non-coding RNA SNHG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to promote malignant development of colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:1402–10.
Chureau C, Chantalat S, Romito A, Galvani A, Duret L, Avner P, et al. Ftx is a non-coding RNA which affects Xist expression and chromatin structure within the X-inactivation center region. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20:705–18.
Liu F, Yuan JH, Huang JF, Yang F, Wang TT, Ma JZ, et al. Long noncoding RNA FTX inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by binding MCM2 and miR-374a. Oncogene. 2016;35:5422–34.
Zhang W, Bi Y, Li J, Peng F, Li H, Li C, et al. Long noncoding RNA FTX is upregulated in gliomas and promotes proliferation and invasion of glioma cells by negatively regulating miR-342-3p. Lab Investig; a J Tech Methods Pathol. 2017;97:447–57.
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Merhautova J, Machackova T, Gutierrez-Garcia I, Garcia-Solano J, Radova L, et al. MiR-215-5p is a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer targeting EGFR ligand epiregulin and its transcriptional inducer HOXB9. Oncogenesis. 2017;6:399.
Chen DL, Lu YX, Zhang JX, Wei XL, Wang F, Zeng ZL, et al. Long non-coding RNA UICLM promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by acting as a ceRNA for microRNA-215 to regulate ZEB2 expression. Theranostics. 2017;7:4836–49.
Lin Y, Jin Y, Xu T, Zhou S, Cui M. MicroRNA-215 targets NOB1 and inhibits growth and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9:466–77.
Zang Y, Wang T, Pan J, Gao F. miR-215 promotes cell migration and invasion of gastric cancer cell lines by targeting FOXO1. Neoplasma. 2017;64:579–87.
Chen Z, Han S, Huang W, Wu J, Liu Y, Cai S, et al. MicroRNA-215 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer by repressing Yin-Yang 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479:482–8.
Yang Y, Jiang C, Yang Y, Guo L, Huang J, Liu X et al. Silencing of LncRNA-HOTAIR decreases drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inactivating autophagy via suppressing the phosphorylation of ULK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018.
He X, Sun F, Guo F, Wang K, Gao Y, Feng Y, et al. Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA FTX inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in renal cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Res. 2017;25:157–66.
Li QW, Zhou T, Wang F, Jiang M, Liu CB, Zhang KR, et al. MicroRNA-215 functions as a tumor suppressor and directly targets ZEB2 in human pancreatic cancer. Genet Mol Res: GMR. 2015;14:16133–45.
Dave JM, Bayless KJ. Vimentin as an integral regulator of cell adhesion and endothelial sprouting. Microcirculation. 2014;21:333–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, X. et al. LncRNA FTX sponges miR-215 and inhibits phosphorylation of vimentin for promoting colorectal cancer progression. Gene Ther 25, 321–330 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-018-0026-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-018-0026-7
This article is cited by
-
Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA FTX in human disorders
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)
-
LncRNA RPLP0P2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Invasion via the miR-129-5p/Zinc Finger and BTB Domain-Containing 20 Axis
Biochemical Genetics (2023)
-
Prognostic significance of long non-coding RNA five prime to XIST in various cancers
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Non-coding RNAs and epithelial mesenchymal transition in cancer: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
Long noncoding RNA Ftx regulates the protein expression profile in HCT116 human colon cancer cells
Proteome Science (2022)