Abstract
Background/objective
To investigate the impact of preoperative immunological and nutritional status, using the prognostic nutritional index (PNI), on completion of planned adjuvant chemotherapy (AC), and the potential additive effects of low PNI and incomplete AC on gastric cancer-specific survival (CSS) after curative resection of stage II/III gastric cancer (GC).
Methods
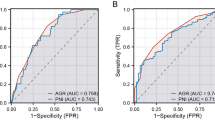
Medical records of 1288 consecutive stage II/III GC patients who underwent curative resection and planned to receive AC between November 2010 and December 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. The optimal cut-off value of PNI for CSS was determined by X-tile. The independent predictive factors for incomplete AC were identified using univariate and multivariate analyses. Cox regression analyses assessed the association of low PNI, incomplete AC and CSS.
Results
Of the 1288 patients, 406 (31.5%) completed at least six cycles of AC within 6 months following initial of AC (complete AC). Low PNI (<43.9, n = 386) was identified to be an independent risk factor for incomplete AC (<6 cycles). Both low PNI and incomplete AC independently predicted poor CSS (hazard ratio (HR): 1.287, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.058–1.565; HR: 1.667, 95% CI: 1.342–2.071). Further analyses confirmed an additive effect with those with both low PNI and incomplete AC having an even worse CSS.
Conclusions
Low preoperative PNI significantly affects completion of AC. Low PNI and incomplete AC has an additive effect and is associated with even worse outcomes. Further prospective studies are needed to clarify whether perioperative nutrition intervention could improve completion of AC and improve prognosis of GC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32.
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, Hundahl SA, Estes NC, Stemmermann GN, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:725–30.
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2014 (ver. 4). Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:1–19.
Ajani JA, D’Amico TA, Almhanna K, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Das P, et al. Gastric cancer, version 3.2016, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:1286–312.
Sakuramoto S, Sasako M, Yamaquchi T, Kinoshita T, Fujii M, Nashimoto A, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer with S-1, an oral fluoropyrimidine. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:10–1820.
Tsuburaya A, Yoshida K, Kobayashi M, Yoshino S, Takahashi M, Takiquchi N, et al. Sequential paclitaxel followed by tegafur and uracil (UFT) or S-1 versus UFT or S-1 monotherapy as adjuvant chemotherapy for T4a/b gastric cancer (SAMIT): a phase 3 factorial randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:886–93.
Cats A, Jansen EPM, van Grieken NCT, Skorsha K, Lind P, Nordsmark M, et al. Chemotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy after surgery and preoperative chemotherapy for resectable gastric cancer (CRITICS): an international, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:616–28.
Noh SH, Park SR, Yang HK, Chung HC, Chung IJ, Kim SW, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine plus oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): 5-year follow-up of an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1389–96.
Morris M, Platell C, Fritschi L, lacopetta B. Failure to complete adjuvant chemotherapy is associated with adverse survival in stage III colon cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2007;96:701–7.
Matsumoto I, Tanaka M, Shirakawa S, Shinzeki M, Toyama H, Asari S, et al. Postoperative serum albumin level is a marker of incomplete adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:2408–24.
Yang Y, Gao P, Song Y, Sun J, Chen X, Zhao J, et al. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016;42:1176–82.
Chan AW, Chan SL, Wong GL, Wong WV, Chong CC, Lai PB, et al. Prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts tumor recurrence of very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:4138–48.
Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Shirai J, Hayashi T, Yamada T, Tsuchida K, et al. Body weight loss after surgery is an independent risk factor for continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:2000–6.
Yamashita K, Kurokawa Y, Yamamoto K, Hirota M, Kawabata R, Mikami J, et al. Compliance with adjuvant S-1 chemotherapy for gastric cancer: a multicenter retrospective study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017;24:2639–45.
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Brierley JD. AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer; 2017.
Xiao H, Xiao Y, Quan H, Liu W, Pan S, Ouyang Y. Intra-abdominal infection after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer: incidence, pathogens, risk factors and outcomes. Int J Surg. 2017;48:195–200.
Xiao H, Liu W, Quan H, Ouyang Y. Peri-operative blood transfusion does not influence overall and disease-free survival after radical gastrectomy for stage II/III gastric cancer: a propensity score matching analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2018;22:1489–500.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Shitara K, Chin K, Yoshikawa T, Katai H, Terashima M, Ito S, et al. Phase II study of adjuvant chemotherapy of S-1 plus oxaliplatin for patients with stage III gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:175–81.
Onodera T, Goseki N, Kosakim G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Zasshi. 1984;85:1001–5.
Shen Q, Liu W, Quan H, Pan S, Li S, Zhou T, et al. Prealbumin and lymphocyte-based prognostic score, a new tool for predicting long-term survival after curative resection of stage II/III gastric cancer. Br J Nutr. 2018;120:1359–69.
Aquina CT, Blumberg N, Becerra AZ, Boscoe FP, Schymura MJ, Noyes K, et al. Association among blood transfusion, sepsis, and decreased long-term survival after colon cancer resection. Ann Surg. 2017;266:311–7.
Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Shields AF, Yoshino T, Paul J, Taieb J, et al. Duration of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer. N Eng J Med. 2018;378:1177–88.
Yoshikawa T, Terashima M, Mizusawa J, Nunobe S, Nishida Y, Yamada T. et al. Four courses versus eight courses of adjuvant S-1 for patients with stage II gastric cancer (JCOG1104 [OPAS-1]): an open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol.2019;4:208–16.
Jang SH, Jung YJ, Kim MG, Kwon SJ. The prognostic significance of compliance with postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage III gastric cancer: an observational study. J Gastric Cancer. 2018;18:48–57.
Aoyama T, Kawabe T, Fujikawa H, Hayashi T, Yamada T, Tsuchida K, et al. Loss of lean body mass as an independent risk factor for continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:2560–6.
Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi T, Kuwabara H, Mikayama Y, Oqata T, et al. Risk factors for 6-months continuation of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:133–9.
Sasako M, Sakuramoto S, Katai H, Kinoshita T, Furukawa H, Yamaquchi T, et al. Five-year outcomes of a randomized phase III trial comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 versus surgery alone in stage II or III gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4387–93.
Kim IH, Park SS, Lee CM, Kim MC, Kwon IK, Min JS, et al. Efficacy of adjuvant S-1 versus XELOX chemotherapy for patients with gastric cancer after D2 lymph node dissection: a retrospective, multi-center observational study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:1176–83.
Bao H, Xu N, Li Z, Ren H, Xia H, Li N, et al. Effect of laparoscopic gastrectomy on compliance with adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancer. Medicine. 2017;96:e6839.
Xu J, Zhong Y, Jing D, Wu D. Preoperative enteral immunonutrition improves postoperative outcome in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. World J Surg. 2006;30:1284–9.
Sun X, Wang J, Liu J, Chen S, Liu X. Albumin concentrations plus neutrophil lymphocyte ratios for predicting overall survival after curative resection for gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:4661–9.
Choi Y, Kim JW, Nam KH, Han SH, Kim JW, Ahn SH, et al. Systemic inflammation is associated with the density of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:602–11.
Zhang B, Wei G, Li R, Wang Y, Yu J, Wang R, et al. n-3 fatty acid-based parenteral nutrition improves postoperative recovery for cirrhotic patients with liver cancer: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 2017;36:1239–44.
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:11–20.
Cho YH, Kim SY, Hong Lee M, Yoo MW, Bang HY, Lee KY, et al. Comparative analysis of the efficacy and safety of chemotherapy with oxaliplatin plus fluorouracil/leucovorin between elderly patients over 65 years and younger patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2012;15:389–95.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank all of the participants in this study and Hunan Cancer Hospital for supporting this study.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (no. 2018JJ6108) and the 2017 Annual Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Hunan Province (no. B2017101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HX, XLY, and YZOY contributed to the conception and the design of the study; HX, HJZ, PZ, HFX, KL, XYC, HQ, BY, RRL, and GH collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data; HX grafted the manuscript. XLY and YZOY critically revised the manuscript. All authors agree to be fully accountable for ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the work, and read and approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, H., Zhou, H., Zhang, P. et al. Association among the prognostic nutritional index, completion of adjuvant chemotherapy, and cancer-specific survival after curative resection of stage II/III gastric cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr 74, 555–564 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-019-0502-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-019-0502-1
This article is cited by
-
Nomogram to predict overall survival of patients receiving radical gastrectomy and incomplete peri-operative adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II/III gastric cancer: a retrospective bi-center cohort study
BMC Cancer (2024)
-
Prognostic value of post-operative serum procalcitonin in gastric adenocarcinoma patients undergoing radical gastrectomy: propensity score matching analysis of extended cohort from a prospective bi-center study
Gastric Cancer (2023)
-
Association among prognostic nutritional index, post-operative infection and prognosis of stage II/III gastric cancer patients following radical gastrectomy
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2022)