Abstract
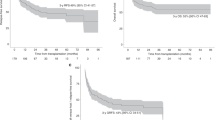
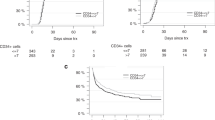
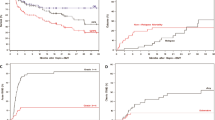
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation is a curative therapy for myelofibrosis. The optimal conditioning regimen has not been well defined. We retrospectively compared transplantation outcomes in patients with myelofibrosis (n = 67) conditioned with myeloablative (MAC, 36%) and reduced-intensity (RIC, 46%) regimens, and more recently with the combination of thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine (TBF, 18%). Patients were transplanted from HLA-matched sibling (n = 26) or unrelated donors (n = 41) between the years 2003 and 2018. The median follow-up was 2.9 years for all patients but shorter in the TBF group (1.1 years). The probability of 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 43%. At 1 year, the rate of PFS was 80%, 54%, and 45% with TBF, MAC, and RIC, respectively (p = 0.031). In a multivariable model, there was a greater risk for death with MAC (hazard ratio [HR] 12.26, p = 0.026) and lower PFS with both MAC (hazard ratio [HR] 7.78, p = 0.017) and RIC (HR 5.43, p = 0.027) compared with TBF. Relapse was higher with RIC (HR 8.20, p = 0.043) while nonrelapse mortality was increased with MAC (HR 9.63 p = 0.049). Our results indicate that TBF is a promising preparative regimen in myelofibrosis patients transplanted from matched sibling or unrelated donors, and should be further explored.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–405. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
Tefferi A. Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. New Engl J Med. 2000;342:1255–65.
Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:799–807. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1110557
Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V, et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:787–98. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1110556
Kroger NM, Deeg JH, Olavarria E, Niederwieser D, Bacigalupo A, Barbui T, et al. Indication and management of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in primary myelofibrosis: a consensus process by an EBMT/ELN international working group. Leukemia. 2015;29:2126–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.233
Kroger N, Giorgino T, Scott BL, Ditschkowski M, Alchalby H, Cervantes F, et al. Impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation on survival of patients less than 65 years of age with primary myelofibrosis. Blood. 2015;125:3347–50. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-10-608315.
Passamonti F, Cervantes F, Vannucchi AM, Morra E, Rumi E, Pereira A, et al. A dynamic prognostic model to predict survival in primary myelofibrosis: a study by the IWG-MRT (International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Research and Treatment). Blood. 2010;115:1703–8. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-09-245837
Gangat N, Caramazza D, Vaidya R, George G, Begna K, Schwager S, et al. DIPSS plus: a refined Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System for primary myelofibrosis that incorporates prognostic information from karyotype, platelet count, and transfusion status. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:392–7. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.32.2446
Tefferi A, Guglielmelli P, Lasho TL, Gangat N, Ketterling RP, Pardanani A, et al. MIPSS70+ version 2.0: Mutation and Karyotype-Enhanced International Prognostic Scoring System for primary myelofibrosis. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:1769–70. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2018.78.9867
Guardiola P, Anderson JE, Bandini G, Cervantes F, Runde V, Arcese W, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: a European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation, Societe Francaise de Greffe de Moelle, Gruppo Italiano per il Trapianto del Midollo Osseo, and Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Collaborative Study. Blood. 1999;93:2831–8.
Kerbauy DM, Gooley TA, Sale GE, Flowers ME, Doney KC, Georges GE, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation as curative therapy for idiopathic myelofibrosis, advanced polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13:355–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.11.004
Mesa RA, Silverstein MN, Jacobsen SJ, Wollan PC, Tefferi A. Population-based incidence and survival figures in essential thrombocythemia and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: an Olmsted County Study, 1976-1995. Am J Hematol. 1999;61:10–15.
Kroger N, Holler E, Kobbe G, Bornhauser M, Schwerdtfeger R, Baurmann H, et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation after reduced-intensity conditioning in patients with myelofibrosis: a prospective, multicenter study of the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2009;114:5264–70. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-234880
Rondelli D, Goldberg JD, Isola L, Price LS, Shore TB, Boyer M, et al. MPD-RC 101 prospective study of reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with myelofibrosis. Blood. 2014;124:1183–91. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-04-572545
Gupta V, Malone AK, Hari PN, Ahn KW, Hu ZH, Gale RP, et al. Reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with primary myelofibrosis: a cohort analysis from the center for international blood and marrow transplant research. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.10.018
Jain T, Kunze KL, Temkit M, Partain DK, Patnaik MS, Slack JL, et al. Comparison of reduced intensity conditioning regimens used in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelofibrosis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54:204–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0226-1
Sanz J, Boluda JC, Martin C, Gonzalez M, Ferra C, Serrano D, et al. Single-unit umbilical cord blood transplantation from unrelated donors in patients with hematological malignancy using busulfan, thiotepa, fludarabine and ATG as myeloablative conditioning regimen. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47:1287–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.13
Ruggeri A, Sanz G, Bittencourt H, Sanz J, Rambaldi A, Volt F, et al. Comparison of outcomes after single or double cord blood transplantation in adults with acute leukemia using different types of myeloablative conditioning regimen, a retrospective study on behalf of Eurocord and the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Leukemia. 2014;28:779–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.259
Giannotti F, Labopin M, Shouval R, Sanz J, Arcese W, Angelucci E, et al. Haploidentical transplantation is associated with better overall survival when compared to single cord blood transplantation: an EBMT-Eurocord study of acute leukemia patients conditioned with thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0655-8
Di Bartolomeo P, Santarone S, De Angelis G, Picardi A, Cudillo L, Cerretti R, et al. Haploidentical, unmanipulated, G-CSF-primed bone marrow transplantation for patients with high-risk hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2013;121:849–57. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-08-453399
Raiola AM, Dominietto A, Ghiso A, Di Grazia C, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical bone marrow transplantation and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide for hematologic malignancies after myeloablative conditioning. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:117–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.08.014
Saraceni F, Labopin M, Hamladji RM, Mufti G, Socie G, Shimoni A, et al. Thiotepa-busulfan-fludarabine compared to busulfan-fludarabine for sibling and unrelated donor transplant in acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. Oncotarget. 2018;9:3379–93. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23273
Saraceni F, Beohou E, Labopin M, Arcese W, Bonifazi F, Stepensky P, et al. Thiotepa, busulfan and fludarabine compared to busulfan and cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplant from matched siblings and unrelated donors for acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:1211–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25225
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:1628–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.07.004
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J, et al. 1994 Consensus conference on acute GVHD grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;15:825–8.
Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, Socie G, Wingard JR, Lee SJ, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11:945–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2005.09.004
Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kröger N, ediotrs. The EBMT handbook: hematopoietic stem cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies. Springer; 2019.
Dulery R, Bastos J, Paviglianiti A, Malard F, Brissot E, Battipaglia G, et al. Thiotepa, busulfan, and fludarabine conditioning regimen in T cell-replete HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1407–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.02.025
Patriarca F, Masciulli A, Bacigalupo A, Bregante S, Pavoni C, Finazzi MC, et al. Busulfan- or thiotepa-based conditioning in myelofibrosis: a phase ii multicenter randomized study from the GITMO Group. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.064
Ballen KK, Shrestha S, Sobocinski KA, Zhang MJ, Bashey A, Bolwell BJ, et al. Outcome of transplantation for myelofibrosis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16:358–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.10.025
Bregante S, Dominietto A, Ghiso A, Raiola AM, Gualandi F, Varaldo R, et al. Improved outcome of alternative donor transplantations in patients with myelofibrosis: from unrelated to haploidentical family donors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:324–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.09.028
Raj K, Eikema DJ, McLornan DP, Olavarria E, Blok HJ, Bregante S, et al. Family mismatched allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: report from the chronic malignancies working party of European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.10.017
McClune BL, Weisdorf DJ, Pedersen TL, Tunes da Silva G, Tallman MS, Sierra J, et al. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1878–87. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4821
Blaise D, Devillier R, Lecoroller-Sorriano AG, Boher JM, Boyer-Chammard A, Tabrizi R, et al. Low non-relapse mortality and long-term preserved quality of life in older patients undergoing matched related donor allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a prospective multicenter phase II trial. Haematologica. 2015;100:269–74. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2014.113571
Versluis J, Labopin M, Niederwieser D, Socie G, Schlenk RF, Milpied N, et al. Prediction of non-relapse mortality in recipients of reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation with AML in first complete remission. Leukemia. 2015;29:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2014.164
Cornelissen JJ, Blaise D. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with AML in first complete remission. Blood. 2016;127:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-07-604546
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by The Varda and Boaz Dotan Research Center in Hemato-Oncology affiliated with the Cancer Biology Research Center—Tel Aviv University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Senior authors: Arnon Nagler, Avichai Shimoni
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shouval, R., Vega, Y., Fein, J.A. et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with fludarabine, busulfan, and thiotepa conditioning is associated with favorable outcomes in myelofibrosis. Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 147–156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-019-0653-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-019-0653-7
This article is cited by
-
The application of JAK inhibitors in the peri-transplantation period of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelofibrosis
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Treosulfan compared to busulfan in allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: a registry-based study from the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2024)
-
Thiotepa–busulfan–fludarabine (TBF) conditioning regimen in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for myelofibrosis: an outcome analysis from the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2021)