Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to compare the efficacy and safety of transurethral enucleation and resection of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Materials and methods
This meta-analysis was conducted through a systematic search before 1 September 2018. All included publications were randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Efficacy was evaluated based on International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), and quality of life (QoL). Perioperative data and complications postoperatively were also assessed. The quality assessment of included studies and results was performed by using the Cochrane System and GRADE (grading of recommendation assessment, development, and evaluation) System.
Results
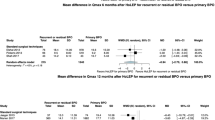
Thirty-one publications involving 26 RCTs with 3283 patients were assessed in this review. The differences between enucleation and resection in IPSS, Qmax, and QoL at 1, 3, and 6 months postoperative were not significant. At 12 months postoperatively, IPSS and Qmax in the enucleation group were significantly better than those in the resection group. The results also suggested a benefit of enucleation over resection in hospital stay, hemoglobin loss, serum sodium decrease, blood transfusion rate, grade II, grade III complications, and early complications. However, resection exhibited a better operative time.
Conclusion
Compared with resection, enucleation showed better efficacy and safety postoperatively with less hematological changes and severe complications, except for longer operative time.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reich O, Seitz M, Gratzke C, Schlenker B, Walther S, Stief C. [Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): surgical therapy options]. Urol A. 2010;49:113–26.
Reich O, Gratzke C, Bachmann A, Seitz M, Schlenker B, Hermanek P, et al. Morbidity, mortality and early outcome of transurethral resection of the prostate: a prospective multicenter evaluation of 10,654 patients. J Urol. 2008;180:246–9.
Rassweiler J, Teber D, Kuntz R, Hofmann R. Complications of transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)--incidence, management, and prevention. Eur Urol. 2006;50:969–79. Discussion 980
Ho HS, Yip SK, Lim KB, Fook S, Foo KT, Cheng CW. A prospective randomized study comparing monopolar and bipolar transurethral resection of prostate using transurethral resection in saline (TURIS) system. Eur Urol. 2007;52:517–22.
Gilling CC, Cass CB, Malcolm AR, Fraundorfer MR. Combination holmium and Nd:YAG laser ablation of the prostate: initial clinical experience. J Endourol. 1995;9:151–3.
Herrmann TR, Bach T, Imkamp F, Georgiou A, Burchardt M, Oelke M, et al. Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP): transurethral anatomical prostatectomy with laser support. Introduction of a novel technique for the treatment of benign prostatic obstruction. World J Urol. 2010;28:45–51.
Kyriazis I, Swiniarski PP, Jutzi S, Wolters M, Netsch C, Burchardt M, et al. Transurethral anatomical enucleation of the prostate with Tm:YAG support (ThuLEP): review of the literature on a novel surgical approach in the management of benign prostatic enlargement. World J Urol. 2015;33:525–30.
Wendt-Nordahl G, Huckele S, Honeck P, Alken P, Knoll T, Michel MS, et al. 980-nm Diode laser: a novel laser technology for vaporization of the prostate. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1723–8.
Neill MG, Gilling PJ, Kennett KM, Frampton CM, Westenberg AM, Fraundorfer MR, et al. Randomized trial comparing holmium laser enucleation of prostate with plasmakinetic enucleation of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2006;68:1020–4.
Rao JM, Yang JR, Ren YX, He J, Ding P, Yang JH. Plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate versus transvesical open prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia>80 mL: 12-month follow-up results of a randomized clinical trial. Urology. 2013;82:176–81.
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:401–6.
Ahyai SA, Chun FK, Lehrich K, Dahlem R, Zacharias MS, Fisch MM, et al. Transurethral holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate and simple open prostatectomy--which procedure is faster? J Urol. 2012;187:1608–13.
Ahyai SA, Lehrich K, Kuntz RM. Holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: 3-year follow-up results of a randomized clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2007;52:1456–63.
Bozzini G, Seveso M, Melegari S, de Francesco O, Buffi NM, Guazzoni G, et al. Thulium laser enucleation (ThuLEP) versus transurethral resection of the prostate in saline (TURis): a randomized prospective trial to compare intra and early postoperative outcomes. Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed). 2017;41:309–15.
Briganti A, Naspro R, Gallina A, Salonia A, Vavassori I, Hurle R, et al. Impact on sexual function of holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: results of a prospective, 2-center, randomized trial. J Urol. 2006;175:1817–21.
Chang CH, Lin TP, Chang YH, Huang WJ, Lin AT, Chen KK. Vapoenucleation of the prostate using a high-power thulium laser: a one-year follow-up study. BMC Urol. 2015;15:40.
Chen YB, Chen Q, Wang Z, Peng YB, Ma LM, Zheng DC, et al. A prospective, randomized clinical trial comparing plasmakinetic resection of the prostate with holmium laser enucleation of the prostate based on a 2-year followup. J Urol. 2013;189:217–22.
Dragoslav Bašic JS, Potic Milan, Ignjatovic Ivan. Holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: a comparison of clinical results. Acta Chir Iugosl. 2013;60:15–20.
Fayad AS, Elsheikh MG, Zakaria T, Elfottoh HA, Alsergany R, Elshenoufy A, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus bipolar resection of the prostate: a prospective randomized study. “Pros and Cons”. Urology. 2015;86:1037–41.
Fayad AS, Sheikh MG, Zakaria T, Elfottoh HA, Alsergany R. Holmium laser enucleation versus bipolar resection of the prostate: a prospective randomized study. Which to choose? J Endourol. 2011;25:1347–52.
Gilling PJ, Wilson LC, King CJ, Westenberg AM, Frampton CM, Fraundorfer MR. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing holmium laser enucleation of the prostate and transurethral resection of the prostate: results at 7 years. BJU Int. 2012;109:408–11.
Gu M, Chen YB, Liu C, Wan X, Cai ZK, Chen Q, et al. Comparison of holmium laser enucleation and plasmakinetic resection of prostate: a randomized trial with 72-month follow-up. J Endourol. 2018;32:139–43.
Gupta N, Sivaramakrishna, Kumar R, Dogra PN, Seth A. Comparison of standard transurethral resection, transurethral vapour resection and holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia of > 40 g. BJU Int. 2006;97:85–9.
Hamouda A, Morsi G, Habib E, Hamouda H, Emam AB, Etafy M. A comparative study between holmium laser enucleation of the prostate and transurethral resection of the prostate: 12-month follow-up. J Clin Urol. 2016;7:99–104.
Jhanwar A, Sinha RJ, Bansal A, Prakash G, Singh K, Singh V. Outcomes of transurethral resection and holmium laser enucleation in more than 60 g of prostate: a prospective randomized study. Urol Ann. 2017;9:45–50.
Kuntz RM, Ahyai S, Lehrich K, Fayad A. Transurethral holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus transurethral electrocautery resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial in 200 patients. J Urol. 2004;172:1012–6.
Li K, Wang D, Hu C, Mao Y, Li M, Si-Tu J, et al. A novel modification of transurethral enucleation and resection of the prostate in patients with prostate glands larger than 80 mL: surgical procedures and clinical outcomes. Urology. 2018;113:153–9.
Luo YH, Shen JH, Guan RY, Li H, Wang J. Plasmakinetic enucleation of the prostate vs plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: comparison of outcomes according to prostate size in 310 patients. Urology. 2014;84:904–10.
A.Eltabey M, Sherif H, A.Hussein A. Holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate. Can J Urol. 2010;17:5447–52.
Mavuduru RM, Mandal AK, Singh SK, Acharya N, Agarwal M, Garg S, et al. Comparison of HoLEP and TURP in terms of efficacy in the early postoperative period and perioperative morbidity. Urol Int. 2009;82:130–5.
Montorsi F, Naspro R, Salonia A, Suardi N, Briganti A, Zanoni M, et al. Holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: results from a 2-center, prospective, randomized trial in patients with obstructive benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2004;172:1926–9.
Świniarski Piotrpaweł, S S, Dudzic waldemar, kęsy Stanisław. Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (TmLEP)vs. transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP):evaluation of early results. Cent Eur J Urol. 2012;65:130–4.
Ran L, He W, Zhu X, Zhou Q, Gou X. Comparison of fluid absorption between transurethral enucleation and transurethral resection for benign prostate hyperplasia. Urol Int. 2013;91:26–30.
Sun N, Fu Y, Tian T, Gao J, Wang Y, Wang S, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus transurethral resection of the prostate: a randomized clinical trial. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014;46:1277–82.
Tan AH, Gilling PJ, Kennett KM, Frampton C, Westenberg AM, Fraundorfer MR. A randomized trial comparing holmium laser enucleation of the prostate with transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of bladder outlet obstruction secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia in large glands (40 to 200 grams). J Urol. 2003;170:1270–4.
Wilson LC, Gilling PJ, Williams A, Kennett KM, Frampton CM, Westenberg AM, et al. A randomised trial comparing holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection in the treatment of prostates larger than 40 grams: results at 2 years. Eur Urol. 2006;50:569–73.
Yang SS, Hsieh CH, Lee YS, Chang SJ. Diode laser (980 nm) enucleation of the prostate: a promising alternative to transurethral resection of the prostate. Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28:353–60.
Yang Z, Liu T, Wang X. Comparison of thulium laser enucleation and plasmakinetic resection of the prostate in a randomized prospective trial with 5-year follow-up. Lasers Med Sci. 2016;31:1797–802.
Yang Z, Wang X, Liu T. Thulium laser enucleation versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial with 18-month follow-up. Urology. 2013;81:396–400.
Zhang K, Sun D, Zhang H, Cao Q, Fu Q. Plasmakinetic vapor enucleation of the prostate with button electrode versus plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic enlargement>90 ml: perioperative and 3-month follow-up results of a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Urol Int. 2015;95:260–4.
Zhao Z, Zeng G, Zhong W, Mai Z, Zeng S, Tao X. A prospective, randomised trial comparing plasmakinetic enucleation to standard transurethral resection of the prostate for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: three-year follow-up results. Eur Urol. 2010;58:752–8.
Zhu L, Chen S, Yang S, Wu M, Ge R, Wu W, et al. Electrosurgical enucleation versus bipolar transurethral resection for prostates larger than 70 ml: a prospective, randomized trial with 5-year followup. J Urol. 2013;189:1427–31.
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, Vauthey JN, Dindo D, Schulick RD, et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg. 2009;250:187–96.
Vuichoud C, Loughlin KR. Benign prostatic hyperplasia:epidemiology, economics and evaluation. Can J Urol. 2015;22(Suppl 1):1–6.
Rasch A, Gruber S, Perleth M. Learning curve in laser treatment of benign prostatic syndrome: a systematic review. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesund. 2013;107:335–43.
Shah HN, Mahajan AP, Sodha HS, Hegde S, Mohile PD, Bansal MB. Prospective evaluation of the learning curve for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Urol. 2007;177:1468–74.
EL-HAKIM A, ELHILALI MM. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate can be taught: the first learning experience. BJU Int. 2002;90:863–9.
Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, Nabi G, Deverill M, Pickard R, et al. Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:iii, ix–x. 1-146, 169-515
Mebust WK, Holtgrewe HL, Cockett, Peters ATK, Transurethral PC. prostatectomy: Immediate and postoperative complications. A cooperative study of 13 participating institutions evaluating 3,885 patients. J Urol. 1989;141:243–7.
Krambeck AE, Handa SE, Lingeman JE. Experience with more than 1,000 holmium laser prostate enucleations for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2010;183:1105–9.
Smith RD, Patel A. Transurethral resection of the prostate revisited and updated. Curr Opin Urol. 2011;21:36–41.
Liao N, Yu J. A study comparing plasmakinetic enucleation with bipolar plasmakinetic resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Endourol. 2012;26:884–8.
Lerner LB, Tyson MD, Mendoza PJ. Stress Incontinence during the learning curve of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Endourol. 2010;24:1655–58.
Kuntz RM, Lehrich K. Transurethral holmium laser enucleation versus transvesical open enucleation for prostate adenoma greater than 100 gm.: a randomized prospective trial of 120 patients. J Urol. 2002;168:1465–9.
Leliefeld HHJ, Stoevelaar HJ, McDonnell J. Sexual function before and after various treatments for symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2002;89:208–13.
Acknowledgements
YZ thanks his girlfriend Yuxiao Zhao, from Wuhan University, for her excellent advises on manuscript revision.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 81702518) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 81500636).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YZ and XL. Methodology: PY, XG, and CW. Formal analysis: ZL. Investigation: XG and CW. Writing: PY and YZ. Writing, review, editing, and revision: DM, YZ, and RL. Supervision: SW and JL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yuan, P., Ma, D. et al. Efficacy and safety of enucleation vs. resection of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 22, 493–508 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-019-0135-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-019-0135-4
This article is cited by
-
Bladder neck contracture following transurethral surgery of prostate: a retrospective single-center study
World Journal of Urology (2024)
-
Enucleation of the prostate as retreatment for recurrent or residual benign prostatic obstruction: a systematic review and a meta-analysis
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2023)
-
Robotic assisted simple prostatectomy versus other treatment modalities for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 6500 cases
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2023)
-
Comparison of surgical procedures for benign prostatic hyperplasia of medium-volume prostates: evaluation of the causes of rehospitalization from the French National Hospital Database (PMSI-MCO)
World Journal of Urology (2023)
-
Peri- and post-operative outcomes, complications, and functional results amongst different modifications of endoscopic enucleation of the prostate (EEP): a systematic review and meta-analysis
World Journal of Urology (2023)