Abstract
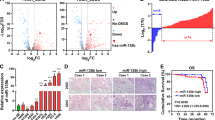
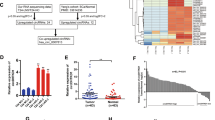
Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis has attracted increasing attention because of its potential contribution to lymph node metastasis. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying lymphangiogenesis in cancer remains elusive. In the current study, we demonstrate that tripartite motif-containing 3 (TRIM3) directly interacts with and induces E3 ligase-dependent proteasomal turnover of importin α3 and α-Actinin-4 (ACTN4), which controls nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity at a well-ordered level. Heterozygous deletion-mediated TRIM3 downregulation led to NF-κB constitutive activation through disruption of the NF-κB-IκB-α negative feedback loop and enhancement of the p65 DNA-binding affinity and transcriptional activity via promoting symmetrical dimethylarginine modification of NF-κB/p65 at Arg30 and Arg35, which consequently promoted lymphatic metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. Treatment with Tecfidera, a medication used to treat multiple sclerosis, restored the negative feedback inhibition of NF-κB by reducing the NF-κB/ACTN4 interaction and decreasing symmetrically dimethylated NF-κB levels, resulting in inhibition of ESCC lymphatic metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our results uncover a novel mechanism for constitutive NF-κB activation in cancer and may represent an attractive strategy to treat ESCC lymphatic metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature. 2005;438:946–53.
Dieterich LC, Detmar M. Tumor lymphangiogenesis and new drug development. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;99:148–60.
Hirakawa S. Regulation of pathological lymphangiogenesis requires factors distinct from those governing physiological lymphangiogenesis. J Dermatol Sci. 2011;61:85–93.
Schoppmann SF, Jesch B, Zacherl J, Riegler MF, Friedrich J, Birner P. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular invasion diminishes prognosis in esophageal cancer. Surgery. 2013;153:526–34.
Saad RS, Lindner JL, Liu Y, Silverman JF. Lymphatic vessel density as prognostic marker in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131:92–98.
Kumagai Y, Tachikawa T, Higashi M, Sobajima J, Takahashi A, Amano K. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factors C and D and lymphangiogenesis at the early stage of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Dis Esophagus. 2018;31:1–7.
Liu P, Zhou J, Zhu H, Xie L, Wang F, Liu B, et al. VEGF-C promotes the development of esophageal cancer via regulating CNTN-1 expression. Cytokine. 2011;55:8–17.
Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo H, Yla-Herttuala S, Jaattela M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1786–90.
Hirakawa S, Brown LF, Kodama S, Paavonen K, Alitalo K, Detmar M. VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites. Blood. 2007;109:1010–7.
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M, Compagni A, Baetens D, Prevo R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 2001;20:672–82.
He W, Zhong G, Jiang N, Wang B, Fan X, Chen C, et al. Long noncoding RNA BLACAT2 promotes bladder cancer-associated lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:861–75.
Feng Y, Hu J, Ma J, Feng K, Zhang X, Yang S, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:2353–63.
Lin C, Song L, Liu A, Gong H, Lin X, Wu J, et al. Overexpression of AKIP1 promotes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2015;34:384–93.
Su C, Chen Z, Luo H, Su Y, Liu W, Cai L, et al. Different patterns of NF-kappaB and Notch1 signaling contribute to tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:85.
Li F, Sethi G. Targeting transcription factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805:167–80.
Baud V, Karin M. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:33–40.
Trial watch: Phase III success for Biogen’s oral multiple sclerosis therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:404–404.
Peng H, Guerau-de-Arellano M, Mehta VB, Yang Y, Huss DJ, Papenfuss TL, et al. Dimethyl fumarate inhibits dendritic cell maturation via nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and mitogen stress-activated kinase 1 (MSK1) signaling. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:28017–26.
Nicolay JP, Muller-Decker K, Schroeder A, Brechmann M, Mobs M, Geraud C, et al. Dimethyl fumarate restores apoptosis sensitivity and inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in CTCL by targeting NF-kappaB. Blood. 2016;128:805–15.
Kastrati I, Siklos MI, Calderon-Gierszal EL, El-Shennawy L, Georgieva G, Thayer EN, et al. Dimethyl fumarate inhibits the nuclear factor kappab pathway in breast cancer cells by covalent modification of p65 protein. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:3639–47.
El-Husseini AE, Fretier P, Vincent SR. Cloning and characterization of a gene (RNF22) encoding a novel brain expressed ring finger protein (BERP) that maps to human chromosome 11p15.5. Genomics. 2001;71:363 –7.
Yan Q, Sun W, Kujala P, Lotfi Y, Vida TA, Bean AJ. CART: an Hrs/actinin-4/BERP/myosin V protein complex required for efficient receptor recycling. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:2470–82.
Schreiber J, Vegh MJ, Dawitz J, Kroon T, Loos M, Labonte D, et al. Ubiquitin ligase TRIM3 controls hippocampal plasticity and learning by regulating synaptic gamma-actin levels. J Cell Biol. 2015;211:569–86.
Mukherjee S, Tucker-Burden C, Zhang C, Moberg K, Read R, Hadjipanayis C, et al. Drosophila Brat and human ortholog TRIM3 maintain stem cell equilibrium and suppress brain tumorigenesis by attenuating notch nuclear transport. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2443–52.
Moskaluk CA, Rumpel CA. Allelic deletion in 11p15 is a common occurrence in esophageal and gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 1998;83:232–9.
Lam CT, Tang CM, Lau KW, Lung ML. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 11 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2002;178:75–81.
Carlotti F, Dower SK, Qwarnstrom EE. Dynamic shuttling of nuclear factor kappa B between the nucleus and cytoplasm as a consequence of inhibitor dissociation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:41028–34.
Chiao PJ, Miyamoto S, Verma IM. Autoregulation of I kappa B alpha activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:28–32.
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Thompson J, Rodriguez MS, Bachelerie F, Thomas D, Hay RT. Inducible nuclear expression of newly synthesized I kappa B alpha negatively regulates DNA-binding and transcriptional activities of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:2689–96.
Aksenova V, Turoverova L, Khotin M, Magnusson KE, Tulchinsky E, Melino G, et al. Actin-binding protein alpha-actinin 4 (ACTN4) is a transcriptional co-activator of RelA/p65 sub-unit of NF-kB. Oncotarget. 2013;4:362–72.
Zhao X, Hsu KS, Lim JH, Bruggeman LA, Kao HY. alpha-Actinin 4 potentiates nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cell (NF-kappaB) activity in podocytes independent of its cytoplasmic actin binding function. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:338–49.
Wei H, Wang B, Miyagi M, She Y, Gopalan B, Huang DB, et al. PRMT5 dimethylates R30 of the p65 subunit to activate NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:13516–21.
Stacker SA, Williams SP, Karnezis T, Shayan R, Fox SB, Achen MG. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodelling in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:159–72.
Ribatti D. Historical overview of lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Immunol. 2018;53:161–6.
Montes Diaz G, Fraussen J, Van Wijmeersch B, Hupperts R, Somers V. Dimethyl fumarate induces a persistent change in the composition of the innate and adaptive immune system in multiple sclerosis patients. Sci Rep. 2018;8:8194.
Smith MD, Calabresi PA, Bhargava P. Dimethyl fumarate treatment alters NK cell function in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol. 2018;48:380–3.
Honda K, Yamada T, Endo R, Ino Y, Gotoh M, Tsuda H, et al. Actinin-4, a novel actin-bundling protein associated with cell motility and cancer invasion. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:1383–93.
Agarwal N, Adhikari AS, Iyer SV, Hekmatdoost K, Welch DR, Iwakuma T. MTBP suppresses cell migration and filopodia formation by inhibiting ACTN4. Oncogene. 2013;32:462–70.
Chakraborty S, Reineke EL, Lam M, Li X, Liu Y, Gao C, et al. Alpha-actinin 4 potentiates myocyte enhancer factor-2 transcription activity by antagonizing histone deacetylase 7. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35070–80.
Khurana S, Chakraborty S, Cheng X, Su YT, Kao HY. The actin-binding protein, actinin alpha 4 (ACTN4), is a nuclear receptor coactivator that promotes proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:1850–9.
Khurana S, Chakraborty S, Zhao X, Liu Y, Guan D, Lam M, et al. Identification of a novel LXXLL motif in alpha-actinin 4-spliced isoform that is critical for its interaction with estrogen receptor alpha and co-activators. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:35418–29.
An HT, Kim J, Yoo S, Ko J. Small leucine zipper protein (sLZIP) negatively regulates skeletal muscle differentiation via interaction with alpha-actinin-4. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:4969–79.
Zhao X, Khurana S, Charkraborty S, Tian Y, Sedor JR, Bruggman LA, et al. alpha actinin 4 (ACTN4) regulates glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transactivation and transrepression in podocytes. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:1637–47.
Lu T, Stark GR. NF-kappaB: regulation by methylation. Cancer Res. 2015;75:3692–5.
Boulay JL, Stiefel U, Taylor E, Dolder B, Merlo A, Hirth F. Loss of heterozygosity of TRIM3 in malignant gliomas. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:71.
Deng W, Tsao SW, Guan XY, Lucas JN, Si HX, Leung CS, et al. Distinct profiles of critically short telomeres are a key determinant of different chromosome aberrations in immortalized human cells: whole-genome evidence from multiple cell lines. Oncogene. 2004;23:9090–101.
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL, Gong LY, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and overall patient survival. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for. Cancer Res. 2008;14:3319–26.
Girard C, Will CL, Peng J, Makarov EM, Kastner B, Lemm I, et al. Post-transcriptional spliceosomes are retained in nuclear speckles until splicing completion. Nat Commun. 2012;3:994.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81830082, 91740119, 91529301, 81621004, 91740118, 81773106 and 81530082); Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Projects (201803010098); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2018B030311009 and 2016A030308002); The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [No. 17ykjc02].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Wu, G., Ke, Z. et al. Targeting TRIM3 deletion-induced tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis prohibits lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 38, 2736–2749 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0621-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0621-5
This article is cited by
-
Advances in the antitumor mechanisms of tripartite motif-containing protein 3
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2024)
-
Tripartite-motif 3 represses ovarian cancer progression by downregulating lactate dehydrogenase A and inhibiting AKT signaling
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2024)
-
Dual roles of TRIM3 in colorectal cancer by retaining p53 in the cytoplasm to decrease its nuclear expression
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
TRIM17-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of RBM38 promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
Cellular Oncology (2023)
-
TRIM3 facilitates estrogen signaling and modulates breast cancer cell progression
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)