Abstract
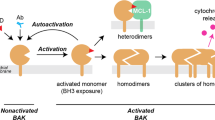
Phosphorylation of Ser/Thr residues is a well-established modulating mechanism of the pro-apoptotic function of the BH3-only protein Bim. However, nothing is known about the putative tyrosine phosphorylation of this Bcl-2 family member and its potential impact on Bim function and subsequent Bax/Bak-mediated cytochrome c release and apoptosis. As we have previously shown that the tyrosine kinase Lyn could behave as an anti-apoptotic molecule, we investigated whether this Src family member could directly regulate the pro-apoptotic function of Bim. In the present study, we show that Bim is phosphorylated onto tyrosine residues 92 and 161 by Lyn, which results in an inhibition of its pro-apoptotic function. Mechanistically, we show that Lyn-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Bim increases its interaction with anti-apoptotic members such as Bcl-xL, therefore limiting mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and subsequent apoptosis. Collectively, our data uncover one molecular mechanism through which the oncogenic tyrosine kinase Lyn negatively regulates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, which may contribute to the transformation and/or the chemotherapeutic resistance of cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomas SM, Brugge JS. Cellular functions regulated by Src family kinases. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:513–609.
Ingley E. Functions of the Lyn tyrosine kinase in health and disease. Cell Commun Signal. 2012;10:21.
Parsons SJ, Parsons JT. Src family kinases, key regulators of signal transduction. Oncogene. 2004;23:7906–9.
Kim LC, Song L, Haura EB. Src kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:587–95.
Harder KW, Parsons LM, Armes J, Evans N, Kountouri N, Clark R, et al. Gain- and loss-of-function Lyn mutant mice define a critical inhibitory role for Lyn in the myeloid lineage. Immunity. 2001;15:603–15.
Hibbs ML, Tarlinton DM, Armes J, Grail D, Hodgson G, Maglitto R, et al. Multiple defects in the immune system of Lyn-deficient mice, culminating in autoimmune disease. Cell. 1995;83:301–11.
Scapini P, Pereira S, Zhang H, Lowell CA. Multiple roles of Lyn kinase in myeloid cell signaling and function. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:23–40.
Ptasznik A, Nakata Y, Kalota A, Emerson SG, Gewirtz AM. Short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug-resistant, BCR-ABL1(+) leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2004;10:1187–9.
Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, Cesaro L, et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:369–78.
Tauzin S, Ding H, Khatib K, Ahmad I, Burdevet D, van Echten-Deckert G, et al. Oncogenic association of the Cbp/PAG adaptor protein with the Lyn tyrosine kinase in human B-NHL rafts. Blood. 2008;111:2310–20.
Goldenberg-Furmanov M, Stein I, Pikarsky E, Rubin H, Kasem S, Wygoda M, et al. Lyn is a target gene for prostate cancer: sequence-based inhibition induces regression of human tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1058–66.
Chen WS, Kung HJ, Yang WK, Lin W. Comparative tyrosine-kinase profiles in colorectal cancers: enhanced arg expression in carcinoma as compared with adenoma and normal mucosa. Int J Cancer. 1999;83:579–84.
Mahon FX, Hayette S, Lagarde V, Belloc F, Turcq B, Nicolini F, et al. Evidence that resistance to nilotinib may be due to BCR-ABL, Pgp, or Src kinase overexpression. Cancer Res. 2008;68:9809–16.
Gamas P, Marchetti S, Puissant A, Grosso S, Jacquel A, Colosetti P, et al. Inhibition of imatinib-mediated apoptosis by the caspase-cleaved form of the tyrosine kinase Lyn in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2009;23:1500–6.
Luciano F, Herrant M, Jacquel A, Ricci JE, Auberger P. The p54 cleaved form of the tyrosine kinase Lyn generated by caspases during BCR-induced cell death in B lymphoma acts as a negative regulator of apoptosis. FASEB J. 2003;17:711–3.
Zonta F, Pagano MA, Trentin L, Tibaldi E, Frezzato F, Gattazzo C, et al. Lyn-mediated procaspase 8 dimerization blocks apoptotic signaling in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2014;123:875–83.
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR. The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell. 2010;37:299–310.
Green DR, Llambi F. Cell death signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7:a006080.
Hubner A, Barrett T, Flavell RA, Davis RJ. Multisite phosphorylation regulates Bim stability and apoptotic activity. Mol Cell. 2008;30:415–25.
Pinon JD, Labi V, Egle A, Villunger A. Bim and Bmf in tissue homeostasis and malignant disease. Oncogene. 2008;27(Suppl 1):S41–52.
Luciano F, Jacquel A, Colosetti P, Herrant M, Cagnol S, Pages G, et al. Phosphorylation of Bim-EL by Erk1/2 on serine 69 promotes its degradation via the proteasome pathway and regulates its proapoptotic function. Oncogene. 2003;22:6785–93.
Puthalakath H, Huang DC, O’Reilly LA, King SM, Strasser A. The proapoptotic activity of the Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by interaction with the dynein motor complex. Mol Cell. 1999;3:287–96.
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DC, Tarlinton DM, Kay TW, Kontgen F, et al. Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science. 1999;286:1735–8.
O’Connor L, Strasser A, O’Reilly LA, Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S, et al. Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J. 1998;17:384–95.
Clybouw C, Merino D, Nebl T, Masson F, Robati M, O’Reilly L, et al. Alternative splicing of Bim and Erk-mediated Bim(EL) phosphorylation are dispensable for hematopoietic homeostasis in vivo. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:1060–8.
Enders A, Bouillet P, Puthalakath H, Xu Y, Tarlinton DM, Strasser A. Loss of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim inhibits BCR stimulation-induced apoptosis and deletion of autoreactive B cells. J Exp Med. 2003;198:1119–26.
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC, et al. Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl + leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:14907–12.
Ricci JE, Lang V, Luciano F, Belhacene N, Giordanengo V, Michel F, et al. An absolute requirement for Fyn in T cell receptor-induced caspase activation and apoptosis. FASEB J. 2001;15:1777–9.
Ban T, Sato GR, Nishiyama A, Akiyama A, Takasuna M, Umehara M, et al. Lyn kinase suppresses the transcriptional activity of IRF5 in the TLR-MyD88 pathway to restrain the development of autoimmunity. Immunity. 2016;45:319–32.
Luciano F, Ricci JE, Auberger P. Cleavage of Fyn and Lyn in their N-terminal unique regions during induction of apoptosis: a new mechanism for Src kinase regulation. Oncogene. 2001;20:4935–41.
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, et al. ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell. 2007;129:1337–49.
Bouillet P, Purton JF, Godfrey DI, Zhang LC, Coultas L, Puthalakath H, et al. BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bim is required for apoptosis of autoreactive thymocytes. Nature. 2002;415:922–6.
Luo S, Garcia-Arencibia M, Zhao R, Puri C, Toh PP, Sadiq O, et al. Bim inhibits autophagy by recruiting Beclin 1 to microtubules. Mol Cell. 2012;47:359–70.
Gogada R, Yadav N, Liu J, Tang S, Zhang D, Schneider A, et al. Bim, a proapoptotic protein, up-regulated via transcription factor E2F1-dependent mechanism, functions as a prosurvival molecule in cancer. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:368–81.
Pecot J, Maillet L, Le Pen J, Vuillier C, Trecesson SC, Fetiveau A, et al. Tight sequestration of BH3 proteins by BCL-xL at subcellular membranes contributes to apoptotic resistance. Cell Rep. 2016;17:3347–58.
Tait SW, Parsons MJ, Llambi F, Bouchier-Hayes L, Connell S, Munoz-Pinedo C, et al. Resistance to caspase-independent cell death requires persistence of intact mitochondria. Dev Cell. 2010;18:802–13.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Egle A, Harris AW, Bouillet P, Cory S. Bim is a suppressor of Myc-induced mouse B cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:6164–9.
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA, Siebert R, Climent J, Fresquet V, et al. Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2007;109:271–80.
Belloc F, Moreau-Gaudry F, Uhalde M, Cazalis L, Jeanneteau M, Lacombe F, et al. Imatinib and nilotinib induce apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells through a Bim-dependant pathway modulated by cytokines. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:912–9.
Sionov RV, Vlahopoulos SA, Granot Z. Regulation of Bim in health and disease. Oncotarget. 2015;6:23058–134.
Ley R, Ewings KE, Hadfield K, Howes E, Balmanno K, Cook SJ. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 are serum-stimulated “Bim(EL) kinases” that bind to the BH3-only protein Bim(EL) causing its phosphorylation and turnover. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:8837–47.
Rooswinkel RW, van de Kooij B, de Vries E, Paauwe M, Braster R, Verheij M, et al. Antiapoptotic potency of Bcl-2 proteins primarily relies on their stability, not binding selectivity. Blood. 2014;123:2806–15.
Ingley E. Src family kinases: regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1784:56–65.
Carpenter RL, Han W, Paw I, Lo HW. HER2 phosphorylates and destabilizes pro-apoptotic PUMA, leading to antagonized apoptosis in cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e78836.
Fox JL, Ismail F, Azad A, Ternette N, Leverrier S, Edelmann MJ, et al. Tyrosine dephosphorylation is required for Bak activation in apoptosis. EMBO J. 2010;29:3853–68.
Nishizumi H, Taniuchi I, Yamanashi Y, Kitamura D, Ilic D, Mori S, et al. Impaired proliferation of peripheral B cells and indication of autoimmune disease in lyn-deficient mice. Immunity. 1995;3:549–60.
Gross AJ, Proekt I, DeFranco AL. Elevated BCR signaling and decreased survival of Lyn-deficient transitional and follicular B cells. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:3645–55.
Leonard JT, Rowley JS, Eide CA, Traer E, Hayes-Lattin B, Loriaux M, et al. Targeting BCL-2 and ABL/LYN in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:354ra114.
Lopez J, Hesling C, Prudent J, Popgeorgiev N, Gadet R, Mikaelian I, et al. Src tyrosine kinase inhibits apoptosis through the Erk1/2- dependent degradation of the death accelerator Bik. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19:1459–69.
Bian Y, Li L, Dong M, Liu X, Kaneko T, Cheng K, et al. Ultra-deep tyrosine phosphoproteomics enabled by a phosphotyrosine superbinder. Nat Chem Biol. 2016;12:959–66.
Mertins P, Mani DR, Ruggles KV, Gillette MA, Clauser KR, Wang P, et al. Proteogenomics connects somatic mutations to signalling in breast cancer. Nature. 2016;534:55–62.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Fondation ARC pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (#PJA 20131200392 and #PGA1RF201702053889), the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (DMP20101120387), the INSERM, the Ministere de la Recherche, and the University of Nice-Sophia-Antipolis. This work and LEA were funded by the French Government (National Research Agency, ANR) through the “Investments for the Future” LABEX SIGNALIFE: program reference #ANR-11-LABX-0028-01. We thank Frederic Larbret for technical support for FACS sorting. We thank Dr. Simon Cook for GST-Bim constructs, Dr. Andreas Villunger for kindly providing the WEHI-231 cell line, Dr. David Rubinsztein for the plasmid encoding human BimEL, and Drs. Doug Green and Stephen Tait for HeLa cells stably expressing Smac-GFP. We thank Drs. Eric Eldering and Fabio Brocco for insights and helpful discussion. We thank the Conseil général des AM et de la région PACA et Corse for its financial support.
Author contributions
SM and PA conceived the project. LEA, EV, PG, and SM conducted the experiments and were assisted by PC, LS, SO, EP. FG and PPJ contributed to the BRET experiments. SM wrote the paper. PA, J-ER, LEA, BB-M, AJ, GR, FL, FG, and PPJ reviewed and edited the paper. SM and PA supervised the study and obtained funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aira, L.E., Villa, E., Colosetti, P. et al. The oncogenic tyrosine kinase Lyn impairs the pro-apoptotic function of Bim. Oncogene 37, 2122–2136 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0112-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0112-0