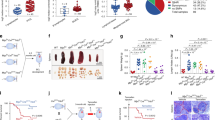
Abstract
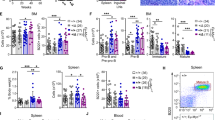
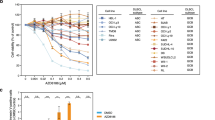
A large body of evidence suggests that B-cell lymphomas with enhanced Myc expression are associated with an aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis, which makes Myc a compelling therapeutic target. Phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B), a main hydrolyzer of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in B cells, was shown to be involved in cell survival and drug resistance in diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL). However, the interrelationship between Myc and PDE4B remains unclear. Here, we first demonstrate the presence of the Myc-PDE4B feed-forward loop, in which Myc and PDE4B mutually reinforce the expression of each other. Next, the combined targeting of Myc and PDE4 synergistically prevented the proliferation and survival of B lymphoma cells in vitro and in a mouse xenograft model. We finally recapitulated this combinatorial effect in Eμ-myc transgenic mice; co-inhibition of Myc and PDE4 suppressed lymphomagenesis and restored B cell development to the wild type level that was associated with marked reduction in Myc levels, unveiling the critical role of the Myc-PDE4B amplification loop in the regulation of Myc expression and the pathogenesis of B cell lymphoma. These findings suggest that the disruption of the Myc-PDE4B circuitry can be exploited in the treatment of B cell malignancies.
Highlights
- 1.
Myc and PDE4B activate expression of each other, forming a positive feedback loop.
- 2.
Co-inhibition of Myc and PDE4 induces synergistic killing of B lymphoma cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ott G. Impact of MYC on malignant behavior. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014;2014:100–6.
Dang CV. MYC on the path to cancer. Cell. 2012;149:22–35.
Eilers M, Eisenman RN. Myc’s broad reach. Genes Dev. 2008;22:2755–66.
Sewastianik T, Prochorec-Sobieszek M, Chapuy B, Juszczynski P. MYC deregulation in lymphoid tumors: molecular mechanisms, clinical consequences and therapeutic implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1846:457–67.
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB, Shi J, Jacobs HM, et al. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell. 2011;146:904–17.
Chaidos A, Caputo V, Karadimitris A. Inhibition of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins (BET) as a potential therapeutic approach in haematological malignancies: emerging preclinical and clinical evidence. Ther Adv Hematol. 2015;6:128–41.
Moon EY, Lerner A. PDE4 inhibitors activate a mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells that is regulated by protein phosphatase 2A. Blood. 2003;101:4122–30.
Ogawa R, Streiff MB, Bugayenko A, Kato GJ. Inhibition of PDE4 phosphodiesterase activity induces growth suppression, apoptosis, glucocorticoid sensitivity, p53, and p21(WAF1/CIP1) proteins in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood. 2002;99:3390–7.
Shipp MA, Ross KN, Tamayo P, Weng AP, Kutok JL, Aguiar RC, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat Med. 2002;8:68–74.
Smith PG, Wang F, Wilkinson KN, Savage KJ, Klein U, Neuberg DS, et al. The phosphodiesterase PDE4B limits cAMP-associated PI3K/AKT-dependent apoptosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105:308–16.
Cooney JD, Aguiar RC. Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors have wide-ranging activity in B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2016;128:2886–90.
Kelly K, Mejia A, Suhasini AN, Lin AP, Kuhn J, Karnad AB, et al. Safety and pharmacodynamics of the PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in advanced B-cell malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:1186–92.
Kim EA, Kim SW, Nam J, Sung EG, Song IH, Kim JY, et al. Inhibition of c-FLIPL expression by miRNA-708 increases the sensitivity of renal cancer cells to anti-cancer drugs. Oncotarget. 2016;7:31832–46.
Kim E, Nam J, Chang W, Zulfugarov IS, Okhlopkova ZM, Olennikov D, et al. Angelica gigas Nakai and Decursin downregulate Myc expression to promote cell death in B-cell lymphoma. Sci Rep. 2018;8:10590.
Balkhi MY, Willette-Brown J, Zhu F, Chen Z, Liu S, Guttridge DC, et al. IKKalpha-mediated signaling circuitry regulates early B lymphopoiesis during hematopoiesis. Blood. 2012;119:5467–77.
Cho Y, Song SH, Lee JJ, Choi N, Kim CG, Dean A, et al. The role of transcriptional activator GATA-1 at human beta-globin HS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:4521–8.
Kwak B, Kim DU, Kim TO, Kim HS, Kim SW. MicroRNA-552 links Wnt signaling to p53 tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 2018;53:1800–8.
Jeong D, Kim J, Nam J, Sun H, Lee YH, Lee TJ, et al. MicroRNA-124 links p53 to the NF-kappaB pathway in B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia. 2015;29:1868–74.
Kim J, Jeong D, Nam J, Aung TN, Gim JA, Park KU, et al. MicroRNA-124 regulates glucocorticoid sensitivity by targeting phosphodiesterase 4B in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Gene. 2015;558:173–80.
Turner SD, Tooze R, Maclennan K, Alexander DR. Vav-promoter regulated oncogenic fusion protein NPM-ALK in transgenic mice causes B-cell lymphomas with hyperactive Jun kinase. Oncogene. 2003;22:7750–61.
Andersson KB, Tasken K, Blomhoff HK. Cyclic AMP downregulates c-myc expression by inhibition of transcript initiation in human B-precursor Reh cells. FEBS Lett. 1994;337:71–6.
Pirson I, Coulonval K, Lamy F, Dumont JE. c-Myc expression is controlled by the mitogenic cAMP-cascade in thyrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1996;168:59–70.
Williamson EA, Burgess GS, Eder P, Litz-Jackson S, Boswell HS. Cyclic AMP negatively controls c-myc transcription and G1 cell cycle progression in p210 BCR-ABL transformed cells: inhibitory activity exerted through cyclin D1 and cdk4. Leukemia. 1997;11:73–85.
Kim SW, Rai D, Aguiar RC. Gene set enrichment analysis unveils the mechanism for the phosphodiesterase 4B control of glucocorticoid response in B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6723–32.
Kim SW, Rai D, McKeller MR, Aguiar RC. Rational combined targeting of phosphodiesterase 4B and SYK in DLBCL. Blood. 2009;113:6153–60.
Suhasini AN, Wang L, Holder KN, Lin AP, Bhatnagar H, Kim SW, et al. A phosphodiesterase 4B-dependent interplay between tumor cells and the microenvironment regulates angiogenesis in B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2016;30:617–26.
Zeller KI, Zhao X, Lee CW, Chiu KP, Yao F, Yustein JT, et al. Global mapping of c-Myc binding sites and target gene networks in human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:17834–9.
Carnevale J, Ross L, Puissant A, Banerji V, Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ, et al. SYK regulates mTOR signaling in AML. Leukemia. 2013;27:2118–28.
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. The pharmacology of mTOR inhibition. Sci Signal. 2009;2:pe24.
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 2017;169:361–71.
Wall M, Poortinga G, Hannan KM, Pearson RB, Hannan RD, McArthur GA. Translational control of c-MYC by rapamycin promotes terminal myeloid differentiation. Blood. 2008;112:2305–17.
Shi Y, Sharma A, Wu H, Lichtenstein A, Gera J. Cyclin D1 and c-myc internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation is regulated by AKT activity and enhanced by rapamycin through a p38 MAPK- and ERK-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:10964–73.
West MJ, Stoneley M, Willis AE. Translational induction of the c-myc oncogene via activation of the FRAP/TOR signalling pathway. Oncogene. 1998;17:769–80.
Wossning T, Herzog S, Kohler F, Meixlsperger S, Kulathu Y, Mittler G, et al. Deregulated Syk inhibits differentiation and induces growth factor-independent proliferation of pre-B cells. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2829–40.
D’Sa C, Tolbert LM, Conti M, Duman RS. Regulation of cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases type 4B and 4D (PDE4) splice variants by cAMP signaling in primary cortical neurons. J Neurochem. 2002;81:745–57.
Verghese MW, McConnell RT, Lenhard JM, Hamacher L, Jin SL. Regulation of distinct cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase (phosphodiesterase type 4) isozymes in human monocytic cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;47:1164–71.
Jin SL, Conti M. Induction of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE4B is essential for LPS-activated TNF-alpha responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:7628–33.
Blackwell TK, Huang J, Ma A, Kretzner L, Alt FW, Eisenman RN, et al. Binding of myc proteins to canonical and noncanonical DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:5216–24.
Grandori C, Mac J, Siebelt F, Ayer DE, Eisenman RN. Myc-Max heterodimers activate a DEAD box gene and interact with multiple E box-related sites in vivo. EMBO J. 1996;15:4344–57.
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, et al. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985;318:533–8.
Langdon WY, Harris AW, Cory S, Adams JM. The c-myc oncogene perturbs B lymphocyte development in E-mu-myc transgenic mice. Cell. 1986;47:11–8.
Cheah CY, Fowler NH. Idelalisib in the management of lymphoma. Blood. 2016;128:331–6.
Meadows S, Rick S, Anella Y, Liu J, Li L, Yue P, et al. Up-regulation of the PI3K signaling pathway mediates resistance to Idelalisib. Blood. 2015;126;3707.
Lasorsa E, Smonksey M, Kirk JS, Rosario S, Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Ellis L. Mitochondrial protection impairs BET bromodomain inhibitor-mediated cell death and provides rationale for combination therapeutic strategies. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e2014.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE, et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:389–99.
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Mazumder S, Hill BT, Smith MR, Bodo J, et al. MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1593.
Lenz G, Wright G, Dave SS, Xiao W, Powell J, Zhao H, et al. Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2313–23.
Acknowledgements
pcDNA-Myc construct is a gift from Dr. Dongchul Kang (Hallym University, Korea) and Ly10 DLBCL cell line was kindly provided by Dr. Yoon Kyung Jeon (Seoul National University Hospital, Korea). This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2013R1A1A2008838 and NRF-2016R1A2B4011758) to S-WK and (NRF-2014R1A5A2010008 and 2018R1A2B2007410) to Y-HL. IP was a recipient of the research fund 2018 through Youngsan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JN performed experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; DK, EK, BK, MK, H-JS, IP and J-YJ performed experiments; A-YO and B-JP helped with mouse breeding; YWK and AK helped with ChIP experiments; HS performed statistical analysis; YJ and J-HL helped with tissue staining and qRT-PCR, respectively; D-KS and Y-HL supervised the study and wrote the manuscript; S- WK designed and supervised the study, planned experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All the authors edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, J., Kim, D., Kim, E. et al. Disruption of the Myc-PDE4B regulatory circuitry impairs B-cell lymphoma survival. Leukemia 33, 2912–2923 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0492-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0492-y