Abstract
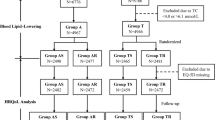
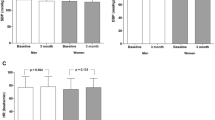
Hypertension (HTN) related to health-promoting behaviors (HPB) and quality of life (QOL) in older Chinese has not been clearly identified. We sought to compare the HPB and QOL of elderly adults (aged ≥60) living with HTN in China to a community normotensive control group. Using multistage stratified cluster sampling, a sample of 543 elderly people with HTN and 550 with normotension were randomly selected and asked to complete questionnaires. The Chinese version of the Health Promoting Lifestyle Profile (HPLP-IICR) and The World Health Organization Quality of life—BREF instrument (WHOQOL-BREF) were used to evaluate the HPB and QOL of elderly adults. As compared to the normotensive elderly, the hypertensive elderly showed significantly lower scores in their spiritual growth and health management (both P < 0.05), but not in the other three domains. Also, the participants with HTN showed significantly lower scores in the QOL overall and physical health (both P < 0.05), but not in other factors, as compared to the participants without HTN. Each HPLP-IICR domain score among the elderly with or without HTN were significantly correlated with their QOL scores (all P < 0.01). It is suggested that more attention should be paid to improving the spiritual growth and health management of HBP, and thus the overall quality of life among hypertensive patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roopa KS, Rama Devi G, Zina TA, Mohamed AFG. Impact of intervention programme on knowledge, attitude, practices in the management of hypertension among elderly. Stud Home Community Sci. 2014;8:11–6.
WHO Hypertension and older people, 2015. http://envejecimiento.csic.es/documentos/documentos/HelpAge-hipertension-personasmayores2014-05-2015.pdf. Accessed 17 May 2017.
Yang ZJ, Liu J, Ge JP, Chen L, Zhao ZG, Yang WY, China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factor in the Chinese population: the 2007–2008 China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:213–20.
Gao Y, Chen G, Tian H, Lin L, Lu J, Weng J, China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. et al. Prevalence of hypertension in china: a cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65938.
Hua Y, Wang B, Wallen GR, Shao P, Chunping N, Hua Q. Health-promoting lifestyles and depression in urban elderly Chinese. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0117998.
Stuifbergen AK. Health-promoting behaviors and quality of life among individuals with multiple sclerosis. Sch Inq Nurs Pract. 1995;9:31–55.
Houle N,Bohannon RW,Frigon L,Maljanian R,Nieszczezewski J, Health promoting behaviors, quality of life, and hospital resource utilization of patients receiving kidney transplants. Nephrol Nurs J. 2002;29:35–40.
Lopez L, Cook EF, Horng MS, Hicks LS. Lifestyle modification counseling for hypertensive patients: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2004. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22:325–31.
Greenlund K, Daviglus M, Croft J. Differences in healthy lifestyle characteristics between adults with prehypertension and normal blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2009;27:955–62.
Sheethal MP, Mahendra BJ, Harish BR. Assessment of quality of life (QoL) in known hypertensive workers of Karnataka State Road Transport Corporation (KSRTC), Mandya district. Int J Med Sci Public Health. 2015;4:1393–5.
Ojo B, Genden EM, Teng MS, Milbury K, Misiukiewicz KJ, Badr H. A systematic review of head and neck cancer quality of life assessment instruments. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:923–37.
Erickson SR, Williams BC, Gruppen LD. Relationship between symptoms and health-related quality of life in patients treated for hypertension. J Pharmacother. 2004;24:344–50.
Maruf FA, Akinpelu AO, Salako BL. Self-reported quality of life before and after aerobic exercise training in individuals with hypertension: a randomised-controlled trial. Appl Psychol Health Well Being. 2013;5:209–24.
Muszalik M, Dijkstra A, Kędziora-Kornatowska K, Zielińska-Więczkowska H, Kornatowski T, Kotkiewicz A. Independence of elderly patients with arterial hypertension in fulfilling their needs, in the aspect of functional assessment and quality of life (QoL). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;52:e204–9.
Trevisol DJ, Moreira LB, Kerkhoff A, Fuchs SC, Fuchs FD. Health-related quality of life and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hypertens. 2011;29:179–88.
Moum T, Naess S, Sorensen T, Tambs K, Holmen J. Hypertension labelling, life events and psychological well-being. Psychol Med. 1990;20:635–46.
Teng HL, Yen M, Fetzer S. Health promotion lifestyle profile-II: Chinese version short form. JAN. 2010;66:1864–73.
Ha NT, Duy HT, Le NH, Khanal V, Moorin R. Quality of life among people living with hypertension in a rural Vietnam community. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:833.
Li YM, Chen CS, Tu H, Cao WJ, Fan SH, Ma Y, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for depression in older people in Xi’an China: a community-based study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012;27:31–9.
Cao WJ, Guo CZ, Ping WW, Tan ZJ, Guo Y, Zheng JZ. A community-based study of quality of life and depression among older adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13:693.
Xia P, Li N, Hau KT, Liu C, Lu Y. Quality of life of Chinese urban community residents: a psychometric study of the mainland Chinese version of the WHOQOL-BREF. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12:37.
Schuit AJ, van Loon AJ, Tijhuis M, Ocké M. Clustering of lifestyle risk factors in a general adult population. Prev Med. 2002;35:219–324.
Moore SC, Patel AV, Matthews CE, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Park Y, Katki HA, et al. Leisure time physical activity of moderate to vigorous intensity and mortality: a large pooled cohort analysis. PLoS Med. 2012;9:1–14.
Shafieyan Z, Qorbani M, Rastegari Mehr B, Mahboubi M, Rezapour A, Safari O, et al. Association between lifestyle and hypertension in patients referred to health care centers of Ilam city in 2014. Glob J Health Sci. 2016;8:161–7.
Carvalho MV, Siqueira LB, Sousa AL, Jardim PC. The influence of hypertension on quality of life. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2013;100:164–74.
Wang R, Zhao Y, He X, Ma X, Yan X, Sun Y, et al. Impact of hypertension on health-related quality of life in a population-based study in Shangai, China. Public Health. 2009;123:534–9.
Mehri A, Solhi M, Garmaroudi G, Nadrian H, Sighaldeh SS. Health promoting lifestyle and its determinants among university students in Sabzevar, Iran. Int J Prev Med. 2016;14:65.
Kemppainen J, Bomar PJ, Kikuchi K, Kanematsu Y, Ambo H, Noguchi K. Health promotion behaviors of residents with hypertension in Iwate, Japan and North Carolina, USA. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2011;8:20–32.
Aoyagi Y, Park H, Watanabe E, Park S, Shephard R. Habitual physical activity and physical fitness in older Japanese adults: The Nakanojo Study. Gerontology. 2009;55:523–31.
Musick M, Traphagan J, Koenig H, Larson D. Spirituality and physical health in aging. J Health Dev. 2000;7:73–86.
King D, Mainous A, Carnemolla M, Everett C. Adherence to healthy lifestyle habits in U.S. adults, 1988–2006. Am J Med. 2009;122:528–34.
Hekler E, Lambert J, Leventhal E, Leventhal H, Jahn E, Contrada R. Commonsense illness beliefs, adherence behaviors, and hypertension control among African Americans. J Behav Med. 2008;31:391–400.
Li W, Liu L, Puente JG, Li Y, Jiang X, Jin S, et al. Hypertension and health-related quality of life: an epidemiological study in patients attending hospital clinics in China. J Hypertens. 2005;23:1667–76.
Bardage C, Isacson DGL. Hypertension and health-related quality of life: an epidemiological study in Sweden. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54:172–81.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81302518), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 2015021185) and Science and Technology Innovation of Changzhi Medical College (No. CX201403). The work was approved by the Ethics Committee of the study sponsor, Chang Zhi Medical College, and all procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, W., Hou, G., Guo, C. et al. Health-promoting behaviors and quality of life in older adults with hypertension as compared to a community control group. J Hum Hypertens 32, 540–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0073-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0073-y
This article is cited by
-
A population-based study of health-promoting behaviors and their predictors in Iranian males, 2019
Archives of Public Health (2021)