Abstract
Background:
Men with diabetes may have a lower risk of prostate cancer than men without diabetes which may be altered by metformin use or race/ethnicity.
Methods:
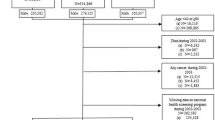
Using administrative databases, from 1994 to 2012, adult (age⩾50 years) men with diabetes were identified. Metformin exposure was defined as a time-dependent variable, stratified first into any use, and into tertiles of cumulative dose. Surname algorithms identified individuals as Chinese or non-Chinese. Multivariable Cox regression estimated the risk of prostate cancer.
Results:
The cohort of 80 001 had a mean age of 64 years and median follow-up of 9 years. Chinese users of metformin aged 50–59, 60–69 and ⩾70 had similar risks of prostate cancer as non-users. Non-Chinese users aged 50–59 (adjusted hazards ratio (aHR): 0.86, 0.74 to 1.00) had a decreased risk whereas men aged 60–69 and ⩾70 did not. However, when metformin exposure was stratified into tertiles, there was no association in any strata except non-Chinese men aged 50–59 in the first (aHR: 0.68, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.55, 0.84), second (aHR: 0.75, 95% CI: 0.61, 0.92) and third (aHR: 0.79, 95% CI: 0.64, 0.96) tertiles of metformin exposure and non-Chinese men aged 60–69 in the first (aHR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.68, 0.95) tertiles of metformin exposure.
Conclusions:
There was no clear association between metformin and risk of prostate cancer in men with diabetes in either race/ethnicity. Our findings suggest a consistent relationship between metformin and prostate cancer across race/ethnicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsilidis KK, Kasimis JC, Lopez DS, Ntzani EE, Ioannidis JPA . Type 2 diabetes and cancer: umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies. BMJ 2015; 350: g7607.
Waters KM, Henderson BE, Stram DO, Wan P, Kolonel LN, Haiman CA . Association of diabetes with prostate cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort. Am J Epidemiol 2009; 169: 937–945.
Rastmanesh R, Hejazi J, Marotta F, Hara N . Type 2 diabetes: a protective factor for prostate cancer? An overview of proposed mechanisms. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2014; 12: 143–148.
Morales DR, Morris AD . Metformin in cancer treatment and prevention. Annu Rev Med 2015; 66: 17–29.
Clements A, Gao B, Yeap SHO, Wong MKY, Ali SS, Gurney H . Metformin in prostate cancer: two for the price of one. Ann Oncol 2011; 22: 2556–2560.
Gandini S, Puntoni M, Heckman-Stoddard BM, Dunn BK, Ford L, DeCensi A et al. Metformin and cancer risk and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis taking into account biases and confounders. Cancer Prev Res 2014; 7: 867–885.
DeCensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B et al. Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res 2010; 3: 1451–1461.
Bansal D, Bhansali A, Kapil G, Undela K, Tiwari P . Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2013; 16: 151–158, S1.
Noto H, Tsujimoto T, Noda M . Significantly increased risk of cancer in diabetes mellitus patients: a meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence in Asians and non-Asians. J Diabetes Investig 2012; 3: 24–33.
Chen R, Ren S, Yiu MK, Fai NC, Cheng WS, Ian LH et al. Prostate cancer in Asia: a collaborative report. Asian J Urol 2014; 1: 15–29.
Franciosi M, Lucisano G, Lapice E, Strippoli GFM, Pellegrini F, Nicolucci A . Metformin therapy and risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes: systematic review. PLoS One 2013; 8: e71583.
Chen Christopher B, Eskin Maxim, Majumdar Sumit, Eurich Dean, Johnson Jeffrey . Metformin, Asian Ethnicity and Risk of Prostate Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [Under Revision].
Colmers IN, Majumdar SR, Yasui Y, Bowker SL, Marra CA, Johnson JA . Detection bias and overestimation of bladder cancer risk in type 2 diabetes: a matched cohort study. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: 3070–3075.
British Columbia Cancer Agency 2016; British Columbia Cancer Agency Registry Data. Population Data BC British Columbia Cancer Agency (2016). Available at http://www.popdata.bc.ca/data.
British Columbia Vital Statistics Agency 2016; Vital Statistics. Population Data BC British Columbia Vital Statistics Agency (2016). Available at http://www.popdata.bc.ca/data.
British Columbia Ministry of Health 2016; Medical Services Plan. Population Data BC British Columbia Ministry of Health (2016). Available at http://www.popdata.bc.ca/data.
British Columbia Ministry of Health 2016; Discharge Abstracts Database. Population Data BC British Columbia Ministry of Health (2016). Available at http://www.popdata.bc.ca/data.
British Columbia Ministry of Health 2016; PharmaNet. British Columbia Ministry of Health Data Stewardship Committee (2016). Available at http://www.popdata.bc.ca/data.
Clottey C, Mo F, LeBrun B, Mickelson P, Niles J, Robbins G . Chronic Diseases in Canada 2002. Available at http://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/295485/publication.html. Accessed on 17 March 2016.
University of Manitoba. Development & Advancement—Concept: Cancer Diagnoses Validity/Agreement In Administrative Health Data n.d http://mchp-appserv.cpe.umanitoba.ca/viewConcept.php?conceptID=1479. Accessed on 19 May 2016.
Quan H, Wang F, Schopflocher D, Norris C, Galbraith PD, Faris P et al. Development and validation of a surname list to define Chinese ethnicity. Med. Care 2006; 44: 328–333..
Statistics Canada. Ethnic Origins of British Columbia. Statistics Canada n.d. http://www12.statcan.gc.ca/nhs-enm/2011/dp-pd/dt-td/Rp-eng.cfm?TABID=2&LANG=E&APATH=3&DETAIL=0&DIM=0&FL=A&FREE=0&GC=0&GK=0&GRP=0&PID=105396&PRID=0&PTYPE=105277&S=0&SHOWALL=0&SUB=0&Temporal=2013&THEME=95&VID=0&VNAMEE=&VNAMEF=Accessed on 27 May 2016.
Wang S-Y, Chuang C-S, Muo C-H, Tu S-T, Lin M-C, Sung F-C et al. Metformin and the incidence of cancer in patients with diabetes: a nested case-control study. Diabetes Care 2013; 36: e155–e156.
Hsieh M-C, Lee T-C, Cheng S-M, Tu S-T, Yen M-H, Tseng C-H . The influence of type 2 diabetes and glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in the Taiwanese. Exp Diabetes Res 2012; 2012: 413782.
Tseng C-H . Metformin significantly reduces incident prostate cancer risk in Taiwanese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Cancer 2014; 50: 2831–2837.
Kaufman JS, Cooper RS . Commentary: considerations for use of racial/ethnic classification in etiologic research. Am J Epidemiol 2001; 154: 291–298.
Margel D, Urbach D, Lipscombe LL, Bell CM, Kulkarni G, Austin PC et al. Association between metformin use and risk of prostate cancer and its grade. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013; 105: 1123–1131.
Tsilidis KK, Allen NE, Appleby PN, Rohrmann S, Nöthlings U, Arriola L et al. Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Int J Cancer 2015; 136: 372–381.
Xu H, Jiang H-W, Ding G-X, Zhang H, Zhang L-M, Mao S-H et al. Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk of different grade or stage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2013; 99: 241–249.
Leitzmann MF, Ahn J, Albanes D, Hsing AW, Schatzkin A, Chang S-C et al. Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial. Cancer Causes Control 2008; 19: 1267–1276.
Fowke JH, Motley SS, Concepcion RS, Penson DF, Barocas DA . Obesity, body composition, and prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2012; 12: 23.
Acknowledgements
CBC was supported by a Canada Graduate Scholarships-Master’s Award from the Canadian Institute for Health Research. DTE Holds a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Chronic Disease Prevention and Management. SRM holds the Endowed Chair in Patient Health Management funded by the Faculties of Medicine and Dentistry and Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences of the University of Alberta. JAJ is a Senior Health Scholar with Alberta Innovates Health Solutions. JAJ will act as the guarantor.
Author contributions
CBC conducted the statistical analysis, wrote the manuscript and helped design the study. SRM, DTE and JAJ edited the manuscript and provided guidance throughout the study design and statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Disclaimer
All inferences, opinions and conclusions drawn in this manuscript are those of the authors, and do not reflect the opinions or policies of the Data Steward(s).
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Eurich, D., Majumdar, S. et al. Metformin and the risk of prostate cancer across racial/ethnic groups: a population-based cohort study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 20, 122–126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2016.65
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2016.65
This article is cited by
-
An effective treatment approach of liposomally encapsulated metformin in colon cancer
Medical Oncology (2024)
-
Population-wide impacts of aspirin, statins, and metformin use on prostate cancer incidence and mortality
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The effect of metformin therapy on incidence and prognosis in prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2019)