Abstract
Background:
To assess the prognostic value of preoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) serum levels for prognostication of biochemical recurrence (BCR) after radical prostatectomy (RP) in a large multi-institutional cohort.
Methods:
Data from 7205 patients treated with RP at five institutions for clinically localized prostate cancer (PCa) were retrospectively analyzed. Preoperative serum levels of CRP within 24 h before surgery were evaluated. A CRP level ⩾0.5 mg dl−1 was considered elevated. Associations of elevated CRP with BCR were evaluated using univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression models. Harrel's C-index was used to assess prognostic accuracy (PA).
Results:
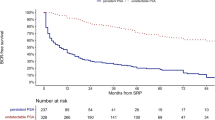
Patients with higher Gleason score on biopsy and RP, extracapsular extension, seminal vesicle invasion, lymph node metastasis, and positive surgical margins status had a significantly elevated preoperative CRP compared to those without these features. Patients with elevated CRP had a lower 5-year BCR survival proportion as compared to those with normal CRP (55% vs 76%, respectively, P<0.0001). In pre- and postoperative multivariable models that adjusted for standard clinical and pathologic features, elevated CRP was independently associated with BCR (P<0.001). However, the addition of preoperative CRP did not improve the accuracy of the standard pre- and postoperative models for prediction of BCR (70.9% vs 71% and 78.9% vs 78.7%, respectively).
Conclusions:
Preoperative CRP is elevated in patients with pathological features of aggressive PCa and BCR after RP. While CRP has independent prognostic value, it does not add prognostically or clinically significant information to standard predictors of outcomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A . Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 5–29.
Abdollah F, Sun M, Thuret R, Jeldres C, Tian Z, Briganti A et al. A competing-risks analysis of survival after alternative treatment modalities for prostate cancer patients: 1988-2006. Eur Urol 2011; 59: 88–95.
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Roehrborn CG, Kattan MW . An updated catalog of prostate cancer predictive tools. Cancer 2008; 113: 3075–3099.
Bensalah K, Lotan Y, Karam JA, Shariat SF . New circulating biomarkers for prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2008; 11: 112–120.
Karam JA, Lotan Y, Roehrborn CG, Ashfaq R, Karakiewicz PI, Shariat SF . Caveolin-1 overexpression is associated with aggressive prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate 2007; 67: 614–622.
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM . C-reactive protein: a critical update. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 1805–1812.
Saito K, Kihara K . C-reactive protein as a biomarker for urological cancers. Nat Rev Urol 2011; 8: 659–666.
Gakis G, Todenhofer T, Renninger M, Schilling D, Sievert KD, Schwentner C et al. Development of a new outcome prediction model in carcinoma invading the bladder based on preoperative serum C-reactive protein and standard pathological risk factors: the TNR-C score. BJU Int 2011; 108: 1800–1805.
Hu Q, Gou Y, Sun C, Ding W, Xu K, Gu B et al. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein in renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol Oncol 2014; 32: 50.e51–58.
de Martino M, Klatte T, Seemann C, Waldert M, Haitel A, Schatzl G et al. Validation of serum C-reactive protein (CRP) as an independent prognostic factor for disease-free survival in patients with localised renal cell carcinoma (RCC). BJU Int 2013; 111: E348–E353.
Prins RC, Rademacher BL, Mongoue-Tchokote S, Alumkal JJ, Graff JN, Eilers KM et al. C-reactive protein as an adverse prognostic marker for men with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC): confirmatory results. Urol Oncol 2012; 30: 33–37.
Ito M, Saito K, Yasuda Y, Sukegawa G, Kubo Y, Numao N et al. Prognostic impact of C-reactive protein for determining overall survival of patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with docetaxel. Urology 2011; 78: 1131–1135.
Xu L, Zhao Q, Huang S, Li S, Wang J, Li Q . Serum C-reactive protein acted as a prognostic biomarker for overall survival in metastatic prostate cancer patients. Tumour Biol 2014; 36: 669–673.
Pond GR, Armstrong AJ, Wood BA, Leopold L, Galsky MD, Sonpavde G . Ability of C-reactive protein to complement multiple prognostic classifiers in men with metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer receiving docetaxel-based chemotherapy. BJU Int 2012; 110 (Pt B): E461–E468.
Liu ZQ, Chu L, Fang JM, Zhang X, Zhao HX, Chen YJ et al. Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J Androl 2014; 16: 467–471.
Hall WA, Nickleach DC, Master VA, Prabhu RS, Rossi PJ, Godette K et al. The association between C-reactive protein (CRP) level and biochemical failure-free survival in patients after radiation therapy for nonmetastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Cancer 2013; 119: 3272–3279.
Thurner EM, Krenn-Pilko S, Langsenlehner U, Stojakovic T, Pichler M, Gerger A et al. The elevated C-reactive protein level is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer 2015; 51: 610–619.
McArdle PA, Qayyum T, McMillan DC . Systemic inflammatory response and survival in patients with localised prostate cancer: 10-year follow-up. Urol Int 2010; 84: 430–435.
Graff JN, Beer TM, Liu B, Sonpavde G, Taioli E . Pooled Analysis of C-Reactive Protein Levels and Mortality in Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2015; 13: e217–e221.
Mortensen RF . C-reactive protein, inflammation, and innate immunity. Immunol Res 2001; 24: 163–176.
Shariat SF, Kattan MW, Traxel E, Andrews B, Zhu K, Wheeler TM et al. Association of pre- and postoperative plasma levels of transforming growth factor beta(1) and interleukin 6 and its soluble receptor with prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 1992–1999.
Bensalah K, Montorsi F, Shariat SF . Challenges of cancer biomarker profiling. Eur Urol 2007; 52: 1601–1609.
Lughezzani G, Briganti A, Karakiewicz PI, Kattan MW, Montorsi F, Shariat SF et al. Predictive and prognostic models in radical prostatectomy candidates: a critical analysis of the literature. Eur Urol 2010; 58: 687–700.
Stephenson AJ, Scardino PT, Eastham JA, Bianco FJ Jr, Dotan ZA, DiBlasio CJ et al. Postoperative nomogram predicting the 10-year probability of prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 7005–7012.
Stephenson AJ, Scardino PT, Eastham JA, Bianco FJ Jr, Dotan ZA, Fearn PA et al. Preoperative nomogram predicting the 10-year probability of prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Natl Cancer Inst 2006; 98: 715–717.
Shariat SF, Karam JA, Walz J, Roehrborn CG, Montorsi F, Margulis V et al. Improved prediction of disease relapse after radical prostatectomy through a panel of preoperative blood-based biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 3785–3791.
Jabs WJ, Busse M, Kruger S, Jocham D, Steinhoff J, Doehn C . Expression of C-reactive protein by renal cell carcinomas and unaffected surrounding renal tissue. Kidney Int 2005; 68: 2103–2110.
Shariat SF, Kattan MW, Erdamar S, Nguyen C, Scardino PT, Spencer DM et al. Detection of clinically significant, occult prostate cancer metastases in lymph nodes using a splice variant-specific rt-PCR assay for human glandular kallikrein. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1223–1231.
Acknowledgements
RM is supported by the scholarship foundation of the Republic of Austria—OeAD and by the EUSP Scholarship—European Association of Urology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sevcenco, S., Mathieu, R., Baltzer, P. et al. The prognostic role of preoperative serum C-reactive protein in predicting the biochemical recurrence in patients treated with radical prostatectomy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 19, 163–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2015.60
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2015.60
This article is cited by
-
Positive surgical margin is associated with biochemical recurrence risk following radical prostatectomy: a meta-analysis from high-quality retrospective cohort studies
World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018)
-
Elevated preoperative neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio predicts upgrading at radical prostatectomy
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2018)