Abstract
Background:
Emerging evidence suggests that diabetes may increase the risk of cancers. However, available evidence on prostate cancer is conflicting. We therefore examined the association between Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer by conducting a detailed meta-analysis of all studies published regarding this subject.
Methods:
PubMed database and bibliographies of retrieved articles were searched for epidemiological studies (published between 1970 and 2011), investigating the relationship between Type 2 diabetes and prostate cancer. Pooled risk ratio (RR) was calculated using random-effects model. Subgroup, sensitivity analysis and cumulative meta-analysis were also done.
Results:
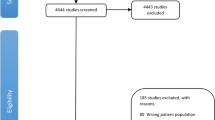
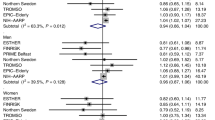
Forty-five studies (29 cohort and 16 case–control studies) involving 8.1 million participants and 132 331 prostate cancer cases detected a significant inverse association between Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer (RR 0.86, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.80–0.92). For cohort studies alone, the RR was 0.87 (95% CI 0.80–0.94), and for case–control studies alone, the RR was 0.85 (95% CI 0.74–0.96). Sensitivity analysis done by excluding one outlier further strengthened our negative association (RR 0.83, 95% CI 0.78–0.87). No evidence of publication bias was observed.
Conclusions:
This meta-analysis provides strongest evidence supporting that Type 2 diabetes is significantly inversely associated with risk of developing prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
GIovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin 2010; 60: 207–221.
Bonovas S, Filioussi K, Tsantes A . Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1071–1078.
Kasper JS, Giovannucci E . A meta-analysis of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006; 15: 2056–2062.
Atchison EA, Gridley G, Carreon JD, Leitzmann MF, McGlynn KA . Risk of cancer in a large cohort of US veterans with diabetes. Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 635–643.
Calton BA, Chang SC, Wright ME, Kipnis V, Lawson K, Thompson FE et al. History of diabetes mellitus and subsequent prostate cancer risk in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Cancer Causes Control 2007; 18: 493–503.
Chodick G, Heymann AD, Rosenmann L, Green MS, Flash S, Porath A et al. Diabetes and risk of incident cancer: a large population-based cohort study in Israel. Cancer Causes Control 2010; 21: 879–887.
Gong Z, Neuhouser ML, Goodman PJ, Albanes D, Chi C, Hsing AW et al. Obesity, diabetes, and risk of prostate cancer: results from the prostate cancer prevention trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006; 15: 1977–1983.
Hense HW, Kajüter H, Wellmann J, Batzler WU . Cancer incidence in type 2 diabetes patients - first results from a feasibility study of the D2C cohort. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2011; 3: 15.
Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T, Sasazuki S, Noda M, Tsugane S . Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Arch Intern Med 2006; 166: 1871–1877.
Kasper JS, Liu Y, Giovannucci E . Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer in the health professionals follow-up study. Int J Cancer 2009; 124: 1398–1403.
Leitzmann MF, Ahn J, Albanes D, Hsing AW, Schatzkin A, Chang SC et alProstate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Trial Project Team. Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk in the prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial. Cancer Causes Control 2008; 19: 1267–1276.
Ogunleye AA, Ogston SA, Morris AD, Evans JM . A cohort study of the risk of cancer associated with type 2 diabetes. Br J Cancer 2009; 101: 1199–1201.
Turner EL, Lane JA, Donovan JL, Davis MJ, Metcalfe C, Neal DE et al. Association of diabetes mellitus with prostate cancer: nested case-control study (prostate testing for cancer and treatment study). Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 440–446.
Velicer CM, Dublin S, White E . Diabetes and the risk of prostate cancer: the role of diabetes treatment and complications. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2007; 10: 46–51.
Wallstrom P, Bjartell A, Gullberg B, Olsson H, Wirfält E . A prospective Swedish study on body size, body composition, diabetes, and prostate cancer risk. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 1799–1805.
Waters KM, Henderson BE, Stram DO, Wan P, Kolonel LN, Haiman CA . Association of diabetes with prostate cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort. Am J Epidemiol 2009; 169: 937–945.
Wotton CJ, Yeates DG, Goldacre MJ . Cancer in patients admitted to hospital with diabetes mellitus aged 30 years and over: record linkage studies. Diabetologia 2011; 54: 527–534.
Hong SK, Oh JJ, Byun SS, Hwang SI, Lee HJ, Choe G et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on the detection of prostate cancer via contemporary multi (12)-core prostate biopsy. Prostate 2012; 72: 51–57.
Lee MY, Lin KD, Hsiao PJ, Shin SJ . The association of diabetes mellitus with liver, colon, lung, and prostate cancer is independent of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and gout in Taiwanese patients. Metabolism 2012; 61: 242–249.
Li C, Balluz LS, Ford ES, Okoro CA, Tsai J, Zhao G . Association between diagnosed diabetes and self-reported cancer among US adults: findings from the 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 1365–1368.
Li Q, Kuriyama S, Kakizaki M, Yan H, Sone T, Nagai M et al. History of diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer: the Ohsaki Cohort Study. Cancer Causes Control 2010; 21: 1025–1032.
Moreira DM, Anderson T, Gerber L, Thomas JA, Banez LL, McKeever MG et al. The association of diabetes mellitus and high-grade prostate cancer in a multiethnic biopsy series. Cancer Causes Control 2011; 22: 977–983.
Rousseau MC, Parent ME, Pollak MN, Siemiatycki J . Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk in a population-based case-control study among men from Montreal, Canada. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 2105–2109.
Tseng CH . Diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a study using the National Health Insurance. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 616–621.
Khan M, Mori M, Fujino Y, Shibata A, Sakauchi F, Washio M et al. Site-specific cancer risk due to diabetes mellitus history: evidence from the Japan Collaborative Cohort (JACC) Study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2006; 7: 253–259.
Pierce BL, Plymate S, Ostrander EA, Stanford JL . Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk. Prostate 2008; 68: 1126–1132.
Wu C, Moreira DM, Gerber L, Rittmaster RS, Andriole GL, Freedland SJ . Diabetes and prostate cancer risk in the REDUCE trial. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2011; 14: 326–331.
Gudmundsson J, Sulem P, Steinthorsdottir V, Bergthorsson JT, Thorleifsson G, Manolescu A et al. Two variants on chromosome 17 confer prostate cancer risk, and the one in TCF2 protects against type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 977–983.
Meyer TE, Boerwinkle E, Morrison AC, Volcik KA, Sanderson M, Coker AL et al. Diabetes genes and prostate cancer in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 19: 558–565.
Pierce BL, Ahsan H . Genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced prostate cancer risk. Hum Hered 2010; 69: 193–201.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000; 283: 2008–2012.
Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses, (Online). 2011; (cited 22 January 2011; available from: URL http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. ).
Song F, Sheldon TA, Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR . Methods for exploring heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Eval Health Prof 2001; 24: 126–151.
Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN . Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ 1997; 315: 1533–1537.
Bagos PG, Nikolopoulos GK . Generalized least squares for assessing trends in cumulative meta-analysis with applications in genetic epidemiology. J Clin Epidemiol 2009; 62: 1037–1044.
Liu JH, Li HW, Tong M, Li M, Na YQ . Genetic risk factors of prostate cancer in Han nationality population in Northern China and a preliminary study of the reason of racial difference in prevalence of prostate cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2004; 84: 364–368.
Peehl DM, Stamey TA . Serum-free growth of adult human prostatic epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 1986; 22: 82–90.
Polychronakos C, Janthly U, Lehoux JG, Koutsilieris M . Mitogenic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factors on PA-III rat prostate adenocarcinoma cells: characterization of the receptors involved. Prostate 1991; 19: 313–321.
Lehrer S, Diamond EJ, Stagger S, Stone NN, Stock RG . Increased serum insulin associated with increased risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate 2002; 50: 1–3.
Jackson FL, Hutson JC . Altered responses to androgen in diabetic male rats. Diabetes 1984; 33: 819–824.
Dhindsa S, Prabhakar S, Sethi M, Bandyopadhyay A, Chaudhuri A, Dandona P . Frequent occurrence of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 5462–5468.
Coffey DS, Isaacs JT, International Union against Cancer Prostate Cancer: a Series of Workshops on the Biology of Human Cancer v. 48. International Union Against Cancer: Geneva, 1979; Report no. 9. UICC Technical Report Series.
Fanning DM, Kay E, Fan Y, Fitzpatrick JM, Watson RW . Prostate cancer grading: the effect of stratification of needle biopsy Gleason Score 4+3 as high or intermediate grade. BJU Int 2010; 105: 631–635.
Vecchia CL, Negri E, Franceschi S, D'Avanzo B, Boyle P . A case-control study of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk. Br J Cancer 1994; 70: 950–953.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Dimple Kondal, Senior scientist (Biostatistician), Centre for excellence, Public Health Foundation, India, for helping with the conduct of data analysis.
Author contributions
DB drafted the protocol, interpreted results and revised the final manuscript. GK and KU developed and ran the search strategy, extracted data from studies and carried out the analysis and wrote the draft manuscript. PT reviewed/edited the manuscript. AB contributed to the discussion and reviewed/edited the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, D., Bhansali, A., Kapil, G. et al. Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 16, 151–158 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Family history, obesity, urological factors and diabetic medications and their associations with risk of prostate cancer diagnosis in a large prospective study
British Journal of Cancer (2022)
-
Prostate cancer genetic propensity risk score may modify the association between this tumour and type 2 diabetes mellitus (MCC-Spain study)
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2022)
-
Differences in the relationship between diabetes and prostate cancer among Black and White non-Hispanic men
Cancer Causes & Control (2021)
-
High glucose: an emerging association between diabetes mellitus and cancer progression
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Prevalent diabetes and risk of total, colorectal, prostate and breast cancers in an ageing population: meta-analysis of individual participant data from cohorts of the CHANCES consortium
British Journal of Cancer (2021)