Abstract
Backgroud:
Recently several clinical trials have focused on the efficacy and safety of silodosin, a new, highly selective α1A-blocker. We tried to verify silodosin’s superiority to placebo and non-inferiority to tamsulosin in treating patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) associated with BPH.
Methods:
All randomized placebo- and active- controlled trials with silodosin were included systematically using Medline, Embase and The Cochrane Library. Primary outcome was International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and IPSS subsores; secondary outcomes were peak urinary flow rate (Qmax), quality of life (QoL) and primary adverse events (AEs) included retrograde ejaculation, dizziness and headache.
Results:
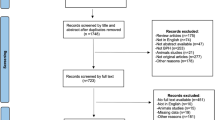
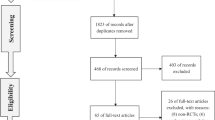
The data of the included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were collected, extracted, and assessed by our protocol. Five RCTs including a total of 2595 patients were identified. Meta-analysis indicated that silodosin achieved significant improvement versus placebo in total IPSS, in IPSS subscores, and in Qmax; silodosin showed a greater improvement in voiding symptoms than tamsulosin, and a higher incidence of retrograde ejaculation than placebo and tamsulosin. No significant differences were observed in total IPSS, in IPSS storage symptoms, in Qmax and in QoL when compared with tamsulosin. Silodosin was associated with the same low incidence of dizziness and headache with placebo and tamsulosin.
Conclusions:
Silodosin is an effective and well-tolerated treatment for both voiding and storage symptoms in patients with LUTS associated with BPH. Despite with increased retrograde ejaculation, its overall efficacy is not inferior to tamsulosin, while at the same time being possibly superior to tamsulosin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Edwin LL . The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol 1984; 132: 474–479.
Chapple C . Medical treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia. BMJ 1992; 304: 1198–1199.
Barry MJ, Cockett AT, Holtgrewe HL, McConnell JD, Sihelnik SA, Winfield HN . Relationship of symptoms of prostatism to commonly used physiological and anatomical measures of the severity of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 1993; 150: 351–358.
Andersson KE, Gratzke C . Pharmacology of α1-adrenoceptor antagonists in the lower urinary tract and central nervous system. Nat Clin Pract Urol 2007; 4: 368–378.
Roehrborn CG, Schwinn DA . α1-Adrenergic receptors and their inhibitors in lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2004; 171: 1029–1035.
Kirby R, Andersson KE, Lepor H, Steers WD . α1-Adrenoceptor selectivity and the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2000; 3: 76–83.
Tatemichi S, Kobayashi K, Maezawa A, Kobayashi M, Yamazaki Y, Shibata N . α1-Adenoceptor subtype selectivity and organ specificity of silodosin (KMD-3213). Yakugaku Zasshi 2006; 126: 209–216.
Shibata K, Foglar R, Horie K, Obika K, Sakamoto A, Ogawa S et al. KMD-3213, a novel, potent, alpha 1a-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist: characterization using recombinant human alpha 1-adrenoceptors and native tissues. Mol Pharmacol 1995; 48: 250–258.
Kawabe K, Yoshida M, Homma Y . Silodosin, a new α1A-adrenoceptor selective antagonist for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a Phase III randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study in Japanese men. BJU Int 2006; 98: 1019–1024.
Yu HJ, Lin AT, Yang SS, Tsui KH, Wu HC, Cheng CL et al. Non-inferiority of silodosin to tamsulosin in treating patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). BJU Int 2011; 108: 1843–1848.
Marks LS, Gittelman MC, Hill LA, Volinn W, Hoel G . Rapid efficacy of the highly selective alpha1 A-adrenoceptor antagonist silodosin in men with signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia: Pooled results of 2 Phase III studies. J Urol 2009; 181: 2634–2640.
Yokoyama T, Hara R, Fukumoto K, Fujii T, Jo Y, Miyaji Y et al. Effects of three types of alpha-1 adrenoceptor blocker on lower urinary tract symptoms and sexual function in males with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Urol 2011; 18: 225–230.
Chapple CR, Montorsi F, Tammela TJ, Wirth M, Koldewijn E, Fernández E et al. Silodosin therapy for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with suspected benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-and active-controlled clinical trial performed in Europe. Eur Urol 2011; 59: 342–352.
Kawabe K, Yoshida M, Arakawa S, Takeuchi H . Long-term evaluation of silodosin, a new α1A-adrenoceptor selective antagonist for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: Phase III long-term study. Jap J Urol Surg 2006; 19: 153–164.
Michel MC . α1-Adrenoceptors and ejaculatory function. Br J Pharmacol 2007; 152: 289–290.
Kobayashi K, Masumori N, Hisasue S, Kato R, Hashimoto K, Itoh N et al. Inhibition of seminal emission is the main cause of an ejaculation induced by a new highly selective α1A-blocker in normal volunteers. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 2185–2190.
Schulman CC . Lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia: Minimizing morbidity caused by treatment. Urology 2003; 62: 24–33.
Sanbe A, Tanaka Y, Fujiwara Y, Tsumura H, Yamauchi J, Cotecchia S et al. α1-Adrenoceptors are required for normal male sexual function. Br J Pharmacol 2007; 152: 332–340.
Hisasue S, Furuya R, Itoh N, Kobayashi K, Furuya S, Tsukamoto T . Ejaculatory disorder caused by alpha-1 adrenoceptor antagonists is not retrograde ejaculation but a loss of seminal emission. Int J Urol 2006; 13: 1311–1316.
Chen TI, Wu TT . The efficacy and safety of tamsulosin in treating symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol ROC 2000; 11: 155–160.
Li NC, Chen S, Yang XH, Du LD, Wang JY, Na YQ et al. Efficacy of low-dose tamsulosin in Chinese patients with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Drug Investig 2003; 23: 781–787.
Park CH, Chang HS, Oh BR, Kim HJ, Sul CK, Chung SK et al. Efficacy of low-dose tamsulosin on lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nonblind multicentre Korean study. Clin Drug Investig 2004; 24: 41–47.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30901484, 30973013, 81200551 and 81270841).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Dong, Q., Liu, L. et al. A meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of the new α1A-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist silodosin for treating lower urinary tract symptoms associated with BPH. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 16, 79–84 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2012.36